©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2026; 32(6): 113529
Published online Feb 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i6.113529
Published online Feb 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i6.113529
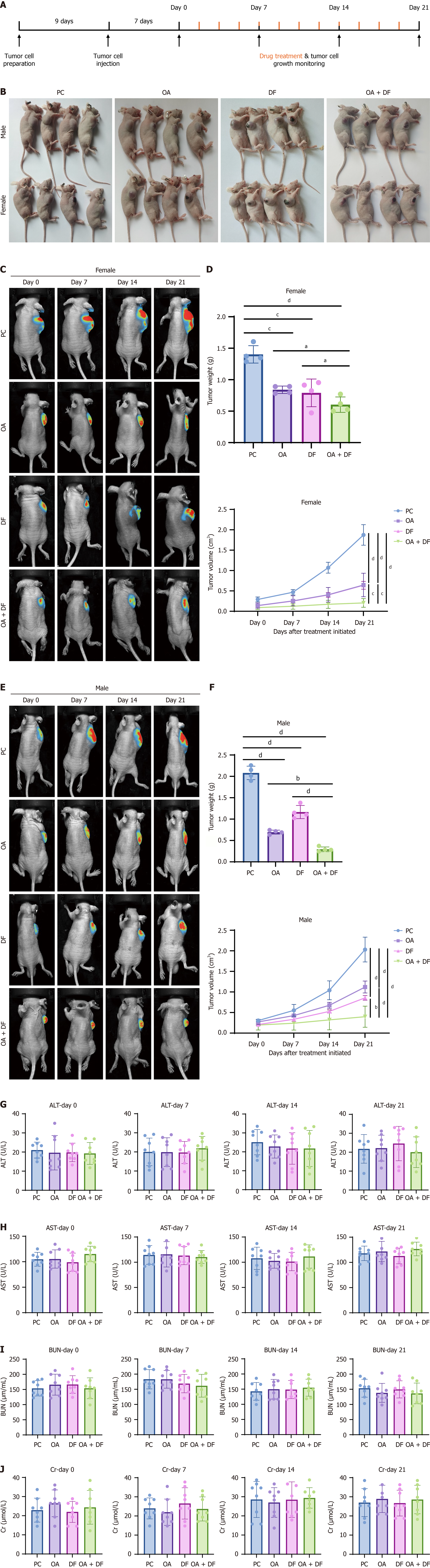
Figure 1 Synergistic antitumor effect of oroxylin A and donafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo.
A: Schematic illustration of the in vivo experimental procedures in a rodent model; B: Representative photographs showing the general status of mice in each group; C-F: In vivo fluorescence images of tumors in female (C) and male (E) mice at 7 days, 14 days, and 21 days post-treatment, enabling non-invasive, longitudinal, and sex-specific monitoring of tumor progression. Tumor volume and weight were measured in female (D) and male (F) mice after surgical resection at the endpoint (day 21); G-J: Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (G), aspartate aminotransferase (H), blood urea nitrogen (I) and creatinine (J) were quantified every 7 days following treatment with oroxylin A and/or donafenib. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. PC: Placebo control; OA: Oroxylin A; DF: Donafenib; OA + DF: Oroxylin A + donafenib; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; Cr: Creatinine.
