Column: BPG News
Authors: Jia-Ru Fan, Jin-Lei Wang, Jia-Ping Yan, Xiang Li, Si Zhao, Jia-Wei Li
Reviewer: Lian-Sheng Ma
Title: 2025 Annual Work Summary of Baishideng Publishing Group
Date: December 31, 2025
2025 Annual Work Summary of Baishideng Publishing Group
1 Overview
As 2025 draws to a close, we look forward to a year of both challenges and opportunities in 2026. Under the guidance of our Founder and CEO, Mr. Lian-Sheng Ma, and with the collaborative efforts of the Administrative Office, Editorial Office, Production Department, and New Technology Development Department—along with all Editorial Board Members and Peer Reviewers—Baishideng Publishing Group (BPG) has successfully completed the editing and publication of its 47 journals. Significant achievements have been made this year, and we are confident that BPG will continue to excel in the coming year.
In 2025, BPG’s 46 English-language journals received a total of 7344 invited manuscript proposals, while World Chinese Journal of Digestology (WCJD) accepted 35 invited proposals. The Reference Citation Analysis (RCA) platform—including its Editorial Board Member, Peer Reviewer, and Scholar registration systems—received 2616 applications, of which 1038 were approved after evaluation. The 46 English journals collectively received 9580 submissions, with Chinese authors contributing the highest number. A total of 17686 Peer-Review Reports were submitted by Editorial Board Members and Peer Reviewers, and 272 registered Editorial Board Members and Peer Reviewers were paid a total of USD 27150 for reviewing 558 manuscripts. Additionally, 8431 manuscripts reached a first decision, 4847 reached a second decision, and 5062 articles were fully produced and published. Overall, the total number of articles published by BPG journals has shown steady growth from 2023 to 2025.
Notably, 12 BPG journals received their latest Impact Factors in the 2025 Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR). Among them, two Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE)-indexed journals remained firmly in the Q1 zone, while eight were ranked in the Q2 zone. Seven journals saw an increase in their Impact Factors: World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) rose to 5.4, World Journal of Clinical Oncology (WJCO) increased to 3.2, and World Journal of Cardiology (WJC) reached 2.8.
This report systematically reviews and summarizes BPG’s work in 2025, covering key areas such as manuscript solicitation, development of Editorial Board Member and Peer Reviewer teams, manuscript receipt, first decision and peer review, second decision, article production and publication, technological development, and related policy updates.
2 Summary of Invited Manuscript Proposals for BPG Journals
2.1 Overview of Number of Invited Manuscript Proposals Across 46 English-Language Journals
Between January 1 and December 23, 2025, the 46 English-language journals published by BPG received a total of 7344 invited manuscript proposals. Of these: (1) 3144 (42.81%) proposals were declined, including 1665 editorials; and (2) 4200 (57.19%) proposals were accepted, among which 1620 have been submitted as full manuscripts, 972 have been formally published, 943 were not submitted by the deadline, and 665 are pending full submission.
Compared with the 4142 proposals received in 2024, the total number of invited proposals in 2025 increased by 3202. Notably, WJG received 1919 proposals in 2025—an increase of 1001 from the 918 received in 2024, representing a significant rise.
2.1.1 Analysis of Invited Manuscript Proposals by Manuscript Type
Among the 4200 accepted proposals across the 46 English-language journals in 2025, review articles constituted the largest share with 1737 (41.36%), followed by 1289 original articles (30.69%), 679 editorials (16.17%), 299 systematic reviews and meta-analyses (7.12%), 191 case reports (4.55%), and 5 manuscripts of other types (0.12%) (Figure 1).
Taking WJG as an example, of its 815 accepted proposals, 374 were reviews (45.89%)—the highest proportion—followed by 245 original articles (30.06%), 163 editorials (20.00%), 28 systematic reviews and meta-analyses (3.43%), 3 case reports (0.37%), and 2 manuscripts of other types (0.25%).
.png)
Figure 1 Number of accepted invited manuscript proposals by manuscript type in 2025.
2.1.2 Analysis of Invited Manuscript Proposals by Journal
Among the 4200 accepted invited proposals across the 46 English-language journals in 2025, the five journals with the highest number of accepted invitations were (in descending order): WJG, 815 (19.40%); World Journal of Clinical Cases (WJCC), 261 (6.21%); World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics (WJCP), 243 (5.79%); World Journal of Hepatology (WJH), 222 (5.29%); and World Journal of Nephrology (WJN), 190 (4.52%). Notably, World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, World Journal of Surgical Procedures, and World Journal of Respirology received no invited proposals during the year (Figure 2).
The six journals indexed in the SCIE in 2025—World Journal of Diabetes (WJD), WJG, World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology (WJGO), World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery (WJGS), World Journal of Psychiatry (WJP), and World Journal of Stem Cells (WJSC)—collectively accepted 1560 invited proposals, an increase of 410 from the 1150 accepted in 2024. The six journals indexed in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)—WJC, WJCO, World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (WJGE), WJH, World Journal of Orthopedics (WJO), and World Journal of Radiology (WJR)—accepted a total of 954 invited proposals in 2025, representing an increase of 436 compared with the 518 accepted in 2024. Seven journals currently under application for ESCI indexing accepted 1084 invited proposals in 2025. While this figure remained largely stable compared with the 1105 accepted in 2024, it marks a substantial 112% increase over the 512 accepted in 2023.
.png)
Figure 2 Number of accepted invited manuscript proposals by journal in 2025.
2.1.3 Analysis by Country of Origin
Among the 4200 accepted invited proposals for the 46 English-language journals in 2025, the top five countries by contribution were: China, 925 (22.02%); India, 723 (17.21%); United States, 364 (8.67%); Italy, 251 (5.98%); and Türkiye, 185 (4.40%).
2.2 Statistics on Invited Manuscripts for World Chinese Journal of Digestology
In 2025, WCJD received 35 invited manuscript proposals, of which 3 were declined and 32 were accepted. All accepted invitations were for commentaries or review articles.
3 Statistics on Registrations via the RCA Platform in 2025
From January 1 to December 24, 2025, a total of 2616 scholars registered via invitation, comprising: (1) 2205 who applied through the Editorial Board Member Registration system to serve as Editorial Board Members or Peer Reviewers. Among these, 10 applied for the role of Editor-in-Chief, 2 for Executive Associate Editor-in-Chief, 44 for Associate Editor, 1205 for Editorial Board Member, 942 for Peer Reviewer, and 2 others whose applications were declined; and (2) 411 who registered through the Scholar Registration system.
3.1 Analysis of Editorial Board Member Applications
3.1.1 Distribution by Position
Of the 2205 applicants, 936 (42.45%) were accepted; 702 (31.84%) were declined; 518 (23.49%) had their accounts closed due to failure to submit revisions or activate accounts in time; 3 (0.13%) are pending activation; and 46 (2.09%) remain under evaluation.
