©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2025; 31(45): 112336
Published online Dec 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i45.112336
Published online Dec 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i45.112336
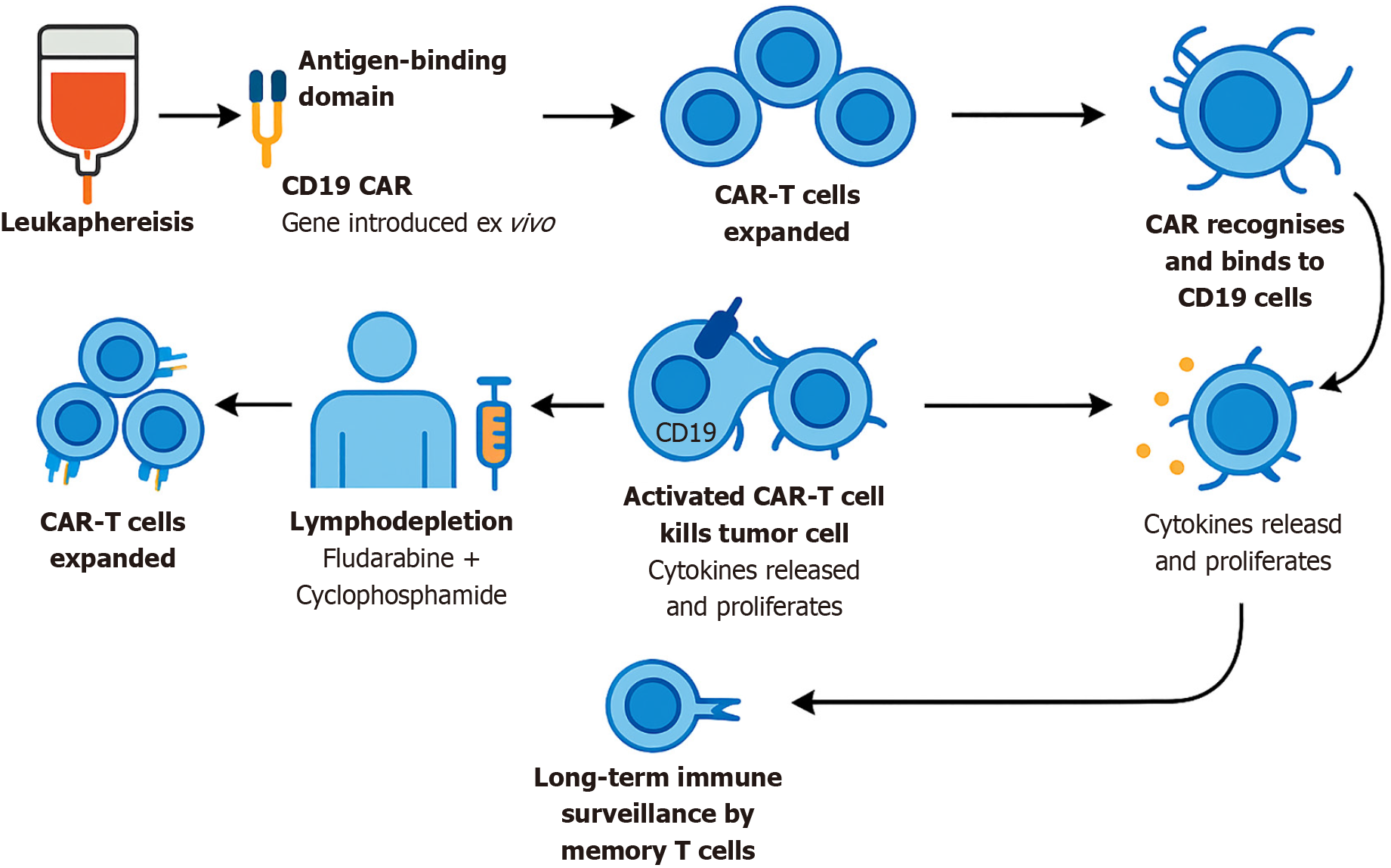
Figure 1 Mechanism of action of cluster of differentiation 19-directed chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy (lisocabtagene maraleu
- Citation: Watanabe T. Emerging role of lisocabtagene maraleucel chimeric antigen receptor-T cell in nodal and gastrointestinal follicular lymphoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(45): 112336
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i45/112336.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i45.112336