©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2014; 20(26): 8572-8582
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8572
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8572
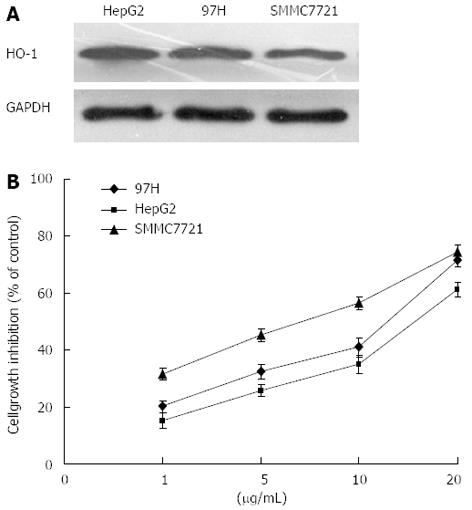
Figure 1 Liver cancer cell lines showed divergent heme oxygenase-1 expression levels, which were associated with variable susceptibility to chemotherapy.
In Western blotting, high levels of heme oxygenase (HO)-1 protein were detected in HepG2 cell line, whereas other cell lines revealed lower expression (A) HepG2 > 97H > SMMC7721. Cell viability was assessed 48 h after application of cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP) via MTT assay. All cell lines showed dose-dependent growth inhibition upon treatment with CDDP. The HepG2 cell line, with the highest HO-1 expression, was significantly more chemoresistant to CDDP than the other cell lines with lower HO-1 expression (B).
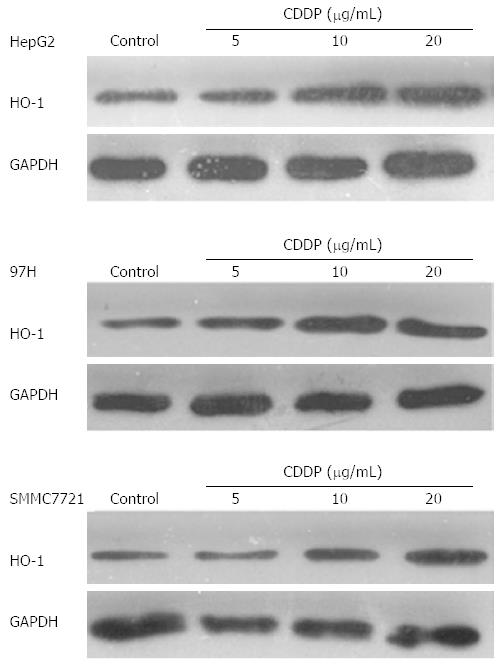
Figure 2 Heme oxygenase-1 could be induced by cis-diaminedichloroplatinum in liver cancer cell lines.
Western blotting showed that heme oxygenase (HO)-1 protein expression was significantly increased after treatment with cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP) for 24 h and achieved a plateau at a concentration of 10 μg/mL in all liver cancer cells.