Among the 936 accepted Editorial Board Members/Peer Reviewers, 1 (0.11%) was appointed as Editor-in-Chief; 2 (0.21%) as Executive Associate Editor-in-Chief; 4 (0.43%) as Associate Editor; 184 (19.66%) as Editorial Board Member; and 745 (79.59%) as Peer Reviewer. Notably, WJCO accepted the highest number of applicants (114), including 2 Associate Editors, 25 Editorial Board Members, and 87 Peer Reviewers.
3.1.2 Distribution by Journal
The ten journals with the highest number of applicants among the 2205 applications were: WJCO, 204; WJG, 200; WJP, 155; WJC, 141; WJO, 140; WJD, 124; WJN, 84; WJGO, 80; WJR, 78; and World Journal of Experimental Medicine (WJEM), 76.
Furthermore, the six SCIE-indexed journals accounted for 694 (31.47%) of the registered scholars; the six ESCI-indexed journals for 683 (30.98%); and the seven journals under ESCI application for 434 (19.68%).
The seven journals under ESCI application accepted 176 Editorial Board Members/Peer Reviewers (Table 1), including 30 Editorial Board Members (17.05%) and 146 Peer Reviewers (82.95%).
Table 1 Number of accepted Editorial Board Members/Peer Reviewers for the seven journals under ESCI application
| Journal | No. of Peer Reviewers | No. of Editorial Board Members |
| World Journal of Experimental Medicine | 22 | 7 |
| World Journal of Nephrology | 23 | 6 |
| World Journal of Methodology | 32 | 2 |
| World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics | 22 | 5 |
| World Journal of Critical Care Medicine | 24 | 6 |
| World Journal of Transplantation | 12 | 2 |
| World Journal of Virology | 11 | 2 |
| Total | 146 | 30 |
3.1.3 Analysis by Country of Origin
A total of 936 scholars from 64 countries/regions were accepted as Editorial Board Members or Peer Reviewers. The top five contributing countries were: China, 528 (56.41%); India, 73 (7.80%); Italy, 45 (4.81%); United States, 45 (4.81%); and Türkiye: 27 (2.88%).
3.2 Scholar Registration Statistics
Between January 1 and December 24, 2025, 412 scholars submitted applications through the Scholar Registration system. The outcomes were as follows: 102 (24.76%) were accepted; 161 (39.08%) were declined; 135 (32.77%) had their accounts closed due to failure to submit revisions or activate accounts in time; 4 (0.97%) are pending activation; and 10 (2.42%) remain under evaluation.
The 102 accepted registrants came from 33 countries/regions. The top five countries were: China, 40 (39.22%); India, 12 (11.76%); Türkiye, 8 (7.84%); Egypt, 4 (3.92%); and Italy, 4 (3.92%).
4 Manuscript Submissions
The Assistant Editor is responsible for managing manuscript submissions, tracking and verifying publication fees, processing inquiries via the Helpdesk platform, and handling related correspondence. As of the current date, the Assistant Editor has largely completed its tasks for 2025. Below is a summary of submissions received by the 46 English-language BPG journals in 2025:
Between January 1 and December 30, 2025, the 46 English-language journals received a total of 9580 submissions from 114 countries, comprising 3488 (36.41%) invited manuscripts and 6092 (63.59%) unsolicited submissions. Of these, 1358 manuscripts (14.18%) were rejected during the initial technical screening due to non-compliance with journal formatting requirements, submission of fraudulent language certificates or ethics approvals, suspected academic misconduct (including paper-mill involvement), or submission of low-quality database articles.
Compared with the 11117 submissions received in 2024, the total number in 2025 decreased by 1537. However, the number of manuscripts rejected during initial technical screening was lower in 2025 (1358) than in 2024 (2,044), representing a reduction of 686.
By authors’ country of origin, submissions to the 46 English-language journals in 2025 were distributed as follows: China, 5398 (56.35%); India, 620 (6.47%); United States, 510 (5.32%); Italy, 241 (2.51%); Türkiye, 219 (2.29%); South Korea, 150 (1.57%); Egypt, 146 (1.52%); Japan, 132 (1.38%); Pakistan, 131 (1.37%); Greece, 119 (1.24%); and other countries, 1914 (19.98%).
5 Summary of Peer Review and First Decision
With the support of Editorial Board Members, Peer Reviewers, and Editors, the Editorial Office has largely completed the peer review and first-decision tasks for the 47 journals in 2025. Details are summarized below:
5.1 Manuscript Peer Review
Between January 1 and December 26, 2025, a total of 775690 peer-review invitations were sent for manuscripts submitted to the 46 English-language journals. The responses were as follows: 28873 (3.7%) invitations were accepted; 30641 (4.0%) were declined; and 716176 (92.3%) received no response (Figure 3).
Of the 28873 accepted invitations, 17686 (61.3%) Peer-Review Reports were returned, 10866 (37.6%) were not submitted by the deadline, and 321 (1.1%) are still pending. The average peer-review cycle in 2025 was 19 days, a reduction of 65.5% from the average of 55 days in 2024. The overall peer-review success rate was 2.3%, calculated as the 17686 reports received divided by the 775690 invitations sent.
.png)
Figure 3 Acceptance and decline of manuscript peer-review invitations by Editorial Board Members and Peer Reviewers for BPG’s 46 English-language journals in 2025.
5.2 Review Fees
Between January 1 and December 26, 2025, BPG’s 46 English-language journals paid review fees to 272 registered Editorial Board Members and Peer Reviewers from 37 countries/regions. Payments covered 558 manuscripts whose reviewers elected to receive an honorarium, totaling USD 27150. The recipients included 2 Editors-in-Chief; 1 Executive Associate Editor-in-Chief; 2 Associate Editors; 50 Editorial Board Members; and 217 Peer Reviewers.
5.3 First Decision
Between January 1 and December 26, 2025, a total of 8431 manuscripts reached a first decision across BPG’s 46 English-language journals. This comprised 3462 (41.1%) invited submissions and 4969 (58.9%) unsolicited ones. The outcomes of first decision were as follows (Figure 4): 5142 (61.0%) manuscripts were provisionally accepted; 1780 (21.1%) were recommended for transfer to another journal; and 1509 (17.9%) were rejected.
Additionally, 88 manuscripts (1.0%) were identified during the first-decision process as originating from paper mills or involving academic misconduct, such as fraudulent language certificates or fabricated ethics approvals. The average time from submission to first decision in 2025 was 32 days, representing a 50% reduction from the 2024 average of 64 days.
