©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2025; 31(42): 111708
Published online Nov 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i42.111708
Published online Nov 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i42.111708
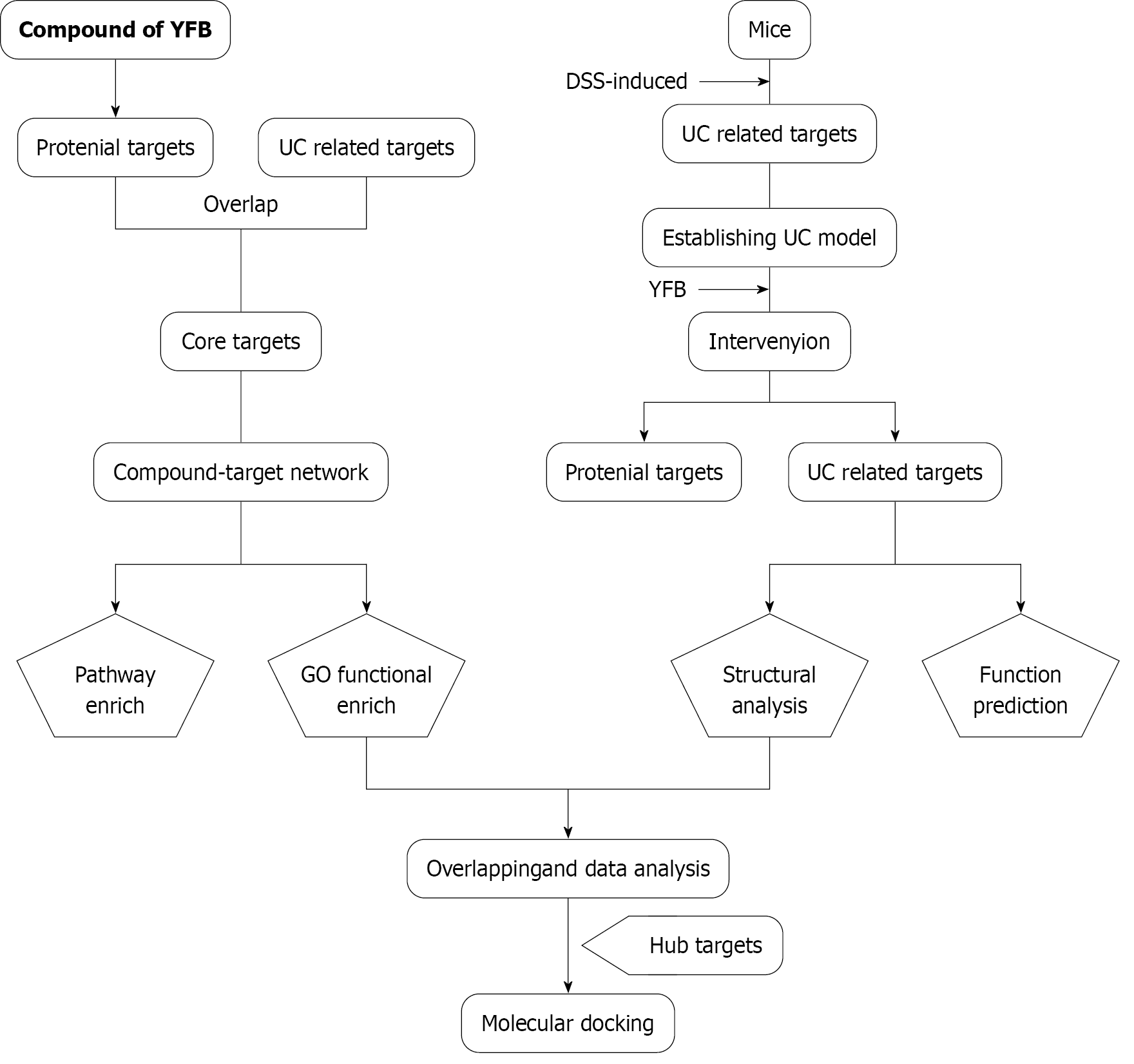
Figure 1 Workflow of the study.
YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder; UC: Ulcerative colitis; GO: Gene Ontology; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
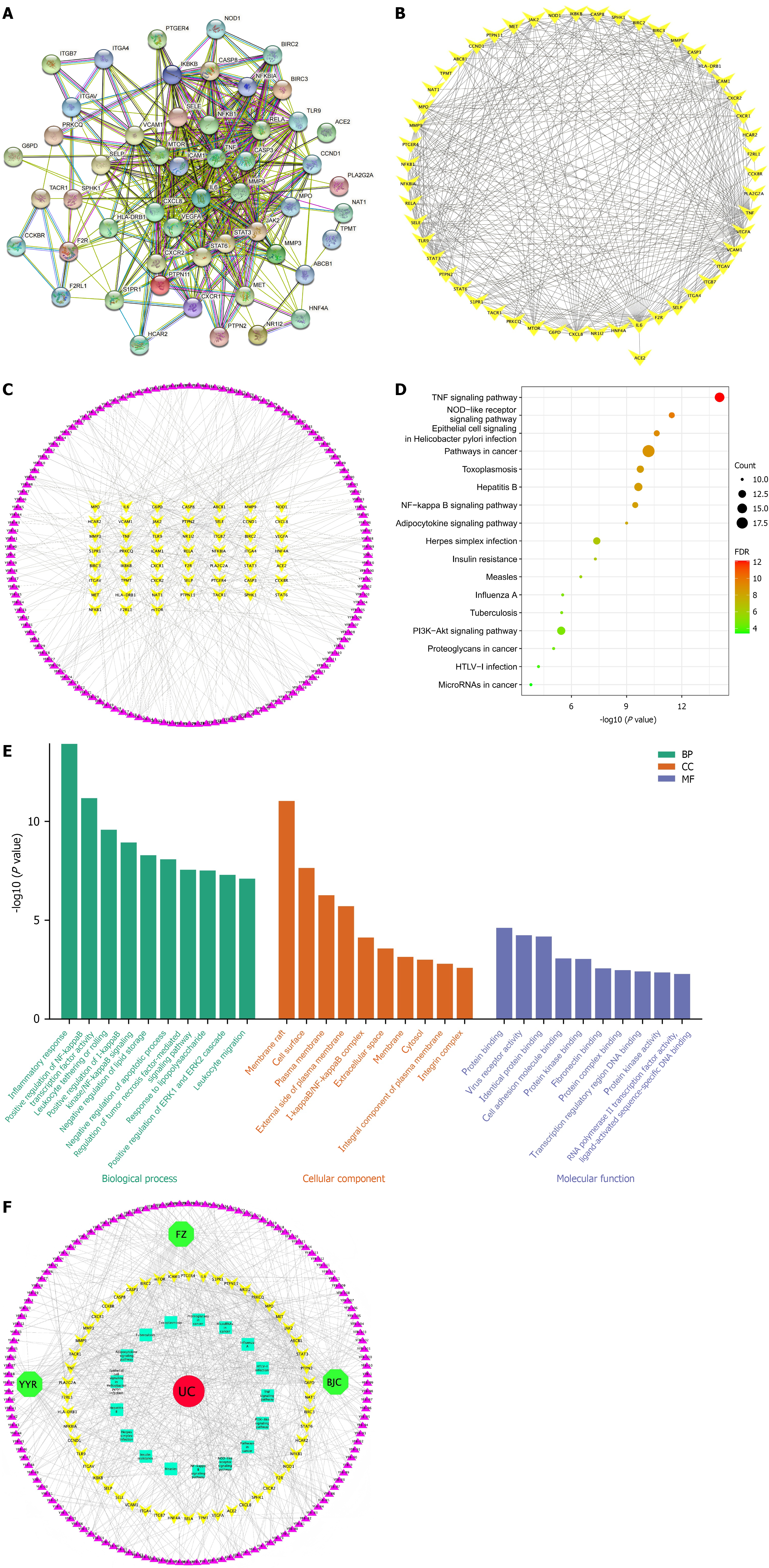
Figure 2 Results of network pharmacology analysis.
A: Protein-protein interaction network of the common targets according to STRING; B: Common genes network according to degree value analyzed by Cytoscape software; C: Key compound-potential targets network according to degree value analyzed by Cytoscape software; D: Location of the top 17 vital pathway in Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway by Database for Annotation Visualization and Integrated Discovery database according to the common target; E: Gene Ontology functional enrichment analysis; F: Traditional Chinese medicine-compound-target-pathway-disease network according to degree value analyzed by Cytoscape software. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NOD: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; HTLV-1: Human T lymphotropic virus type 1; FDR: False discovery rate; BP: Biological processes; CC: Cell composition; MF: Molecular function; FZ: Fuzi; UC: Ulcerative colitis; YYR: Yiyiren; BJC: Baijiangcao.
