©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2026; 32(2): 114057
Published online Jan 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i2.114057
Published online Jan 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i2.114057
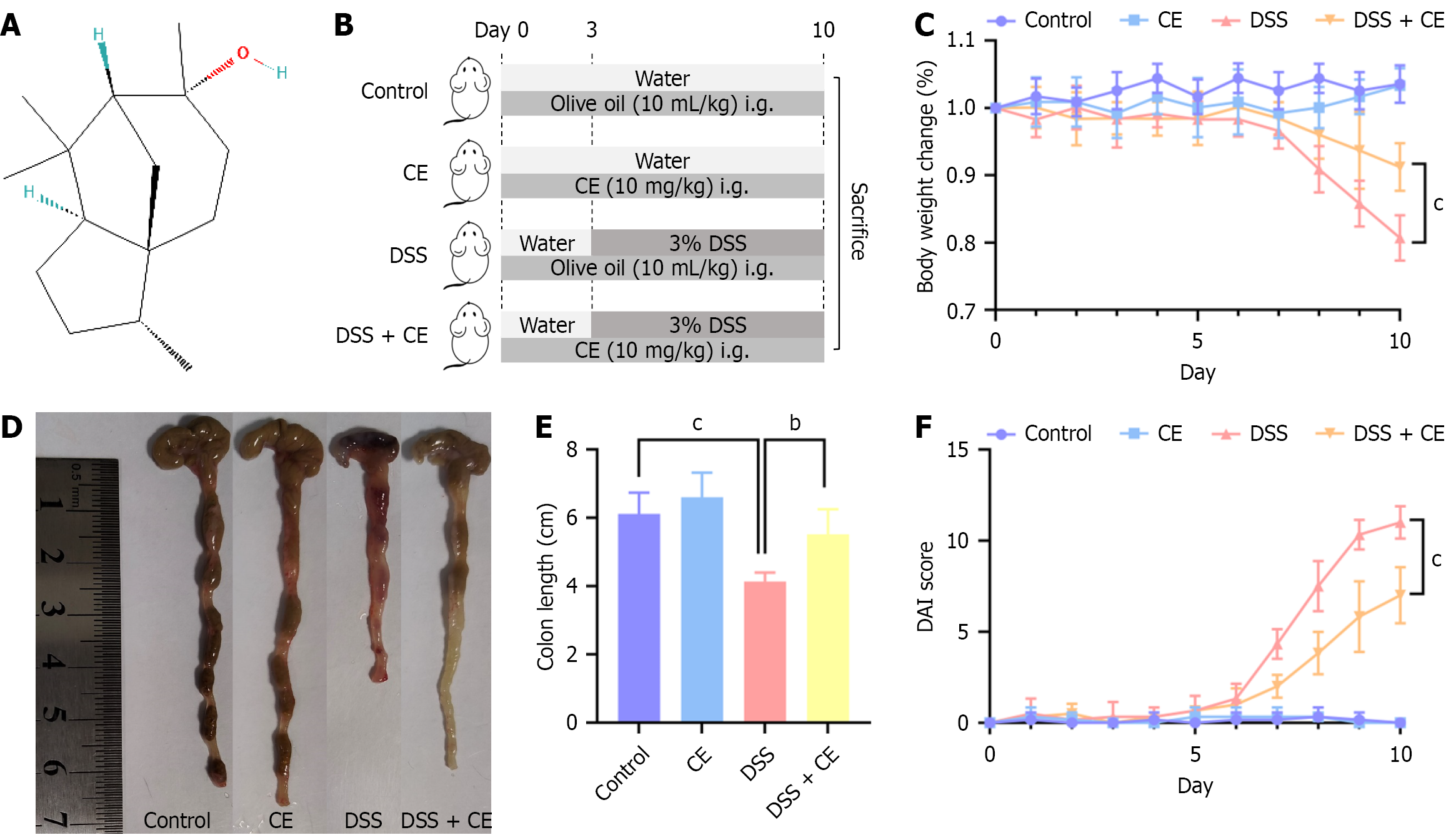
Figure 1 Cedrol ameliorated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis symptoms.
A: Chemical structure of cedrol; B: Experimental scheme diagram; C: Body weight changes during the experimental period; D: Representative colons from each group; E: Quantitative analysis of colon length; F: Disease activity index scores. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CE: Cedrol; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; i.g.: Gavage; DAI: Disease activity index.
