©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2025; 17(12): 112100
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.112100
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.112100
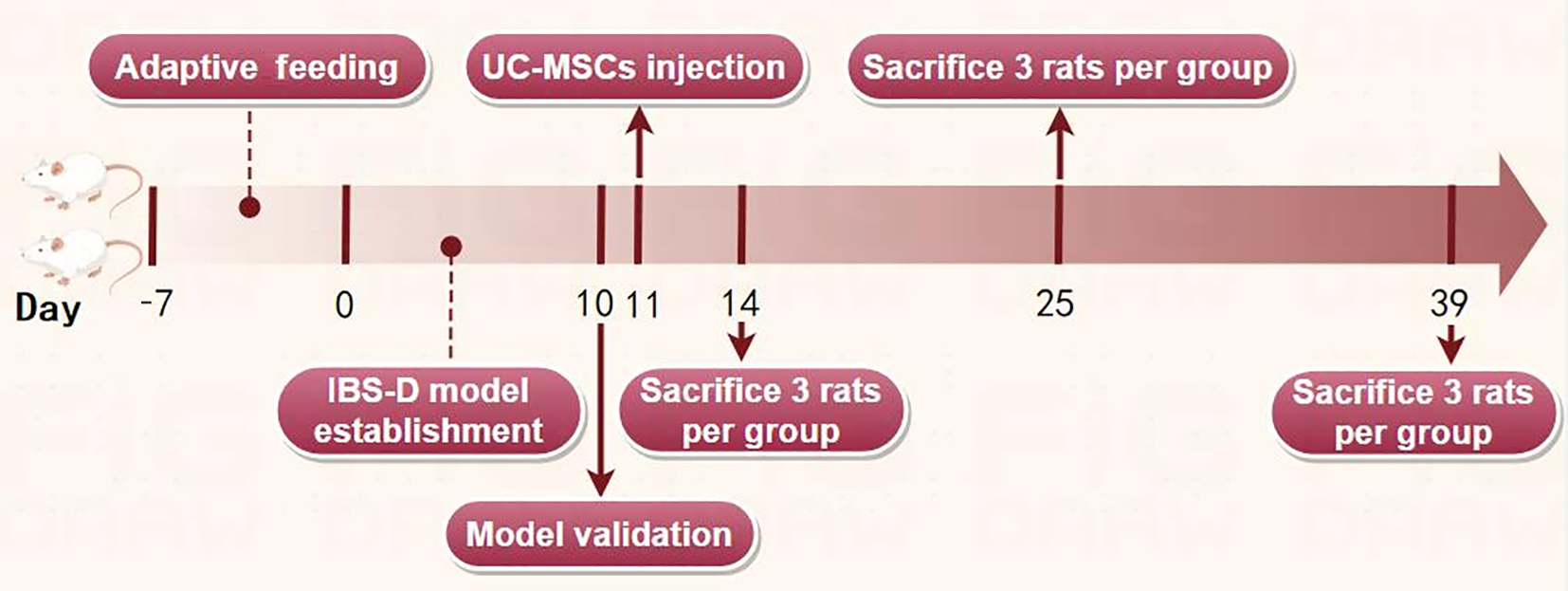
Figure 1 Experimental time point and the corresponding treatment of rats.