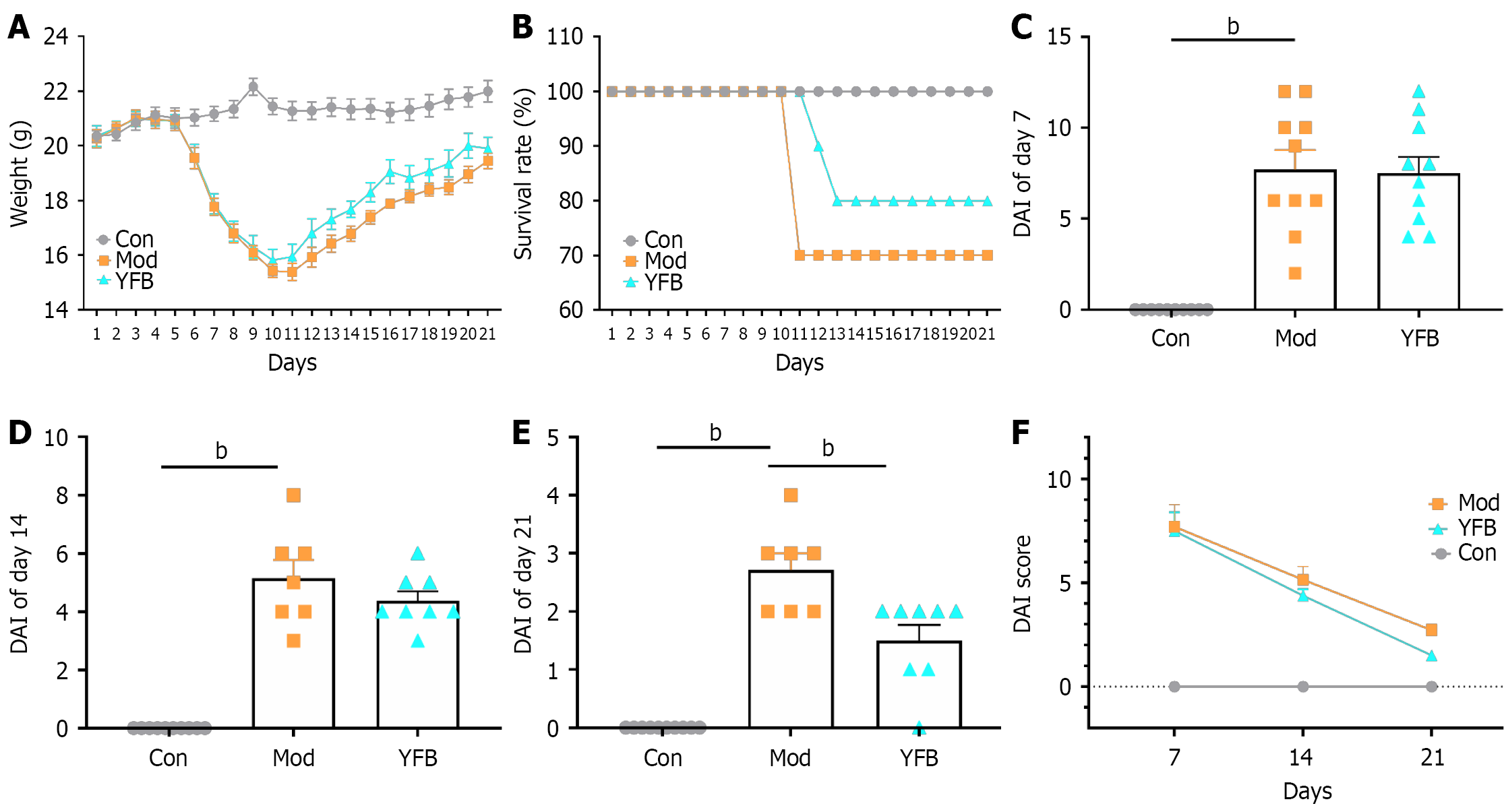
Figure 3 General situation of mice.
A: Effects of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder on body weight of mice with ulcerative colitis-induced during the 21-day monitoring period; B: Survival rate from different groups during the 21-day monitoring period; C: Disease activity index (DAI) score of mice in different groups 7 days after dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) intervention; D: DAI score of mice in different groups 14 days after DSS intervention; E: DAI score of mice in different groups 21 days after DSS intervention; F: Colitis severity indicated by DAI score. bP < 0.01. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 7-10. Con: Control; Mod: Model; YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder; DAI: Disease activity index.
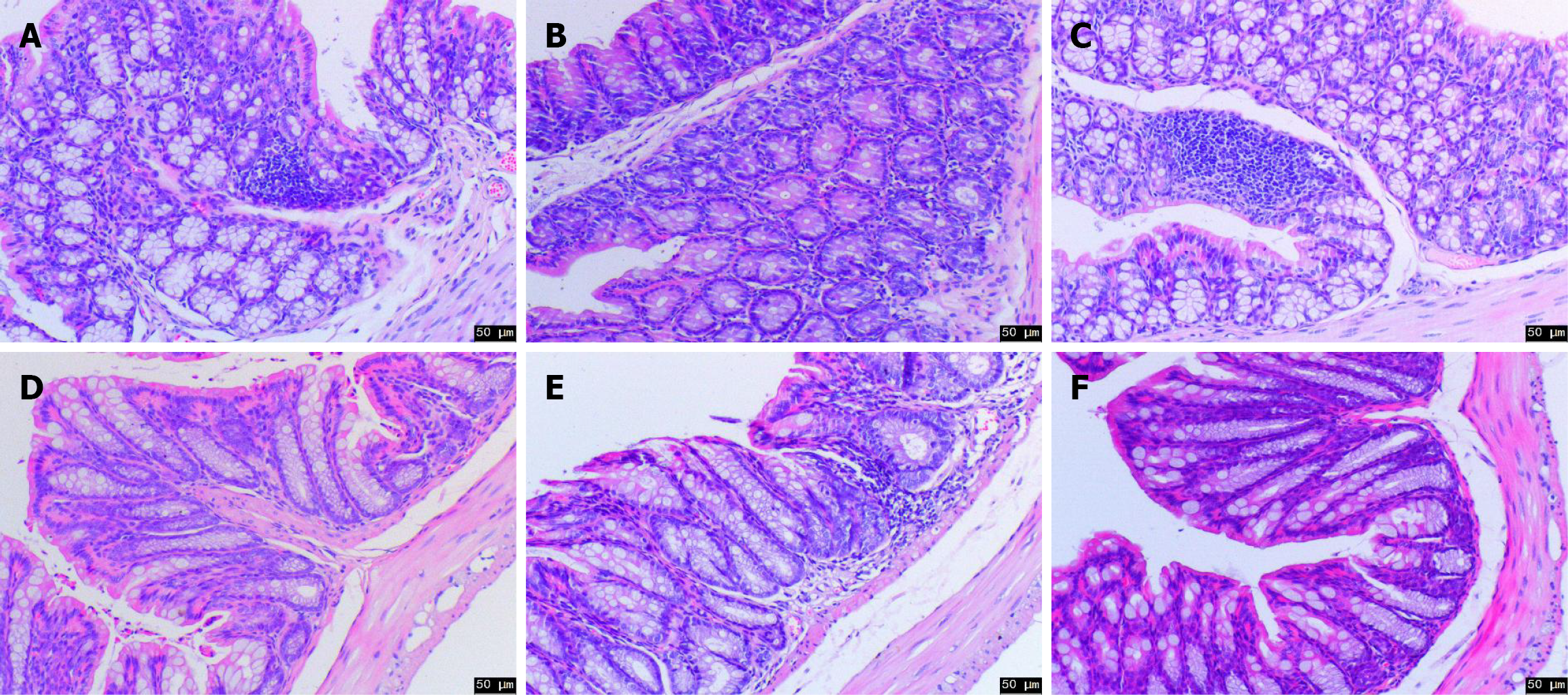
Figure 4 Representative histopathological images of the colon by hematoxylin and eosin staining for experimental animals around 21 days.
