©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2019; 11(11): 1005-1019
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i11.1005
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i11.1005
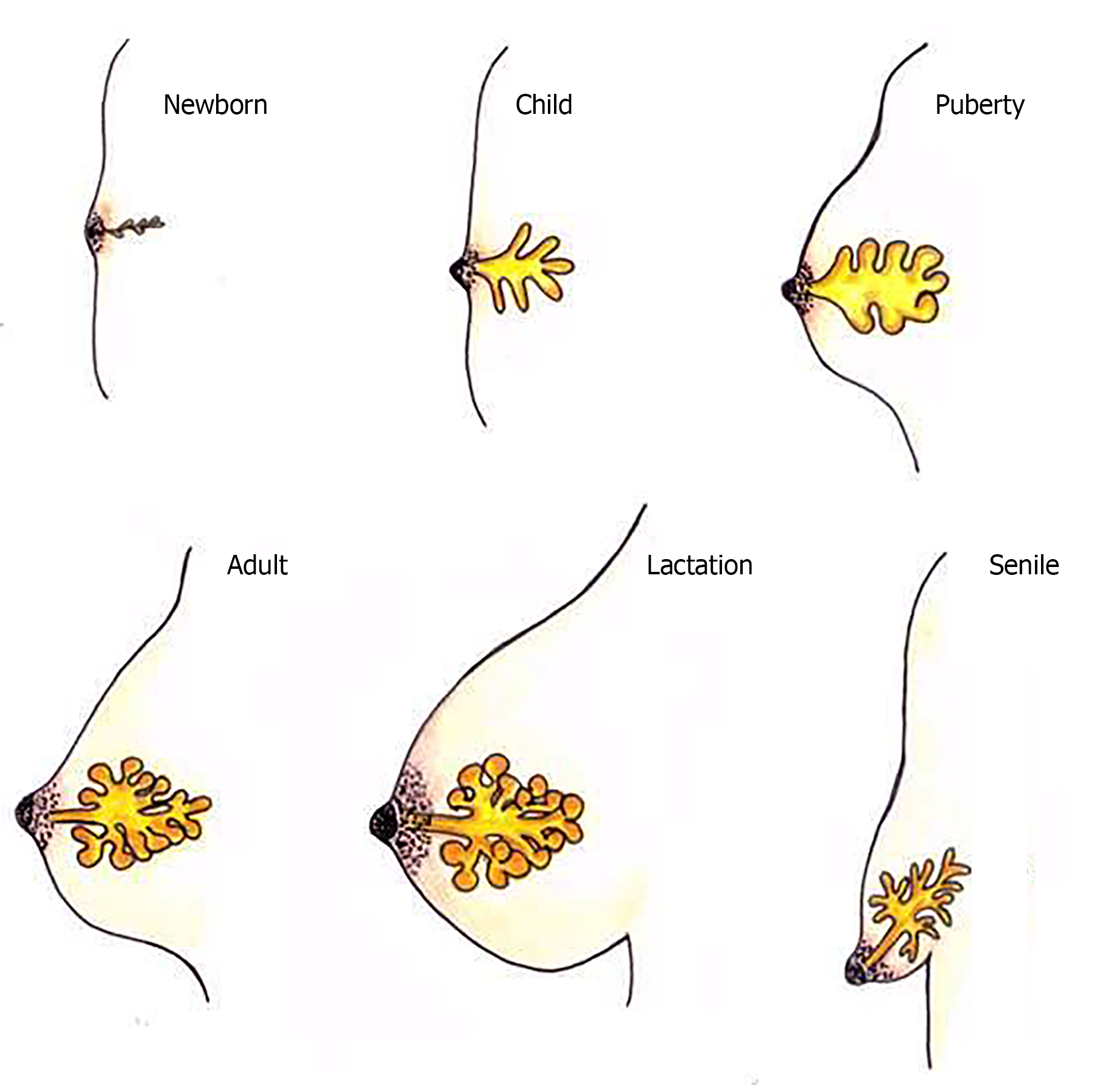
Figure 1 Transformation of the mammary gland throughout life.
