©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. May 15, 2004; 10(10): 1480-1486
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1480
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1480
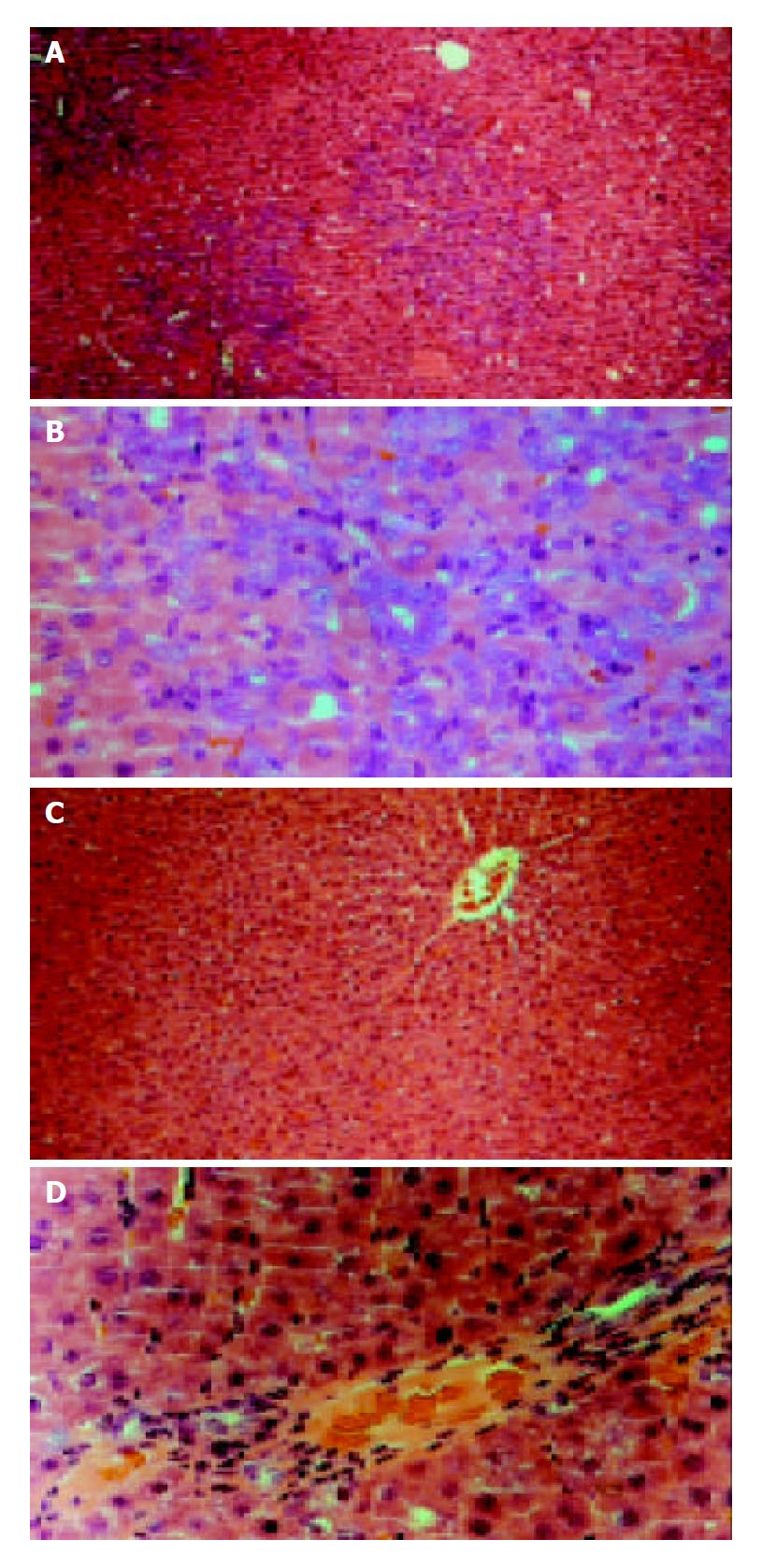
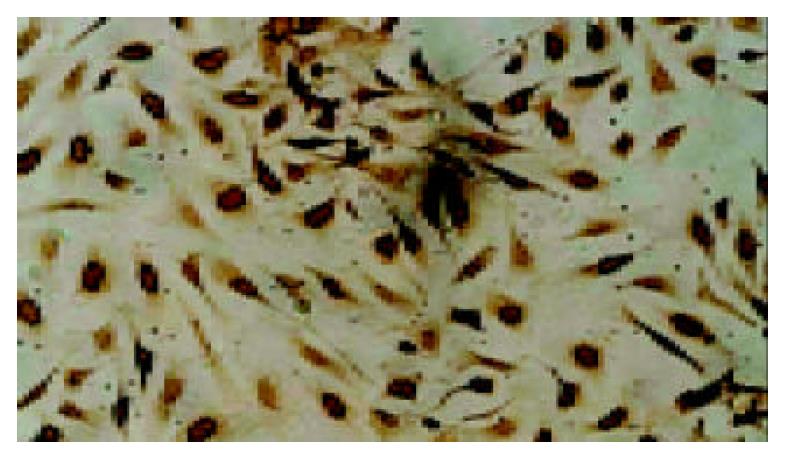
Figure 1 Rat liver sections obtained from 2-AAF/PH (11 d after operation) and control.
Sections were stained with he-matoxylin-eosin. (A and B) show liver sections obtained from 2-AAF/PH-treated rats at low (× 100) and high (× 400) magnification. Small oval cells (arrows) can be seen close prox-imity to proliferating