©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2026; 32(6): 113010
Published online Feb 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i6.113010
Published online Feb 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i6.113010
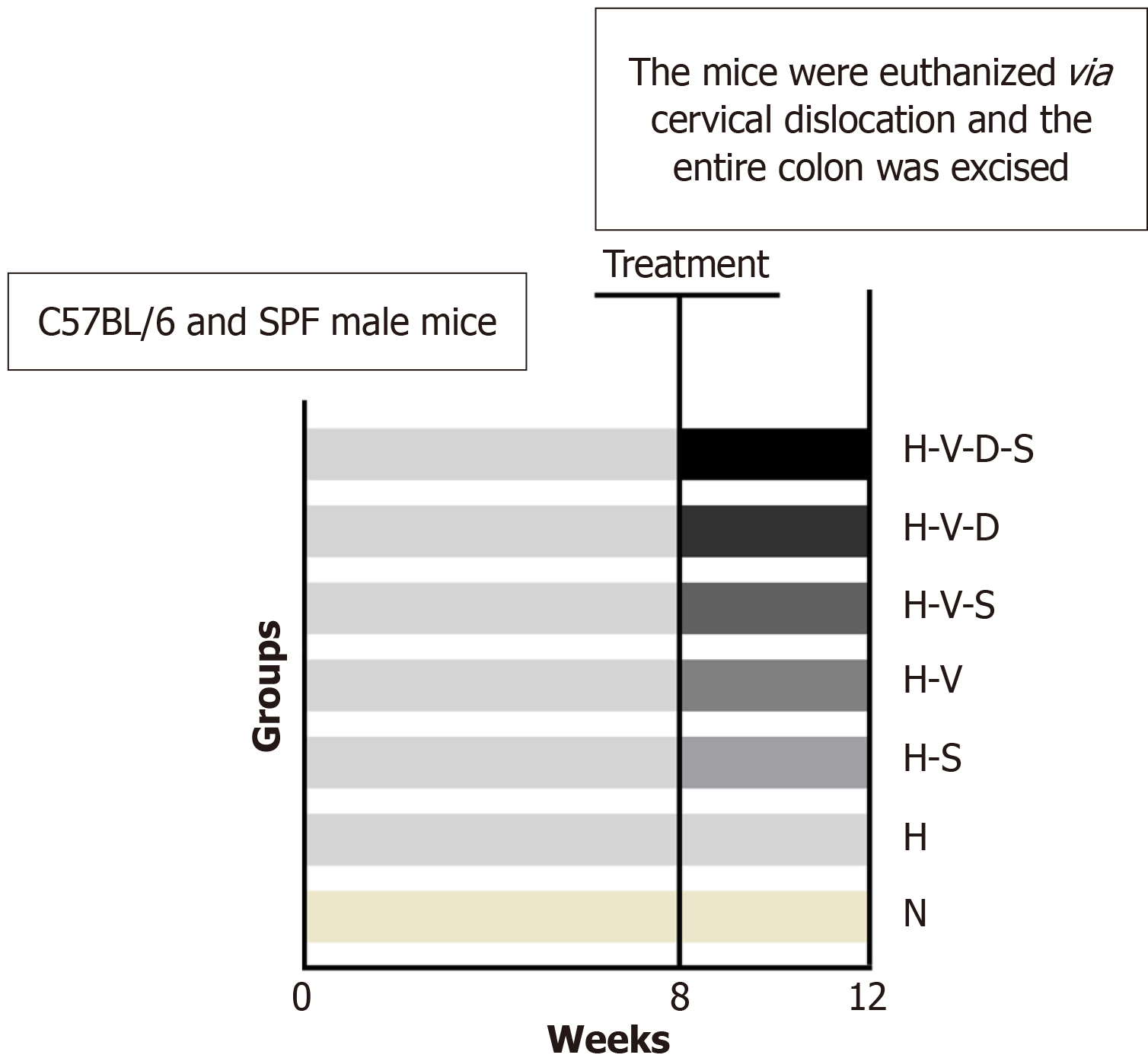
Figure 1 Grouping of mice and the procedures involved.