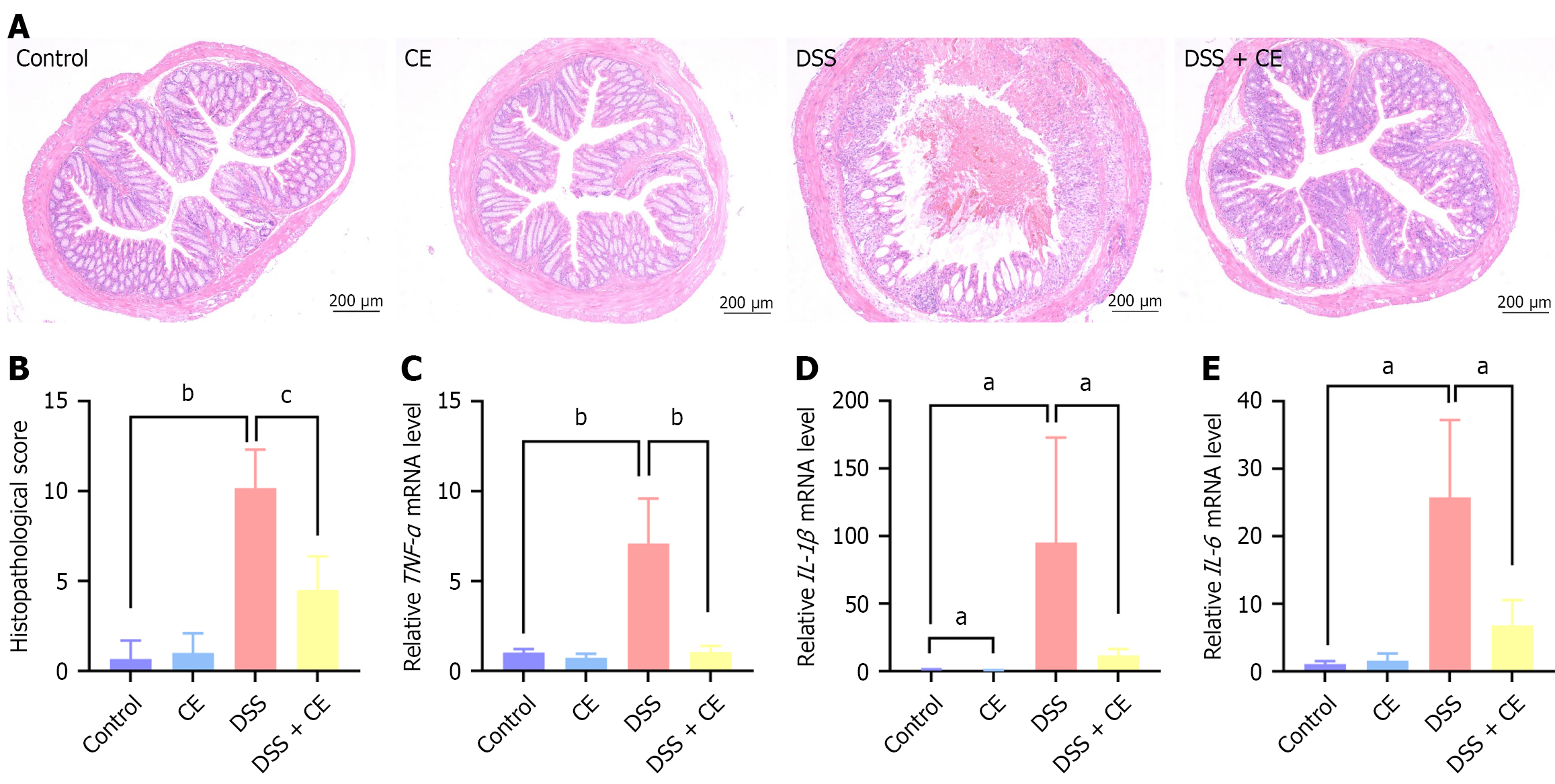
Figure 2 Cedrol attenuated histopathological damage and inflammatory cytokine expression in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.
A: Typical hematoxylin and eosin colon sections (× 100); B: Histopathological scores; C-E: Transcript levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (C), interleukin (IL)-1β (D), and IL-6 (E) messenger RNA in colonic tissues were measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CE: Cedrol; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; mRNA: Messenger RNA.
