©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2781-2791
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2781
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2781
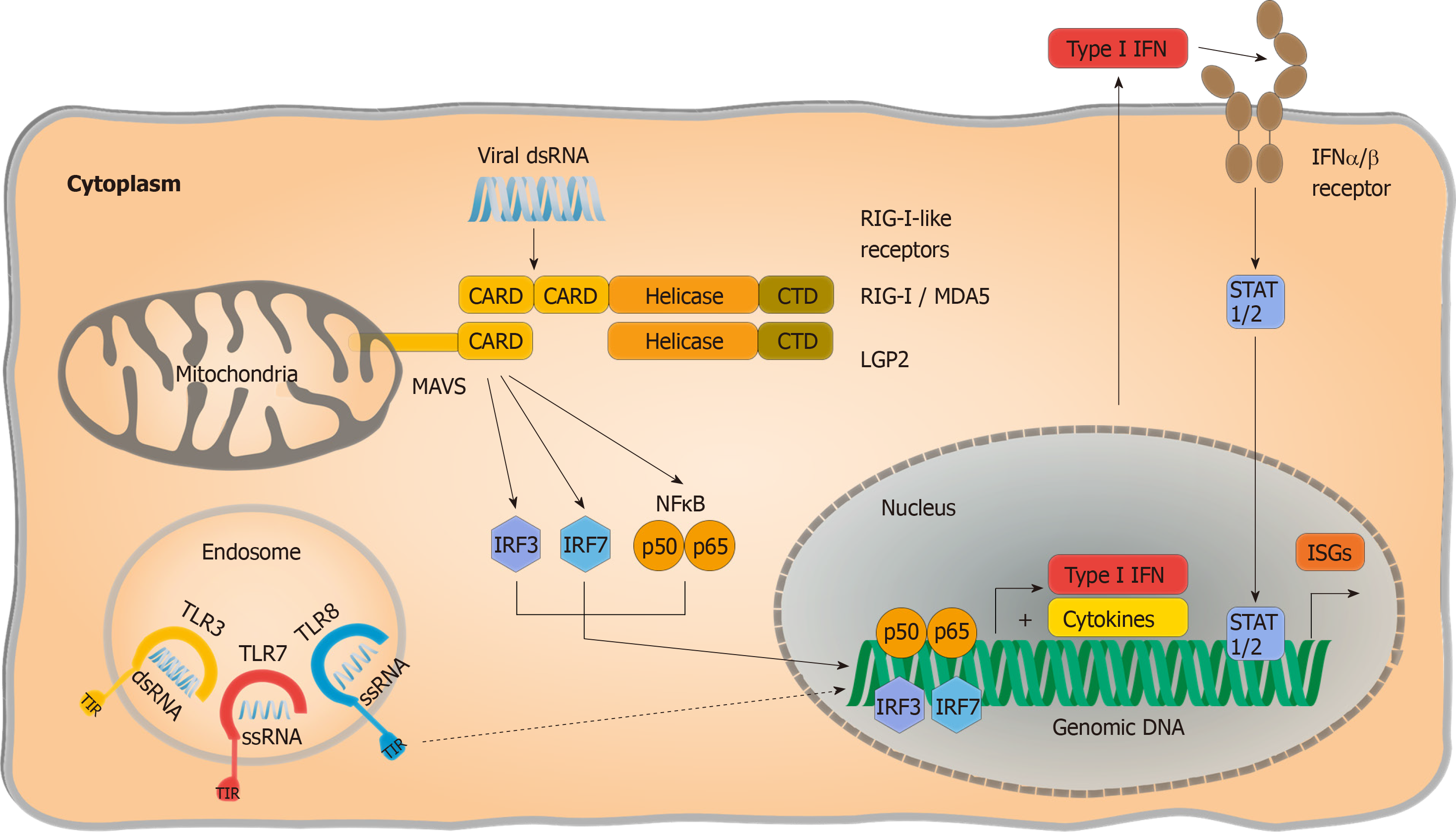
Figure 1 RNA-sensing by pattern recognition receptors.
Intracellular pathogenic RNA is sensed by endosomal Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and retinoic acid inducible gene I (RIG I) like receptors. TLR3 detects double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), whereas TLR7 and TLR8 detect single-stranded RNA in a sequence-specific manner and signal via their Toll/interleukin-1 receptor homology domains. RIG I and melanoma differentiation antigen 5 bind cytoplasmatic dsRNA structures and activate conformational changes leading to the exposure of Caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs). Signalling-deficient laboratory of genetics and physiology 2 only consists of a helicase and a C-terminal domain and functions as an accessory receptor. This enables interaction of CARDs with mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein (MAVS), resulting in subsequent signalling cascades that release nuclear factor “kappa-light-chain-enhancer” of activated B-cells inducing a proinflammatory cytokine response. MAVS also activates interferon regulatory factor 3/7 signalling and signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/2-dependent type I interferon production and antiviral state with upregulation of interferon-stimulated genes in the host cell. TLRs: Toll-like receptors; RIG I: Retinoic acid inducible gene I; LGP2: Laboratory of genetics and physiology 2; ssRNA: Single-stranded RNA; CTD: C-terminal domain; RLRs: RIG I like receptors; NF-κB: Nuclear factor “kappa-light-chain-enhancer” of activated B-cells; MAVS: Mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein; TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor; dsRNA: Double-stranded RNA; MDA5: Melanoma differentiation antigen 5; CARDs: Caspase activation and recruitment domains; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; STAT1/2: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/2; Type I IFN: Type I interferon; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes.