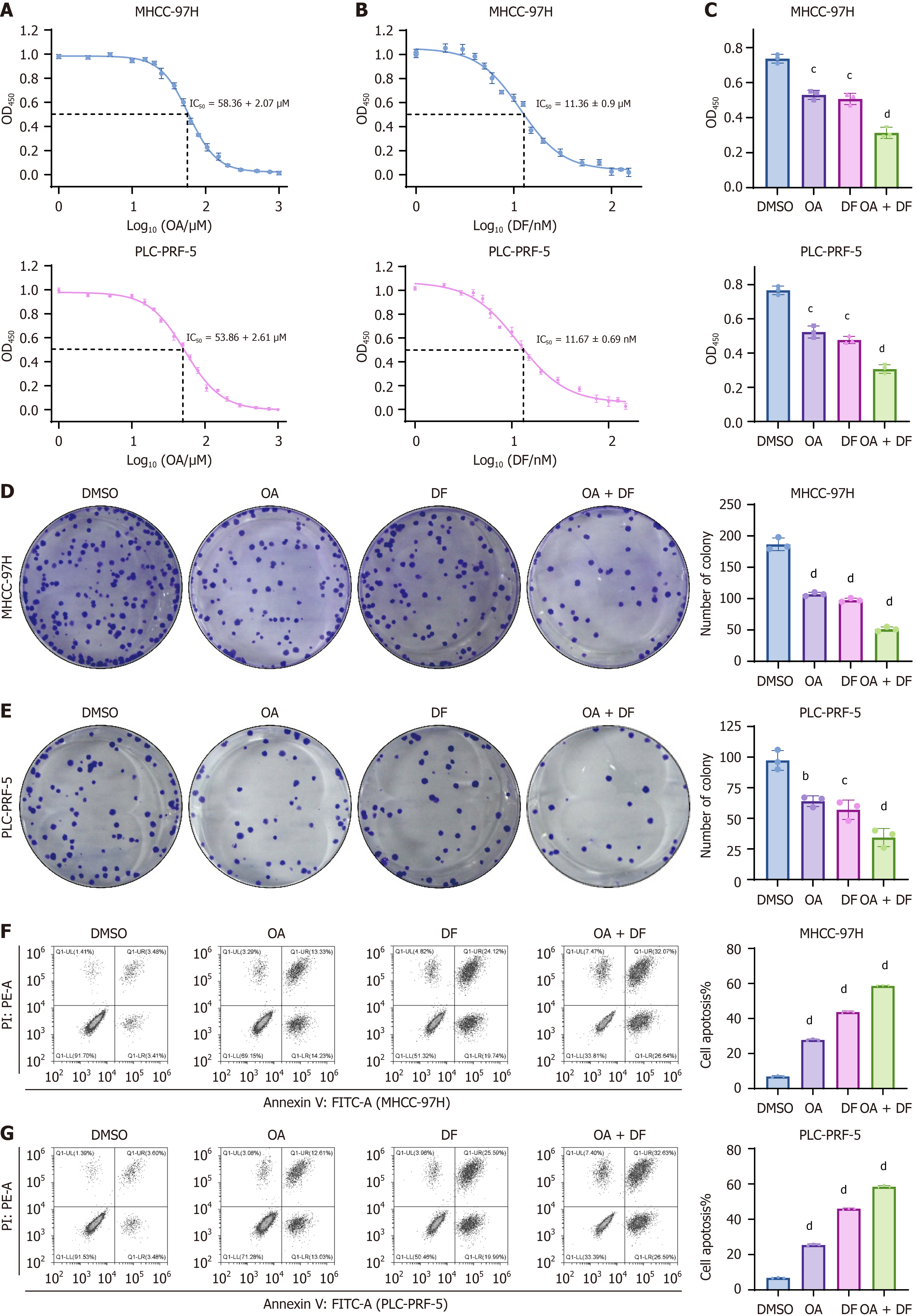
Figure 2 Synergistic anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of oroxylin A and donafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A and B: The half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of oroxylin A (A) and donafenib (B) were determined in MHCC-97H and PLC-PRF-5 cell lines; C-E: MHCC-97H and PLC-PRF-5 cell proliferation were detected using Cell Counting Kit-8 assay (C) and colony formation assay (D and E) after treatment with oroxylin A and/or donafenib; F and G: Cell apoptosis was assessed using flow cytometry after treatment with oroxylin A and/or donafenib in MHCC-97H (F) and PLC-PRF-5 (G) cell lines. Data are presented as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; OA: Oroxylin A; DF: Donafenib; OA + DF: Oroxylin A + donafenib.