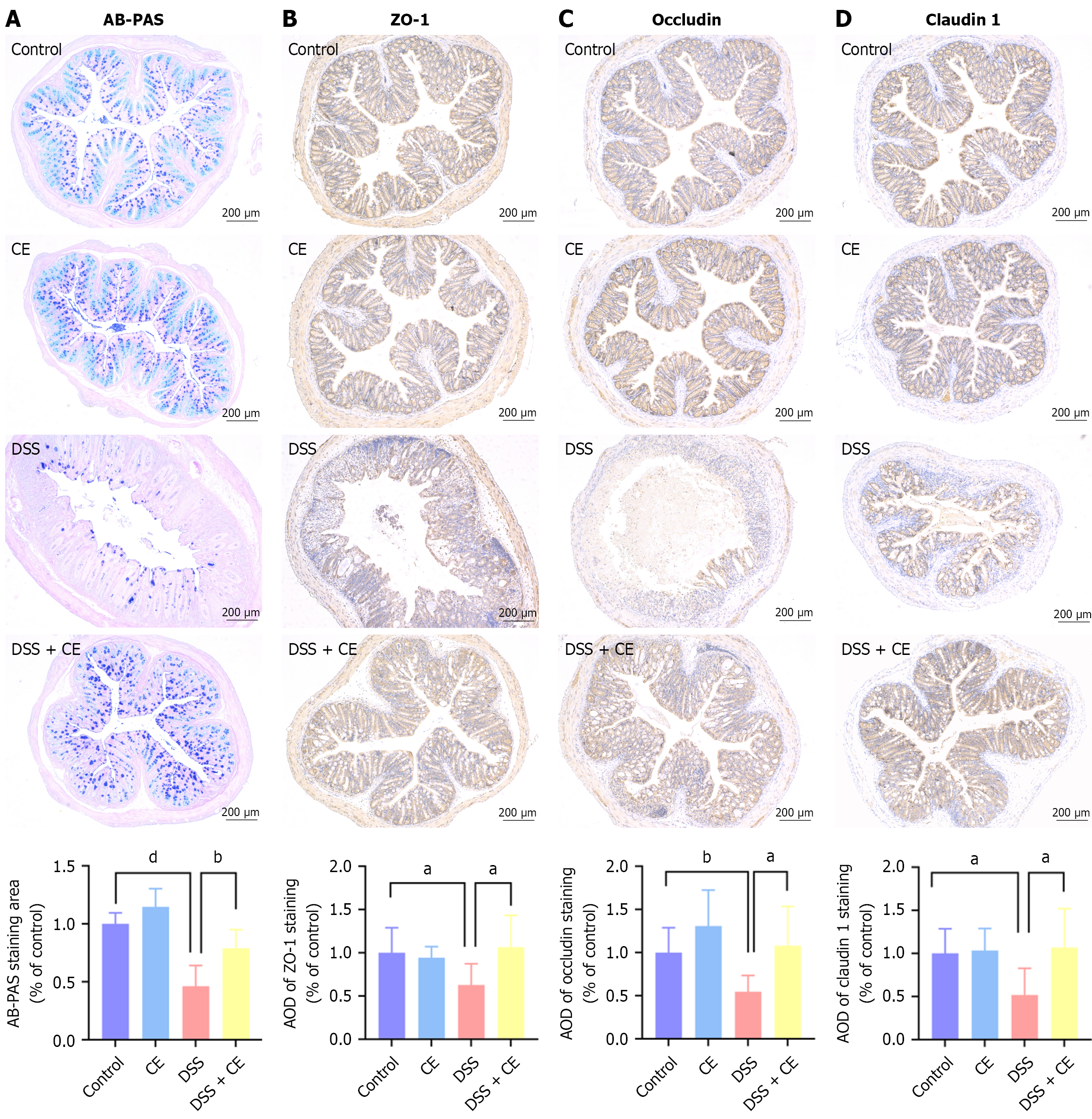
Figure 3 Cedrol re-established intestinal barrier integrity in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.
A: Characteristic alcian blue periodic acid-Schiff staining (× 100) and histogram of stained regions; B-D: Representative immunohistochemistry images (× 100) and statistical analysis of the average optical density for zonula occludens 1 (B), occludin (C), and claudin 1 (D). Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. dP < 0.0001. CE: Cedrol; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; AB-PAS: Alcian blue periodic acid-Schiff staining; AOD: Average optical density; ZO-1: Zonula occludens 1.
