©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2025; 17(12): 114170
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.114170
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.114170
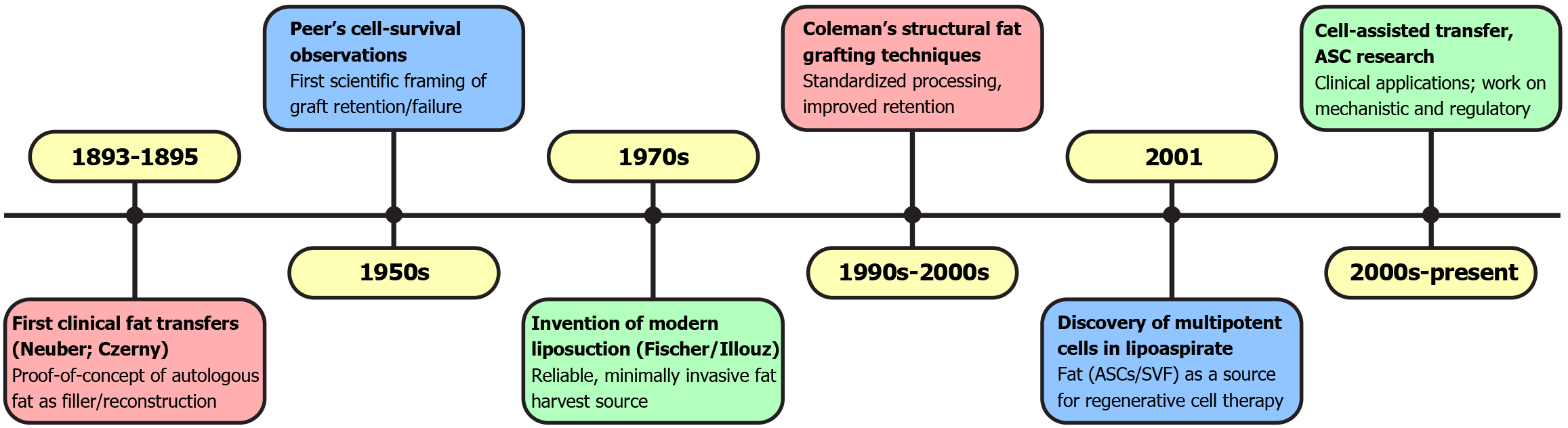
Figure 1 Historical background of adipose tissue use in therapy.
SVF: Stromal vascular fraction; ASCs: Adipose-derived stem cells.
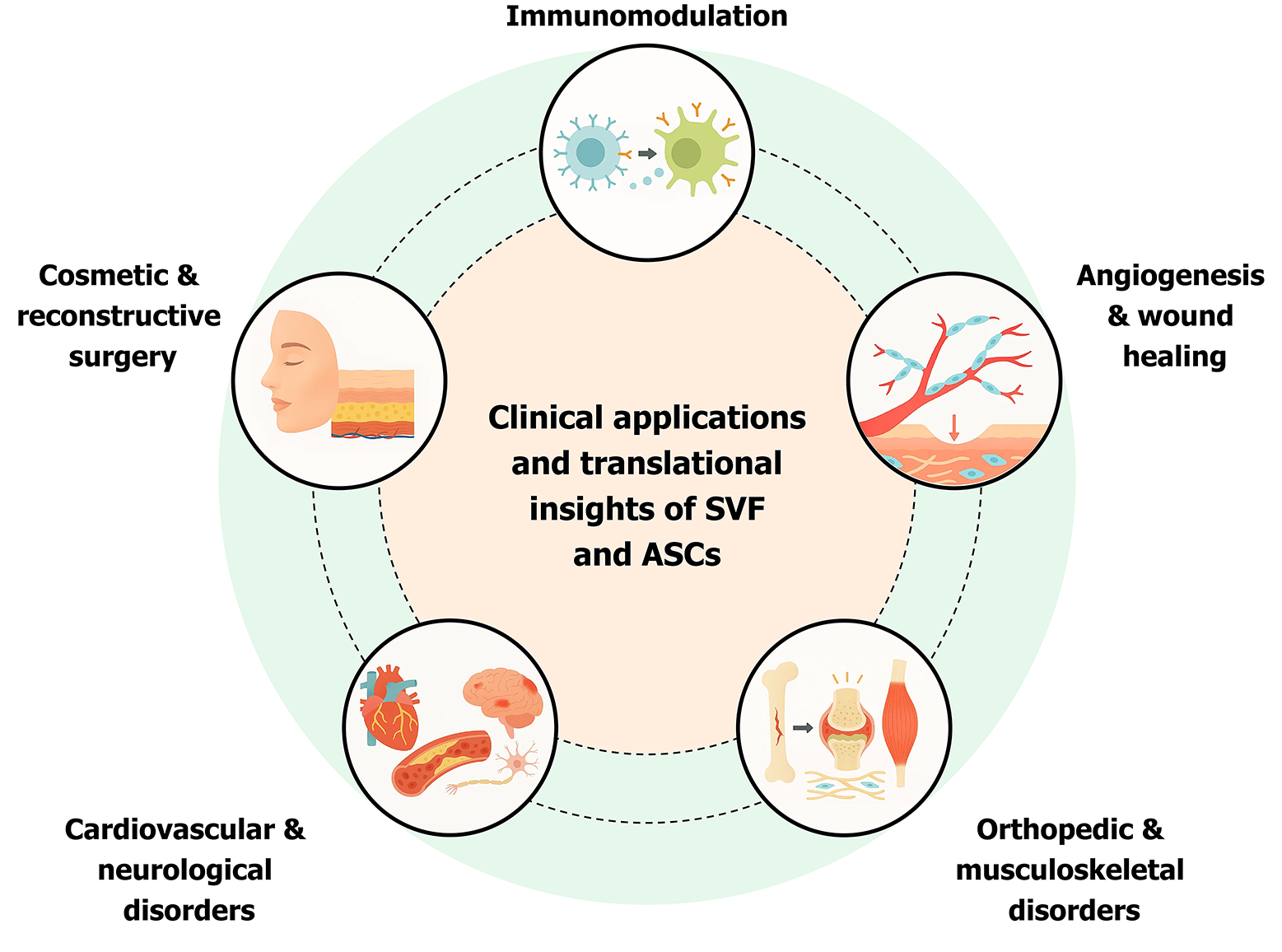
Figure 2 Clinical applications and translational insights of stromal vascular fraction and adipose-derived stem cells.