bile ducts and in areas of ductular pro-liferation or in acinar arrangements around hepatocytes. The oval cells radiate from the periportal region, forming primi-tive ductular structures with poorly defined lumen. (C and D) show liver tissue from control rats at low and high magnification. Hepatoctye proliferation can be seen in the typical liver architecture. Central vein (CV) and portal triad region can be seen.
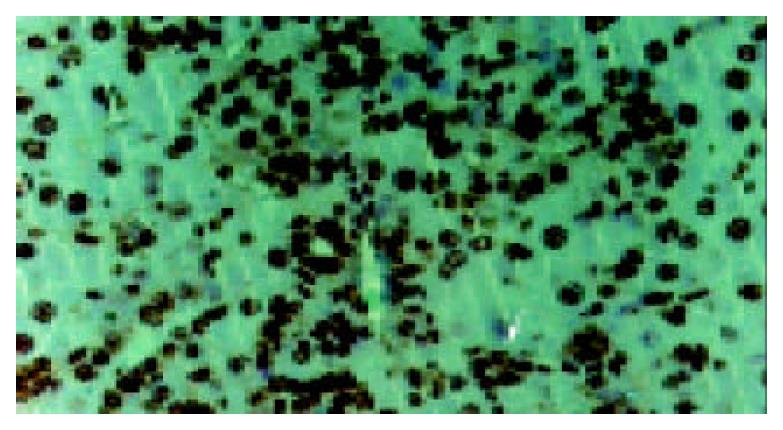
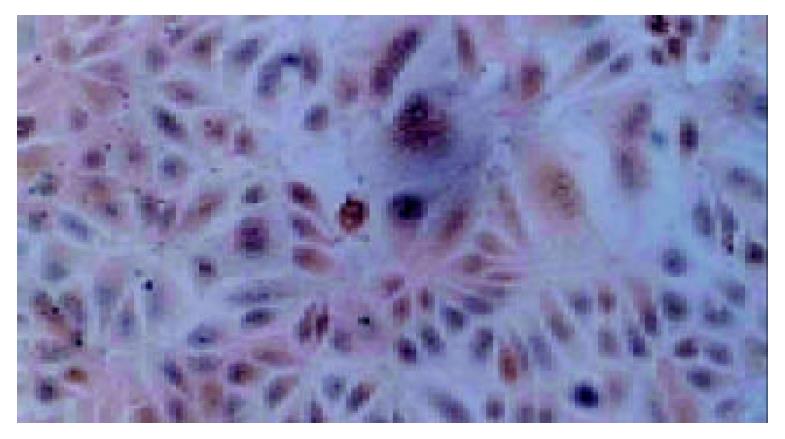
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry of liver sections obtained from 112-AAF/PH rats.