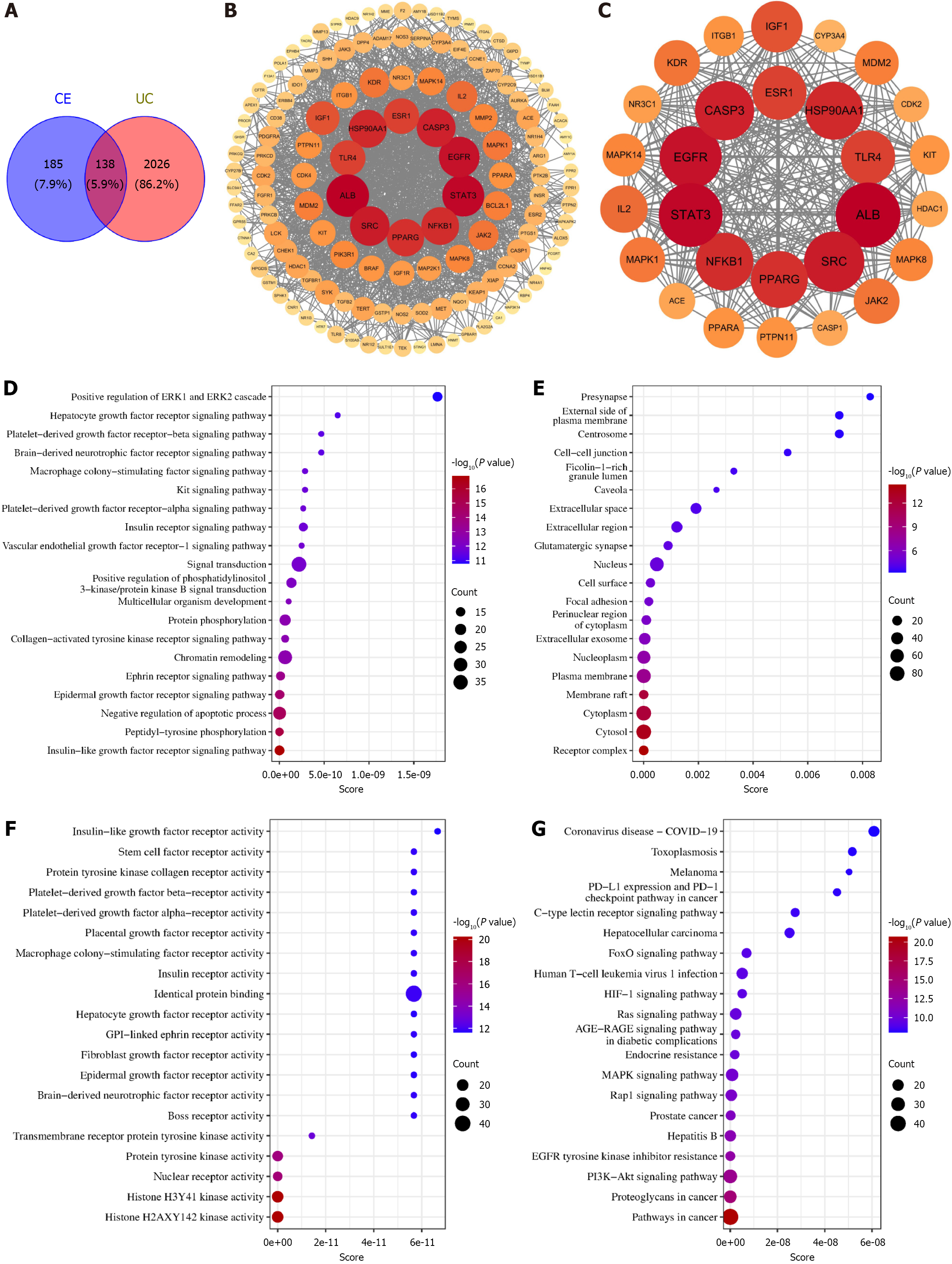
Figure 4 Network-based pharmacological investigation.
A: Venn diagram identifying 138 overlapping targets between cedrol and ulcerative colitis; B: Comprehensive protein-protein interaction network of overlapping targets; C: Core target subnetwork (28 high-connectivity nodes); D-F: Bubble plots for gene ontology-biological processes, gene ontology-cellular components, and gene ontology-molecular functions; G: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment bubble plot (top 20 pathways by significance). CE: Cedrol; UC: Ulcerative colitis; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinase; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor; AGE: Advanced glycation end products; RAGE: Receptor for advanced glycation end products; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B.