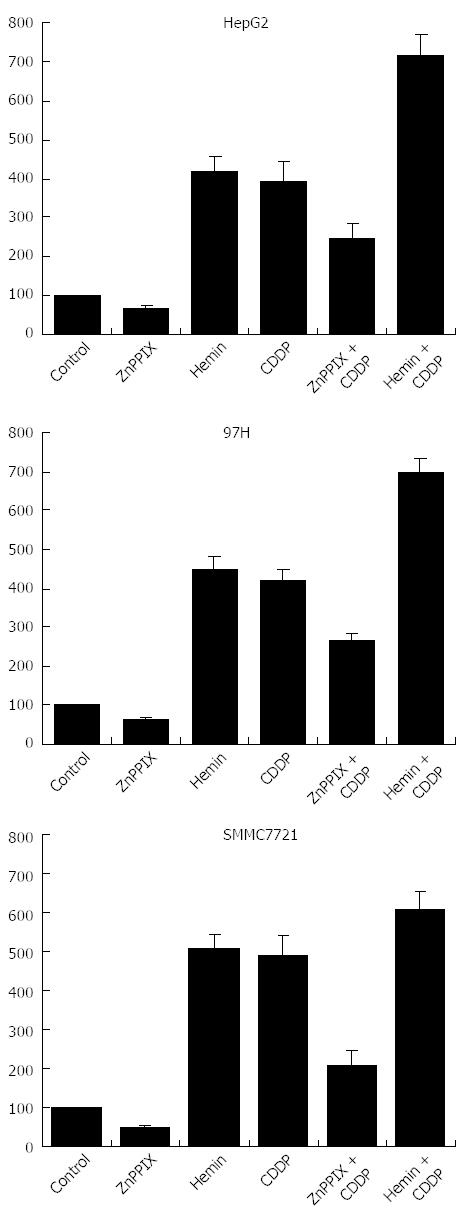
Figure 3 Targeted inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 activity by zinc protoporphyrin IX in liver cancer cell lines.
Heme oxygenase (HO)-1 activity was measured by determining the level of bilirubin generated in isolated microsomes in cells treated with 10 μmol/L zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) IX, 10 μmol/L hemin, and/or 10 μg/mL cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP) for 24 h. ZnPP IX significantly inhibited HO-1 activity and decreased cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP)-induced HO-1 activity in all liver cancer cell lines compared with controls or cells treated with cisplatin alone (P < 0.05). In contrast, hemin increased CDDP-induced HO-1 activity in all liver cancer cell lines (P < 0.05).
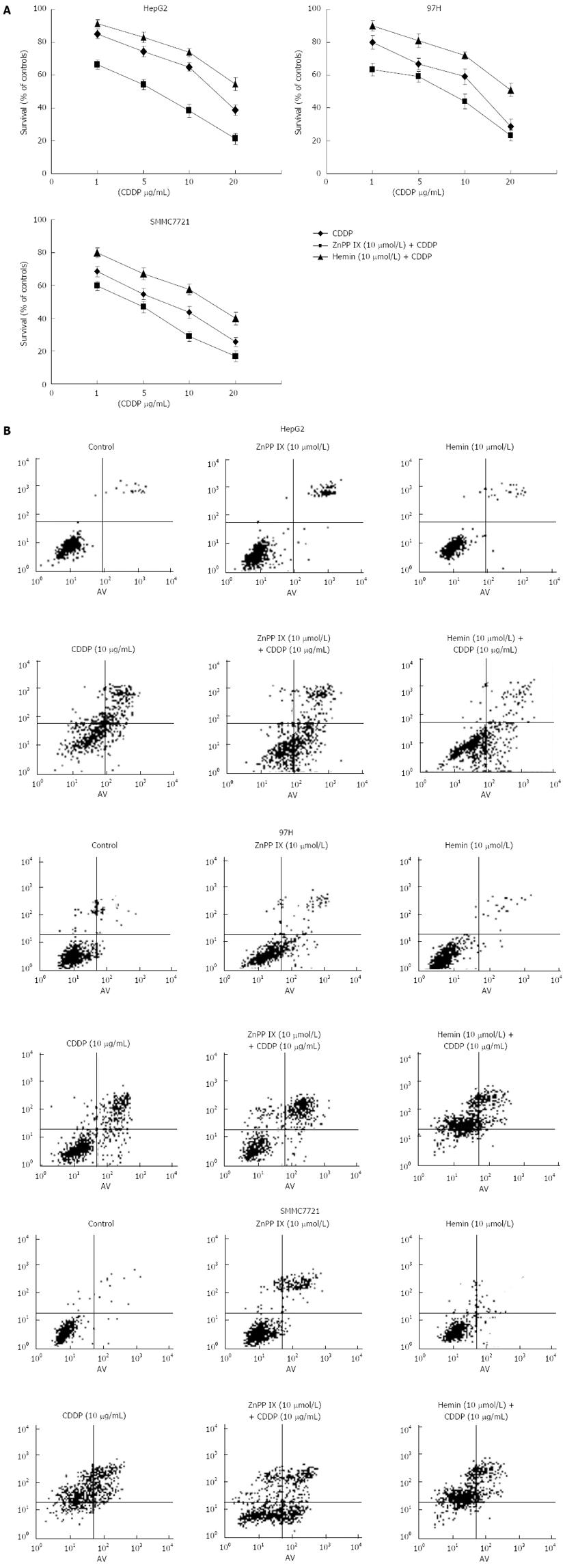
Figure 4 Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 activity led to increased susceptibility to chemotherapy in vitro.
