©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2006; 12(24): 3859-3865
Published online Jun 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3859
Published online Jun 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3859
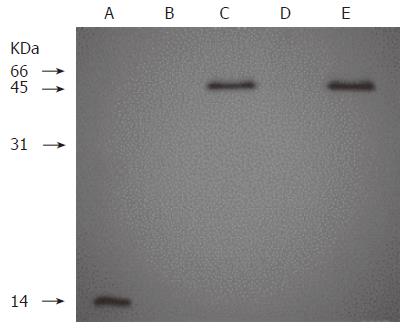
Figure 1 Western blot analysis of recombinant humanized sFv antibody/IL-2 fusion proteins stably expressed in 293 cells.
Lane A: 0.5 μg of rhIL 2; Lanes B, C, D and E: The supernants from conditioned medium of 293 cells, 293 cells transfected with pcDNA-H520C9sFv-hIL-2, pcDNA3.1 (+) and pcDNA-H520C9sFv-mhIL-2, respectively. Samples were separated on a 15% SDS-polyacrylamide gel under reducing conditions, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and immunoblotted using the anti-human IL-2 polyclonal antibody, EP100. The fusion proteins, H520C9sFv-hIL-2 and H520C9sFv-mhIL-2 were shown to migrate as single bands of 45 kD.
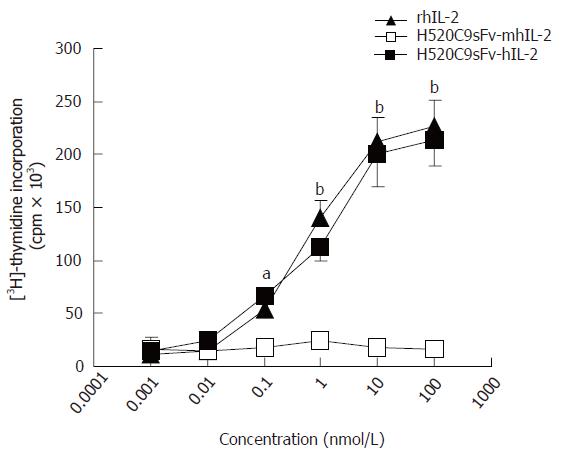
Figure 2 IL 2 activity of recombinant humanized sFv antibody/IL-2 fusion proteins.
IL 2 activity of rhIL-2, or conditioned medium from 293 cells transfected with either pcDNA-H520C9sFv hIL 2 or pcDNA-H520C9sFv mhIL 2 was measured by [3H] thymidine incorporation in CTLL 2 cells. The data are the mean ± SD from three separate experiments. bP < 0.01 for rhIL-2 vs H520C9sFv mhIL 2, and P > 0.05 vs H520C9sFv hIL 2; aP < 0.05 for rhIL-2 vs H520C9sFv mhIL 2, and P > 0.05 vs H520C9sFv hIL 2.
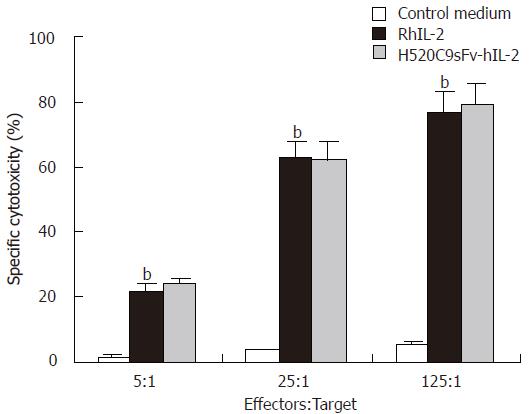
Figure 3 LAK cell-mediated cytotoxicity induced by H520C9sFv-hIL-2 fusion protein.
Human LAK cells (effector) were generated by incubation of fresh PBMCs with either conditioned medium from control 293 cells transfected with pcDNA 3.1 (+), rhIL 2 or equivalent dose of H520C9sFv hIL 2. Lysis of Daudi cells (target) was determined using a 4 h Calcein AM release assay. The data are the mean ± SD from three separate experiments. bP < 0.01 for rhIL-2 vs control medium, and P > 0.05 vs H520C9sFv hIL 2.
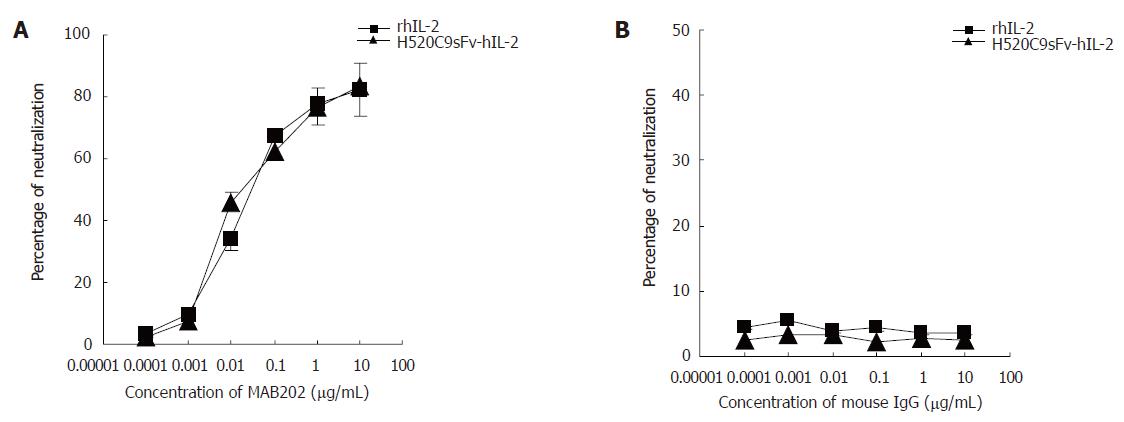
Figure 4 Inhibition of stimulatory effects of rhIL 2 or H520C9sFv hIL 2 on CTLL 2 cells by the anti human IL 2 neutralizing antibody, MAB202.