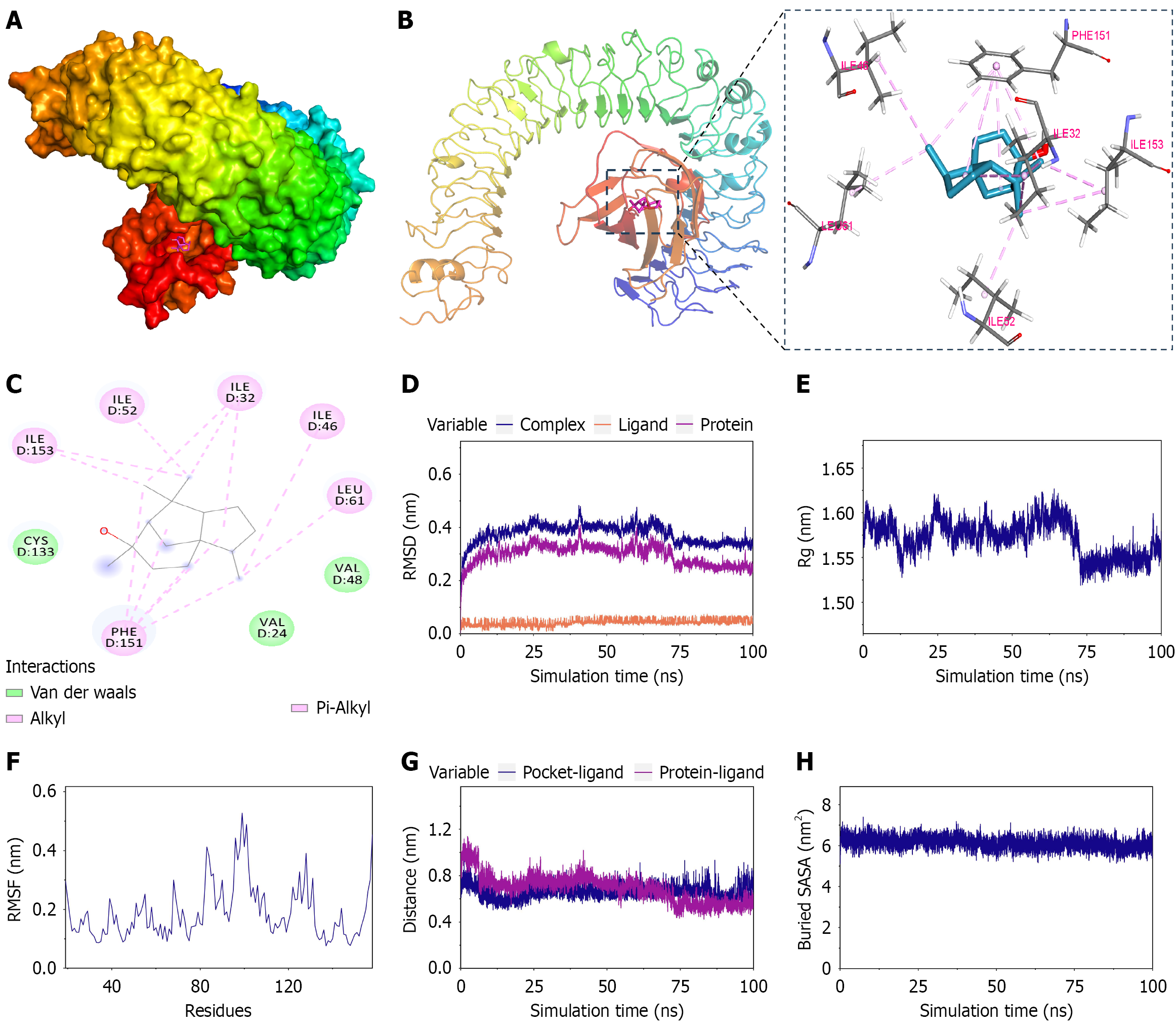
Figure 5 Computational docking and molecular dynamics simulations.
A-C: Docking results of cedrol and the toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 2 complex; D-H: Root mean square deviation (D), radius of gyration (E), root mean square fluctuation (F), centroid evolution (G), and buried solvent accessible surface area analysis (H) during molecular dynamics simulations. RMSD: Root mean square deviation; Rg: Radius of gyration; RMSF: Root mean square fluctuation; SASA: Solvent accessible surface area.