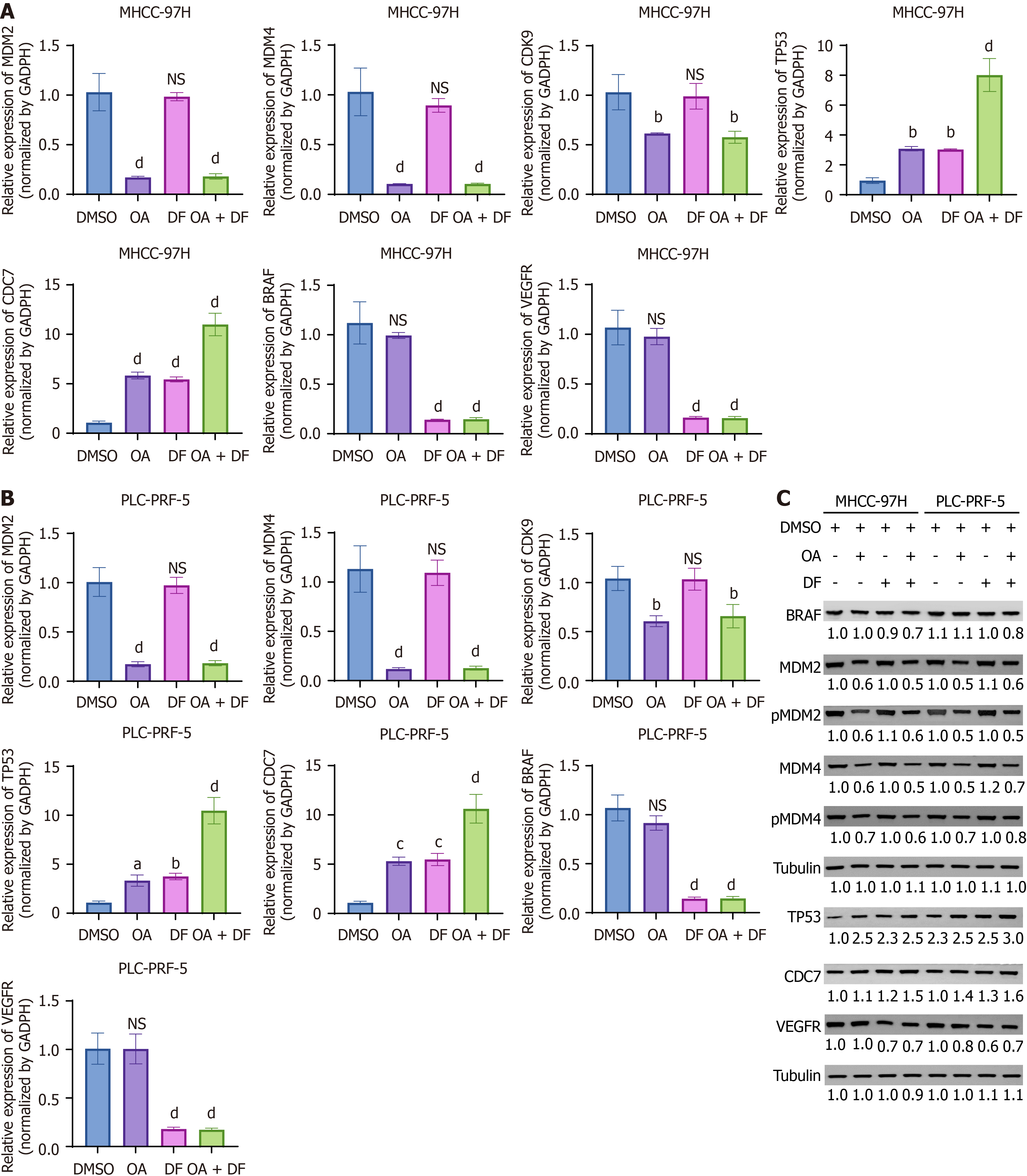
Figure 3 Synergistic activation of the TP53 signaling pathway by oroxylin A and donafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A and B: The mRNA expression of tumor protein p53, murine double minute 2 (MDM2), MDM4, cyclin-dependent kinase 9, B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, and cell division cycle 7 in MHCC-97H (A) and PLC-PRF-5 (B) cells was measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction after treatment with oroxylin A and/or donafenib; C: The protein levels of tumor protein p53, MDM2, MDM4, phosphorylated MDM2, phosphorylated MDM4, cyclin-dependent kinase 9, and B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, and cell division cycle 7 were examined using Western blot analysis in both cell lines following treatment with oroxylin A and/or donafenib. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001, ns: P > 0.05. DMSO: Dimethyl Sulfoxide; OA: Oroxylin A; DF: Donafenib; OA + DF: Oroxylin A + donafenib; MDM2: Murine double minute 2; MDM4: Murine double minute 4; CDK9: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9; TP53: Tumor protein p53; CDC7: Cell division cycle 7; BRAF: B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; p-MDM2: Phosphorylated murine double minute 2; p-MDM4: Phosphorylated murine double minute 4.