A: Histopathological performance of proximal colon in control group (50 μm); B: Histopathological performance of proximal colon in model group (50 μm); C: Histopathological performance of proximal colon in Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang (YFB) group (50 μm); D: Histopathological performance of distal colon in control group (50 μm); E: Histopathological performance of distal colon in model group (50 μm); F: Histopathological performance of distal colon in YFB group (50 μm), n = 7-10. YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder.
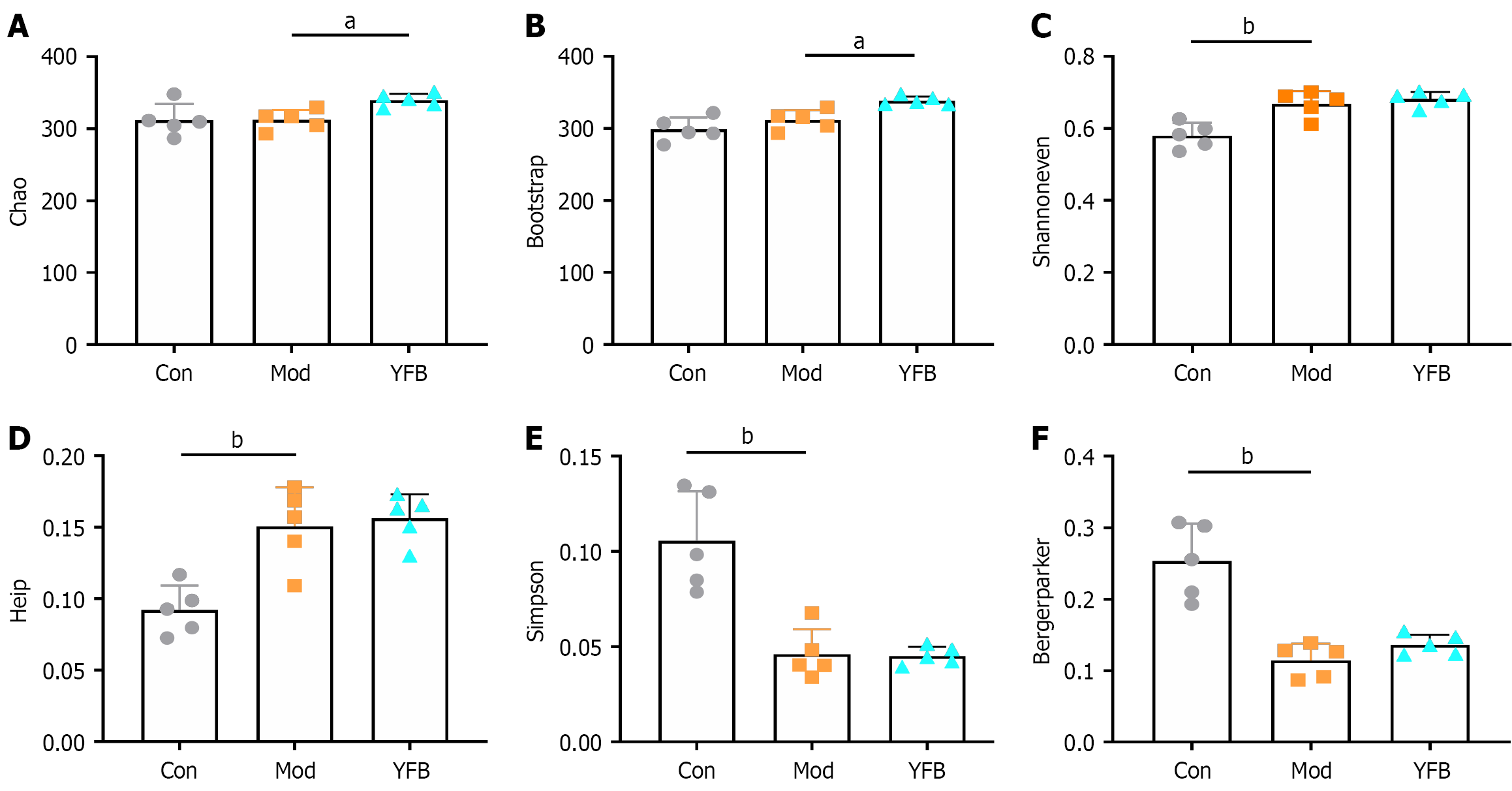
Figure 5 Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder effects on alpha diversity analysis of intestinal flora in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice.
A: Chao indices; B: Bootstrap indices; C: Shannoneven indices; D: Heip indices; E: Simpson indices; F: Bergerparker indices. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 5 in each group. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. Con: Control; Mod: Model; YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder.