Based on the molecular mass of either IL-2 or H520C9sFv-hIL-2 fusion protein, the neutralization dose 50 for 2 ng/ml rhIL 2 or the same dose of H520C9sFv hIL 2 was determined to be approximately 0.0176 and 0.022 μg/mL MAB202, respectively (A). No inhibitory effect was observed using control mouse IgG (B). The data are the mean ± SD from three separate experiments (B). A: P > 0.05 for rhIL-2 vs H520C9sFv hIL 2; B: P > 0.05 for rhIL-2 vs H520C9sFv hIL 2.
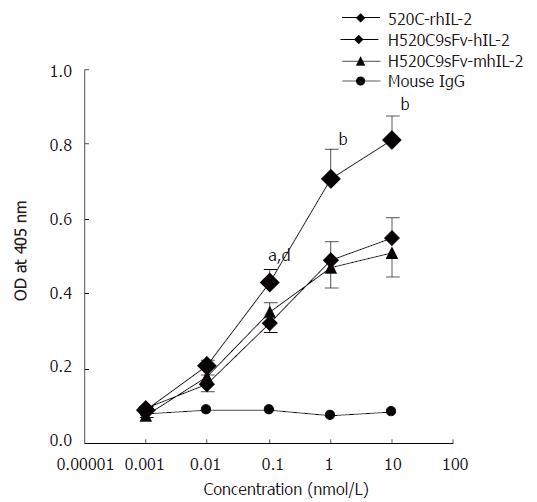
Figure 5 Determination of antigen-binding activity of H520C9sFv-hIL-2 fusion protein.
Antigen binding activity was measured by indirect ELISA using cultured SKOV 3ip1. Bound fusion protein was recognised with the anti-human IL2 polyclonal antibody EP100. The fusion proteins, H520C9sFv-hIL-2 and H520C9sFv-mhIL-2 were shown to bind to p185 positive cells SKOV 3ip1. A chemically-conjugated molecule containing the intact parental 520C9 mAb and rhIL-2(520C9-rhIL-2) was used as a positive control. As a negative control, mouse IgG failed to show any binding activity. The data are the mean ± SD from three separate experiments. bP < 0.01 vs mouse IgG; bP < 0.01 for 520C9-rhIL-2 vs H520C9sFv-hIL-2 and H520C9sFv-mhIL-2; dP < 0.01 vs mouse IgG; aP < 0.05 for 520C9-rhIL-2 vs H520C9sFv-hIL-2 and H520C9sFv-mhIL-2.
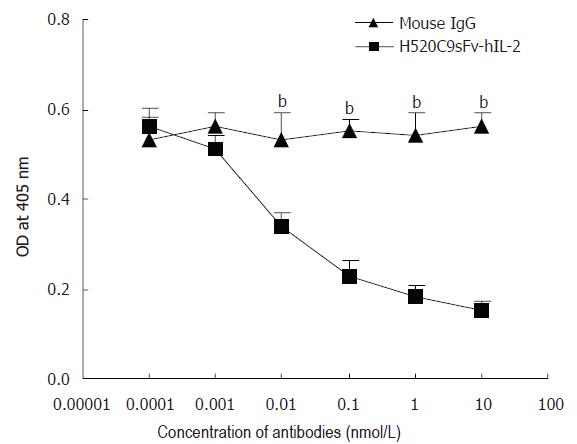
Figure 6 Anti-p185 mAb, 520C9, specifically blocks the binding of H520C9sFv hIL 2 fusion protein to SKOV 3ip1 cells.
SKOV 3ip1 cells, pre-exposed to serially diluted intact 520C9 monoclonal antibody or to mouse IgG (0.0001 to 10 nmol/L), then incubated with 10 nmol/L H520C9sFv hIL 2 fusion protein. Bound fusion protein was measured by indirect ELISA using the anti human IL 2 polyclonal antibody, EP100. 520C9 mAb caused a dose-dependent decrease in the binding of the fusion protein to SKOV 3ip1 cells. Control mouse IgG had no effect on the binding of the fusion protein. The data are the mean ± SD from three separate experiments. bP < 0.01 vs mouse IgG, P > 0.05 vs mouse IgG.
- Citation: Shen YC, Wang XH, Wang XM, Chen ZL, Shen XP, Zhao CC, Li J. High efficient mammalian expression and secretion of a functional humanized single-chain Fv/human interleukin-2 molecules. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(24): 3859-3865
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i24/3859.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3859