©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2025; 17(8): 108898
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.108898
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.108898
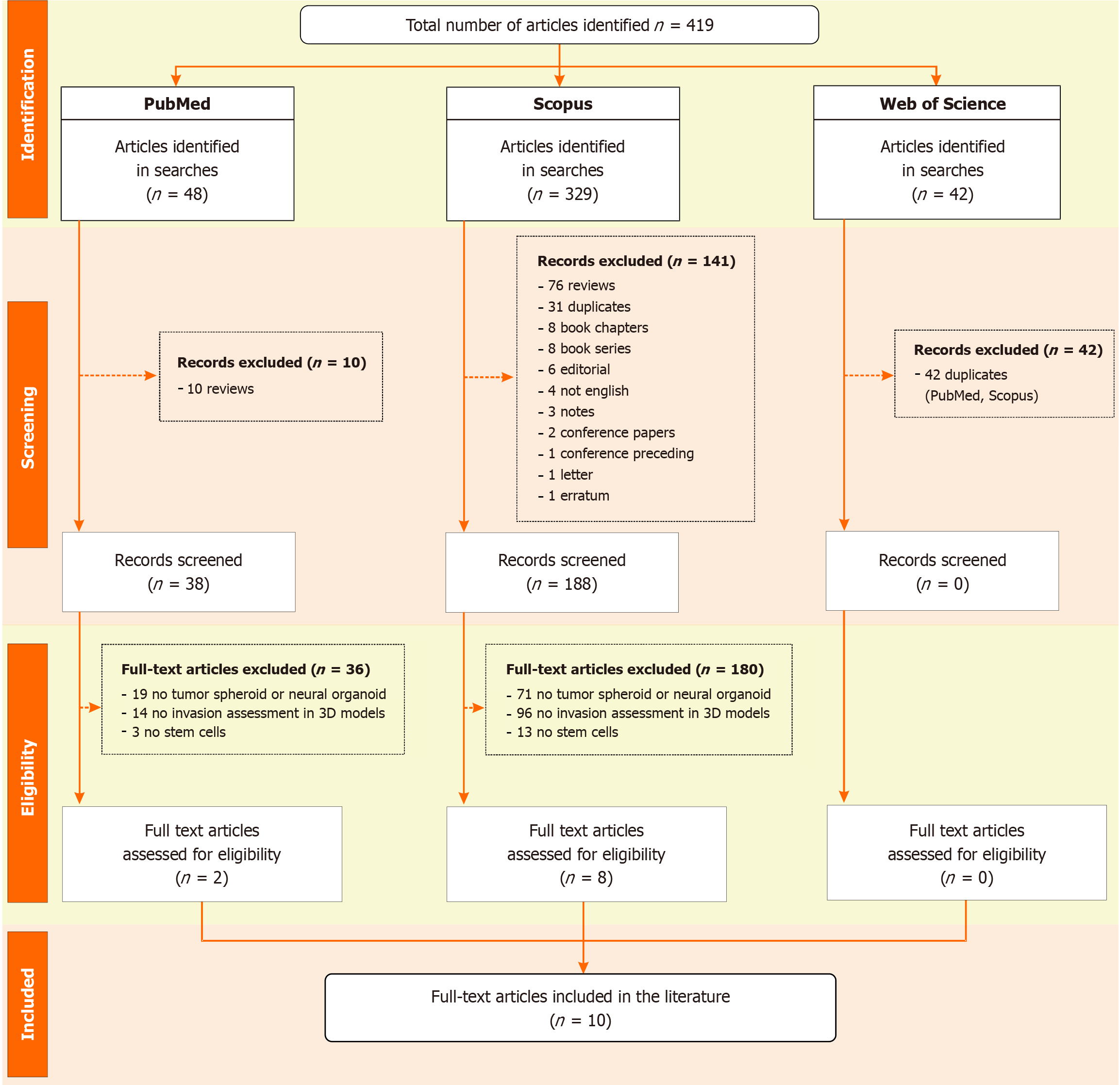
Figure 1 Flowchart of the systematic review process based on PRISMA guidelines.