IBS-D: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome; UC-MSCs: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
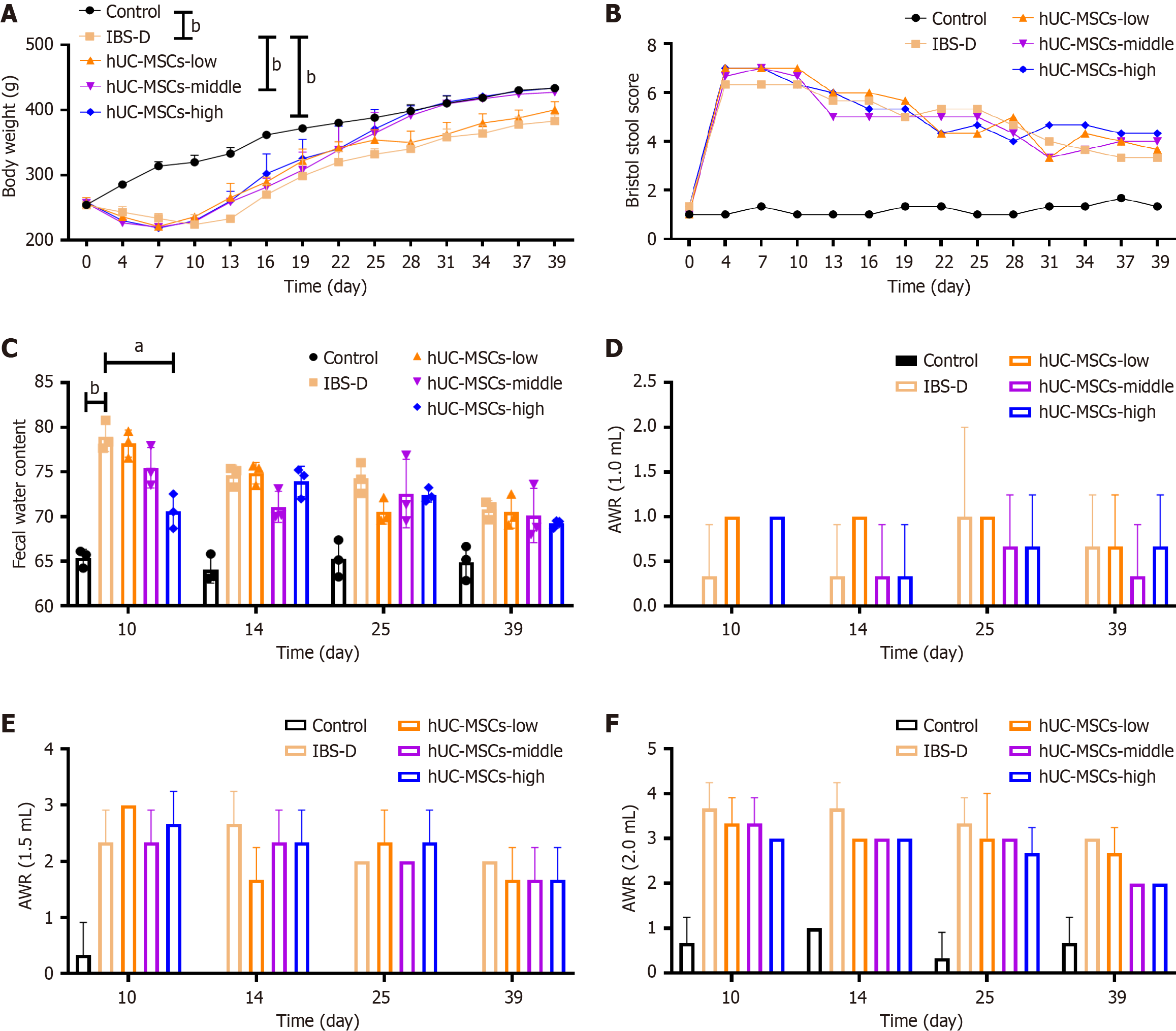
Figure 2 Body weight, fecal status, and intestinal sensitivity in rats.
A: Body weight of rats; B: Bristol stool score of rats; C: Fecal water content of rats; D: Abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) score at 1.0 mL balloon expansion; E: AWR score at 1.5 mL balloon expansion; F: AWR score at 2.0 mL balloon expansion. hUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; IBS-D: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
Figure 3 Serum level of inflammatory factors in rats.
