©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2013; 5(4): 188-195
Published online Oct 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.188
Published online Oct 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.188
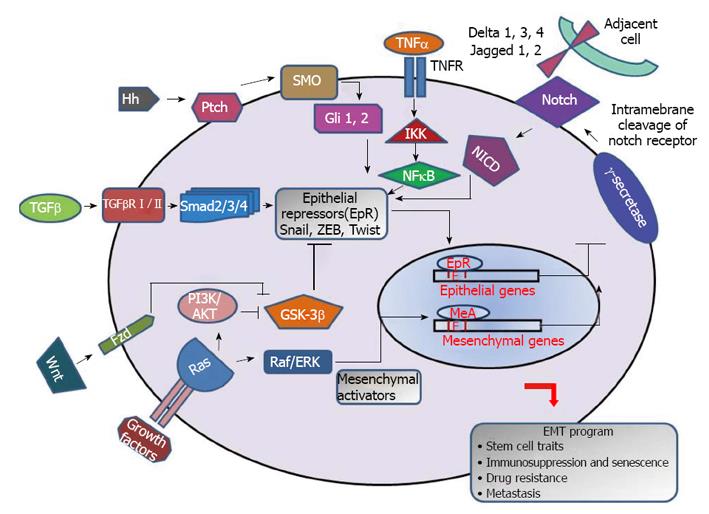
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of embryonic signaling pathways mediating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.
Wnt, Notch, hedgehog, transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) along with other growth factors of cytokines transduce signal cascades, modulate the expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) regulators and allow them to translocate to nucleus. They act as epithelial repressors (EpR) and/or mesenchymal activators (MeA) and bind with E box of promoter regions of epithelial genes and mesenchymal genes respectively. These complexes have an inductive effect on EMT program by repressing epithelial genes and activating mesenchymal genes. IKK: IκB kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; SMO: Smoothened; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; Fzd: Frizzled.
- Citation: Garg M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition - activating transcription factors - multifunctional regulators in cancer. World J Stem Cells 2013; 5(4): 188-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v5/i4/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.188