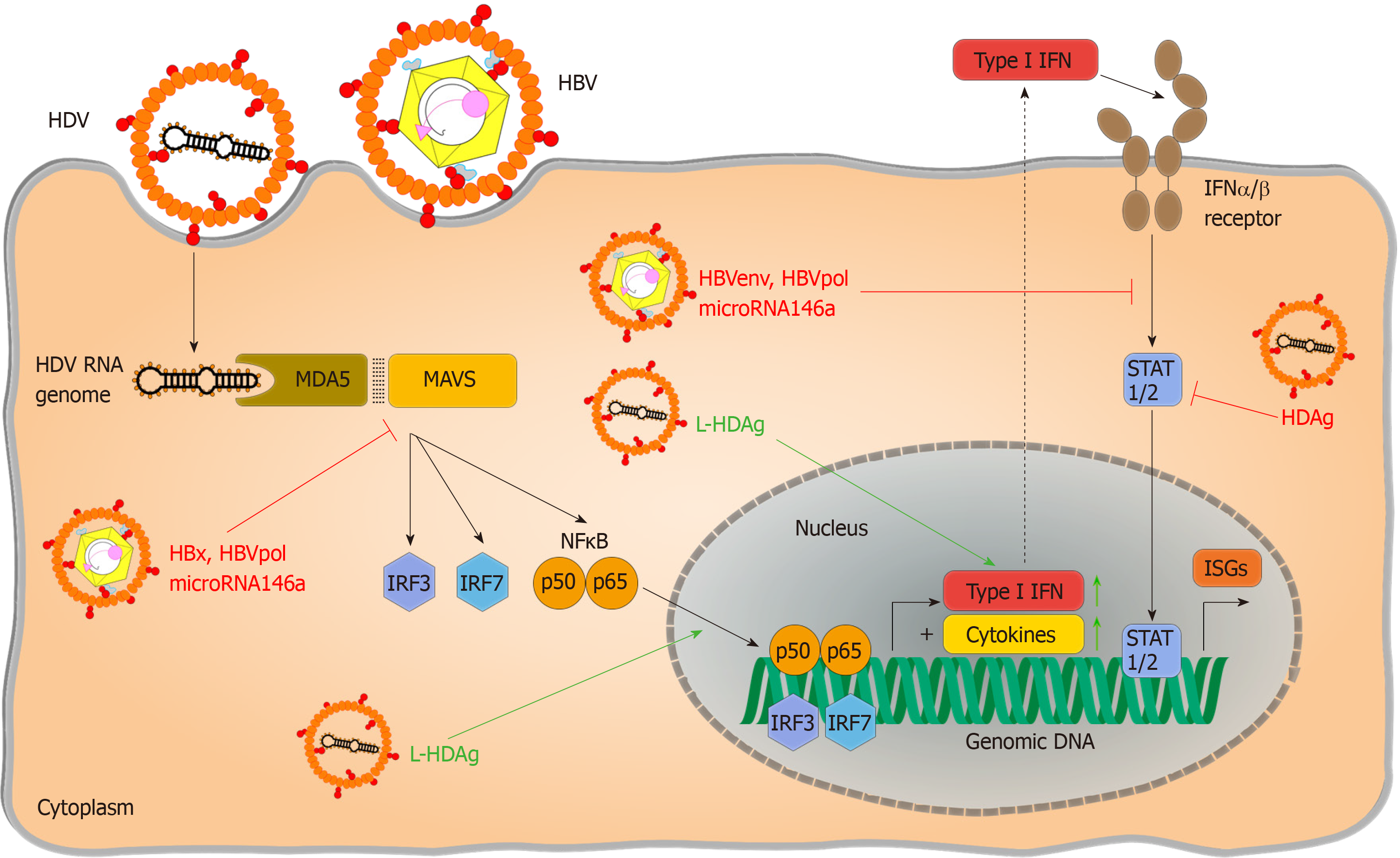
Figure 2 Immune evasion and immunomodulation in hepatitis D virus infection.
Pattern recognition of hepatitis D virus RNA was reported to be both inhibited by hepatitis B virus (HBV) specific proteins like HBV X protein, HBV envelope proteins, HBV polymerase as well as the hepatitis delta antigen and in particular its large variant. Inhibitions of major pathways are indicated with red flat arrows, activation of cytokine response is indicated in green pointed arrows. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HDV: Hepatitis D virus; HBx: Hepatitis B virus X protein; HBV env: Hepatitis B virus envelope proteins; HBV pol: Hepatitis B virus polymerase; HDAg: Hepatitis delta antigen; L-HDAg: Large hepatitis delta antigen; TLRs: Toll-like receptors; RIG I: Retinoic acid inducible gene I; LGP2: Laboratory of genetics and physiology 2; ssRNA: Single-stranded RNA; CTD: C-terminal domain; RLRs: RIG I like receptors; NF-κB: Nuclear factor “kappa-light-chain-enhancer” of activated B-cells; MAVS: Mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein; TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor; dsRNA: Double-stranded RNA; MDA5: Melanoma differentiation antigen 5; CARDs: Caspase activation and recruitment domains; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; STAT1/2: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/2; Type I IFN: Type I interferon; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes.
- Citation: Jung S, Altstetter SM, Protzer U. Innate immune recognition and modulation in hepatitis D virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2781-2791
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2781