Cell viability was assessed via MTT assay. zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) IX (10 μmol/L) significantly increased apoptosis in cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP)-treated cells, compared with those treated with CDDP alone (A) (P < 0.05). In contrast, hemin decreased apoptosis induced by CDDP in all liver cancer cell lines. FACS analysis with propidium iodide staining also showed that downregulation of heme oxygenase (HO)-1 by ZnPP IX increased apoptosis after exposure to CDDP in comparison with the control group (P < 0.05), whereas increased expression of HO-1 by hemin resulted in decreased sensitivity to CDDP (B).
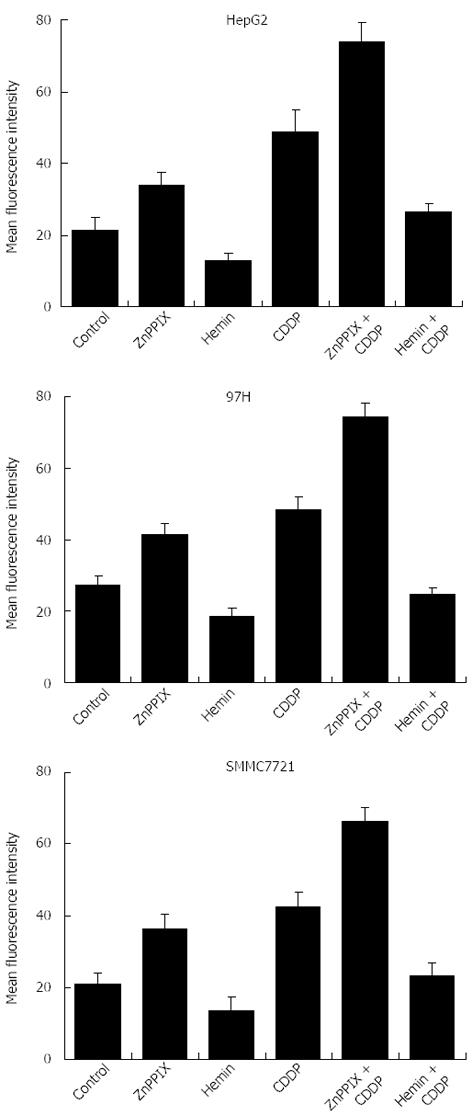
Figure 5 Cytotoxicity of zinc protoporphyrin IX is related to increased oxidative stress.
Induction of intracellular ROS was evaluated by flow cytometry by measuring CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence. Each cell line was treated with 10 μmol/L zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) IX, 10 μmol/L hemin, and/or 10 μg/mL cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP) for 24 h. Mean fluorescence intensity was quantified for these treatments. ZnPP IX increased the fluorescence intensity of the cells and drug-induced ROS in liver cancer cell lines compared with controls or cells treated with CDDP alone. In contrast, hemin decreased CDDP-induced ROS in all liver cancer cell lines.