A: Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) level on days 14, 25, and 39 (n = 3); B: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) level on days 14, 25, and 39 (n = 3); C: IL-1β level on days 14, 25, and 39 (n = 3). hUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; IBS-D: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
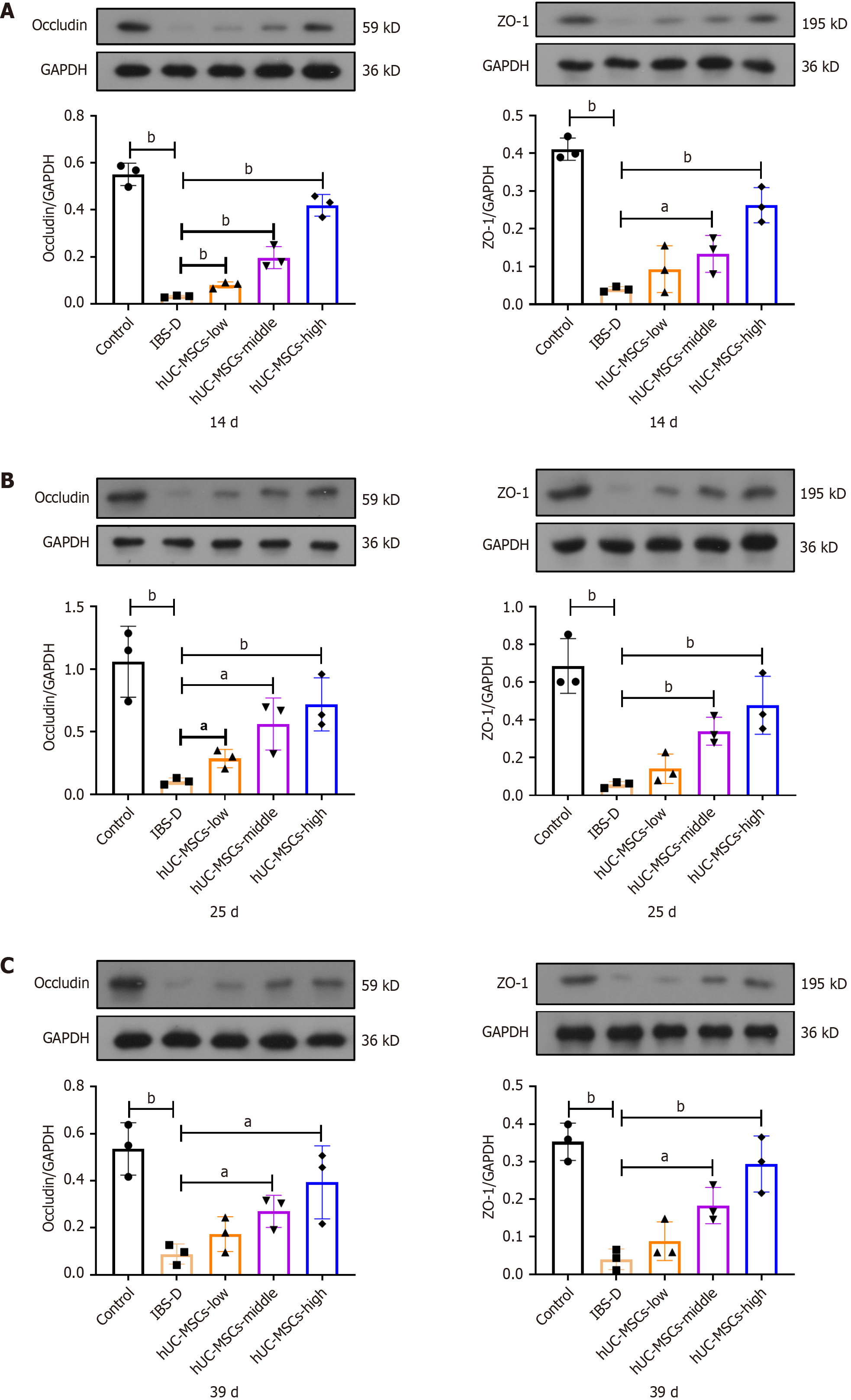
Figure 4 Expression levels of occludin and zonula occludens-1.