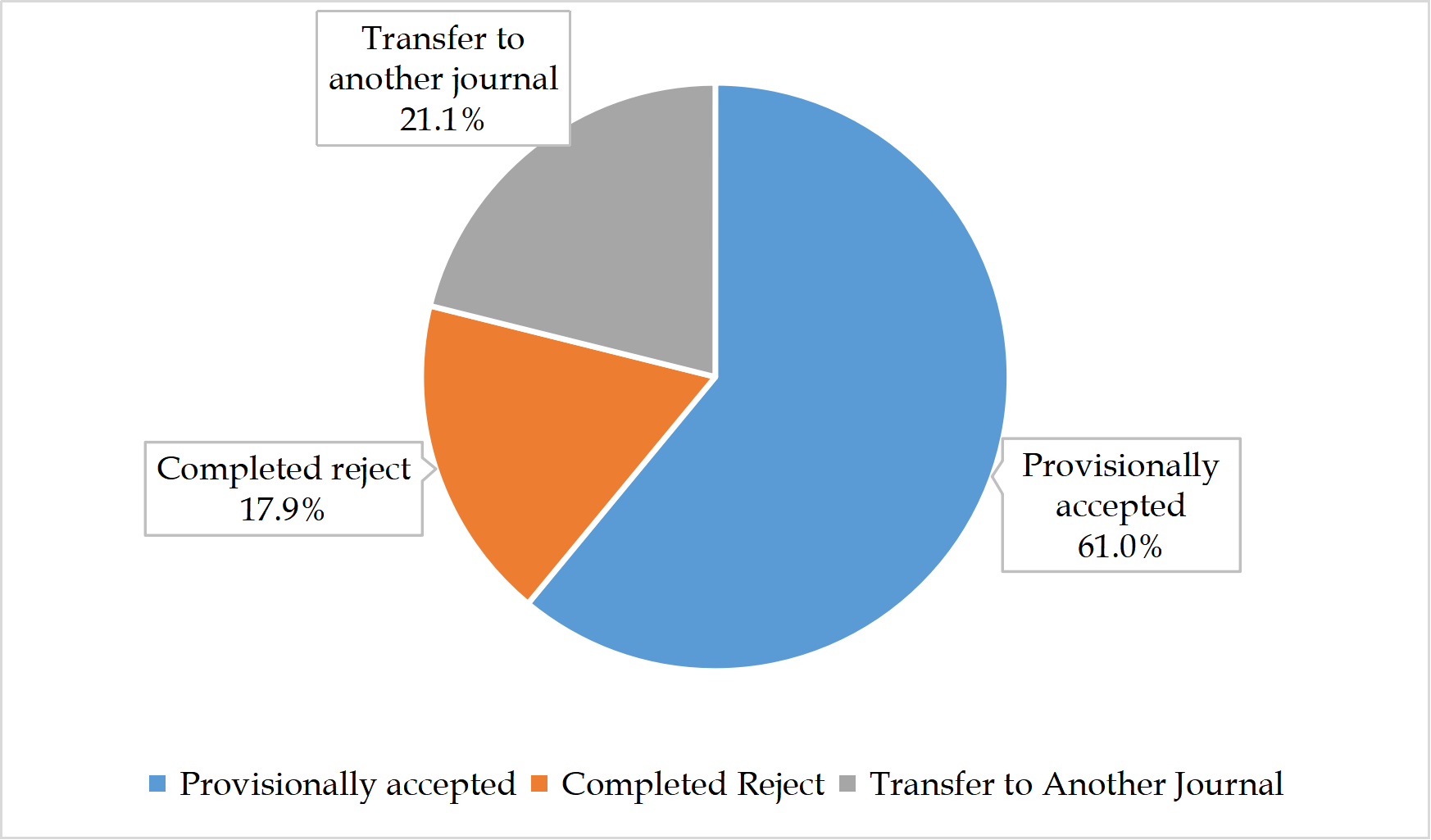
Figure 4 First decisions for BPG’s 46 English-language journals in 2025.
6.1 Overview of Manuscripts
Table 2 Number of manuscripts reaching a second decision in 2023-2025
|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
| No. of unsolicited manuscripts | 1943 | 2727 | 2543 |
| No. of invited manuscripts | 1056 | 1985 | 2304 |
| Total | 2999 | 4712 | 4847 |
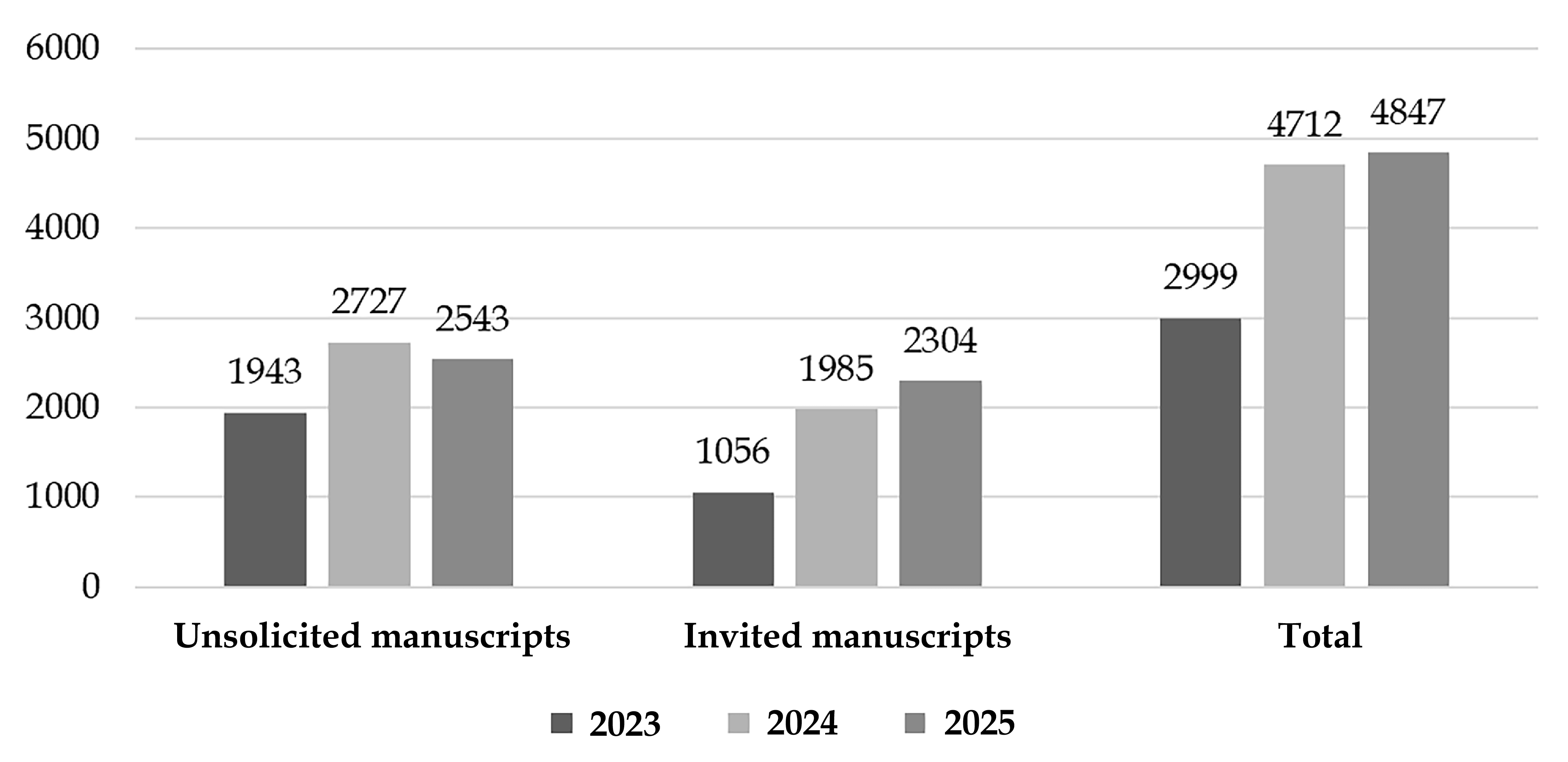
Figure 5 Number of manuscripts reaching a second decision in 2023-2025.