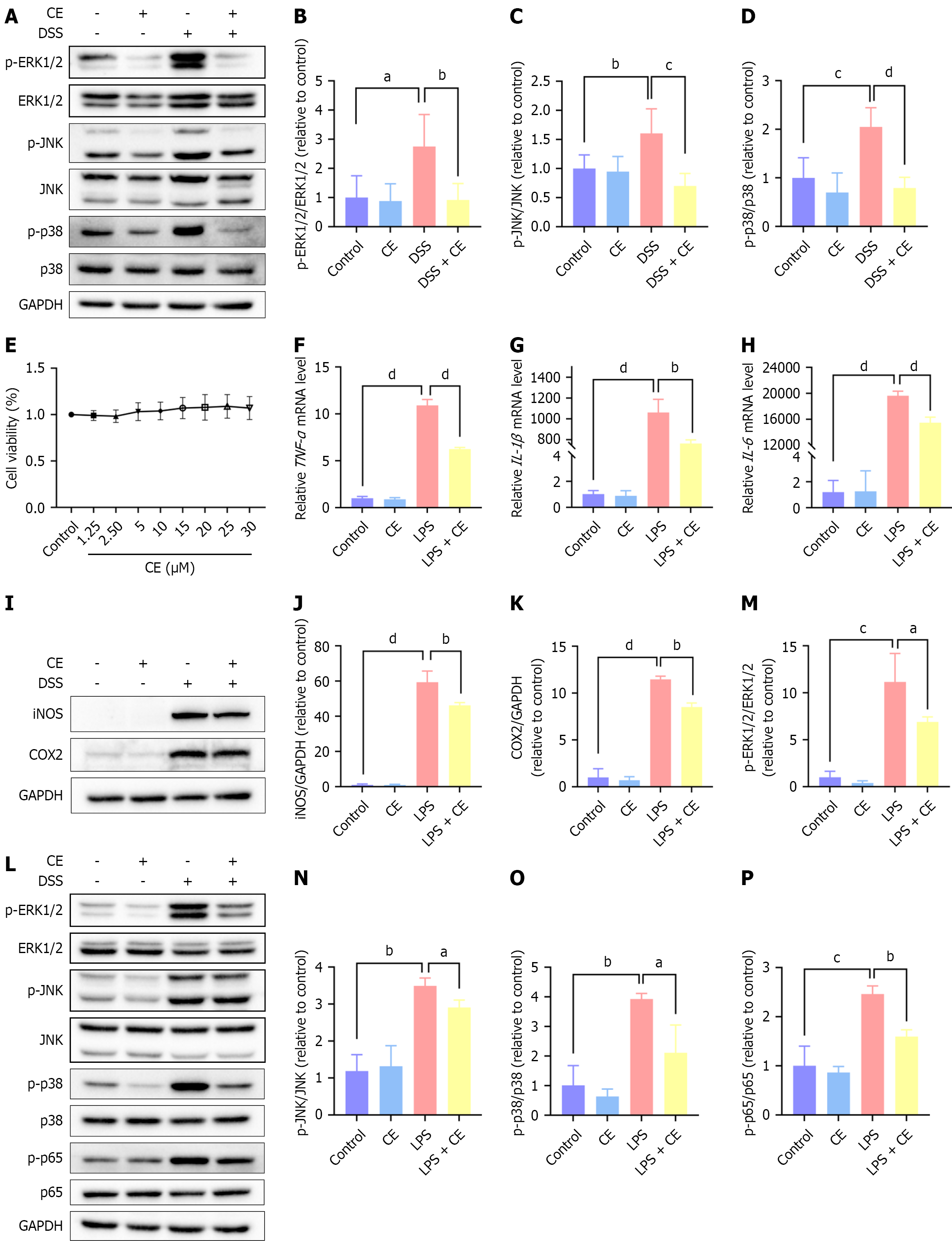
Figure 6 Cedrol inhibited toll-like receptor 4-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor kappa B signaling in vivo and in vitro.
A-D: Phosphorylated and total protein abundance of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling molecules [extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK)1/2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38] in colonic tissues of mice (n = 6); E: Cellular viability was quantified with the cell counting kit-8 method (n = 3); F-H: Proinflammatory cytokine expression in RAW264.7 macrophages across experimental groups (n = 3); I-K: Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 protein expression in RAW264.7 cells across groups (n = 3); L-P: Phosphorylated and total protein expression of ERK1/2, JNK, p38 and nuclear factor kappa B p65 in RAW264.7 macrophages (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. CE: Cedrol; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinase; p-ERK: Phospho-extracellular regulated protein kinase; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; p-JNK: Phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinase; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; mRNA: Messenger RNA; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2.