SPF: Specific pathogen free; H-V-D-S: High-fat diet with vancomycin, deoxycholic acid, and Bifidobacterium; H-V-D: High-fat diet with vancomycin and deoxycholic acid; H-V-S: High-fat diet with vancomycin and Bifidobacterium; H-V: High-fat diet with vancomycin; H-S: High-fat diet supplemented with Bifidobacterium; H: High-fat diet; N: General.
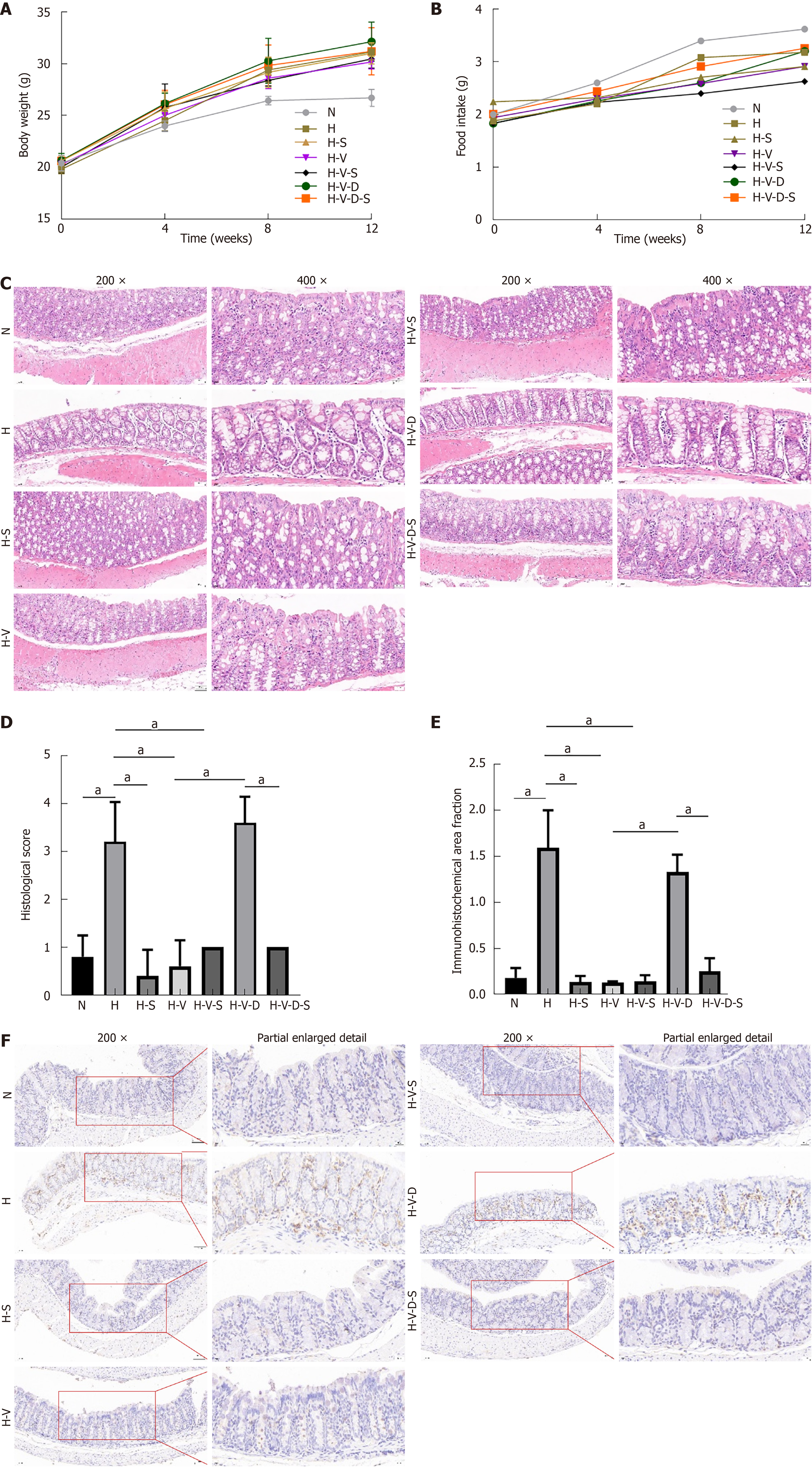
Figure 2 Changes in the weight and feeding pattern in mice with hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry of colonic tissue.