6.1.1 Overall Trend
The total volume of manuscripts reaching a second decision has shown significant growth, with the rate of increase gradually moderating.
Sustained growth in total volume: The aggregate number increased from 2999 in 2023 to 4847 in 2025, representing a three-year growth of 61.6%. This upward trend reflects the sustained and growing appeal or influence of the BPG journal portfolio.
6.1.2 Change in Manuscript Composition
Overall analysis indicates that the change in manuscript composition is primarily characterized by a significant increase in the proportion of invited manuscripts.
Rapid growth of invited manuscripts: The number of invited manuscripts rose from 1056 in 2023 to 2304 in 2025, an increase of 118.2%, which significantly outpaces the growth rate of the total manuscript volume.
Notable shift in composition: The share of invited manuscripts increased from 35.2% in 2023 to 47.5% in 2025, indicating a strategic editorial emphasis on active solicitation.
6.2 Manuscripts Reaching a Second Decision for Six SCIE-Indexed BPG Journals in 2023-2025
6.2.1 Summary of Volume of Manuscripts Reaching a Second Decision for the Six SCIE-Indexed Journals
From 2023 to 2025, the volume of manuscripts reaching a second decision across the six SCIE-indexed BPG journals demonstrated an overall growth trend (Figure 6). The growth rates were generally substantial, suggesting that these journals are in a phase of rapid expansion. With the exception of WJSC, which started from a lower base, each of the other journals consistently processed over 150 manuscripts annually at this stage. This is likely associated with factors such as the journals' established influence and submission scope, as SCIE-indexed journals typically represent more mature and larger-scale publications.
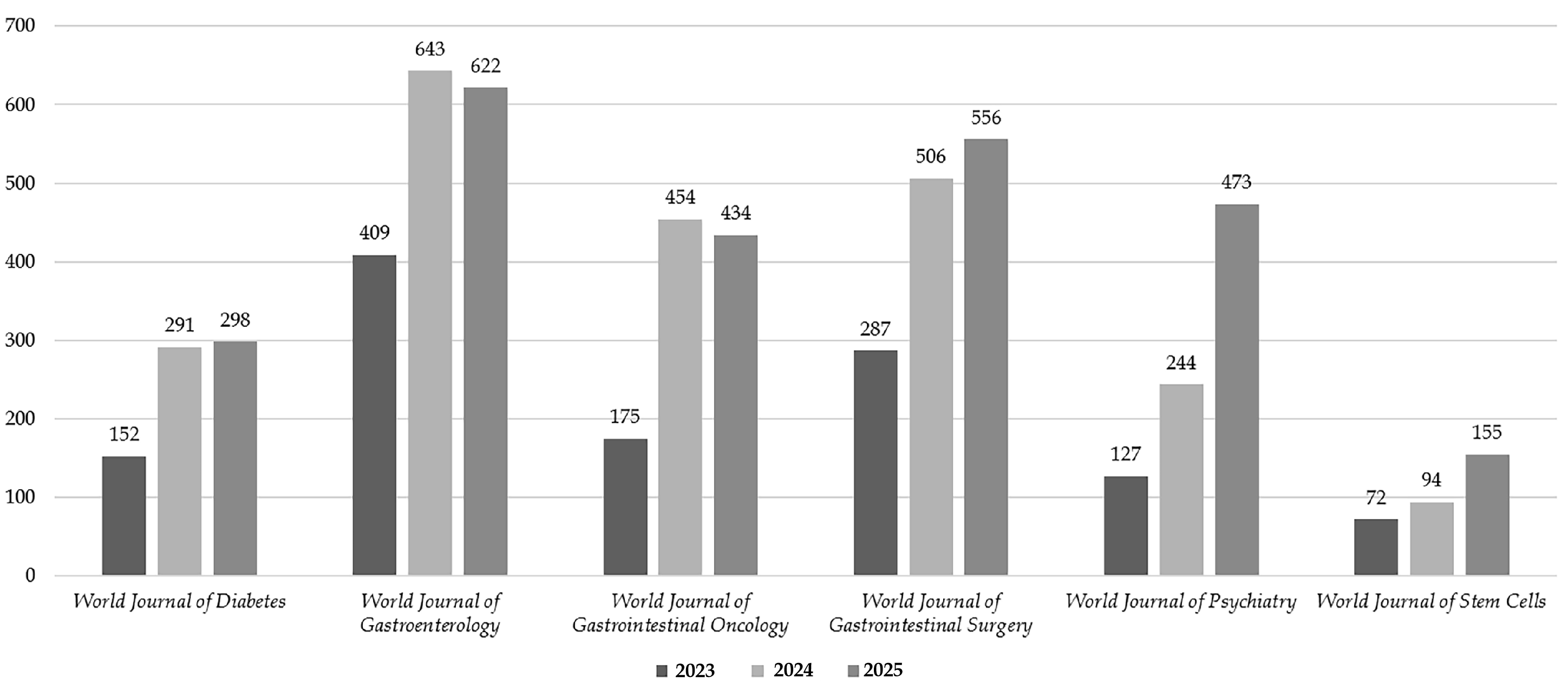
Figure 6 Manuscripts reaching a second decision for six SCIE-indexed BPG journals in 2023-2025.
6.2.2 Performance of the Six SCIE-Indexed Journals
WJG consistently had the highest number of manuscripts reaching a second decision, reaching 643 in 2024 before a slight decline to 622 in 2025. WJP showed the most rapid growth. WJD exhibited continuous growth, rising from 152 in 2023 to 298 in 2025. WJGO also displayed an initial increase followed by a minor decrease, growing from 175 in 2023 to 454 in 2024 before dropping to 434 in 2025. WJGS sustained steady growth, increasing from 287 in 2023 to 556 in 2025. WJSC recorded substantial growth, rising from 72 in 2023 to 155 in 2025.
