©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2025; 31(3): 96582
Published online Jan 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i3.96582
Published online Jan 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i3.96582
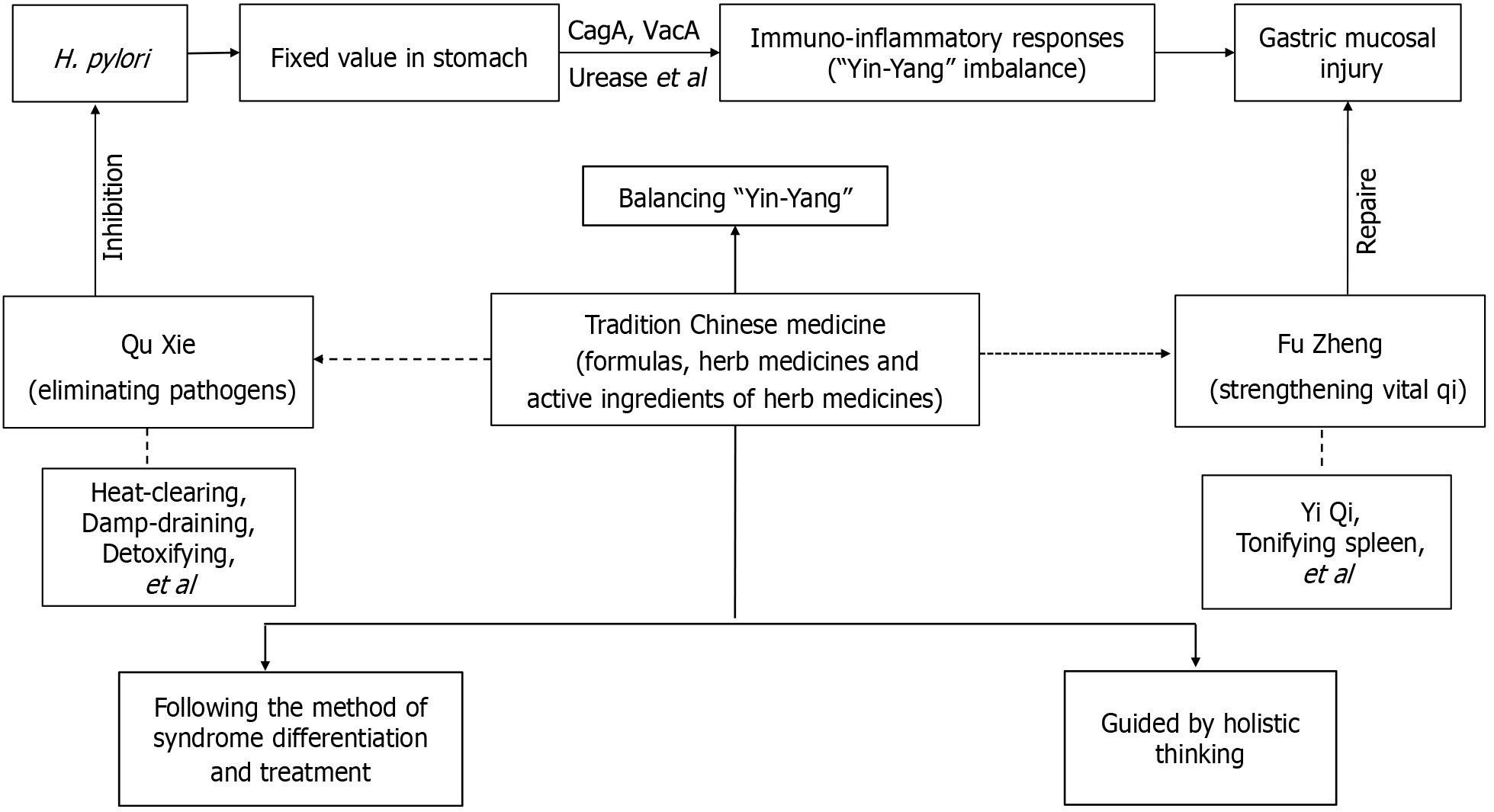
Figure 1 The approach of traditional Chinese medicine therapy for Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; CagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A; VacA: Vacuolating cytotoxin A.
