©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2026; 32(1): 112496
Published online Jan 7, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i1.112496
Published online Jan 7, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i1.112496
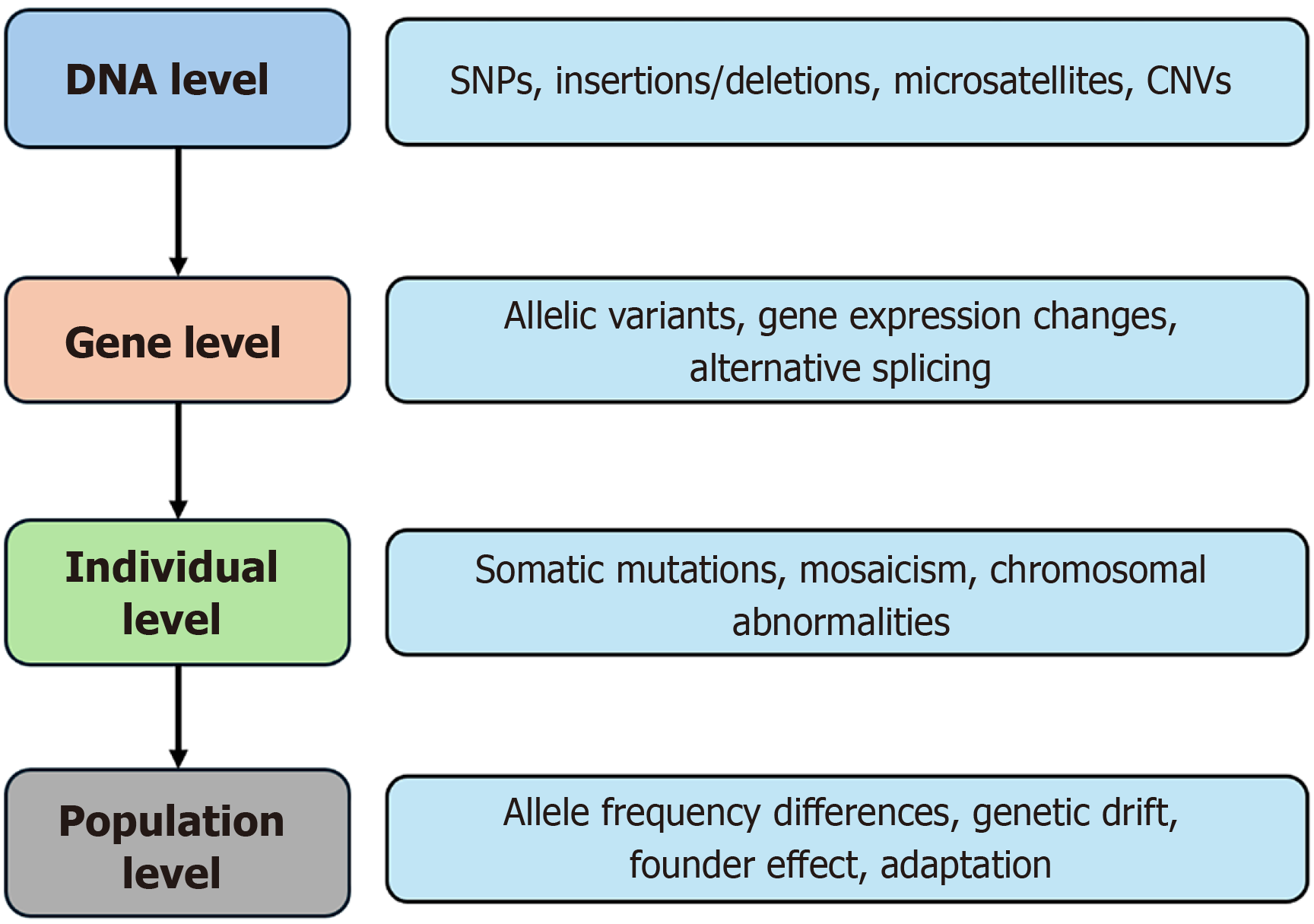
Figure 1 Genetic variation at different levels.
SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; CNV: Copy number variation.