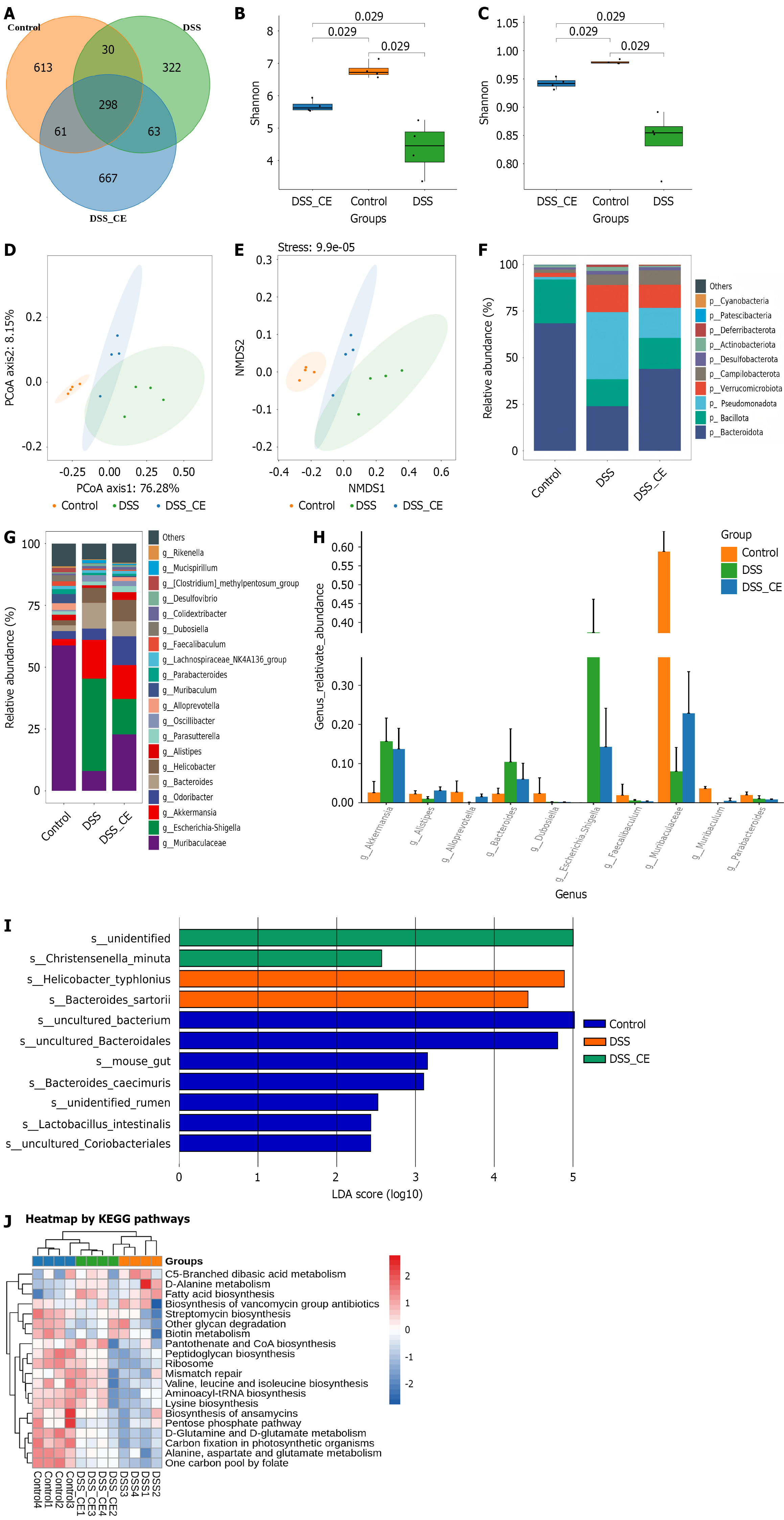
Figure 7 Cedrol ameliorated dextran sulfate sodium-induced gut microbiota dysbiosis.