A: Changes in the weight of mice of each group over time; B: Changes in the feeding pattern of the mice of each group over time; C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the colonic tissue of the mice of each group (scale bar: 200 ×, 100 μm; 400 ×, 60 μm); D: Colon histological scores of the mice of each group; E: Proportion of the positive area of colon immunohistochemistry in mice (%); F: Immunohistochemistry of the mice colonic tissues (F4/80) (scale bars: 50 μm). n = 6. aP < 0.05. H-V-D-S: High-fat diet with vancomycin, deoxycholic acid, and Bifidobacterium; H-V-D: High-fat diet with vancomycin and deoxycholic acid; H-V-S: High-fat diet with vancomycin and Bifidobacterium; H-V: High-fat diet with vancomycin; H-S: High-fat diet supplemented with Bifidobacterium; H: High-fat diet; N: General.
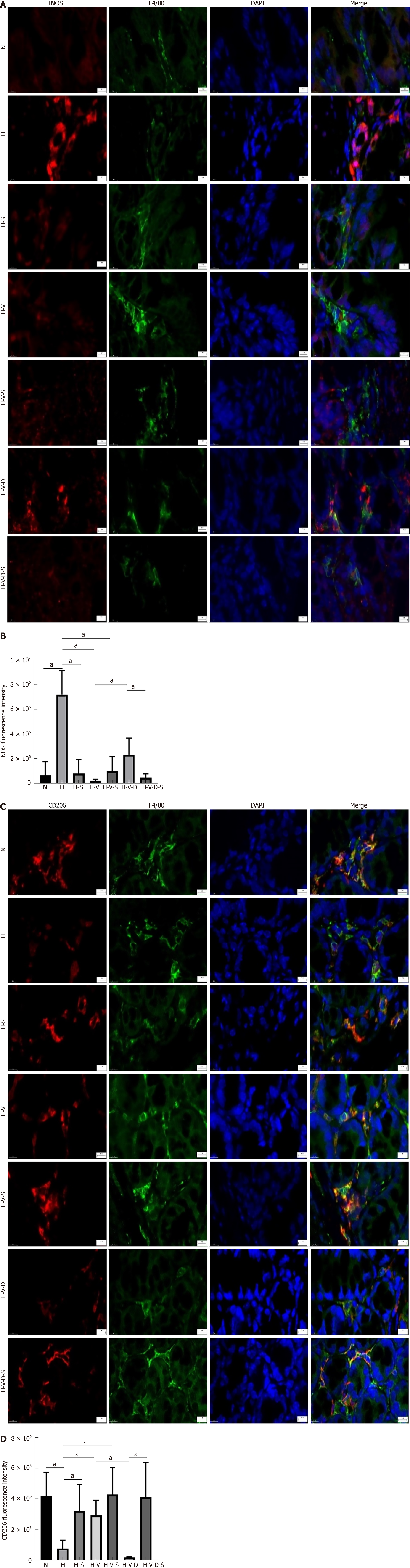
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence staining of mice colonic tissue (inducible nitric oxide synthase + F4/80, CD206+ F4/80).