SVF: Stromal vascular fraction; ASCs: Adipose-derived stem cells.
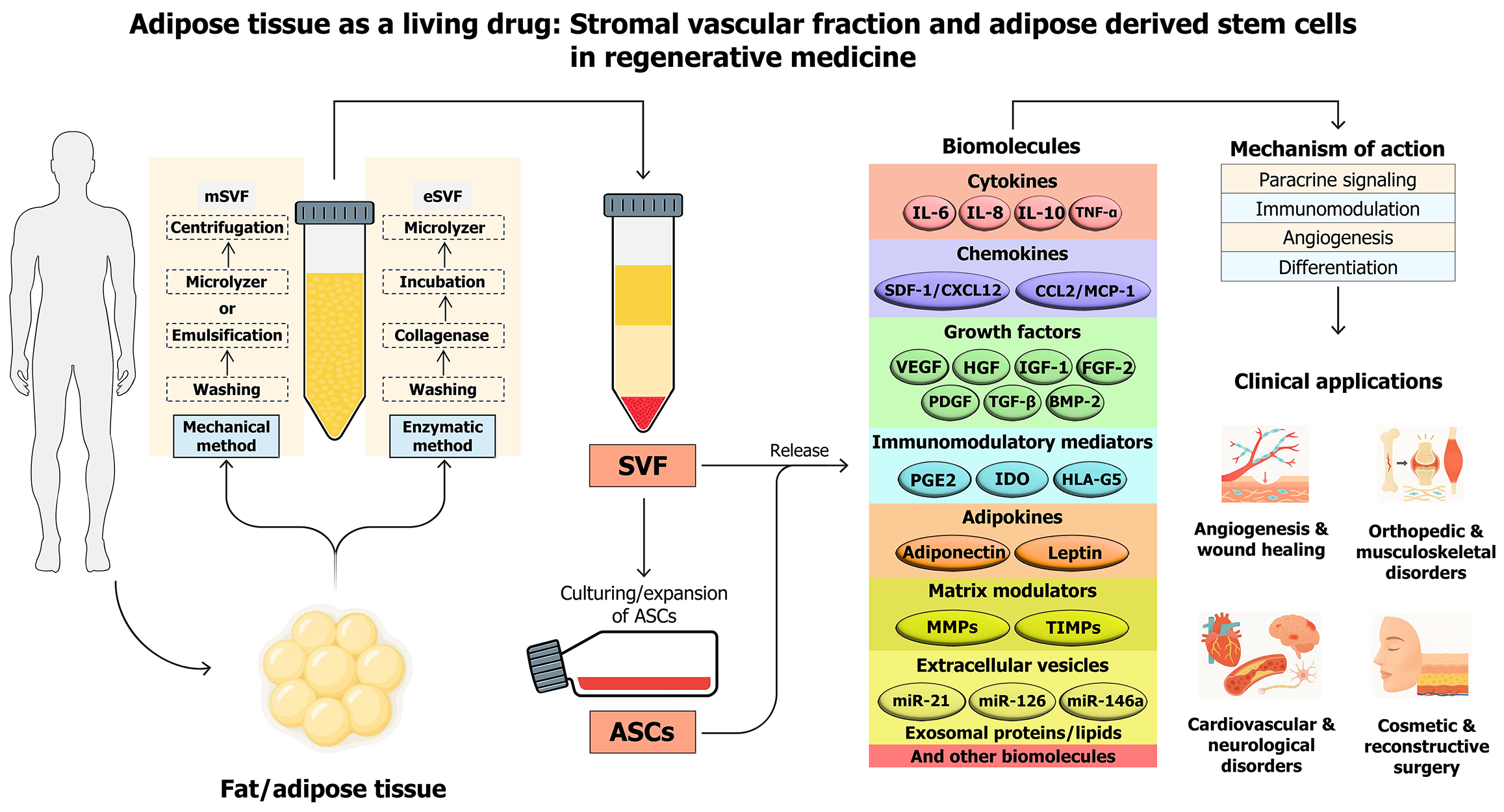
Figure 3 Adipose tissue as a living drug: Stromal vascular fraction and adipose-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine.
SVF: Stromal vascular fraction; ASCs: Adipose-derived stem cells; mSVF: Mechanical isolation of stromal vascular fraction; eSVF: Enzymatic isolation of stromal vascular fraction; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; SDF-1: Stromal-derived factor-1; CXCL12: C-X-C motif ligand 12; CCL2: C-C motif ligand 2; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; FGF-2: Fibroblast growth factor-2; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; BMP-2: Bone morphogenetic protein-2; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; TIMPs: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases.
- Citation: Choudhery MS, Niaz A, Arif T, Mahmood R. Adipose tissue as a living drug: Stromal vascular fraction and adipose tissue-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(12): 114170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i12/114170.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.114170