A-C: Ratio of occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression on day 14 (A), day 25 (B), and day 39 (C) (n = 3). hUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; IBS-D: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
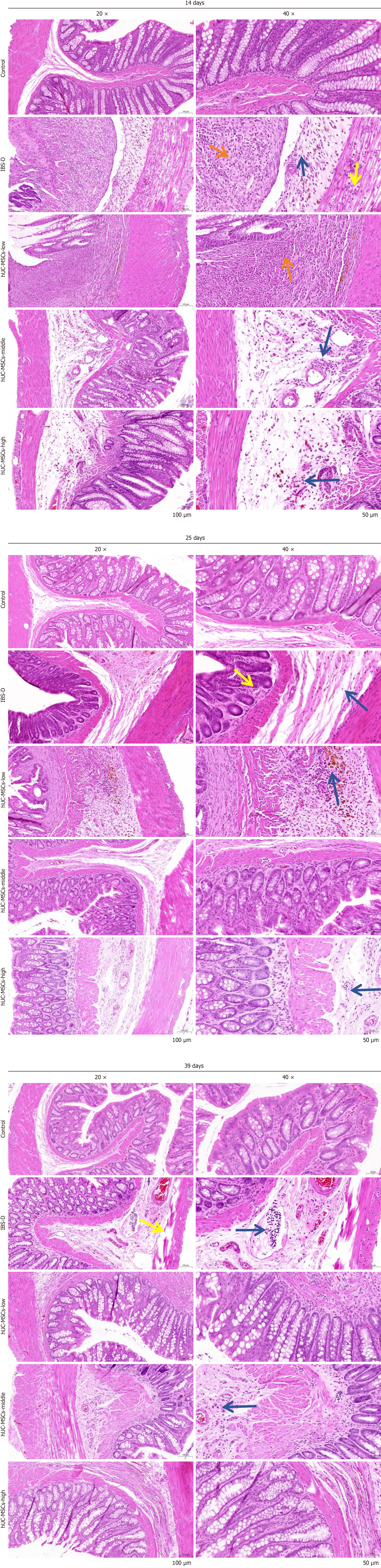
Figure 5 Morphology and structure of colon tissue with hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Morphology and structure of colon tissue of different groups on days 14, 25, and 39. Orange arrows indicate inflammatory cell infiltration; blue arrows indicate that the ulcer has invaded the submucosa and been replaced by proliferating the connective tissue; yellow arrows indicate loose edema of the inner annular muscle and the outer longitudinal muscle. hUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; IBS-D: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome.
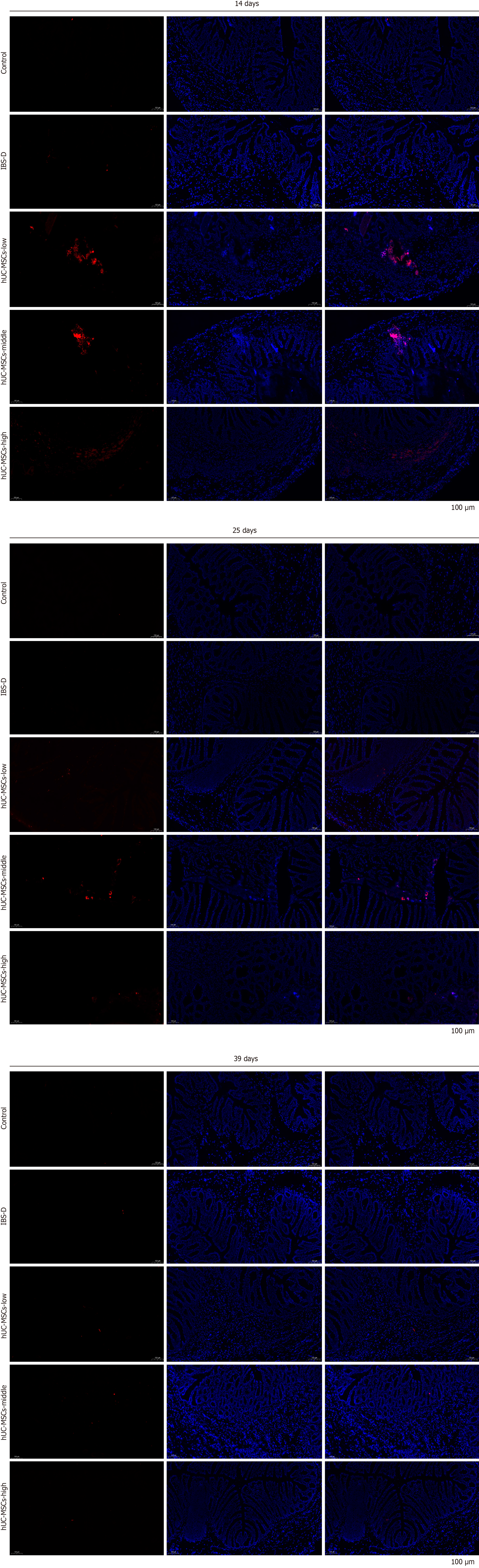
Figure 6 Distribution of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in colon tissues.