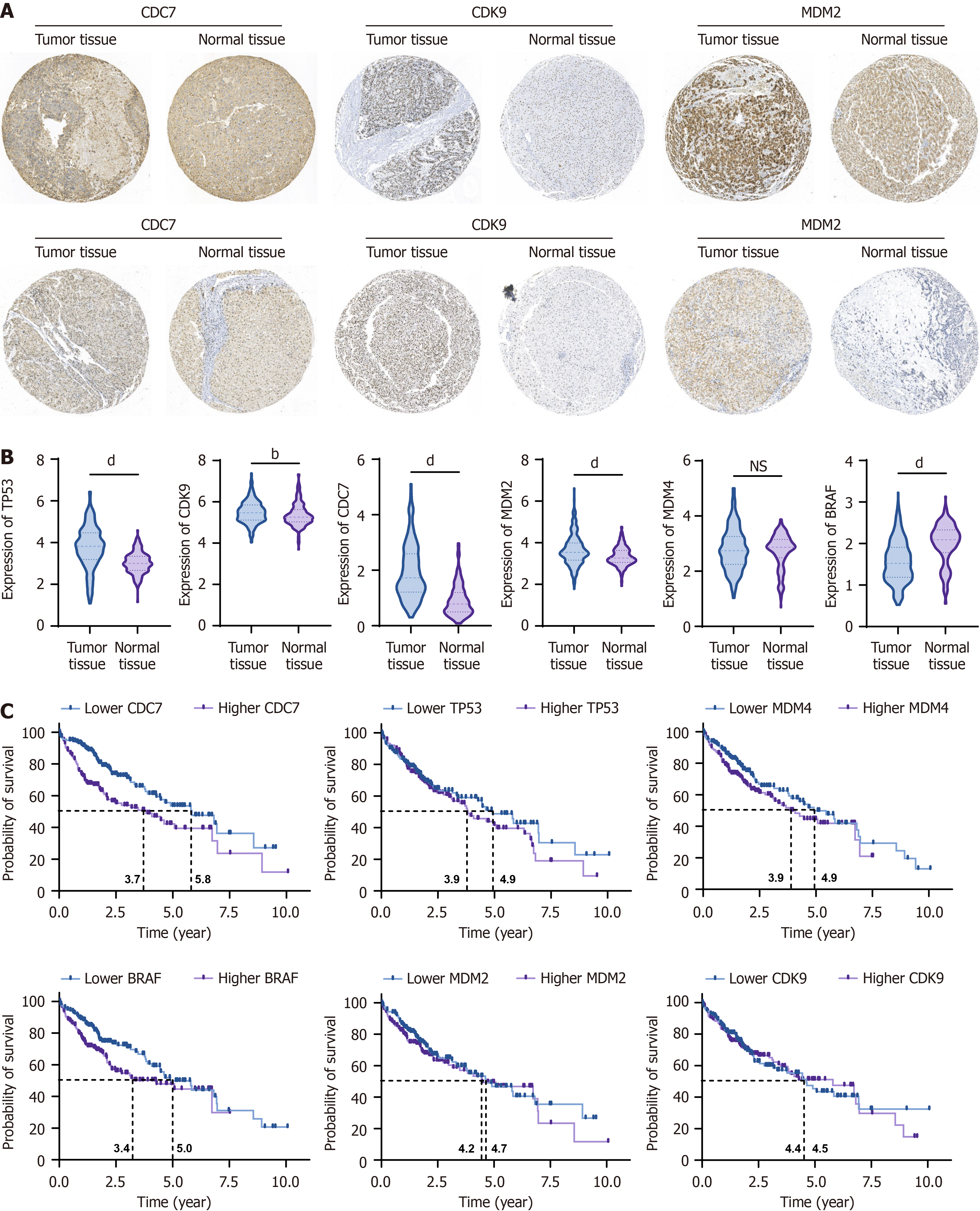
Figure 4 Upregulation of tumor protein p53, murine double minute 2, murine double minute 4, and cyclin-dependent kinase 9 correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
A: The expression of murine double minute 2 (MDM2), phosphorylated MDM2, MDM4, phosphorylated MDM4, cell division cycle 7 (CDC7), and cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) in clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimens was assessed using immunohistochemical analysis; B: The mRNA levels of tumor protein p53, MDM2, MDM4, CDC7, CDK9, and B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase were analyzed in HCC patients using datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus repositories; C: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis were performed based on the expression of tumor protein p53, MDM2, MDM4, CDC7, CDK9, and B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase and their regulatory proteins, showing a significant correlation with overall survival in HCC patients. Data are presented as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001, ns: P > 0.05. CDC7: Cell division cycle 7; CDK9: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9; MDM2: Murine double minute 2; TP53: Tumor protein p53; MDM4: Murine double minute 4; BRAF: B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase.