A: Immuno
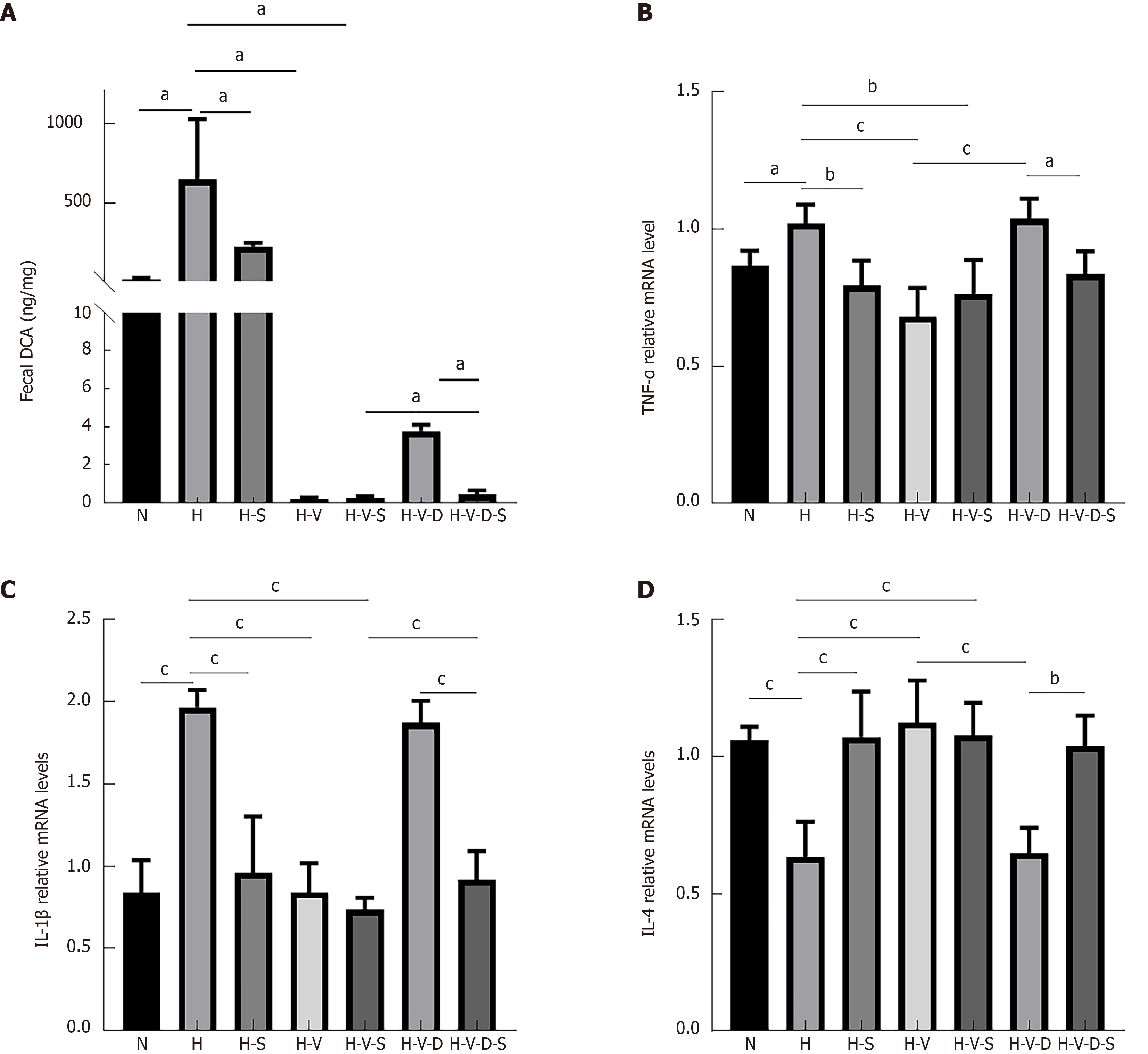
Figure 4 Fecal deoxycholic acid levels in mice and inflammatory factor expression in colonic tissue.
A: Fecal deoxycholic acid content of mice in each group; B-D: Expression levels of interleukin-1β, tumour necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-4 in mouse colonic tissue. n = 6. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and cP < 0.001. DCA: Deoxycholic acid; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; H-V-D-S: High-fat diet with vancomycin, deoxycholic acid, and Bifidobacterium; H-V-D: High-fat diet with vancomycin and deoxycholic acid; H-V-S: High-fat diet with vancomycin and Bifidobacterium; H-V: High-fat diet with vancomycin; H-S: High-fat diet supplemented with Bifidobacterium; H: High-fat diet; N: General.