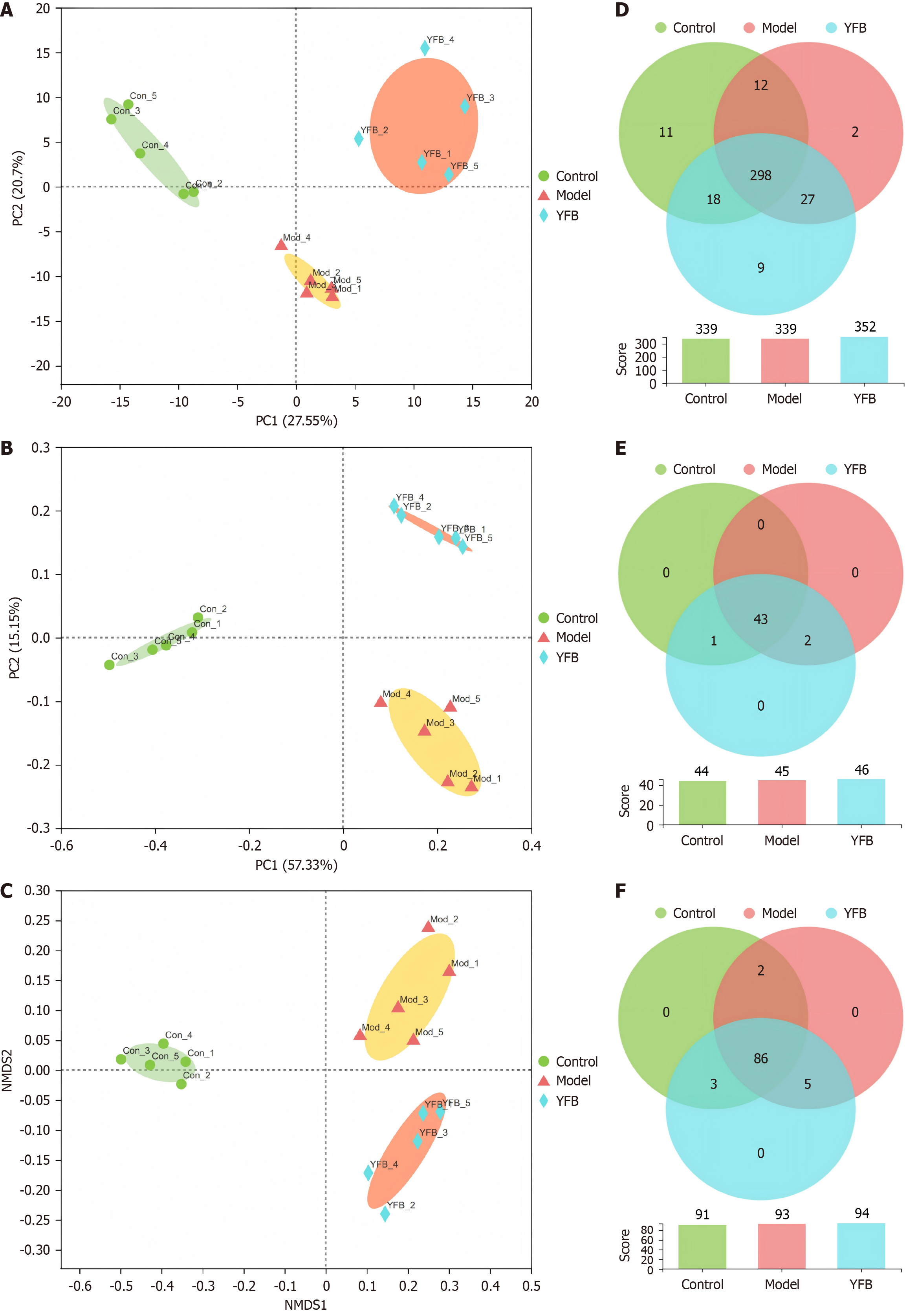
Figure 6 Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder effects on beta diversity analysis and different level Venn diagram of intestinal flora in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice.
A: Principal component analysis of intestinal flora; B: Principal coordinate analysis of intestinal flora; C: Non-metric multidimensional scale analysis of intestinal flora; D: Venn diagram of gut flora at the operational taxonomic unit level; E: Venn diagram of gut flora at the family level; F: Venn diagram of gut flora at the genus level. PC: Principal component; NMDS: Non-metric multidimensional scale analysis; Con: Control; Mod: Model; YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder.