BrdU staining of oval cells in proliferative state. Arrows inidicate oval cells.
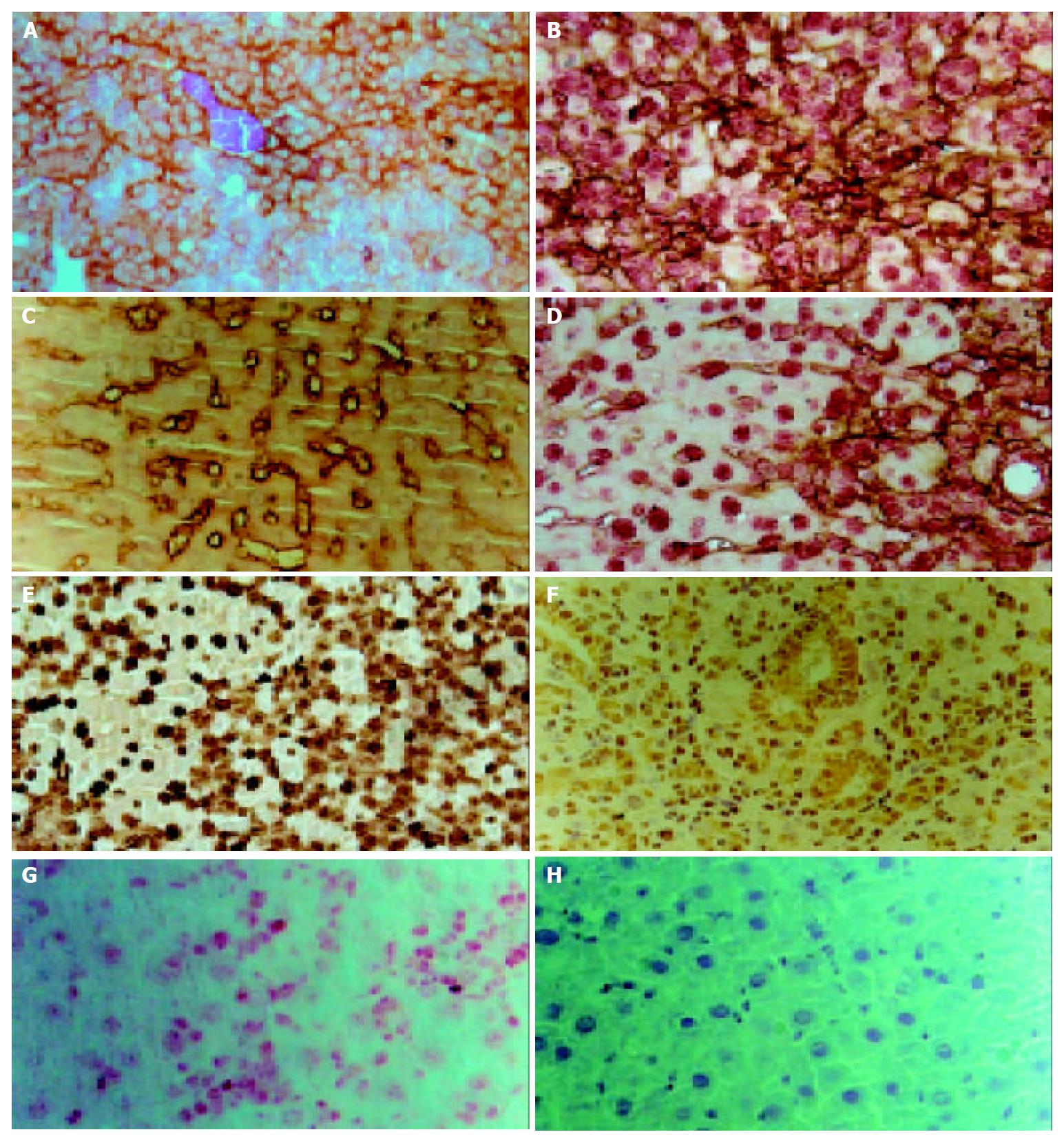
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining of liver sections from rat liver exposed to 2-AAF/PH (d 11) at high magnification.