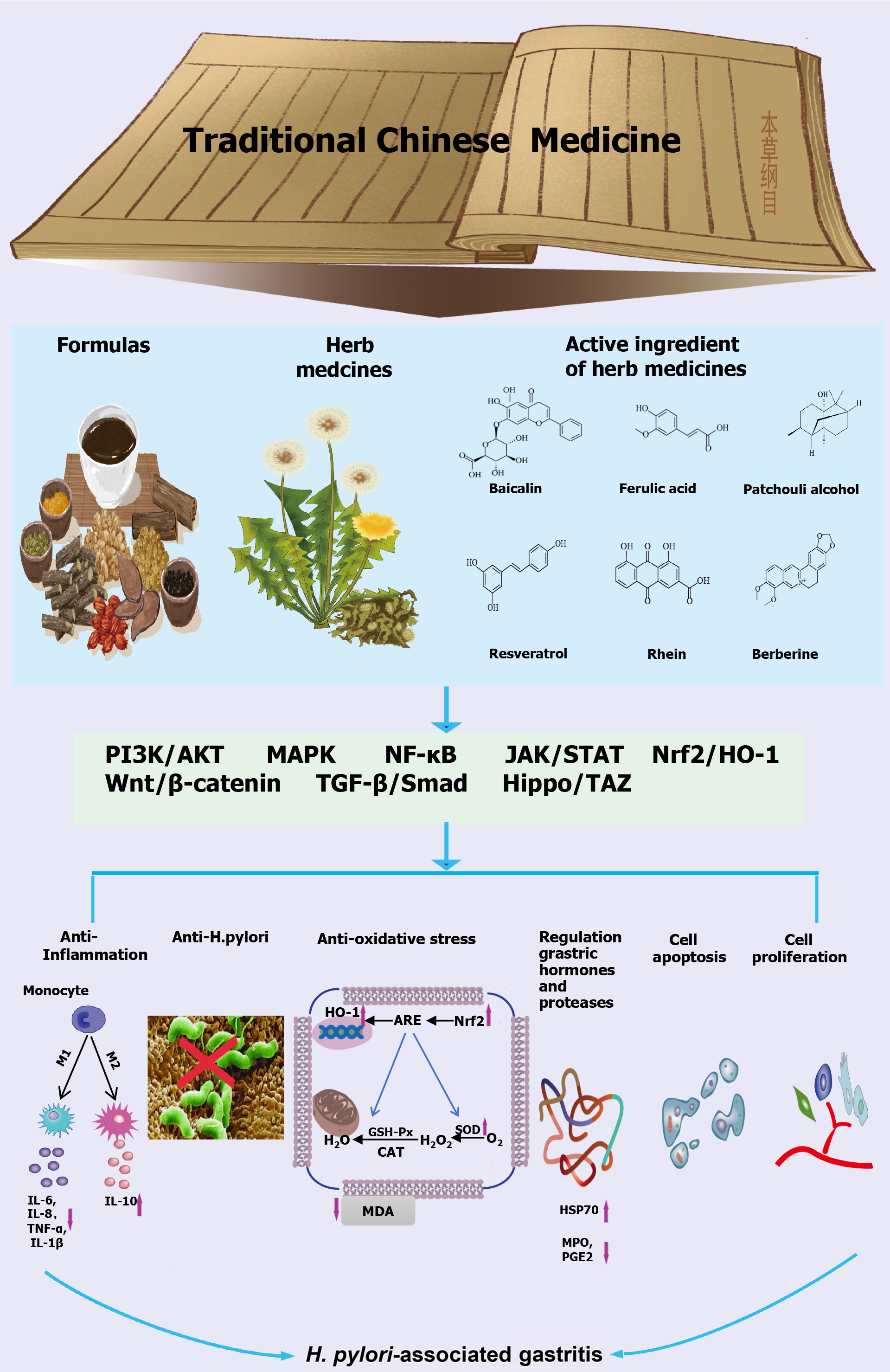
Figure 2 The signalling pathways of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TGF: Transforming growth factor; JAK: Janus activated kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; TAZ: Transcriptional coactivator with the PDZ-binding motif; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1: Heme oxygenase 1; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; ARE: Antioxidant response element; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; CAT: Catalase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; HSP70: Heat shock protein70.
- Citation: Zhang PP, Li L, Qu HY, Chen GY, Xie MZ, Chen YK. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis: The mechanisms of signalling pathway regulations. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(3): 96582
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i3/96582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i3.96582