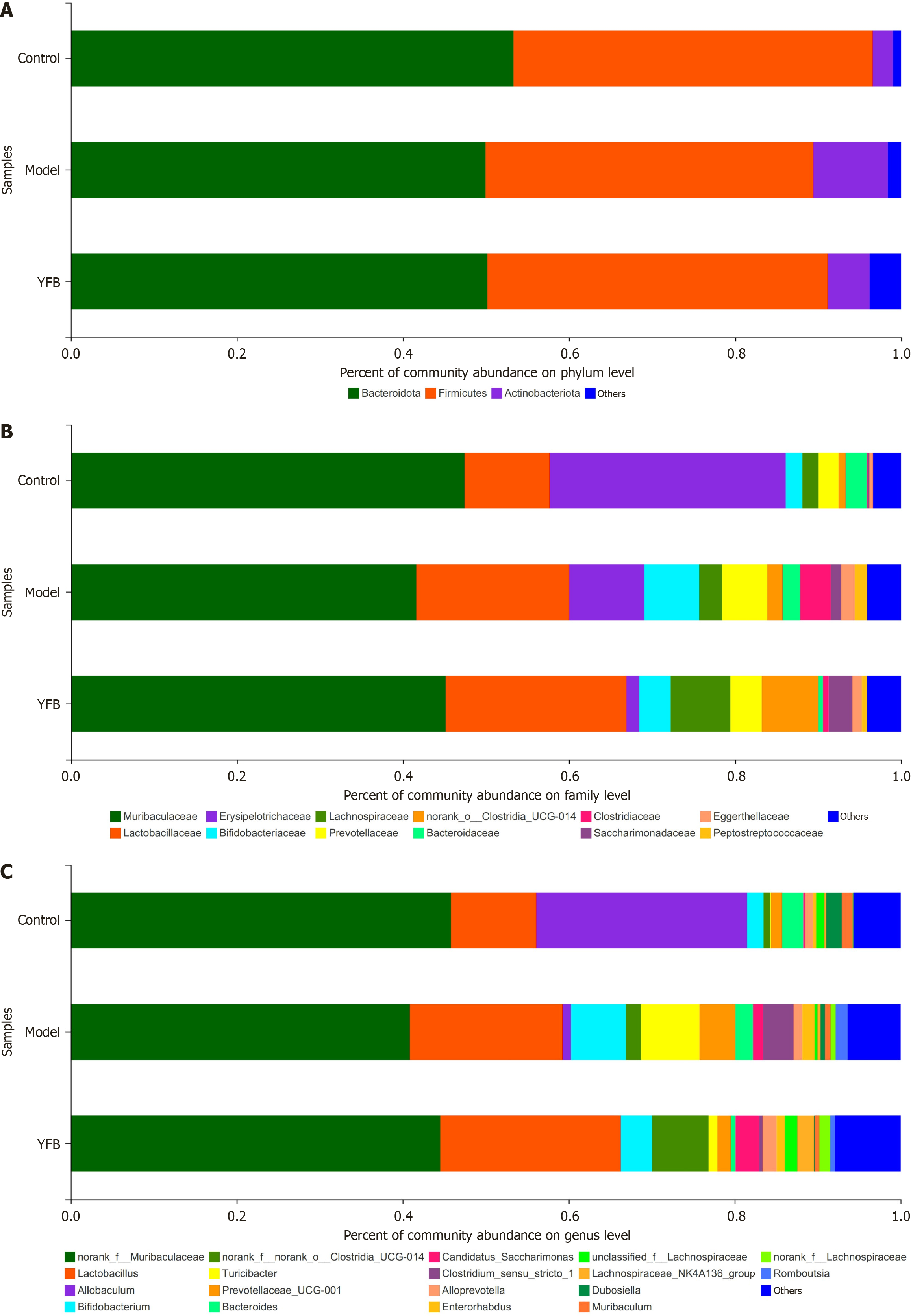
Figure 7 Impact of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder on the species composition of intestinal flora at various levels in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice.
A: The species composition at the phylum level; B: The species composition at the family level; C: The species composition at the genus level. YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder.
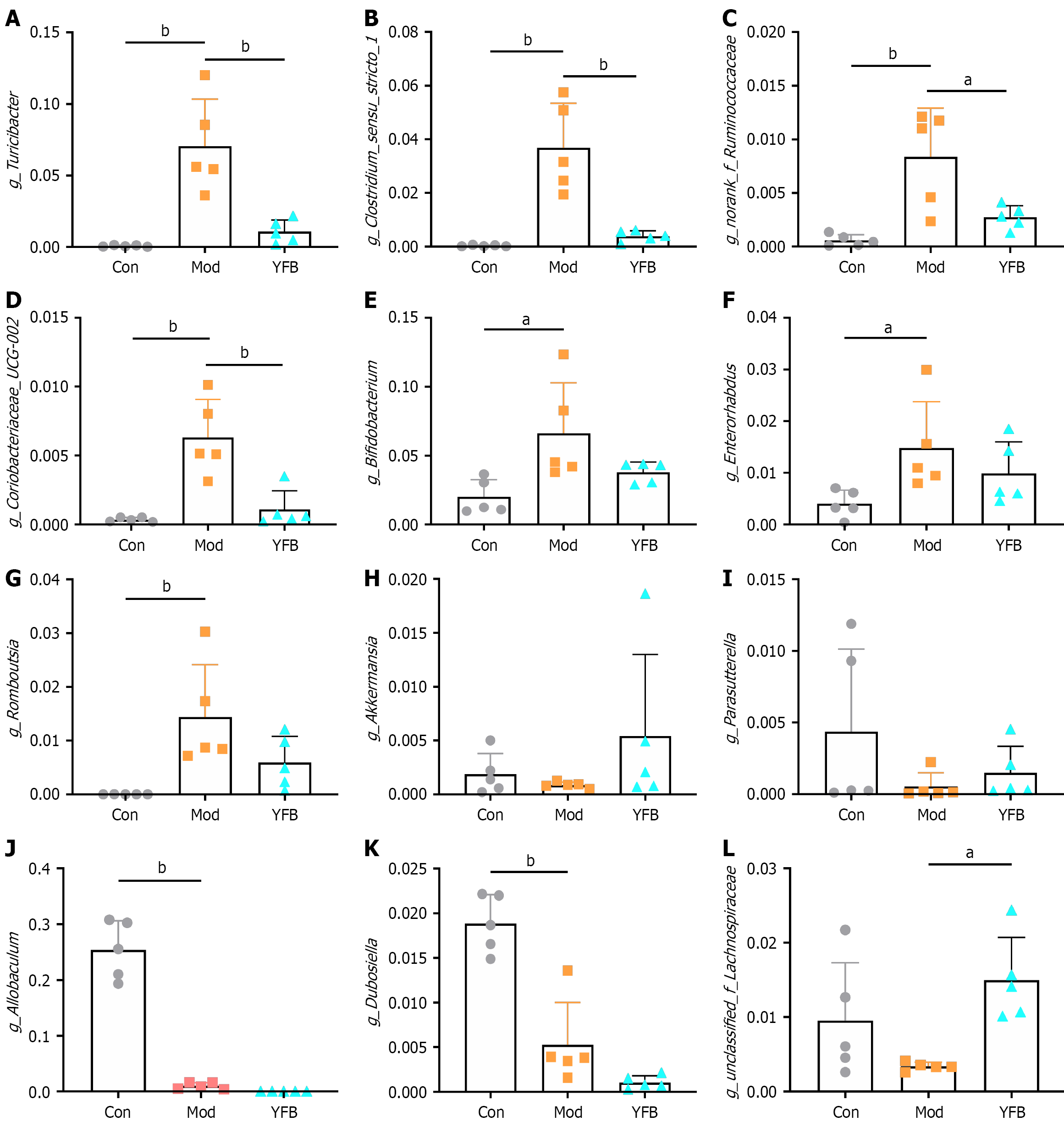
Figure 8 Gut microbial alterations at various taxonomic levels in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice.