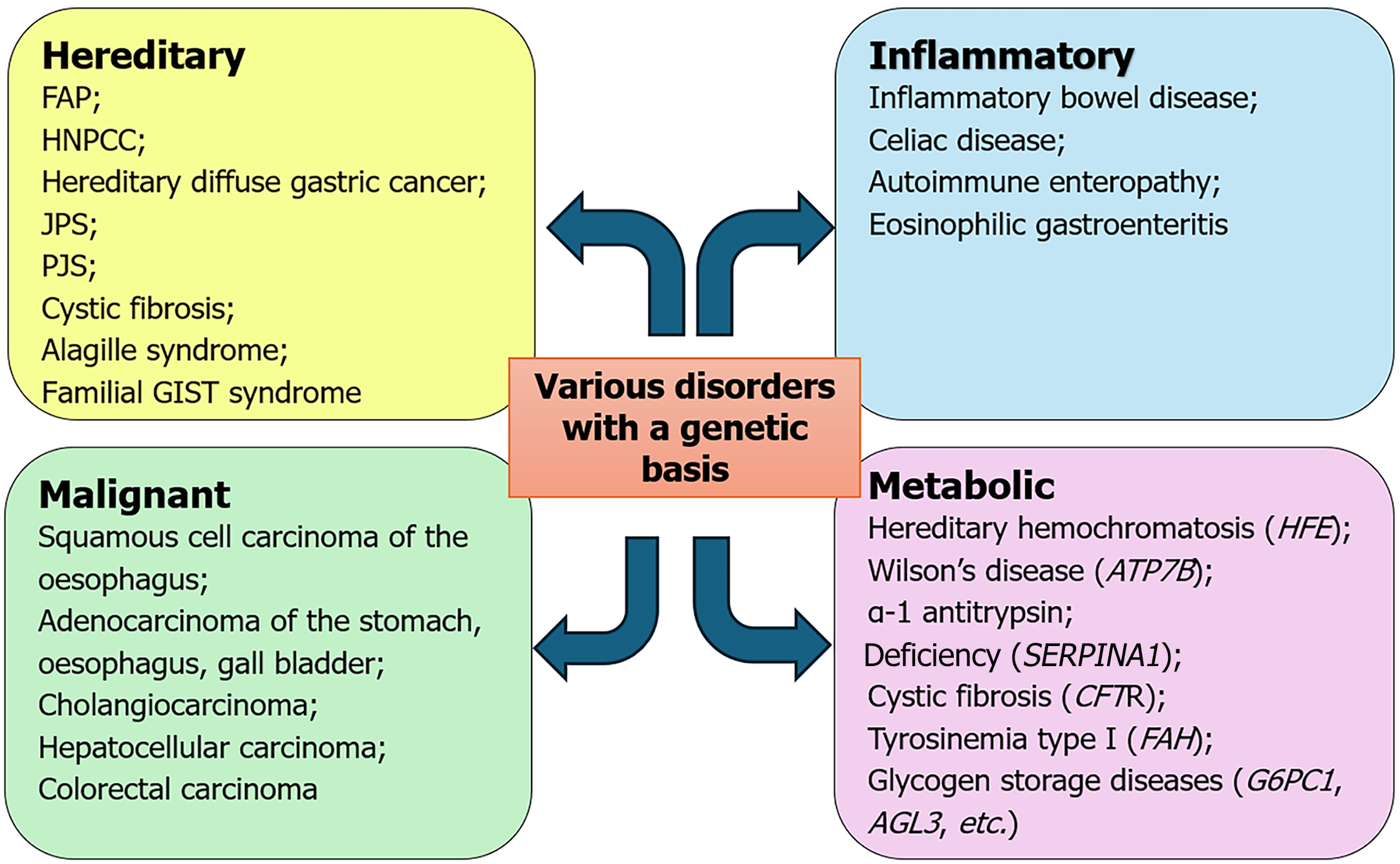
Figure 2 Disorders of gastrointestinal tract.
FAP: Familial adenomatous polyposis; HNPCC: Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer; JPS: Juvenile polyposis syndrome; PJS: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
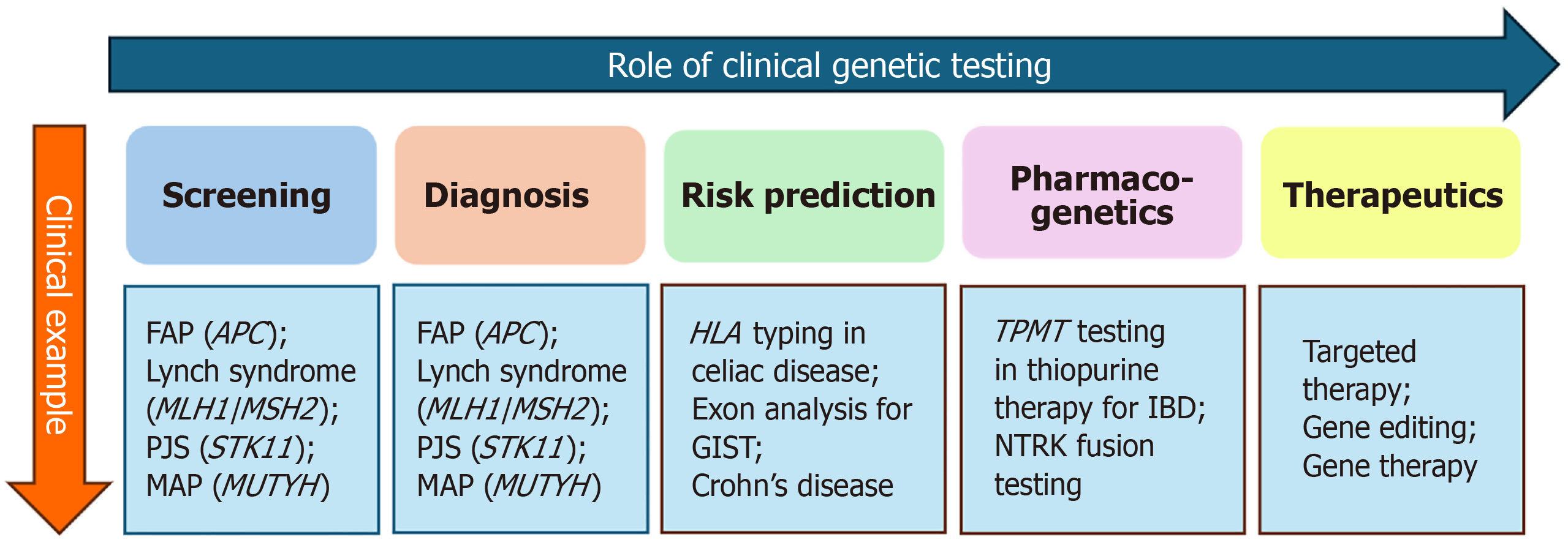
Figure 3 Role of clinical genetic testing.