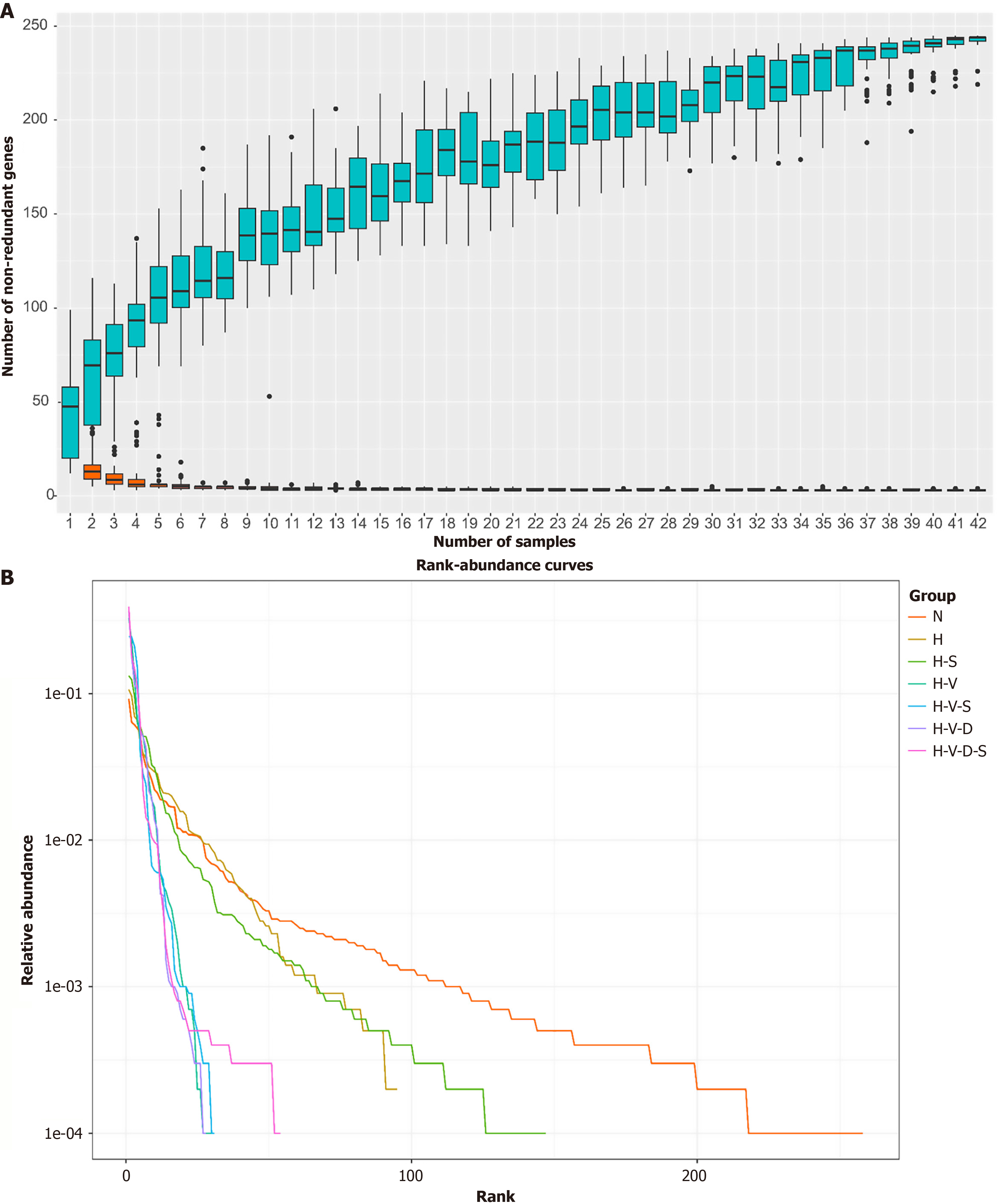
Figure 5 Species accumulation curve vs the rank-abundance curve analysis.
A: Cumulative plot of the genus-level species; B: Group rank-abundance plots.
