©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2016; 22(23): 5454-5458
Published online Jun 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5454
Published online Jun 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5454
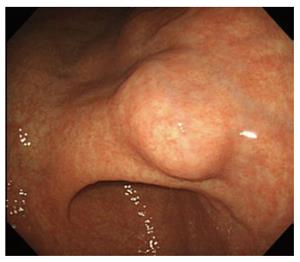
Figure 1 Endoscopic view of the lesion.
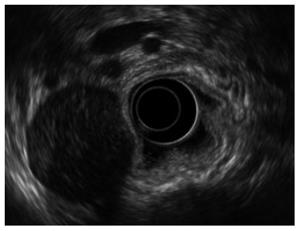
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound.
Endoscopic ultrasonography showed a heterogenic hypoechoic mass with extraluminal growth originating from the muscularis propria layer.
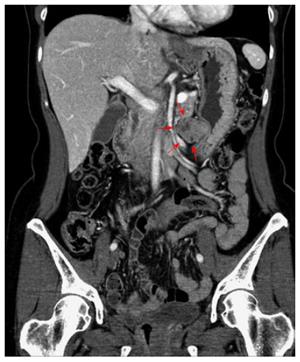
Figure 3 Abdominal computerized tomography scan showing the 3.
5 cm × 2.5 cm tumor with exophytic growth.
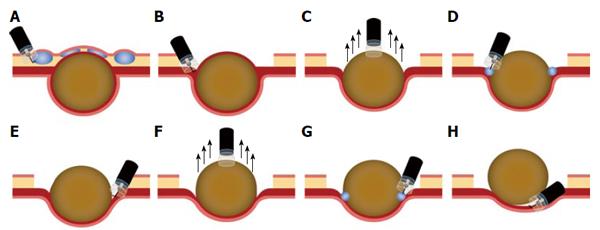
Figure 4 Illustration of the endoscopic suction excavation technique.
A: After submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate, a circumferential incision and removal of the overlying mucosa were performed; B, E: Careful muscular dissection between the tumor and serosa with a hook knife; C, F: Endoscopic suction using the end of a cap-fitted endoscope attached to the tumor; D, G: Submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate; H: Tumor fully extracted after repeated careful dissection and endoscopic suction.
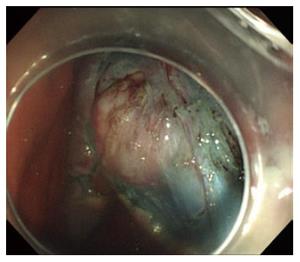
Figure 5 Tumor was exposed after removing the overlying mucosa.
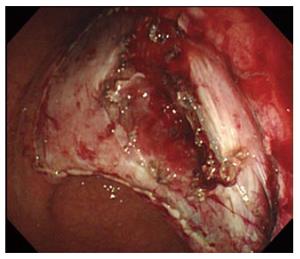
Figure 6 Extraction showing no perforation.
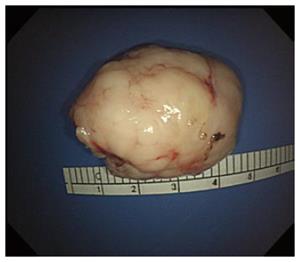
Figure 7 Extracted tumor after repeated muscular dissection and endoscopic suction.
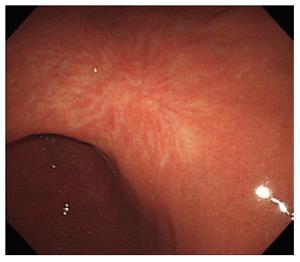
Figure 8 Endoscopic submucosal dissection scar after 5 years.
- Citation: Choi HS, Chun HJ, Kim KO, Kim ES, Keum B, Jeen YT, Lee HS, Kim CD. Endoscopic en bloc resection of an exophytic gastrointestinal stromal tumor with suction excavation technique. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(23): 5454-5458
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i23/5454.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5454