Figure 5 Knockdown of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 affects oroxylin A/donafenib-induced dysregulation of tumor protein p53 signaling-related proteins.
A and B: The protein expression of tumor protein p53, cell division cycle 7, cyclin-dependent kinase 9, murine double minute 2 (MDM2), phosphorylated MDM2, MDM4, phosphorylated MDM4, B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor was detected using western blot analysis after the genetic silencing of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 and exposure to oroxylin A (A) or donafenib (B) for 24 hours in MHCC-97H and PLC-PRF-5 cell lines. OA: Oroxylin A; DF: Donafenib; CDK9: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9; BRAF: B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase; CDC7: Cell division cycle 7; MDM4: Murine double minute 4; p-MDM4: Phosphorylated murine double minute 4; MDM2: Murine double minute 2; p-MDM2: Phosphorylated murine double minute 2; TP53: Tumor protein p53; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
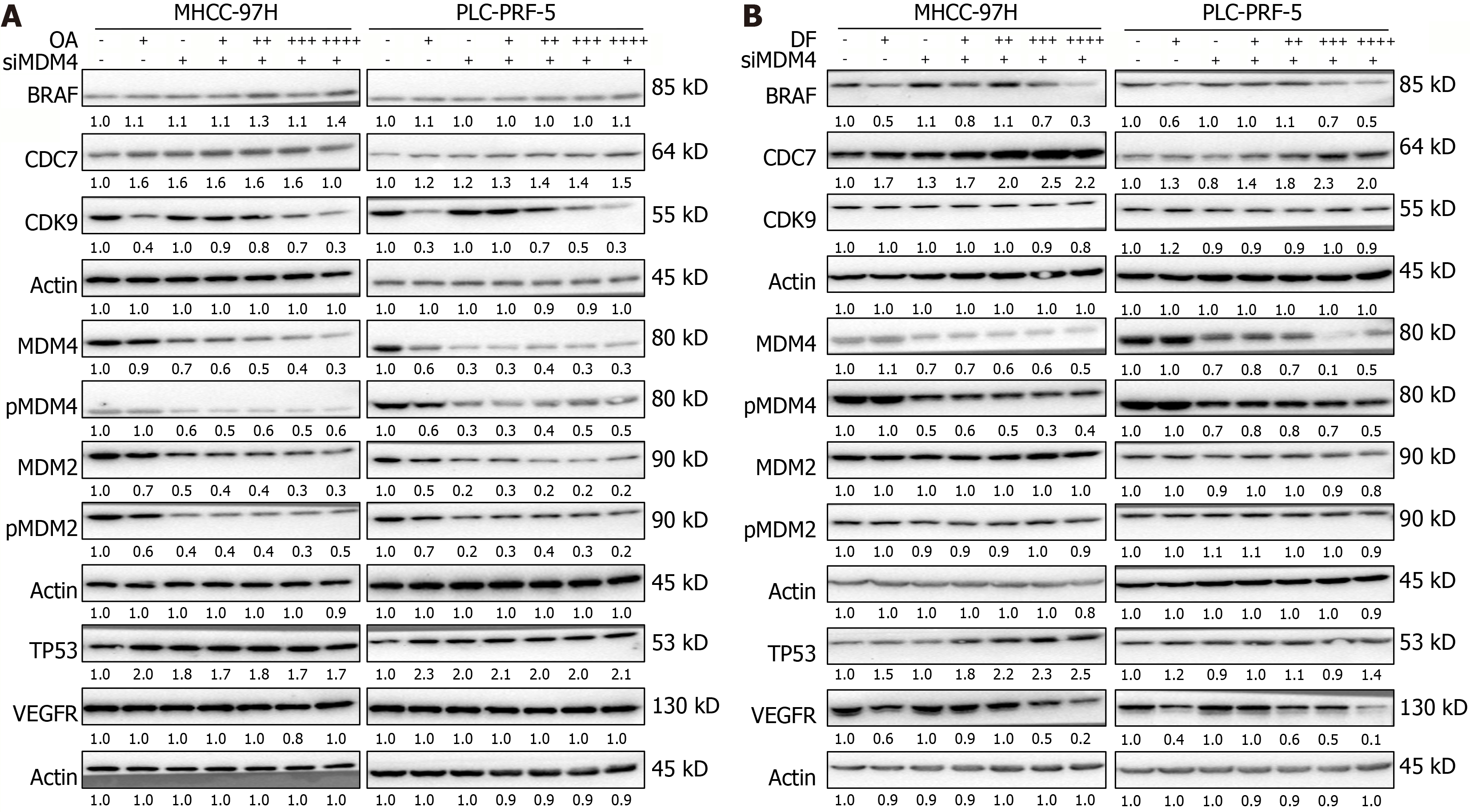