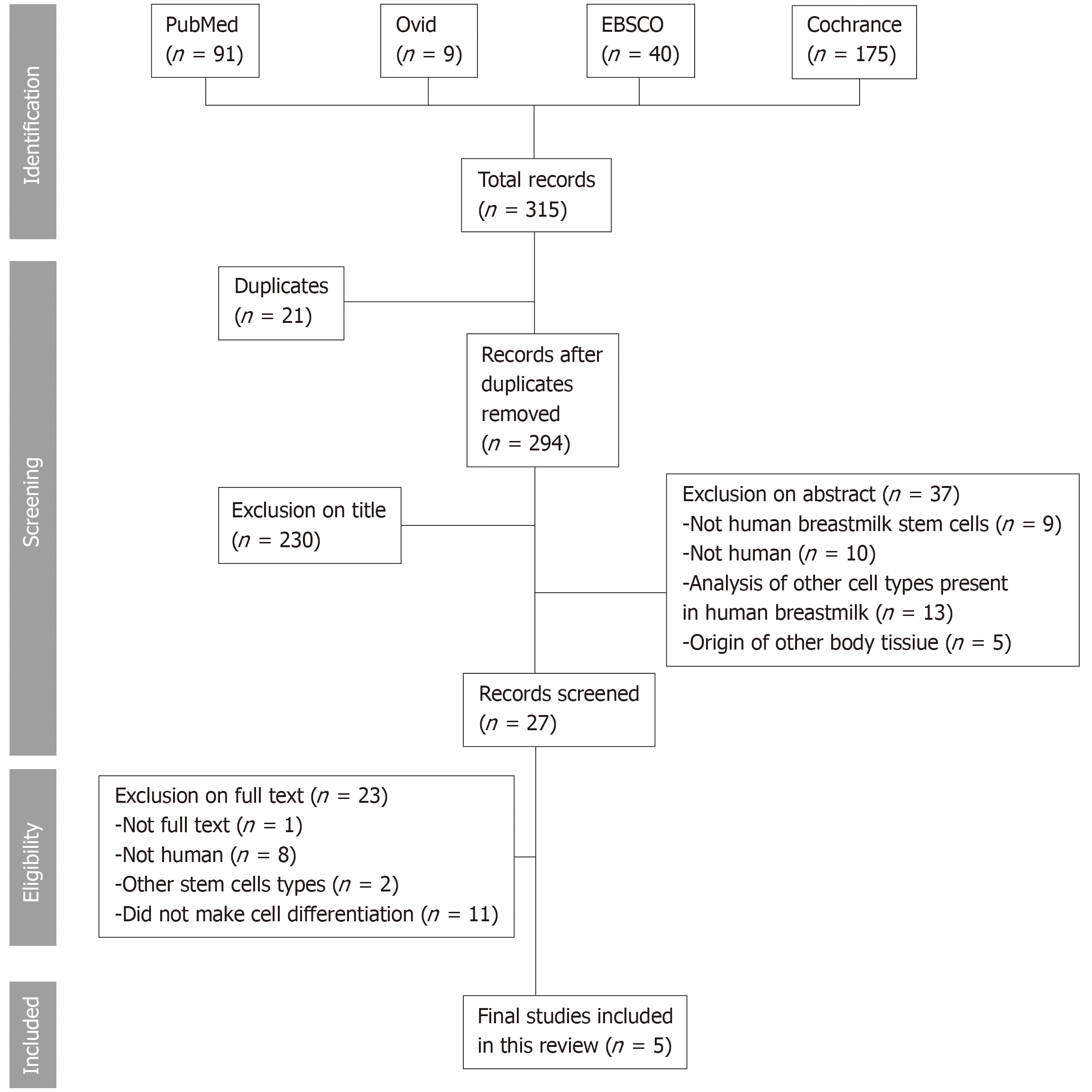
Figure 2 Flow chart demonstrating the search results with excluded and included studies.
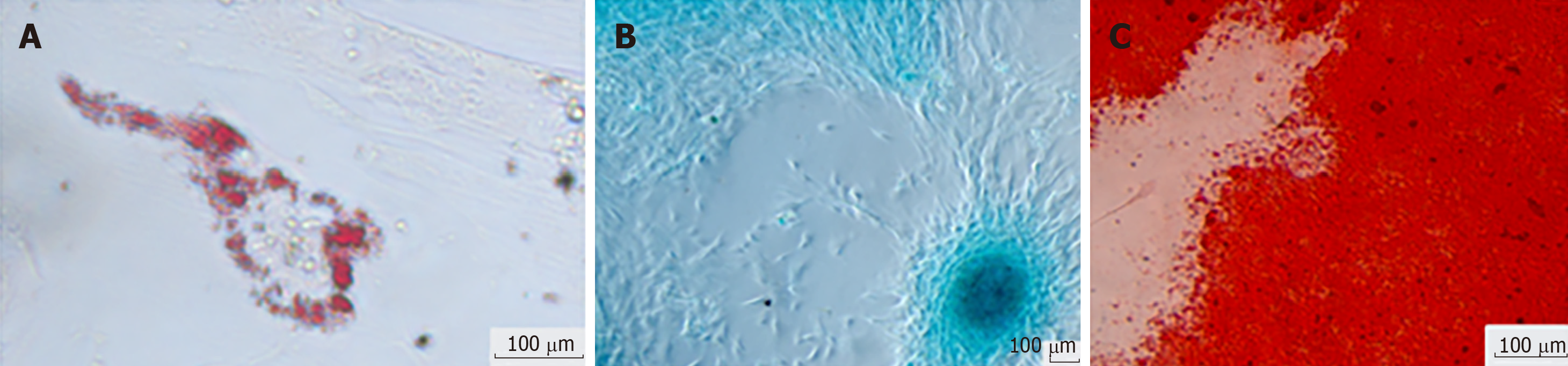
Figure 3 The hBSCs have the ability to differentiate into different cell types of mesodermal origin in vitro.
