©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2001; 7(2): 254-258
Published online Apr 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i2.254
Published online Apr 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i2.254
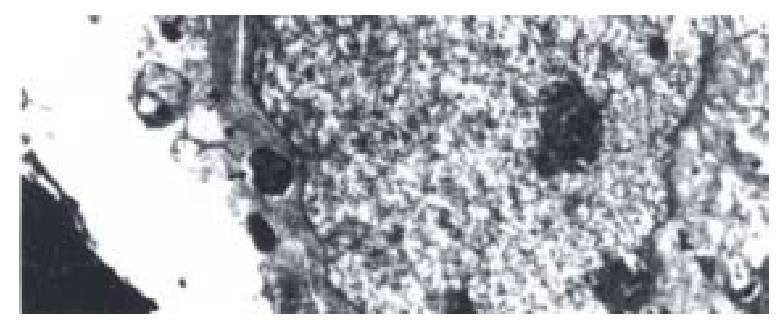
Figure 1 Invasion of coccoid H.
pylori into Hep-2 cell. Transmission electron microscope, × 15 000
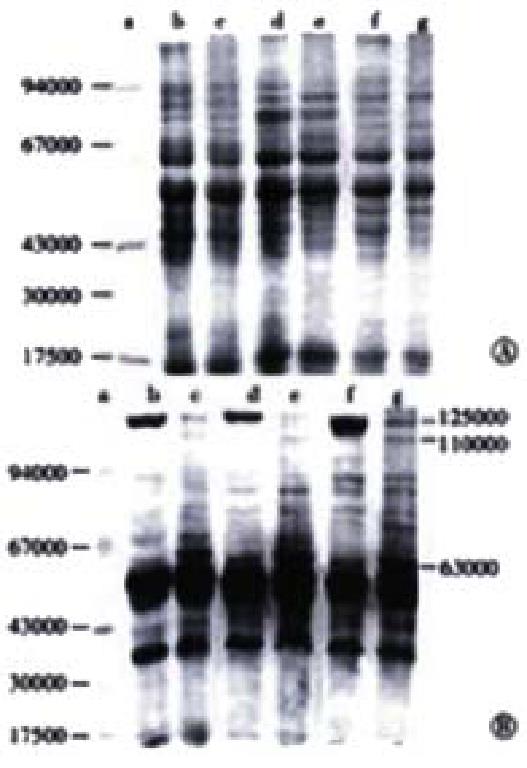
Figure 2 A.
SDS-PAGE pattern of whole cell proteins of H. pylori, B. Western blot pattern of the proteins of H. pylori. a. marker; b.d.f. spiral forms of H.pyloriF44, F45 and F49, respectively; c.e.g. coccoid forms of H.pylori F44, F45 and F49, respectively.
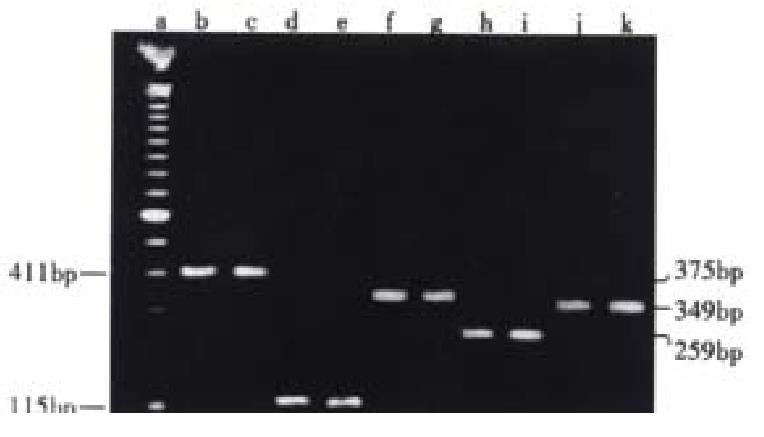
Figure 3 The results of PCR of H.
pylori F44. a. PCR marker 100bp lader; b.c. ureA gene; d.e. ureB gene; f.g. hpaA gene; h.i. vacA gene; j.k. cagA gene; b.d.f.h.j. spiral forms of H.pylori; c.e.g.i.k. coccoid forms of H.pylori.
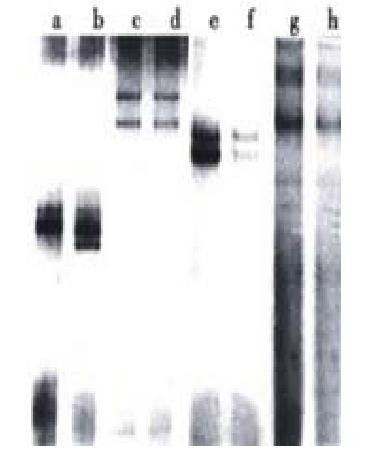
Figure 4 The pattern of PCR-SSCP of H.
pylori F44. a.b. vacA gene; c.d. ureA gene; e.f. cagA gene; g.h. hpaA gene; a.c.e.g. spiral forms of H. pylori; b.d.f.h. coccoid forms of H.pylori.
-
Citation: She FF, Su DH, Lin JY, Zhou LY. Virulence and potential pathogenicity of coccoid
Helicobacter pylori induced by antibiotics. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(2): 254-258 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i2/254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i2.254