Figure 6 Knockdown of murine double minute 4 affects oroxylin A/donafenib-induced dysregulation of tumor protein p53 signaling-related proteins.
A and B: The protein expression of tumor protein p53, cell division cycle 7, cyclin-dependent kinase 9, murine double minute 2 (MDM2), phosphorylated MDM2, MDM4, phosphorylated MDM4, B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor was detected using western blot analysis after the genetic silencing of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 and exposure to oroxylin A (A) or donafenib (B) for 24 hours in MHCC-97H and PLC-PRF-5 cell lines. OA: Oroxylin A; DF: Donafenib; MDM4: Murine double minute 4; BRAF: B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase; CDC7: Cell division cycle 7; CDK9: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9; p-MDM4: Phosphorylated murine double minute 4; MDM2: Murine double minute 2; p-MDM2: Phosphorylated murine double minute 2; TP53: Tumor protein p53; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
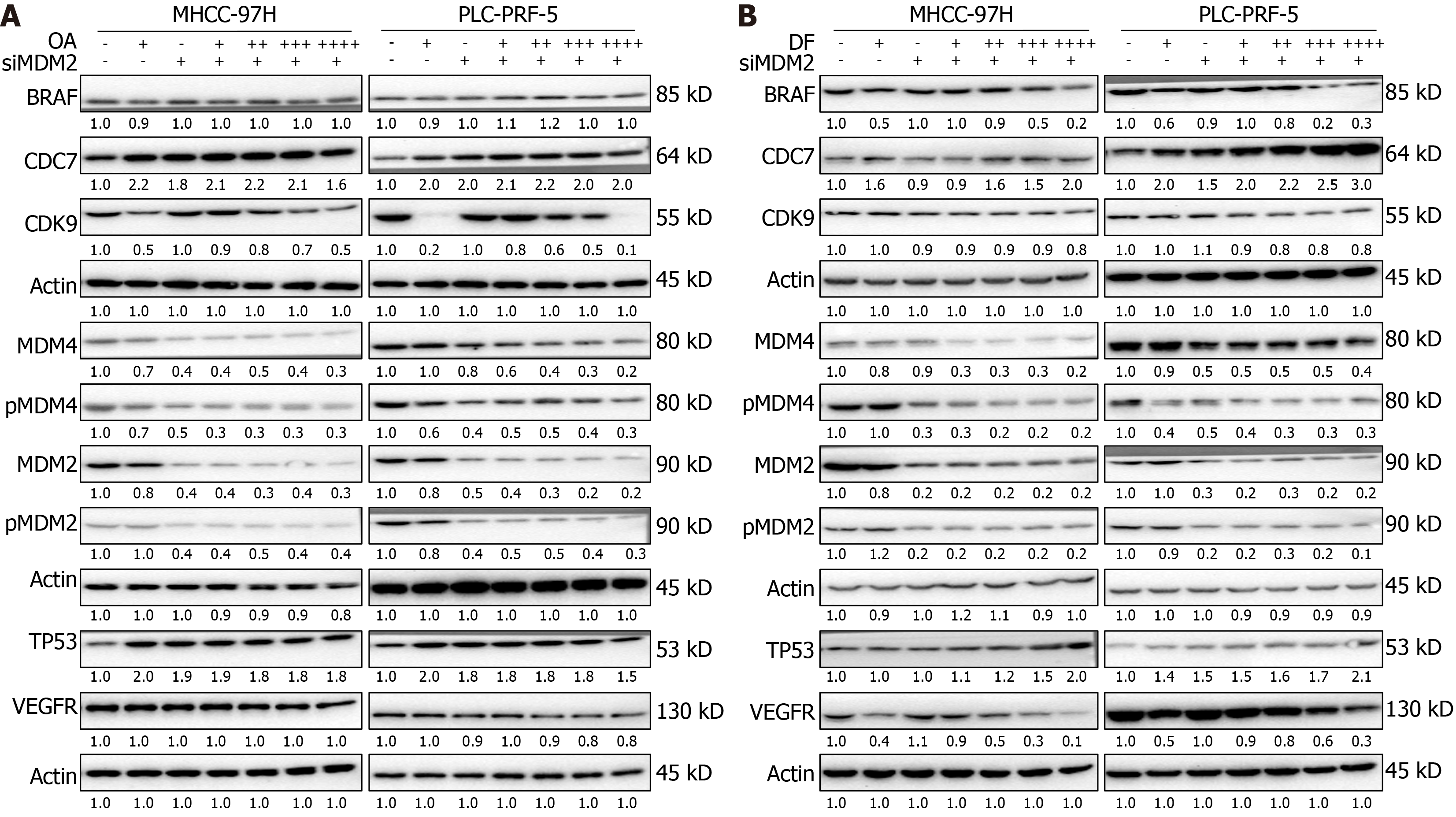
Figure 7 Knockdown of murine double minute 2 affects oroxylin A/donafenib-induced dysregulation of tumor protein p53 signaling-related proteins.
A and B: The protein expression of tumor protein p53, cell division cycle 7, cyclin-dependent kinase 9, murine double minute 2 (MDM2), phosphorylated MDM2, MDM4, phosphorylated MDM4, B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor was detected using western blot analysis after the genetic silencing of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 and exposure to oroxylin A (A) or donafenib (B) for 24 hours in MHCC-97H and PLC-PRF-5 cell lines. OA: Oroxylin A; DF: Donafenib; MDM2: Murine double minute 2; BRAF: B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase; CDC7: Cell division cycle 7; CDK9: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9; MDM4: Murine double minute 4; p-MDM4: Phosphorylated murine double minute 4; p-MDM2: Phosphorylated murine double minute 2; TP53: Tumor protein p53; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
- Citation: Zhang MY, Sun RQ, Min Q, Zhu YQ, Qin SK, Guo QL. Synergistic antitumor effect of oroxylin A and donafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma through tumor protein p53 signaling pathway activation. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(6): 113529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i6/113529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i6.113529