©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2026; 32(3): 113187
Published online Jan 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.113187
Published online Jan 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.113187
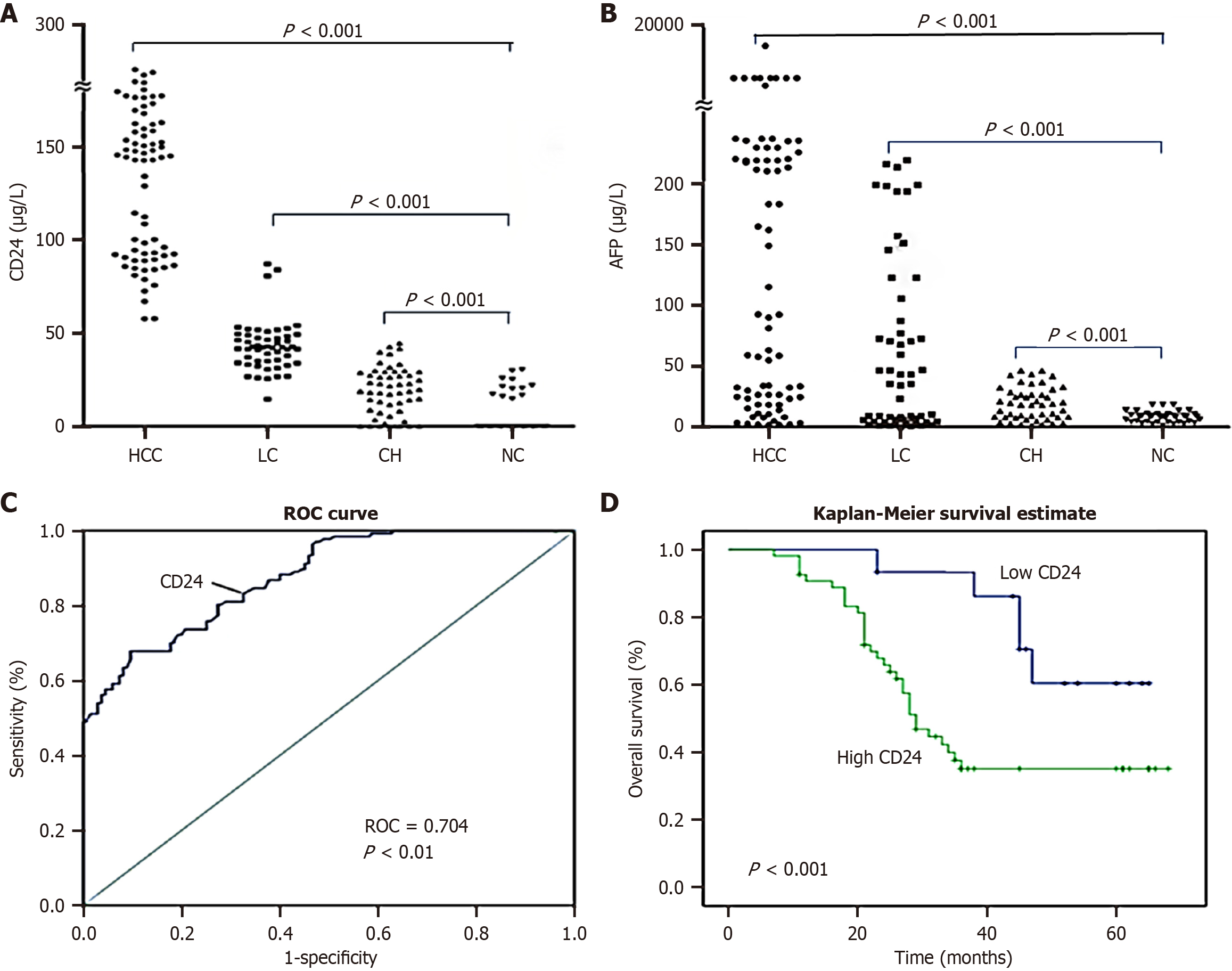
Figure 1 Comparative analysis of serum clusters of differentiation 24 expression among patients with chronic liver diseases.
A: Clusters of differentiation (CD) 24 expression in the serum of patients with chronic hepatitis (CH), liver cirrhosis (LC), or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or healthy individuals; B: Alpha-fetoprotein expression in the serum of patients with CH, LC, or HCC or healthy individuals; C: Receiver operating characteristic curve of circulating CD24 for the diagnosis of HCC patients; D: Survival curves of circulating CD24 levels in HCC patients generated by the Kaplan-Meier method. The green line represents the high CD24 group, and the blue line represents the low CD24 group. CH: Chronic hepatitis; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; CD: Clusters of differentiation; NC: Normal control.