FAP: Familial adenomatous polyposis; PJS: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; MAP: MUTYH-associated polyposis; GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; NTRK: Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase.
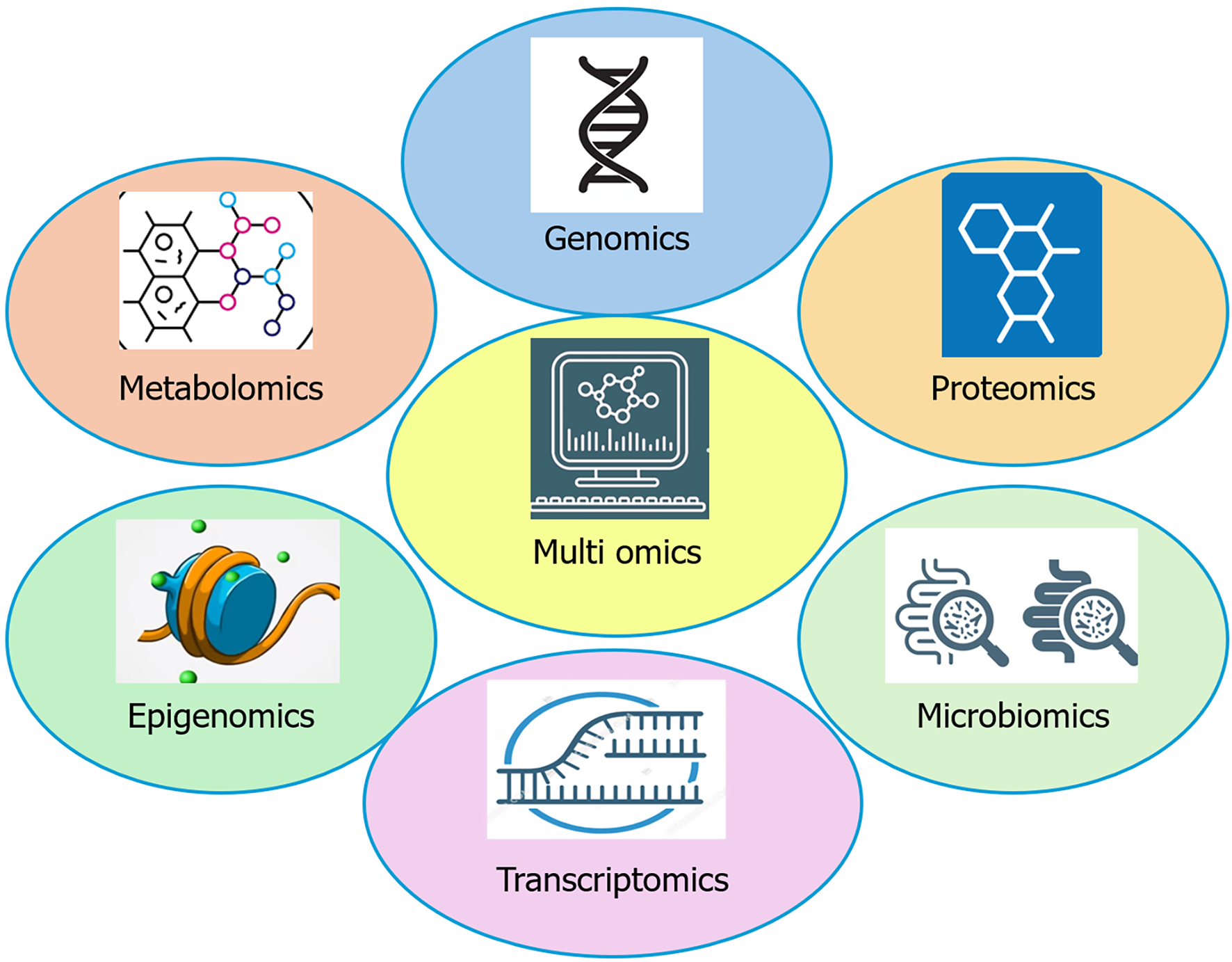
Figure 4 Various components of multi-omics.
- Citation: Kumar A, Sarangi Y, Kaw P. Gene, genetics and genetic medicines in gastroenterology: Current status and its future. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(1): 112496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i1/112496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i1.112496