Distribution of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) in the colon tissue of different groups on days 14, 25, and 39. IBS-D: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome.
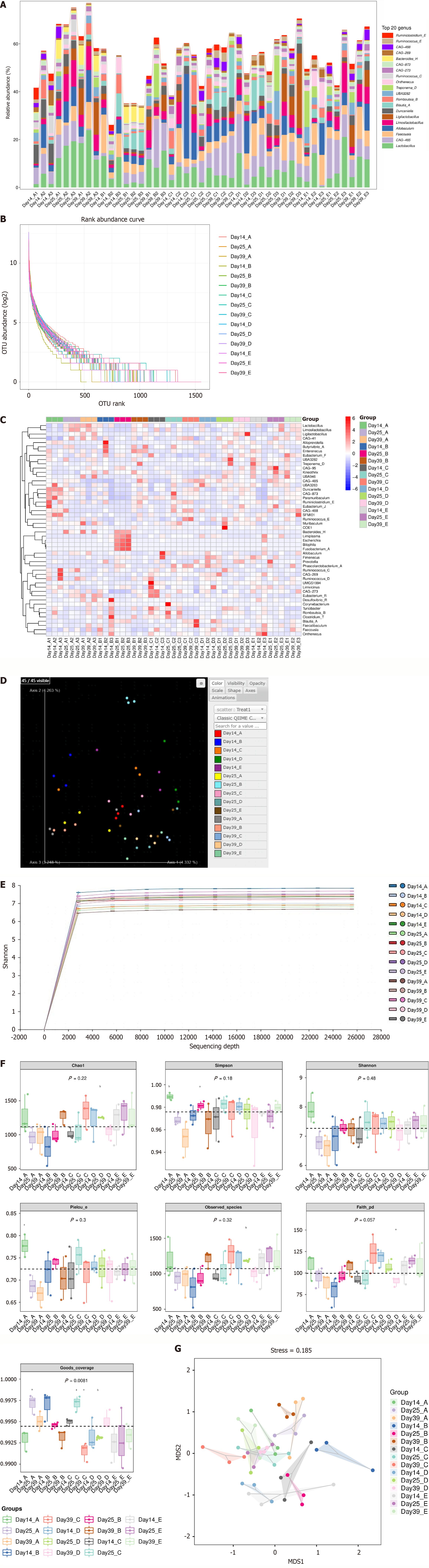
Figure 7 Gut microbial abundance and diversity.
A: Histogram of genus-level species composition; B: Abundance grade plot; C: Heat map of genus-level species composition on days 14, 25, and 39 (three samples per group at each time point) for species clustering; D: Three-dimensional ordering diagram of samples by principal component analysis; E: Sparse curve graph of the alpha diversity index; F: Grouped box plot of the alpha diversity index; G: Two-dimensional sorting diagram by non-metric multidimensional scaling. In each picture, A: Control group; B: Diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome group; C: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (hUC-MSC)-low group; D: HUC-MSC-middle group; E: HUC-MSC-high group; Day 14_A: Control group on day 14. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Zhang HM, Zhang Y, Luo GJ, Zhang AX, Li RC, Dong HB, Dong TY, Yu PC, An Y, Li Y. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviated diarrhea-type irritable bowel syndrome by improving intestinal function. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(12): 112100
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i12/112100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.112100