In summary, the journals with the largest growth magnitudes were WJP, WJSC, and WJD, with WJP showing the fastest growth.
6.3 Manuscripts Reaching a Second Decision for Six ESCI-Indexed BPG Journals in 2023-2025
6.3.1 Summary of Volume of Manuscripts Reaching a Second Decision for the Six ESCI-Indexed Journals
From 2023 to 2025, the volume of manuscripts reaching a second decision across the six ESCI-indexed BPG journals showed continuous growth (Figure 7). The total for the six ESCI-indexed journals increased from 432 in 2023 to 823 in 2024 (a growth of 90.5%), and further rose to 1218 in 2025 (a corresponding growth of 47.9%). This represents three consecutive years of uninterrupted growth, illustrating a classic two-phase pattern of "capacity expansion followed by sustained momentum."
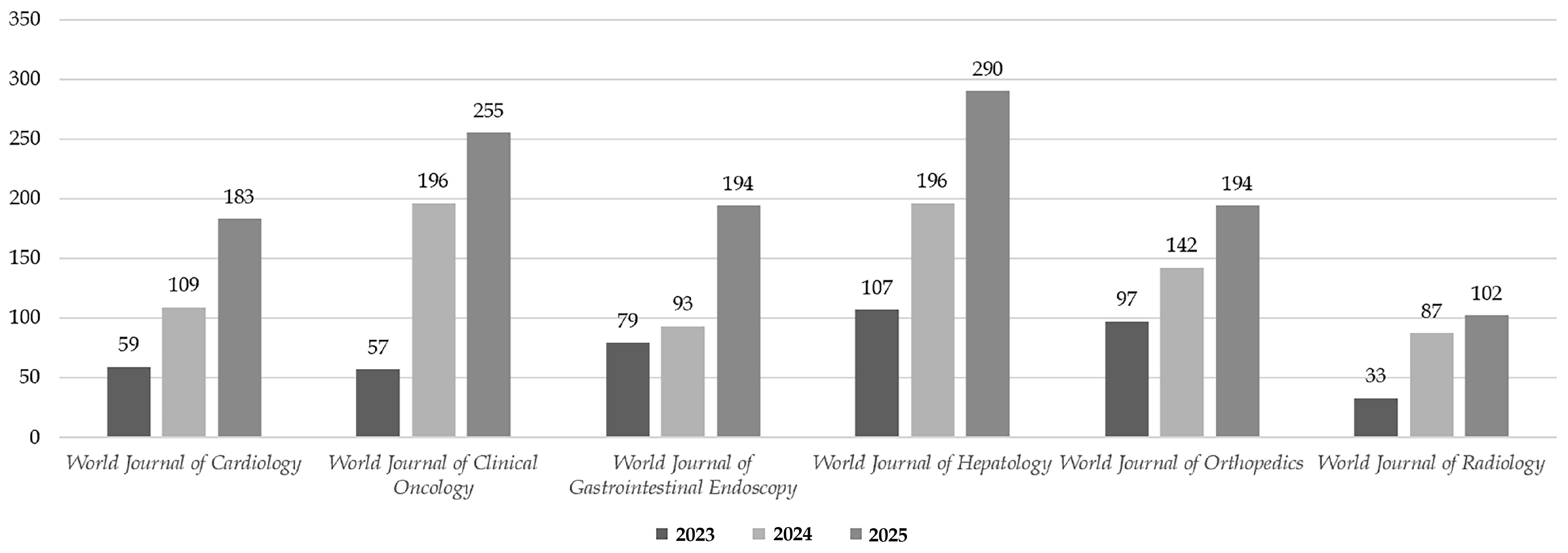
Figure 7 Manuscripts reaching a second decision for six ESCI-indexed BPG journals in 2023-2025.
6.3.2 Performance of the Six ESCI-Indexed Journals
WJH and WJCO showed significant growth, reaching 290 and 255 articles in 2025, respectively, approaching the scale of SCIE-indexed journals. WJC grew from 59 to 183 articles, an increase of 210%, representing the fastest growth rate among the ESCI-indexed journals. WJR had the lowest baseline but still increased from 33 to 102 articles over three years (growth of 209%), indicating a rapid start-up phase. WJGE grew from 93 articles in 2024 to 194 in 2025, a 108.6% increase. WJO maintained steady growth, rising from 97 articles in 2023 to 194 in 2025.
Overall, the ESCI-indexed journals with the largest growth magnitudes were WJC, WJR, and WJGE, with WJC showing the fastest growth. The generally high growth rates across ESCI-indexed journals may be attributed to their lower starting points and greater development potential as they strive for eventual SCIE inclusion.
6.4 Analysis and Outlook for Manuscripts Reaching a Second Decision
From 2023 to 2025, the number of manuscripts reaching a second decision showed an overall upward trend for both SCIE- and ESCI-indexed journals. SCIE-indexed journals achieved steady growth from a high baseline, while ESCI-indexed journals adopted a "fast-follower" strategy of high growth rates. The substantial growth rates across most journals indicate that they are in a phase of rapid expansion, possibly reflecting a trend among open-access journals to increase publication volume to enhance influence. The total volume for SCIE-indexed journals far exceeded that of ESCI-indexed journals and grew rapidly, with the number of manuscripts reaching a second decision approaching 3000 in 2025. Although the total volume for ESCI-indexed journals is smaller, their growth rate is remarkable, with a three-year increase of 182%, indicating rapid expansion. The journals with the highest growth rates are not necessarily those with the largest publication volumes. WJP ranked first with a growth rate of 272%. Among the top ten journals by growth rate, six are ESCI-indexed. This strongly demonstrates that ESCI-indexed journals as a group are in a faster developmental and expansion phase, actively increasing their scale to pursue SCIE database inclusion. WJG, as the journal with the largest publication volume, had the lowest growth rate (52%), suggesting that it has entered a relatively mature and stable phase where focus may shift from scaling volume to enhancing quality.
Rapid increases in publication volume must be accompanied by rigorous peer review; otherwise, they risk diluting a journal’s academic reputation and future impact factor. Subsequent changes in impact factors should be monitored to guard against the risk of "salami-slicing" or low-quality output. For the Editorial Office, ESCI-indexed journals now account for nearly half of the total publication volume. The next strategic focus should shift from "increasing quantity" to "boosting citations"–for example, through special issue invitations and curated content on hot topics–to quickly improve the JCR performance of ESCI-indexed journals and build momentum for future SCIE promotion.