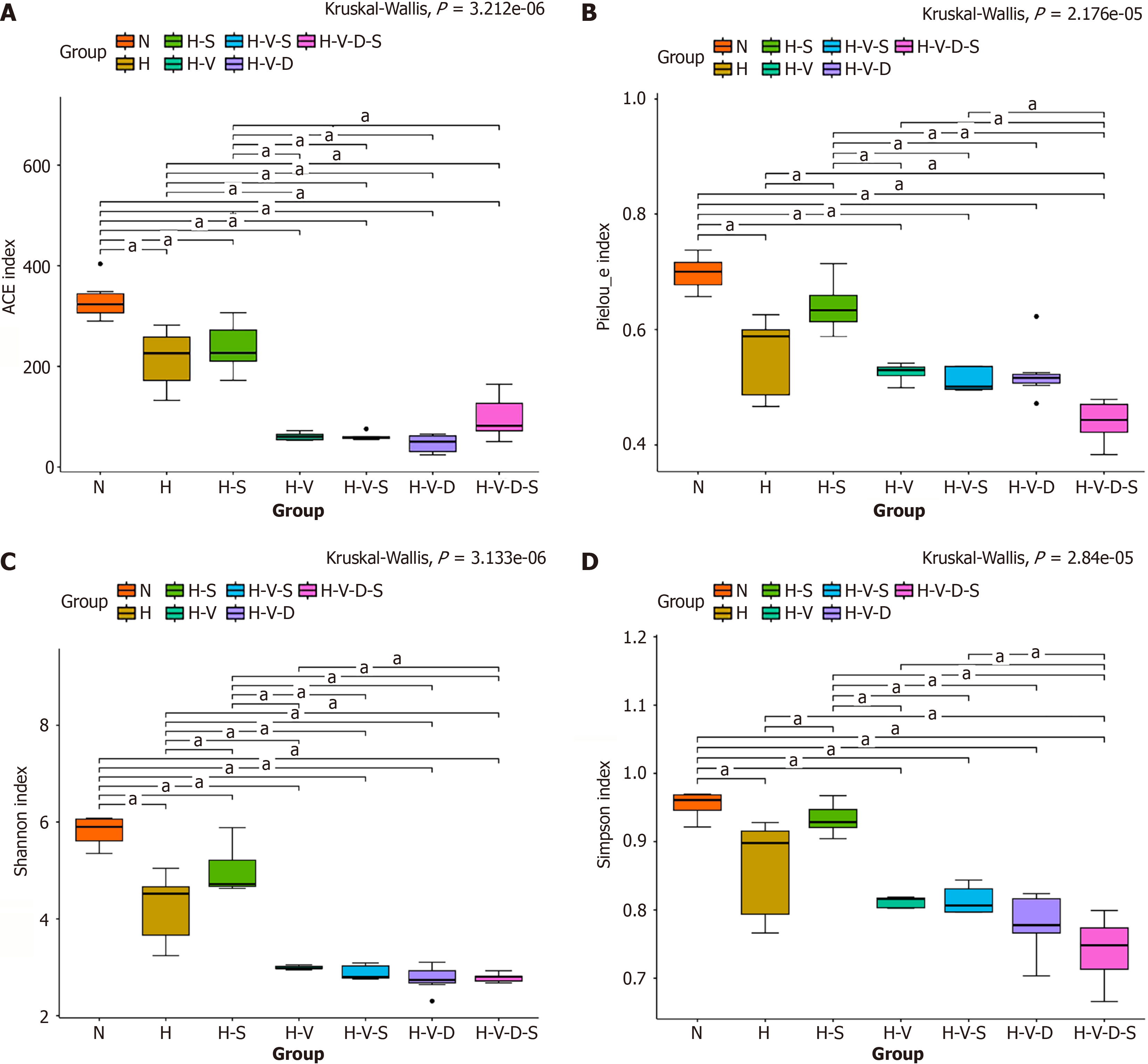
Figure 6 Effects of Bifidobacterium and vancomycin on microbial alpha diversity in the mouse colon.
A: Ace index comparison among groups (violinplot); B: Pielou_e index comparison among groups (violinplot); C: Shannon index comparison among groups (violinplot); D: Simpson index comparison among groups (violinplot). aP < 0.05.