It details the number of records identified, screened, and excluded, along with the main reasons for exclusion at each stage. A total of 10 studies met all criteria and were included in the final review.
Figure 2 Risk of bias assessment of the included studies using the Risk of Bias in Non-Randomized Studies of Intervention-I.
A: Visual representation of the domain-level risk of bias judgments (D1 to D7) for each study. Each cell indicates the assigned risk level based on consensus among reviewers: Green (+) for low risk, yellow (–) for moderate risk, and red (×) for serious risk. The “Overall” column reflects the overall risk of bias rating across all seven domains; B: Summary plot showing the proportion of studies rated as “Low”, “Moderate”, or “Serious” risk of bias within each domain. Higher proportions of moderate or serious risk were observed in domains related to confounding (D1) and selection of participants (D2), while other domains predominantly showed low risk of bias.
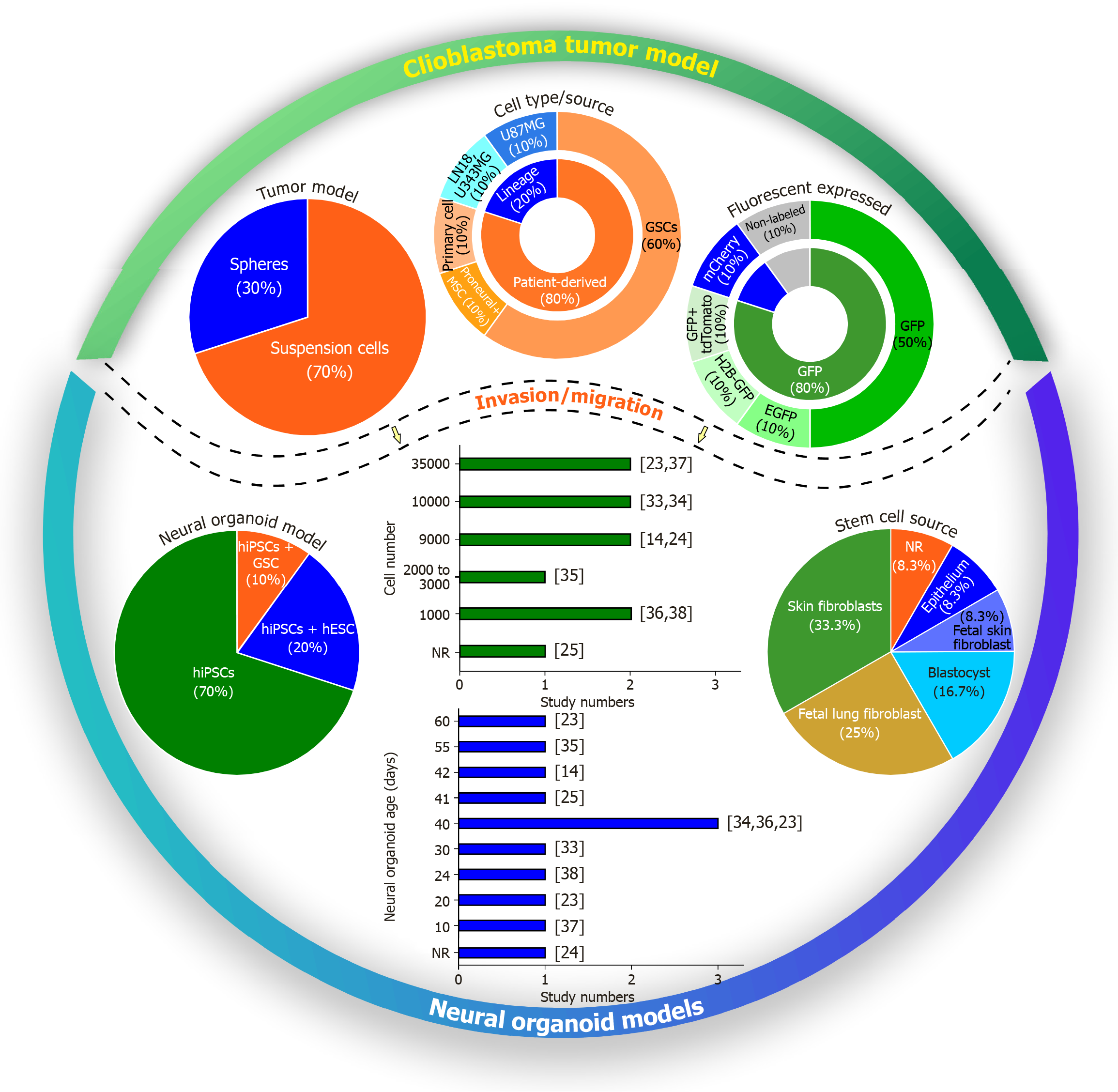
Figure 3 Characterization of experimental models used to investigate glioblastoma invasion in neural organoids.