6.5 Language Editing Services
To ensure the language quality of manuscripts submitted by non-native English speakers, BPG has established a detailed language policy (Language Editing for Manuscripts Submitted by Non-Native Speakers of English; see: https://www.wjgnet.com/bpg/gerinfo/240). This policy requires non-native English-speaking authors to submit a "language certificate" at the time of submission. Additionally, Peer Reviewers evaluate the quality of language expression during manuscript review, and their comments provide important reference points for the Editorial Office in assessing language quality. At the final review stage, the Editorial Office Director re-examines the language quality of manuscripts. If the language is deemed substandard, the Editorial Office Director arranges for professional language editing and polishing.
From January 1 to December 31, 2025, four language editors polished a total of 1005 manuscripts. All associated language editing costs were covered by BPG. In 2025, BPG paid these four language editors a total of USD 68890.9 in service fees.
7 Summary of Articles Produced and Published by the Production Department
BPG currently publishes 46 English-language journals and 1 Chinese-language journal. In 2025, the Production Department produced and published 5062 articles, comprising 4942 English-language manuscripts and 120 Chinese-language manuscripts. Compared with 2021-2024, the publication volume shows a steady growth trend (Figure 8).
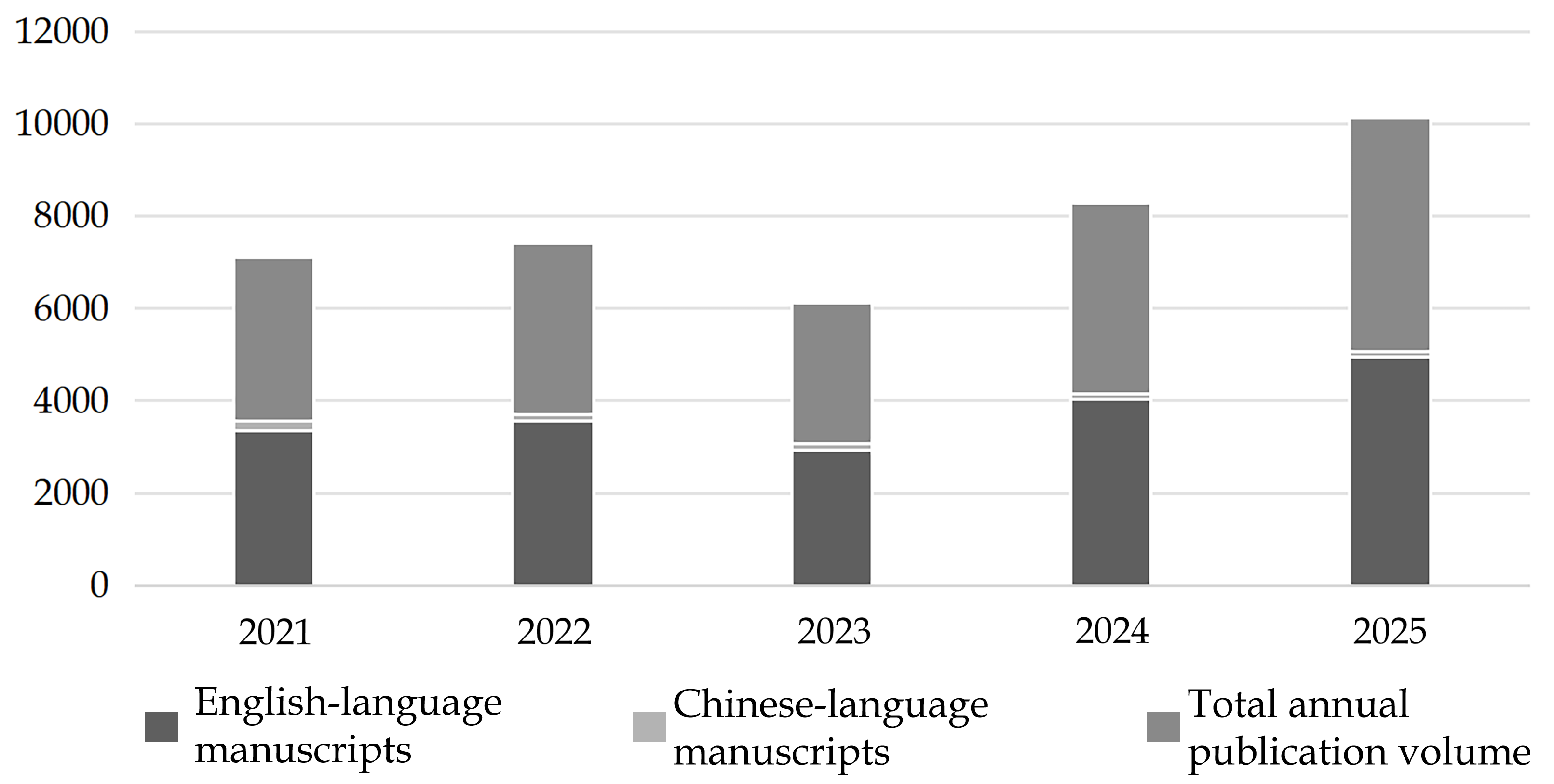
Figure 8 Number of articles published across 47 BPG journals in 2021-2025.
To better understand the publication performance of individual journals in 2025, the following analysis compares changes between 2024 and 2025 from the perspectives of manuscript source, journal indexing, and publication volume. Details are outlined below:
7.1 Comparison by Manuscript Source
Among the English-language articles published in 2025, unsolicited manuscripts accounted for 2662 articles (53.86%), an increase of 319 from 2024, representing a growth rate of 13.63%. Invited manuscripts totaled 2280 articles (46.14%), an increase of 599 from 2024, corresponding to a growth rate of 35.63% (Table 3).
Table 3 Number of English-language articles published by BPG in 2024 and 2025, by manuscript source
|
| 2024 |
| 2025 |
| Growth in manuscript output (2024 vs 2025) |
|
| Manuscript count | % of Total manuscripts | Manuscript count | % of Total manuscripts | Growth in count | Growth rate | |
| Unsolicited manuscripts | 2343 | 58.23% | 2662 | 53.86% | 319 | 13.62% |
| Invited manuscripts | 1681 | 41.77% | 2280 | 46.14% | 599 | 35.63% |
7.2 Comparison of Published Articles Across Database Indexes
Among the articles published in 2025, the distribution by database indexing is as follows: (1) The 6 SCIE-indexed journals published 2544 articles, accounting for 50.26% of the total manuscript output, thereby serving as the core pillar with over half of all publications. Compared with 2024, this represents an increase of 632 articles, a growth rate of 33.05%; (2) the 6 ESCI-indexed journals published 1165 articles, making up 23.01% of the total output. This marks an increase of 427 articles from 2024, corresponding to a substantial growth rate of 57.86%, making this group the fastest-growing category and reflecting a notable rise in both volume and share; (3) PubMed-indexed journals published 1171 articles, accounting for 23.13% of the total. Compared with 2024, this represents a decrease of 153 articles (-11.56%), indicating a decline in both volume and overall proportion (Table 4).
