©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2018; 24(26): 2878-2885
Published online Jul 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2878
Published online Jul 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2878
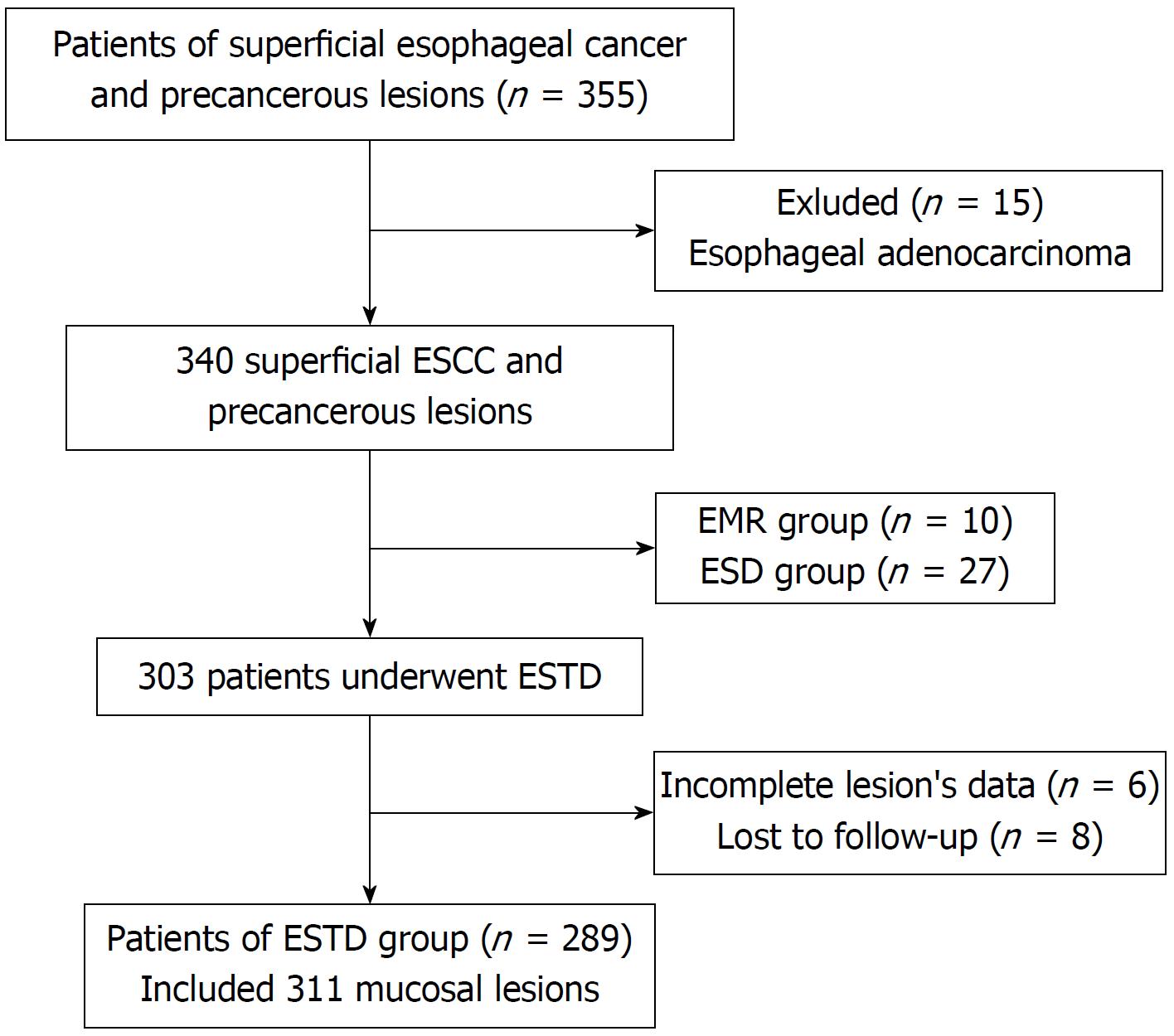
Figure 1 Flowchart of the enrollment process.
ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; ESTD: Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection; EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection
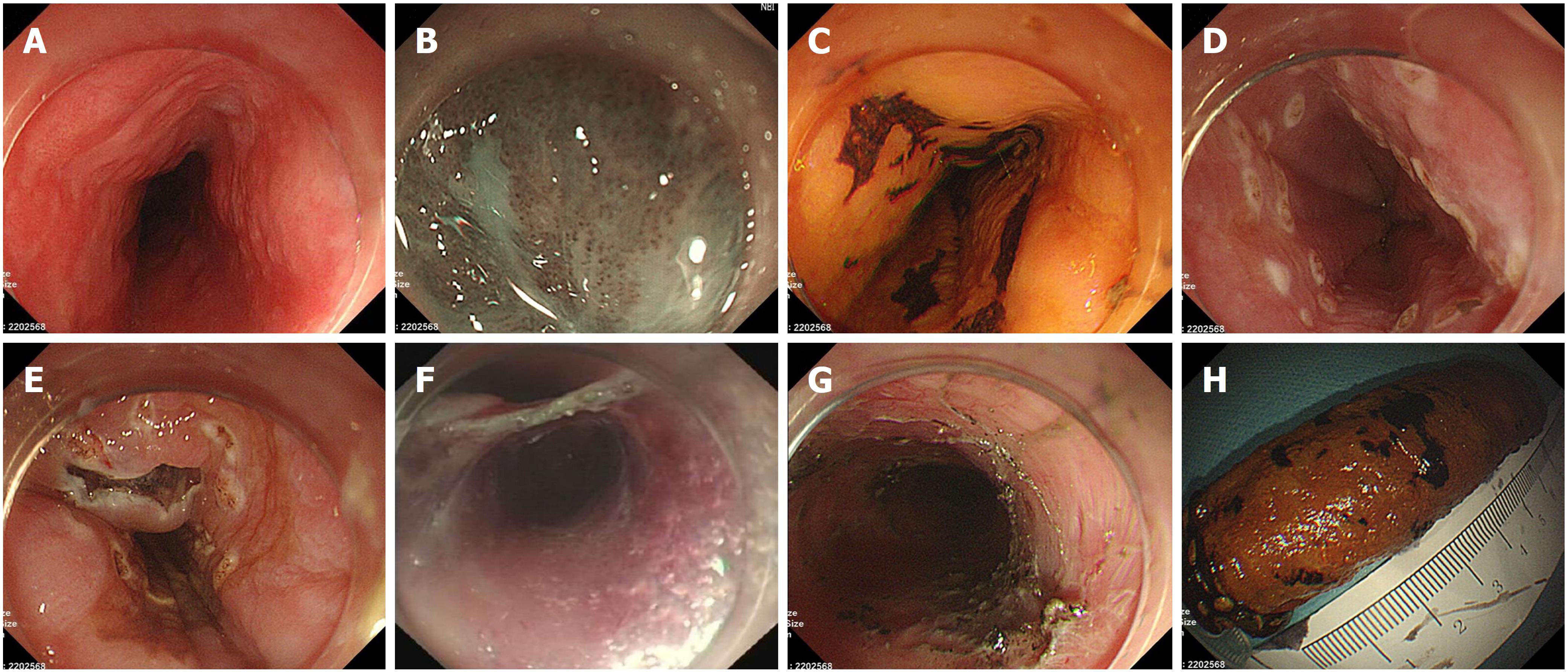
Figure 2 Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection procedures.
A: Lesion was detected under white light endoscopy; B: Lesion was observed under narrow band imaging (NBI); C: Lesion was observed under iodine staining; D: The margin of the lesion was marked; E: Anal-side and oral-side incisions after submucosal injection; F: Creating the submucosal tunnel and resecting the lesion; G: The artificial wound after endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection; H: The in vitro specimen encircled in the body of a syringe after iodine staining.
- Citation: Wang J, Zhu XN, Zhu LL, Chen W, Ma YH, Gan T, Yang JL. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(26): 2878-2885
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i26/2878.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2878