©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2025; 31(36): 110210
Published online Sep 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i36.110210
Published online Sep 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i36.110210
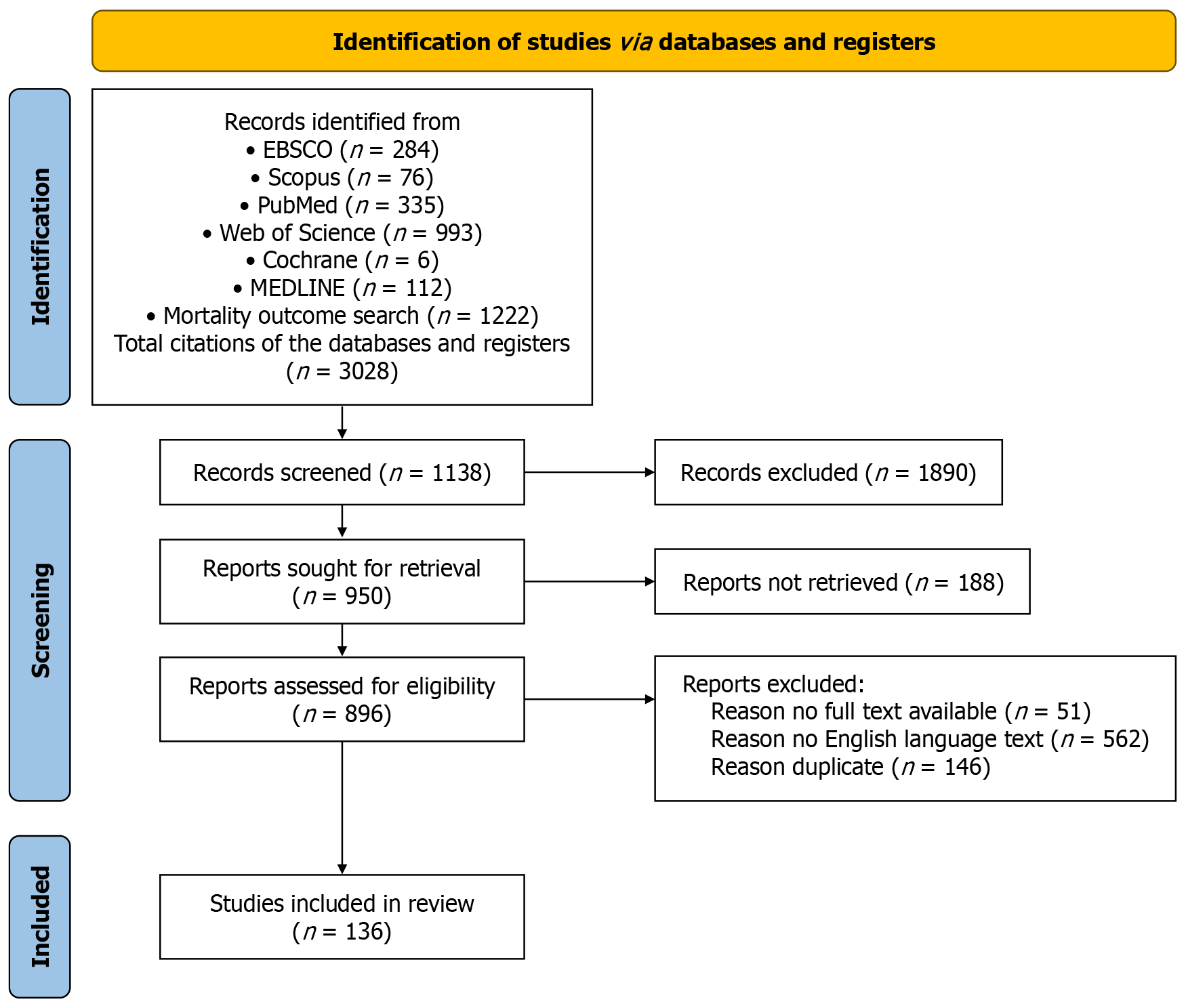
Figure 1
The PRISMA flow diagram of this study.