Table 4 Number of articles published by BPG in 2024 and 2025, by database index
|
| 2024 |
| 2025 |
| Growth in manuscript output (2024 vs 2025) |
|
| Manuscript count | % of Total manuscripts | Manuscript count | % of Total manuscripts | Growth in count | Growth rate | |
| SCIE | 1912 | 46.14% | 2544 | 50.26% | 632 | 33.05% |
| ESCI | 738 | 17.81% | 1165 | 23.01% | 427 | 57.86% |
| PubMed | 1324 | 31.95% | 1171 | 23.13% | -153 | -11.56% |
| Other journals (including the Chinese-language journal) | 170 | 4.10% | 182 | 3.60% | 12 | 7.06% |
7.3 Analysis of Publication Volume for Prominent SCIE- and ESCI-Indexed Journals
The publication volumes of SCIE-, ESCI-, and PubMed-indexed journals in 2024 and 2025 are as follows: (1) SCIE-Indexed Journals (6 journals in 2025): Compared with 2024, all six journals showed robust growth, with increases ranging from 16.92% to 97.09%. The most notable growth was seen in the WJP, whose publication count rose from 206 in 2024 to 406 in 2025, an increase of 97.09%; (2) ESCI-Indexed Journals (6 journals in 2025): Compared with 2024, these journals demonstrated clear growth, with increases ranging from 15.12% to 105.75%. WJGE showed the highest increase (105.75%), rising from 87 articles in 2024 to 179 in 2025. WJCO and WJH saw similar growth rates of 72.33% and 72.29%, respectively, both achieving substantial progress. Only WJR and WJO recorded relatively moderate growth, in the range of 15.12%-16.43%; and (3) PubMed-Indexed Journals (11 journals in 2025): Compared with 2024, growth performance varied but showed an overall significant upward trend.
8 Summary of the New Technology Development Department in 2025
During 2025, the New Technology Development Department carried out a series of system optimizations and feature expansions, including: (1) Developing the peer-review “Question” function and Peer-Reviewer star-rating statistics, as well as optimizing and expanding functions related to review-fee management, statistics, payment, and notifications; (2) Adjusting system service configurations, deploying standalone interface programs, and optimizing the performance of the BPG website and the F6Publishing system; (3) Optimizing and developing new features for the F6Publishing system’s editorial workload pricing, the BPG payroll management system, annual salary statistics, and salary calculation functions; (4) Optimizing and refining manuscript-handling workflows in the F6Publishing system; (5) Developing, testing, and deploying integrations with artificial intelligence platforms; (6) Creating the domain storage.wjgnet.com, mapping it to BPG’s cloud storage, and configuring security certificates; (7) Implementing Elastic Search to comprehensively optimize the article-search function on BPG platforms; (8) Developing a labor-contract management platform for BPG staff; (9) Developing the “Ordinary Register” function in the RCA platform; (10) Optimizing file-download and log-recording functions in the RCA platform to reduce server costs; (11) Enhancing data acquisition, cleaning, import, and storage functions in the RCA platform; (12) Developing and deploying system-protection and bot-detection services for RCA and the BPG website; (13) Optimizing article-related functions on BPG website and RCA, including export-citation tools, sharing features, table-zoom functions, and sticky top-toolbar development; (14) Optimizing email data in the F6Publishing system and RCA, and developing scheduled automatic-cleanup functions; and (15) Optimizing cloud-service costs. Based on Elastic Search, we developed and launched reviewer-search and high-impact-scientist-paper-search functions in the F6Publishing system, along with data-import features to replace the current Azure AI Search service.
9 Policy Updates at BPG in 2025
9.1 Updates to Three Key Documents
In 2025, we updated three key documents: Guidelines for Manuscript Review by Registered Editorial Board Members and Peer Reviewers, Guidelines for Manuscript Decision Process, and Publication Ethics Policy.
9.2 Adjustment of Publication Model
To enhance publishing efficiency and accelerate workflows, starting in 2025, all 46 English-language journals published by BPG transitioned from “consecutive page numbering” to “article numbers” publication.
9.3 Editorial Board Members, Peer Reviewers, and Scholars
Between January 1 and December 30, 2025, the “Find a Contributing Scholar” platform officially included 4492 scholars from 113 countries across multiple disciplines, comprising: (1) 2300 Editorial Board Members; (2) 2087 Peer Reviewers; and (3) 103 Scholars. The “Find a Contributing Scholar” platform is available at: https://www.referencecitationanalysis.com/searchscholar.
10 Readership and Downloads of BPG Journals
Between January 1 and December 30, 2025, BPG’s 46 English-language journals demonstrated broad academic influence globally. Readers from over 200 countries/regions generated a total of 43673328 visits and 26341714 downloads, reflecting high engagement and practical value. The six SCIE-indexed journals served as the main contributors, accounting for 21327481 visits (48.83%) and 13641947 downloads (51.79%). For example, WJG alone received 13418313 visits and 8165193 downloads.
10.1 Reader Visits by Country
The top five countries by total visits were: United States (16157153), China (6635312), India (846934), United Kingdom (835963), and Ireland (717081).
10.2 Reader Downloads by Country
The top five countries by total downloads were: United States (12311078), China (2587591), Germany (1947880), Brazil (1554697), and Singapore (1347610).
In summary, the visit and download data reflect the strong academic influence of BPG journals in regions such as North America, Asia, and Europe.
11 Post-Publication Article Quality Tracking
11.1 Article Quality Tracking-Peer-Review
After the formal publication of each article, the Editorial Office invites Editorial Board Members/Peer Reviewers to evaluate the scientific quality of newly published content. In 2025, the 46 English-language journals received a total of 729 post-publication quality assessment reports from Editorial Board Members.
11.2 Author Reviews
To continually improve editorial and publishing quality, BPG journals invite authors to evaluate various stages of the process—including manuscript submission, peer review, revision, language editing, article-processing charges, and electronic/online publishing—after each article is published. In 2025, the 46 English-language journals received 4383 pieces of author feedback.
11.3 Reader Comments
For each issue published across the 46 English-language journals, the Editorial Office sends targeted invitations to relevant scholars, inviting them to comment on articles of interest as readers and submit their comments online. Scholars may also choose to submit a formal Letter to the Editor, which is exempt from article-processing charges. In 2025, a total of 2042302 invitation emails were sent, resulting in 249 reader comments received.
12 Work Quality Evaluation for BPG Staff
Since September 2025, to ensure the quality of manuscript handling across all editorial staff, the F6Publishing system has enabled online tracking of technical assessments conducted by the Editorial Office on finalized manuscripts and by the Production Department on accepted manuscripts. During monthly workload accounting, reports titled “Technical Evaluation of Scientific Editors’ Work by the Editorial and Production Departments” and “Production Department’s Technical Evaluation of Production Editors’ Work” can be generated and downloaded via the F6Publishing system. These reports detail specific issues identified in manuscripts handled by science editors and production editors, along with their respective error rates. Editors are then assigned a work quality rating based on their error rate. Following each monthly accounting cycle, the Deputy General Manager announces the quality ratings for both science editors and production editors. Error rate is calculated as (Number of manuscripts with issues)/(Total manuscripts processed). Quality rating criteria are: Good, 0-20% error rate; Fair, 21-40%; and Poor, 41-100%. Each employee’s cumulative quality rating during their contract term serves as a key factor in the company’s decision regarding contract renewal.