The figure presents the main methodological parameters reported in the included studies, including tumor model type (suspension cells or spheroids), cell type and source (including glioblastoma stem cells and established line), fluorescent markers used, stem cell types used for organoid generation (human induced pluripotent stem cells, and human embryonic stem cells) and their sources. It also shows the number of tumor cells used in invasion/migration assays and the age of the organoids at the time of analysis. GSCs: Glioblastoma stem cells; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; EGFP: Enhanced green fluorescent protein; H2B-GFP: Histone-fused construct green fluorescent protein; hiPSCs: Human induced pluripotent stem cells; hESCs: Human embryonic stem cells; NR: Not reported.
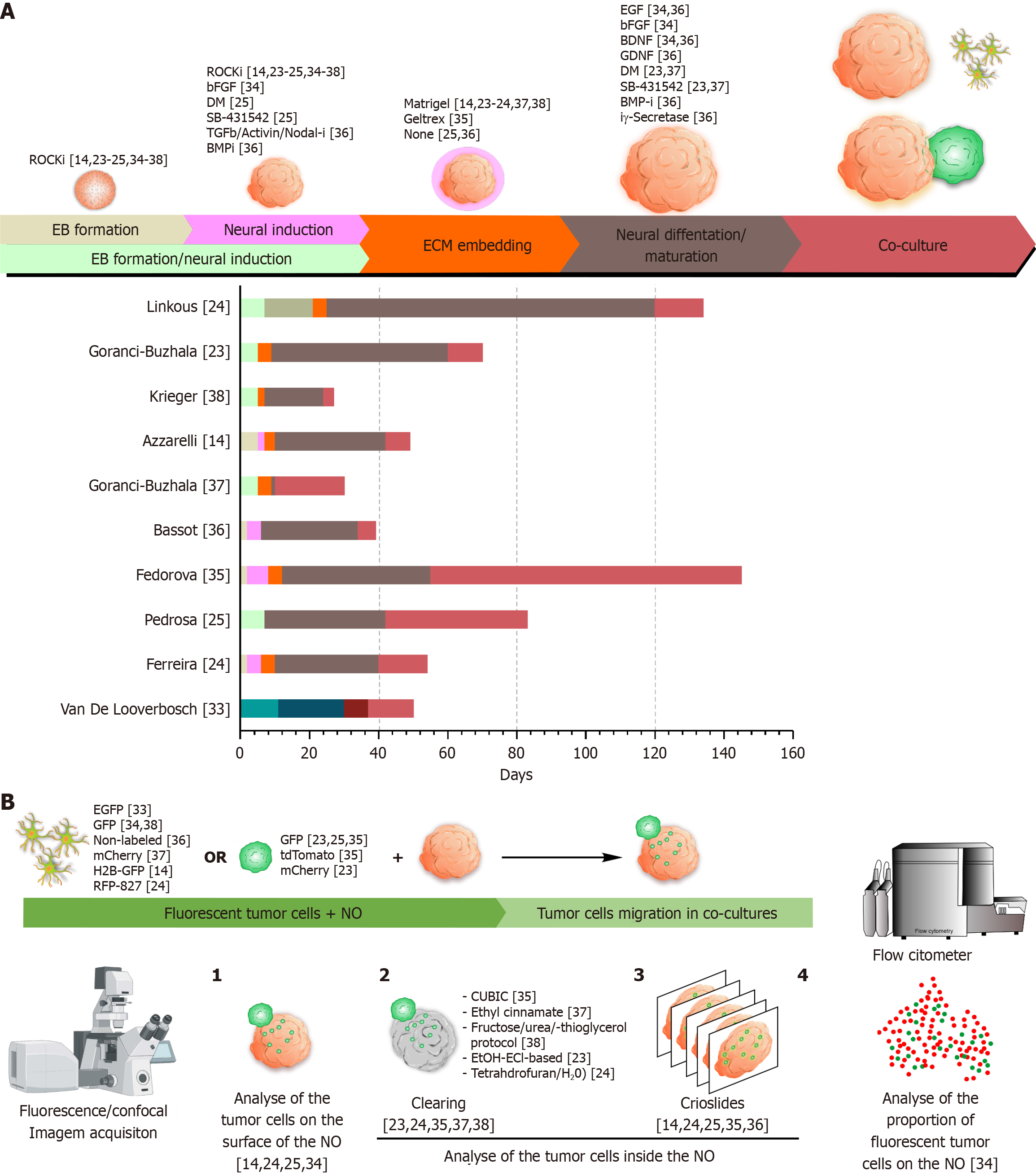
Figure 4 Overview of neural organoid generation protocols, glioblastoma multiforme co-culture strategies, and analytical methodologies.
A: Top: Schematic representation of the main phases involved in the generation of neural organoids (NOs), including: (1) Embryoid body formation; (2) Neural induction; (3) Simultaneous embryoid body formation and neural induction; (4) Embedding in extracellular matrix; (5) Neural differentiation and maturation; and (6) Co-culture with 2D glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells or three-dimensional GBM spheroids. Most of the factors applied during these steps were specific to guided protocols designed to direct NOs toward a cortical identity, with the exception of the ROCK inhibitor, which was universally used in the early stages to enhance cell viability. Bottom: Temporal timeline (in days) of each phase