A: Adipogenic; B: Chondrogenic; C: Osteogenic. Differentiation of hBSCs was stained with Oil Red O, Alcian Blue, and Alizarin Red, respectively (inversion optical microscope, 100x). Original figure from approved project No. 1.324.098 (11/16/2015) of the Human Ethical Committee of the Pequeno Príncipe Faculty. hBSC: Human breastmilk stem cell.
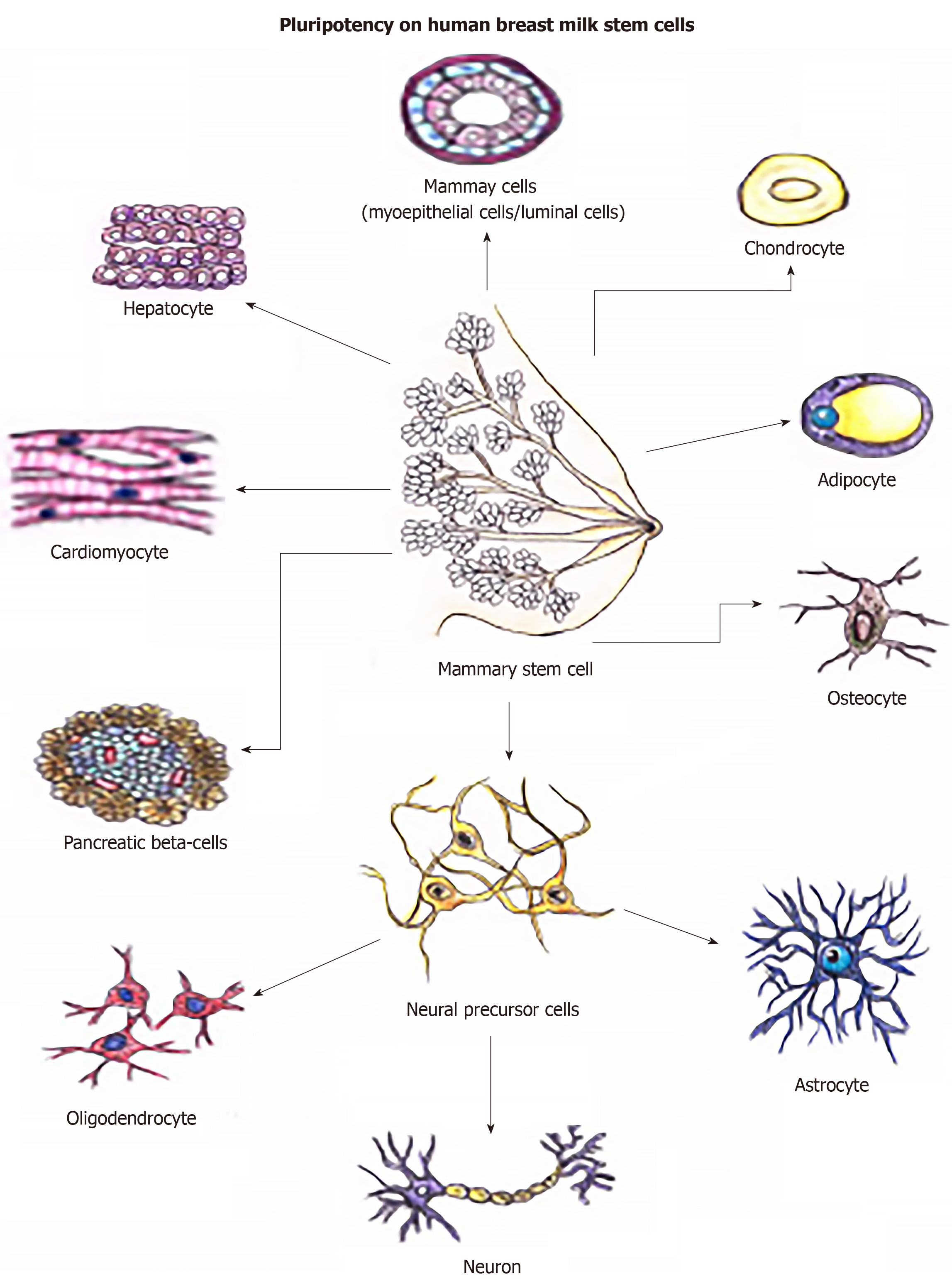
Figure 4 Multilineage potential of hBSCs.
These cells can differentiate into mesodermal lineages, endodermal lineages, and the neuroectodermal lineage. hBSC: Human breastmilk stem cell.
- Citation: Pacheco CMR, Ferreira PE, Saçaki CS, Tannous LA, Zotarelli-Filho IJ, Guarita-Souza LC, de Carvalho KAT. In vitro differentiation capacity of human breastmilk stem cells: A systematic review. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(11): 1005-1019
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i11/1005.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i11.1005