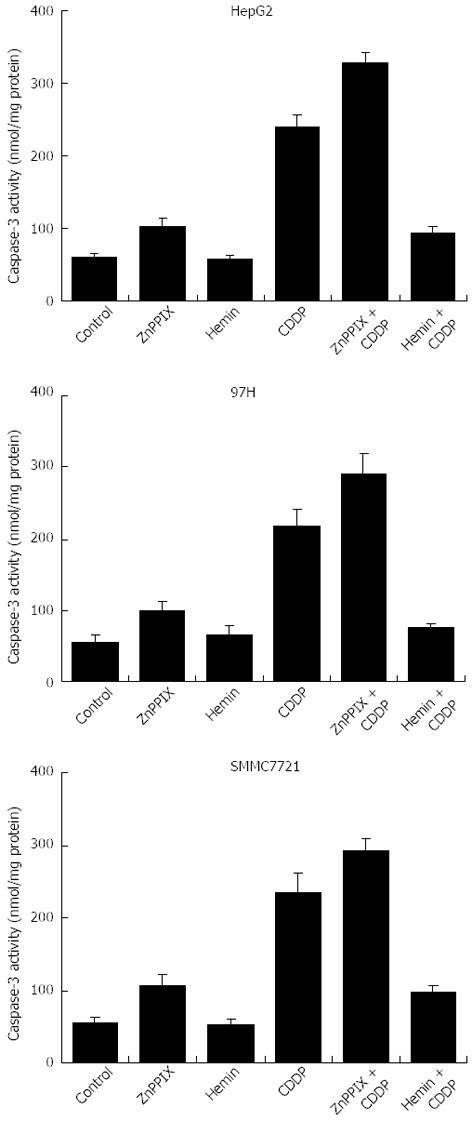
Figure 6 Caspase-3 activity in treated and untreated liver cancer cells.
Inhibition of heme oxygenase (HO)-1 activity increased caspase-3 induced by cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP) in all liver cancer cell lines. Caspase-3 activity was significantly increased in all cells after treatment with cisplatin (10 μg/mL) and re-elevated by addition of zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) IX (10 μmol/L). The caspase-3 activity induced by CDDP was markedly reduced in the presence of hemin (10 μmol/L) in all liver cancer cell lines.
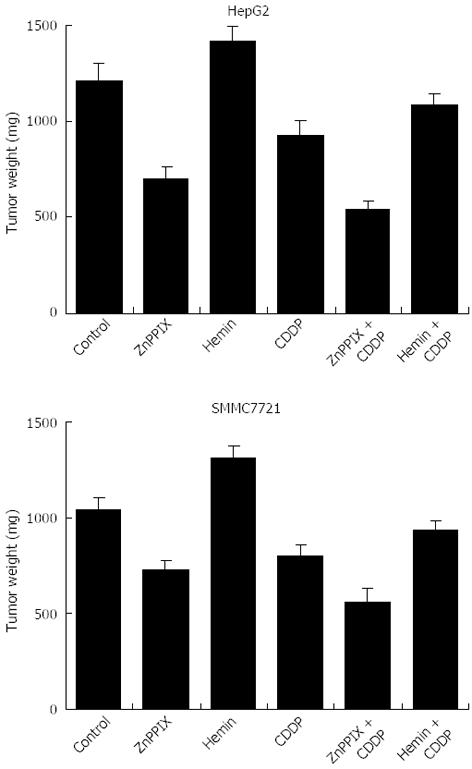
Figure 7 Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 expression increases susceptibility to chemotherapy in vivo.
Each nude mouse was treated with 5 mg/kg zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) IX, 10 mg/kg hemin, and/or 5 mg/kg cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin; CDDP) for 6 wk and tumor weight was assessed after the last treatment. ZnPP IX treatment significantly reduced tumor growth in CDDP-treated mice, compared with those treated with CDDP alone. CDDP in combination with hemin in mice significantly increased tumor weight compared with CDDP treatment alone.
- Citation: Liu YS, Li HS, Qi DF, Zhang J, Jiang XC, Shi K, Zhang XJ, Zhang XH. Zinc protoporphyrin IX enhances chemotherapeutic response of hepatoma cells to cisplatin. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(26): 8572-8582
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i26/8572.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8572