Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2006; 12(24): 3829-3834
Published online Jun 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3829
Published online Jun 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3829
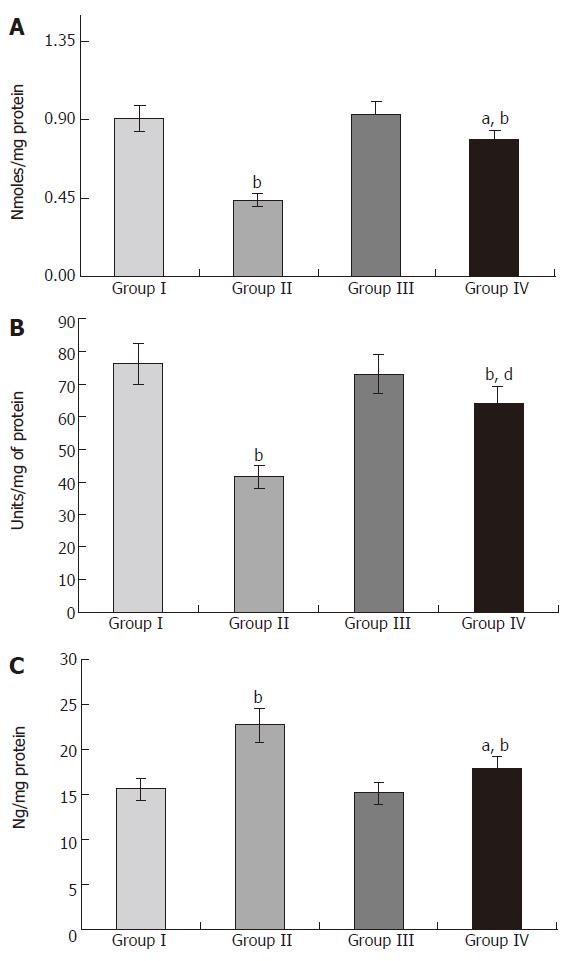
Figure 1 Various effects of S.
polycystum against acetaminophen-induced toxic hepatitis in rats. A: Effect of S. polycystum on cytochrome P450 during acetaminophen-induced toxic hepatitis; B: Efficacy of S. polycystum on cytochrome b5 against acetaminophen-induced toxic hepatitis; C: Effect of S. polycystum on the status of microsomal cytochrome P450 reductase. Values are expressed as mean ± SD for six rats. bP < 0.01 vs group I, dP < 0.001 vs group II, aP < 0.05 vs group I.
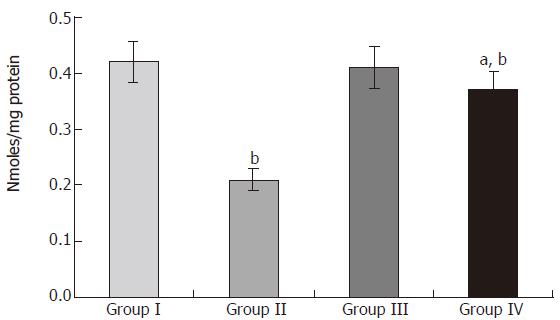
Figure 2 Effect of S.
polycystum on TNF-α in serum of control and experimental group of rats. Values are expressed as mean ± SD for six rats. aP < 0.05 vs group I, bP < 0.01 vs group I, dP < 0.001 vs group II.
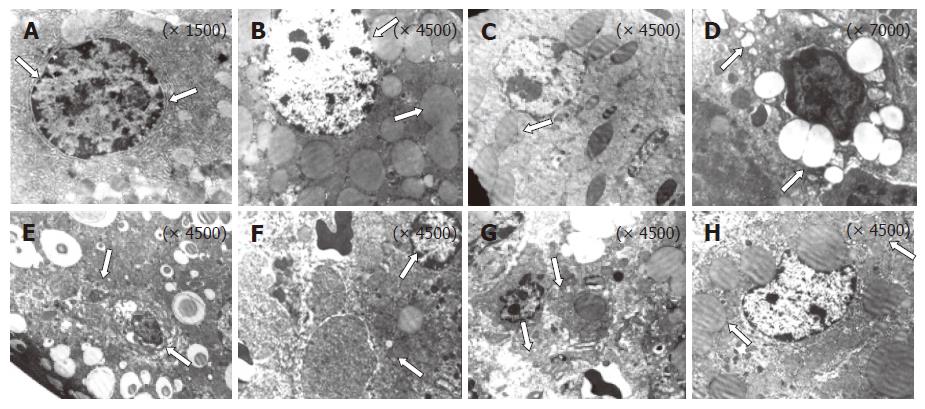
Figure 3 Structural features of liver examined by transmission electron microscopy.
A: Normal cellular structure of rat liver without any destruction; B, C and D: Effect of acetaminophen on fine ultrastructural changes during toxic hepatitis in rats; E, F, G and H: Effect of S. polycystum against acetaminophen-induced alterations in structural integrity during toxic hepatitis.
- Citation: raghavendran HB, Sathivel A, Devaki T. Defensive nature of Sargassum polycystum (Brown alga) against acetaminophen-induced toxic hepatitis in rats: Role of drug metabolizing microsomal enzyme system, tumor necrosis factor-α and fate of liver cell structural integrity. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(24): 3829-3834
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i24/3829.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3829