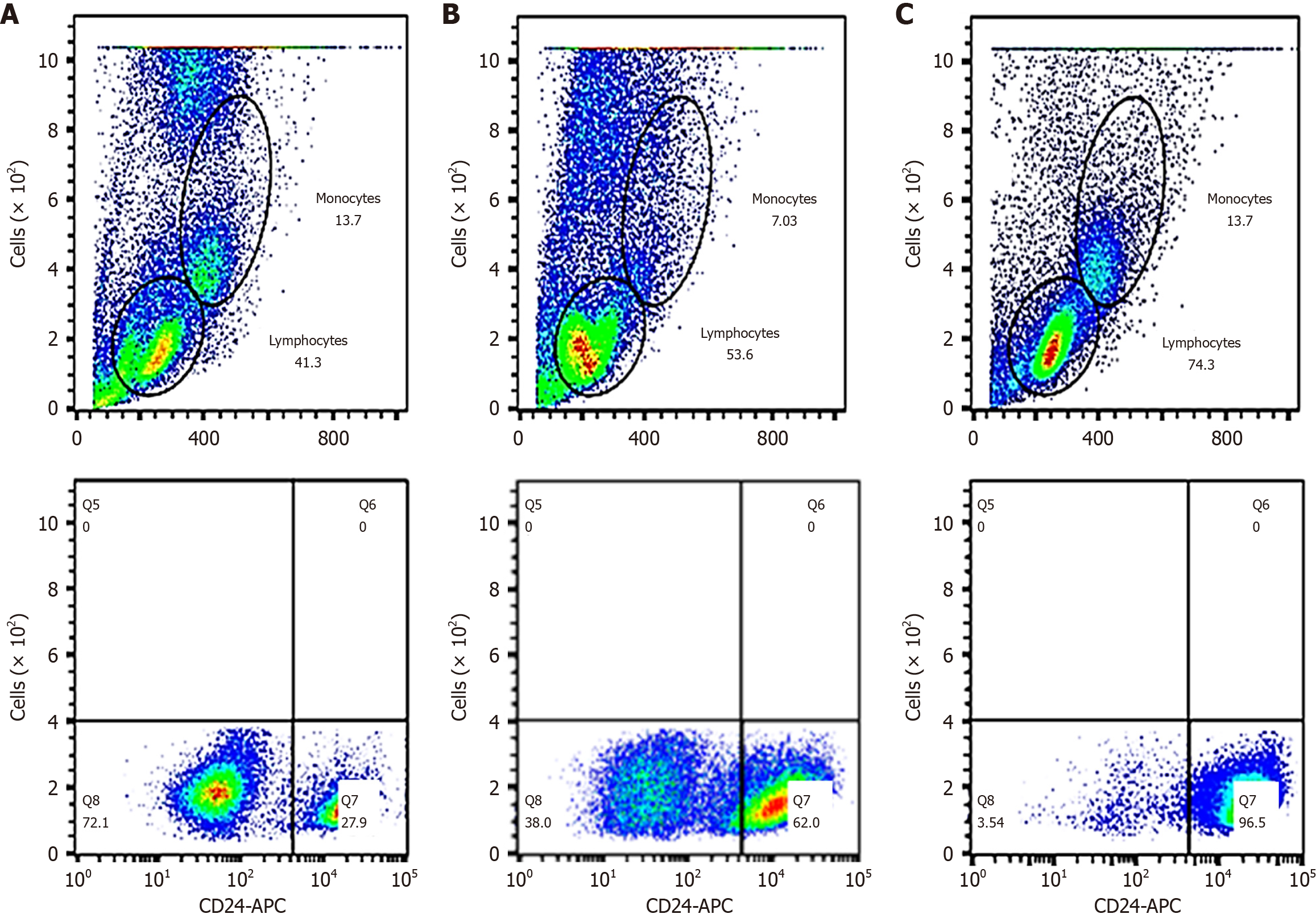
Figure 2 Blood mononuclear cell population and clusters of differentiation 24+ T lymphocyte ratio (%).
A: Mononuclear or clusters of differentiation (CD) 24+ T cells in the normal control group; B: Mononuclear or CD4+ T cells in the chronic hepatitis group; C: Mononuclear or CD24+ T cells in the hepatocellular carcinoma group. CD: Clusters of differentiation.