as applied in the studies included in this review; B: Summary of methodologies used to assess GBM cell migration and invasion in NO models. Migration and invasion can be visualized using fluorescence or confocal microscopy, either by: (1) Tracking fluorescently labeled GBM cells on the surface of whole NOs; (2) Visualizing internal invasion using optical clearing techniques in whole NOs; and (3) Sectioning organoids into cryoslides for detailed imaging of GBM cells invasion. Alternatively, GBM cell invasion can be quantified by dissociating co-cultured NOs into single cells and analyzing them via flow cytometry, enabling the measurement of the proportion of GBM cells that infiltrated the organoids. ROCKi: ROCK inhibitor; bFGF: Basic fibroblasts growth factor; DM: Dorsomorphin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; BMPi: Bone morphogenetic protein inhibitor; EGF: Endothelial growth factor; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; EB: Embryoid body; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EGFP: Enhanced green fluorescent protein; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; H2B-GFP: Histone-fused construct green fluorescent protein; RFP: Red fluorescent protein; NO: Neural organoid.
- Citation: Alves ADH, Ennes do Valle NM, Yokota-Moreno BY, Galanciak MCDS, Felix da Silva K, Mamani JB, Sertie AL, de Oliveira FA, Nucci MP, Gamarra LF. Stem cell-derived neural organoids as platforms to investigate glioblastoma invasion and migration: A systematic review. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(8): 108898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i8/108898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.108898