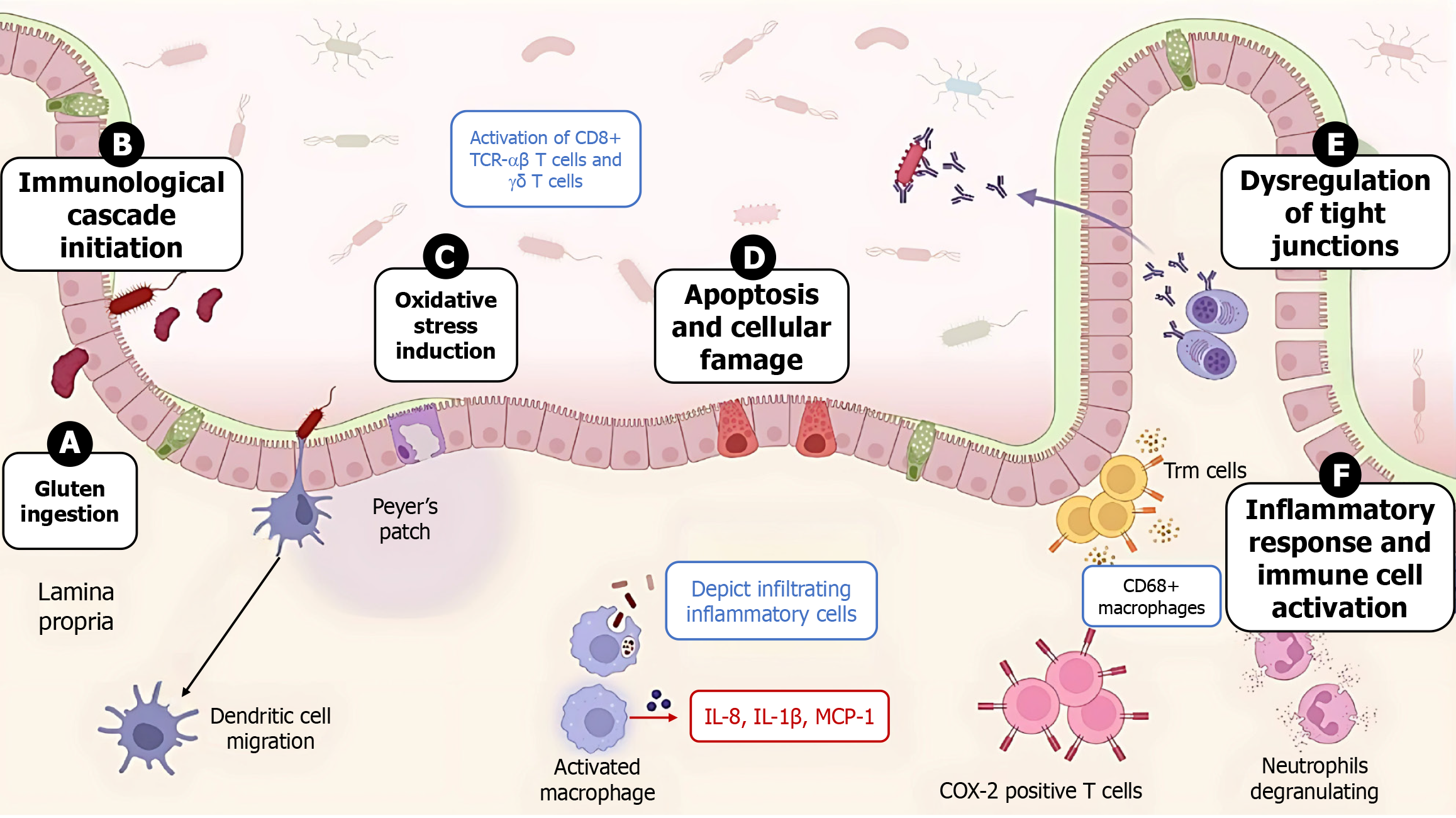
Figure 2 Immunopathogenesis of celiac disease upon exposure to gluten.
A: Upon gluten ingestion and presence in the lumen of individuals with genetically determined celiac disease; B: The inflammatory cascade is activated upon introduction to antigen-presenting cells and the recruitment of chronic inflammatory cells, with the help of chemoattractants, which include interleukin-8, interleukin-1β and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, followed by the initiation of oxidative stress reactions; C: Further damage and alteration of the intestinal barrier; D: The apoptosis of enterocytes and the dysregulation of tight junctions; E: The inflammatory and immune responses are promoted because of further cellular and chemoattractant reactivations; F: T-cell receptor-αβ, interleukin, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 are also activated. MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; TCR: T-cell receptor; IL: Interleukin; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; Trm cells: Tissue-resident memory T cells.
- Citation: Khayyat YM. Colonic neoplasia and celiac disease: A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(36): 110210
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i36/110210.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i36.110210