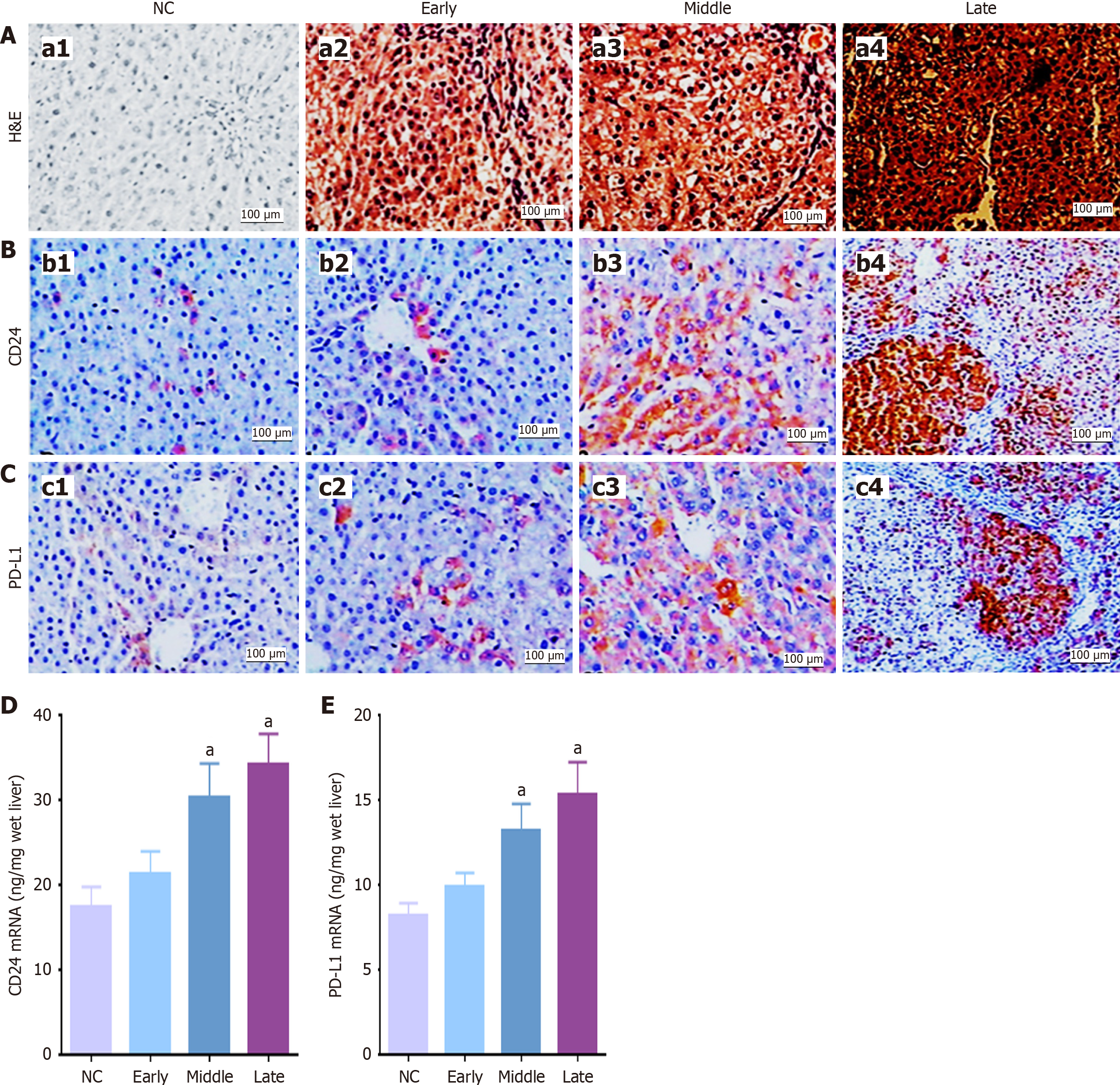
Figure 3 Verification of dynamic clusters of differentiation 24 activation in rat hepatocarcinogenesis.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of control livers (a1); a2: Liver pathology at an early stage; a3: Liver pathology at the middle stage; a4: Liver pathology at a late stage; B: Clusters of differentiation (CD) 24 expression in control livers (b1); b2: CD24 expression at the early stage; b3: CD24 expression at the middle stage; b4: CD24 expression at the late stage; C: Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in control rat livers (c1); c2: PD-L1 expression at the early stage; c3: PD-L1 expression at the middle stage; c4: PD-L1 expression at the late stage; D: Dynamic CD24 mRNA expression during hepatocarcinogenesis; E: Dynamic PD-L1 mRNA expression during hepa
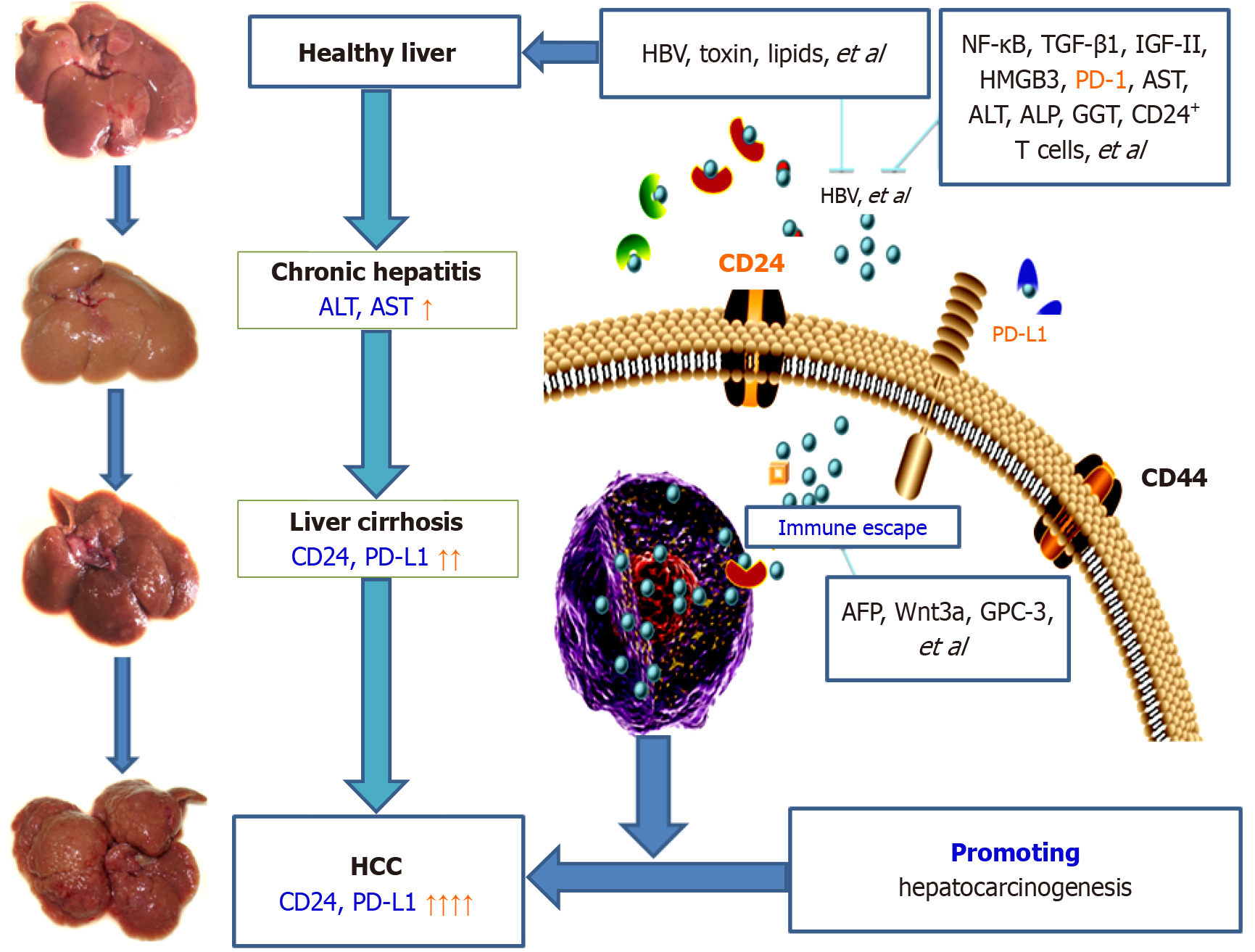
Figure 4 Mechanism through which clusters of differentiation 24 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis.
Chronic liver diseases involve a small subpopulation of cells called liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs), which are key drivers of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) formation or progression. Clusters of differentiation (CD) 24, like other HCC biomarkers, is involved in HCC progression, with abnormal expression at the protein or mRNA level, and provides a concise overview of the molecular pathogenesis of the HCC sequence. CD24 might be an important progenitor in hepatocarcinogenesis in the immune escape microenvironment. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor β1; PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; CD: Clusters of differentiation; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein.
- Citation: Cai Y, Liu LY, Xia XX, Tang H, Xu M, Sai WL, Yao DF, Yao M. Stemness CD24 activation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via an immune escape mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(3): 113187
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i3/113187.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.113187