A: Venn diagram of amplicon sequence variants for each group; B and C: Alpha diversity analysis (Shannon and Simpson indices); D and E: Beta diversity was displayed via principal coordinates analysis and non-metric multidimensional scaling based on weighted UniFrac algorithm; F: Phylum-level abundance distribution; G: Genus-level relative abundance; H: Differences in bacterial abundance were analyzed at the genus level across various groups (P < 0.05); I: Linear discriminate analysis effect size-derived linear discriminant analysis scores; J: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes functional prediction heatmap. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 4). CE: Cedrol; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; PCoA: Principal co-ordinates analysis; NMDS: Non-metric multidimensional scaling; LDA: Linear discriminate analysis; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
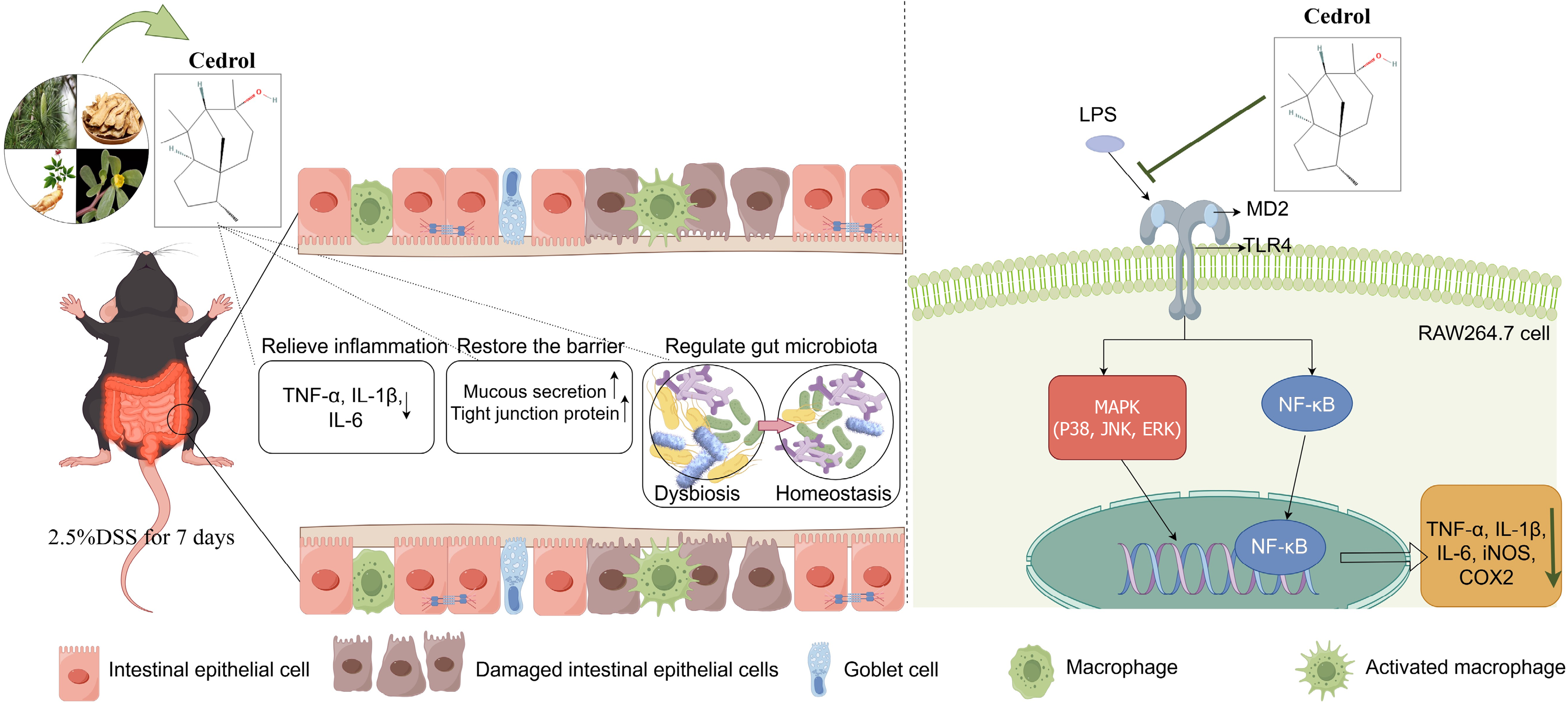
Figure 8 Cedrol treated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting inflammation, restoring the intestinal barrier, and rebalancing gut microbiota.
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MD2: Myeloid differentiation factor 2; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinase; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2.
- Citation: Zhao YQ, Zhang Y, Qin Y, Zhang RY, Wang JP. Cedrol ameliorates ulcerative colitis via myeloid differentiation factor 2-mediated inflammation suppression, with barrier restoration and microbiota modulation. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(2): 114057
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i2/114057.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i2.114057