12.1 Issues Identified During Second Decision Process
During the second decision process, common issues attributed to science editors included: Improper handling of author-submitted files; Discrepancies between the order of authors in the institution list and the author list; Spelling errors; Formatting inconsistencies such as missing capitalization after colons or absence of spaces between words; incomplete citation of references within the text; Inconsistent capitalization of text in figures; and Omission of full-term explanations for abbreviations in figure captions.
The Editorial Office notified the relevant science editors of these specific issues via the “Editorial Comments” function in F6Publishing. Upon receiving such notifications, science editors were required to verify and correct the issues, and then respond within the system.
Recent data showed that in September 2025, among 15 science editors, 13 (86.67%) received a “Poor” rating, while only 2 were rated “Good”. By October 2025, none of the 15 science editors received a “Poor” rating, and all achieved a “Good” rating. Among them, 14 had an error rate of 0%, and 1 had an error rate of 1.38%—still within the “Good” range. In November 2025, all 15 science editors maintained a “Good” rating. Six had a 0% error rate, and the highest error rate was 5.26%, which still qualified as “Good.”
12.2 Issues Identified by the Production Department
During the final pre-publication review by the Production Department, issues were mainly related to production and editorial aspects. Production Editors commonly encountered problems such as: Incorrect character display in PDF-exported tables; Missing hyperlinks in references; Invalid or broken links to supplementary materials; Large blank areas in pages; Incorrect font sizes in figures; Omitted content in footnotes; and Non-compliant spacing between axis titles and values in graphs. Science editors were typically responsible for editorial issues such as formatting inconsistencies (e.g., missing capitalization after colons and missing spaces between units and numbers); Missing annotations for superscript letters in tables; Incorrect unit labels; Abbreviations introduced without full terms at first use; Non-standard wording in tables; and Discrepancies between author initials in the Contributed By section and the References section.
The Production Department notified the relevant production editors and science editors of these issues via the “Editorial Comments” function in F6Publishing. Upon notification, editors were required to verify, correct, and reply within the system.
Recent data showed that in September 2025, among 10 production editors, 8 (80%) received a “Poor” rating, and 2 were rated “Fair.” By October 2025, among 11 production editors, none received a “Poor” rating; all were rated “Good.” Eight had an error rate of 0%, and the highest error rate was 8.33%—still within the “Good” range. In November 2025, all 11 production editors continued to receive “Good” ratings, with no “Poor” ratings. Six had a 0% error rate, and the highest error rate was 11.11%, which still fell within the “Good” category.
In summary, through rigorous departmental management and systematic follow-up, the work quality of the editorial team has shown significant improvement since October 2025.
13 Overview of Journals Under ESCI Application
To further expand its indexing coverage, BPG submitted applications in June 2025 for the inclusion of seven journals in the ESCI. The journals include WJCP, World Journal of Critical Care Medicine (WJCCM), WJEM, World Journal of Methodology (WJM), WJN, World Journal of Transplantation (WJT), and World Journal of Virology (WJV).
To improve the likelihood of acceptance, the Editorial Office has undertaken several strategic initiatives: (1) Proactively soliciting high-quality manuscripts to enhance academic standards and ensure stable publication output; (2) Actively inviting international scholars to join the Editorial Boards and serve as Peer Reviewers, thereby expanding the reviewer pool and strengthening the journals’ global visibility; and (3) Systematically refining journal websites and publicly available information in alignment with Clarivate’s 28 evaluation criteria (24 quality criteria and 4 impact criteria).
As of December 30, 2025, the seven journals have officially appointed 154 Editorial Board Members and 312 Peer Reviewers. Furthermore, since the adjustment of the publication model in 2023, each journal has shown an increase in published articles to varying degrees (Table 5). Compared with 2023, the most substantial growth among the seven journals in 2025 was seen in WJN, with an increase of 377.78%. WJCP recorded an increase of 277.42%, WJCCM 248%, and WJEM 376.47%. WJM, WJT, and WJV showed increases of 110.64%, 241.67%, and 111.54%, respectively. This steady expansion in publication volume provides a solid foundation for meeting ESCI’s quantitative requirements and enhancing the academic impact of these journals.
Table 5 Number of articles published by the seven journals under ESCI application in 2023-2025
| Journal | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
| World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics | 31 | 54 | 117 |
| World Journal of Critical Care Medicine | 25 | 49 | 87 |
| World Journal of Experimental Medicine | 17 | 53 | 81 |
| World Journal of Methodology | 47 | 59 | 99 |
| World Journal of Nephrology | 18 | 29 | 86 |
| World Journal of Transplantation | 36 | 66 | 123 |
| World Journal of Virology | 26 | 51 | 55 |
| Total | 200 | 361 | 648 |
14 Summary
In 2025, BPG made significant progress in the scale, quality, and operational efficiency of its academic publishing. Through the RCA platform, 1038 scholars were successfully recruited as Editorial Board Members or Peer Reviewers, and the "Find a Contributing Scholar" platform was established with a total of 4492 scholars, forming a robust academic network. Suspected cases of academic misconduct in manuscripts were identified and rejected during both the technical pre-screening and editorial stages, ensuring publication quality. Process improvements further shortened the peer-review cycle, significantly accelerating the overall publishing timeline. The proportion of invited manuscripts within the total manuscript structure increased markedly to 47.5%, reflecting the Editorial Office’s proactive approach to content planning. A total of 5062 articles were produced and published throughout the year, representing a 22.2% increase over 2024 and maintaining steady growth over the past five years. Overall, submissions, finalized manuscripts, and publications across all journals showed an upward trend. While the six SCIE-indexed journals maintained stable publication output, the six ESCI-indexed journals achieved a growth rate of 57.86% in publications, far exceeding other journal categories and laying a solid foundation for future SCIE inclusion.
15 Acknowledgments
Throughout 2025, BPG has achieved significant milestones in editing, publishing, and new technology development, laying a solid foundation for future progress. We hereby extend our sincerest gratitude and heartfelt New Year wishes to all who have supported the growth of BPG—including our Editorial Board Members, Peer Reviewers, dedicated staff, authors, and readers. As we look forward to a promising 2026, we are confident that under the guidance and leadership of our Founder and CEO, Mr. Lian-Sheng Ma, BPG will continue its steady development, strive for further excellence, and make even greater contributions to advancing academic prosperity and knowledge dissemination in clinical, basic, and translational medicine.