A: Relative abundance of g_Turicibacter; B: Relative abundance of g_Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1; C: Relative abundance of g_norank_f_Ruminococcaceae; D: Relative abundance of g_Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002; E: Relative abundance of g_Bifidobacterium; F: Relative abundance of g_Enterorhabdus; G: Relative abundance of g_Romboutsia; H: Relative abundance of g_Akkermansia; I: Relative abundance of g_Parasutterella; J: Relative abundance of g_Allobaculum; K: Relative abundance of g_Dubosiella; L: Relative abundance of g_unclassified_f_Lachnospiraceae. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 5 in each group. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. Con: Control; Mod: Model; YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder.
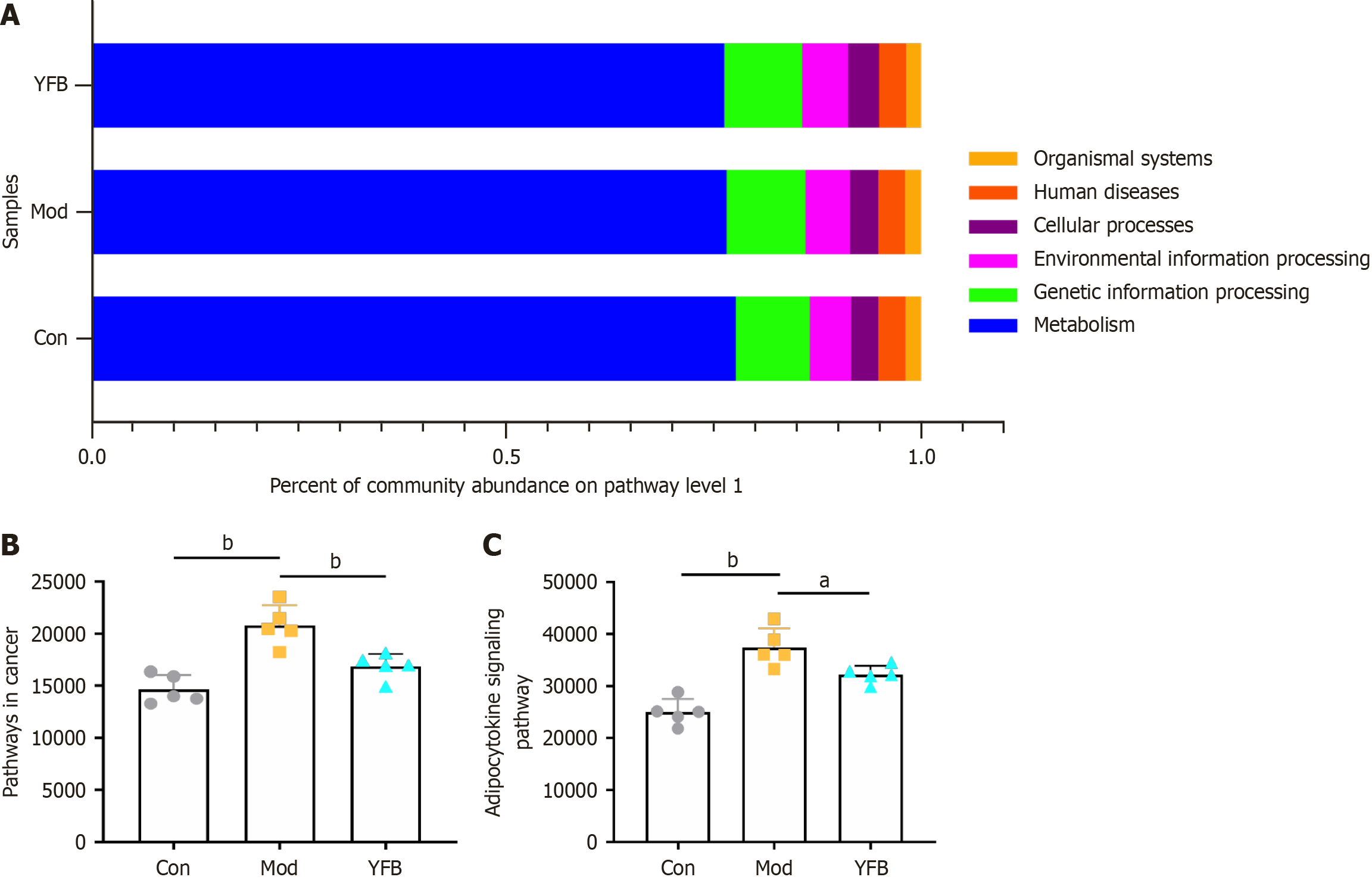
Figure 9 Effects of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder on function prediction of ulcerative colitis mice intestinal flora.