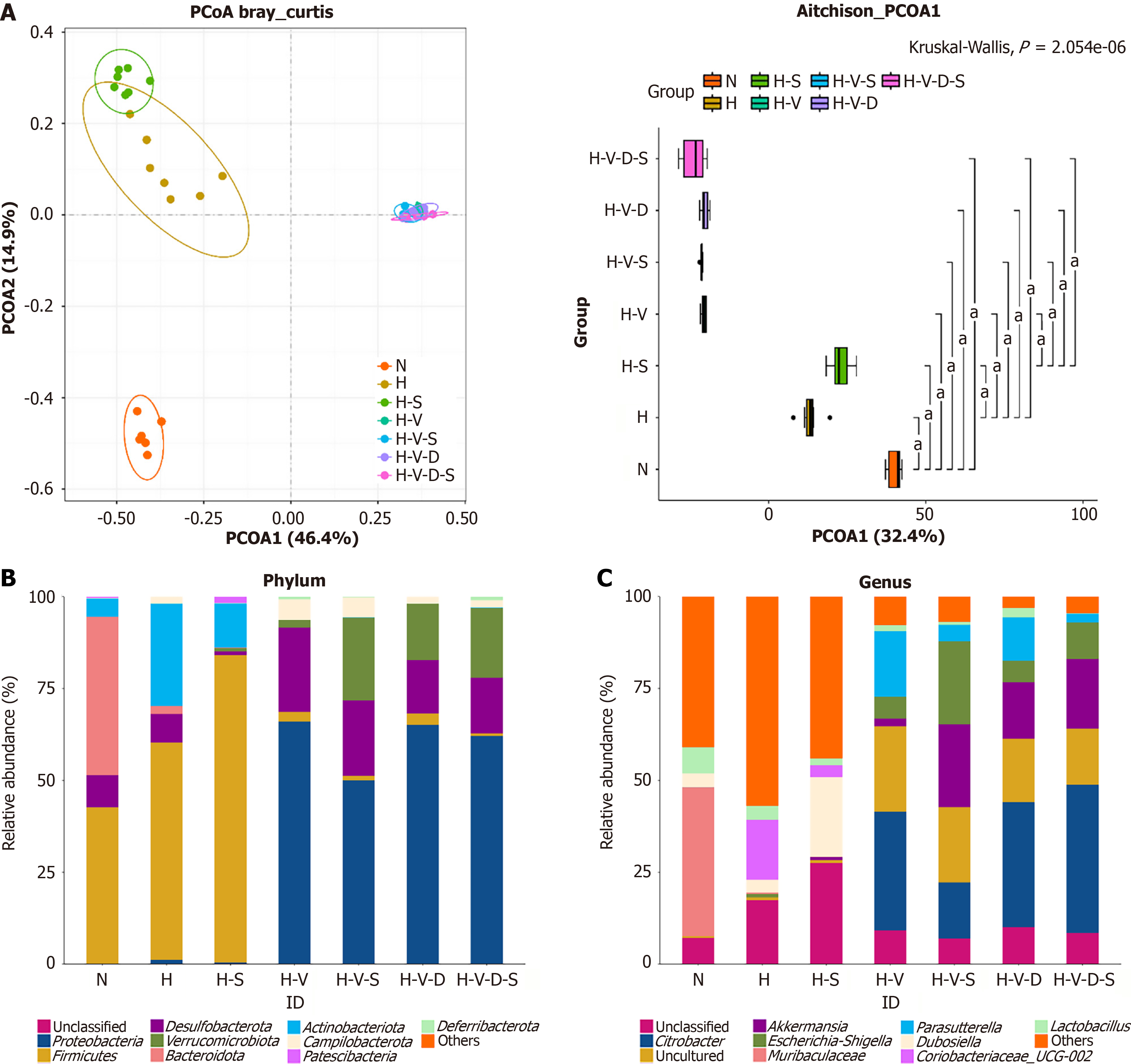
Figure 7 Effects of Bifidobacterium and vancomycin on microbial beta diversity in mouse colon.
A: Principal coordinate analysis (2D) analysis; B: Microbial composition diagram at the phylum level; C: Microbial composition diagram at the genus level. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Yang PC, Xiao CY, Wang J, Yan CH, Li QY, Li SY, Li J, Zhang LJ, Dai CB. Effects and mechanism of Bifidobacterium on intestinal inflammation resulting from deoxycholic acid-induced M1 polarization of macrophages. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(6): 113010
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i6/113010.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i6.113010