A: Staining for OV6, Arrows point to OV6-positive oval cells.B: Double immunohitstochemical staining for OV6 (brown) and albu-min (red). C: Staining for cytokeratin19 (CK19). Ductular lumen face and oval cells were positive. Arrows point ot CK19-positive cells. D: Double immunhistochemical staining for CK19 (brown) and albumin (red). Arrows point to oval cells with tow markers. E: Staining for AFP. F: Staining for connexin43, Arrows point to connexin43 positive oval cells. G: Staining for C-kit, Oval cells were stained with red. H: Negative control.
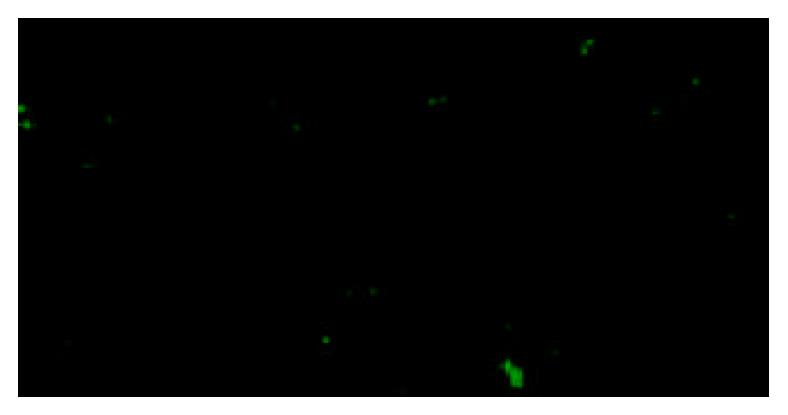
Figure 4 Immunocytochemistry for OV6 on cytocentrifuged preparations of C-kit+ MACS sorted cells from 2-AAF/PH treated rats.
The sorted C-kit+ cells were stained with oval cell-specific antibody OV6 (green).
Figure 5 Phase contrast photomicrographs showing forma-tion of a colony by a sorted C-kit+ oval cell after cultured in vitro for 2 wk.
(A: × 100; B: × 200).
Figure 6 Double immnocytochemistry for BrdU incorpora-tion and C-kit staining on sorted c-kit+ oval cell clony on d 7.
Most cells had their nuclei stained with BrdU (arrow). Though they came from one precusor, many cells lost c-kit marker, just some of them were still c-kit positive stained blue. (arrowheads). (× 400).
Figure 7 Dual staining of cultured sorted oval cell clony with albumin (dark blue) and CK19 (brown).
Some cells were stained with both markers (Arrows) and the others were stained only one marker. (× 400).
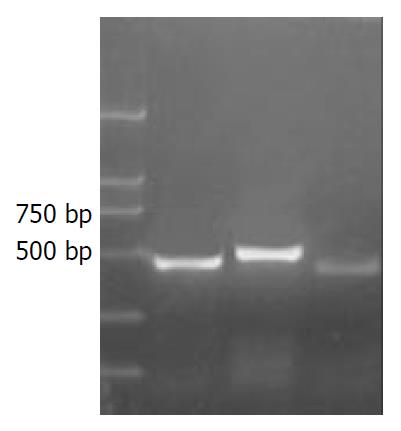
Figure 8 RT-PCR analysis of gene expression.
RNA was iso-lated from sorted cell colony.
- Citation: Qin AL, Zhou XQ, Zhang W, Yu H, Xie Q. Characterization and enrichment of hepatic progenitor cells in adult rat liver. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(10): 1480-1486
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i10/1480.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1480