A: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes function; B: Pathways in cancer; C: Adipocytokine signaling pathway. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 5 in each group. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. Con: Control; Mod: Model; YFB: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder.
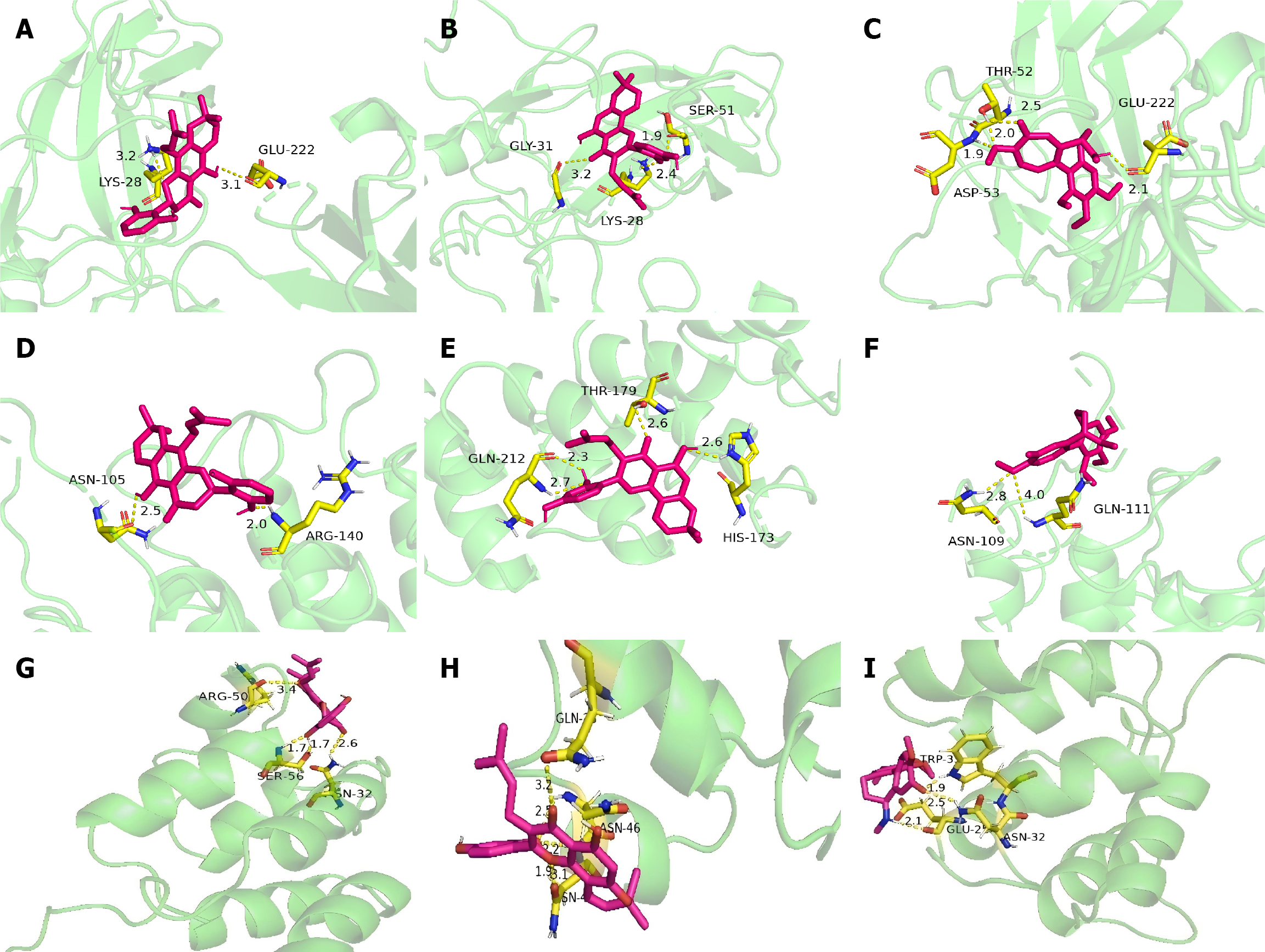
Figure 10 Molecular docking diagram of main compounds binding to key target genes.
A: Molecular docking diagram of RELA and orotinin; B: Molecular docking diagram of RELA and morusin; C: Molecular docking diagram of RELA and colchamine; D: Molecular docking diagram of nuclear factor kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFKBIA) and orotinin; E: Molecular docking diagram of NFKBIA and morusin; F: Molecular docking diagram of NFKBIA and colchamine; G: Molecular docking diagram of NFKB1 and crotinin; H: Molecular docking diagram of NFKB1 and morusin; I: Molecular docking diagram of NFKB1 and colchamine. GLU: Glutamic acid; LYS: Lysine; GLY: Glycine; SER: Serine; THR: Threonine; ASP: Aspartic acid; ASN: Asparagine; ARG: Arginine; GLN: Glutamine; HIS: Histidine; THR: Histidine.
- Citation: Zhang LK, Gu WC, Chen J. Unveiling Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder: Microecological and network pharmacology approach to ulcerative colitis treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(42): 111708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i42/111708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i42.111708