©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Meta-Anal. Sep 18, 2025; 13(3): 107588
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v13.i3.107588
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v13.i3.107588
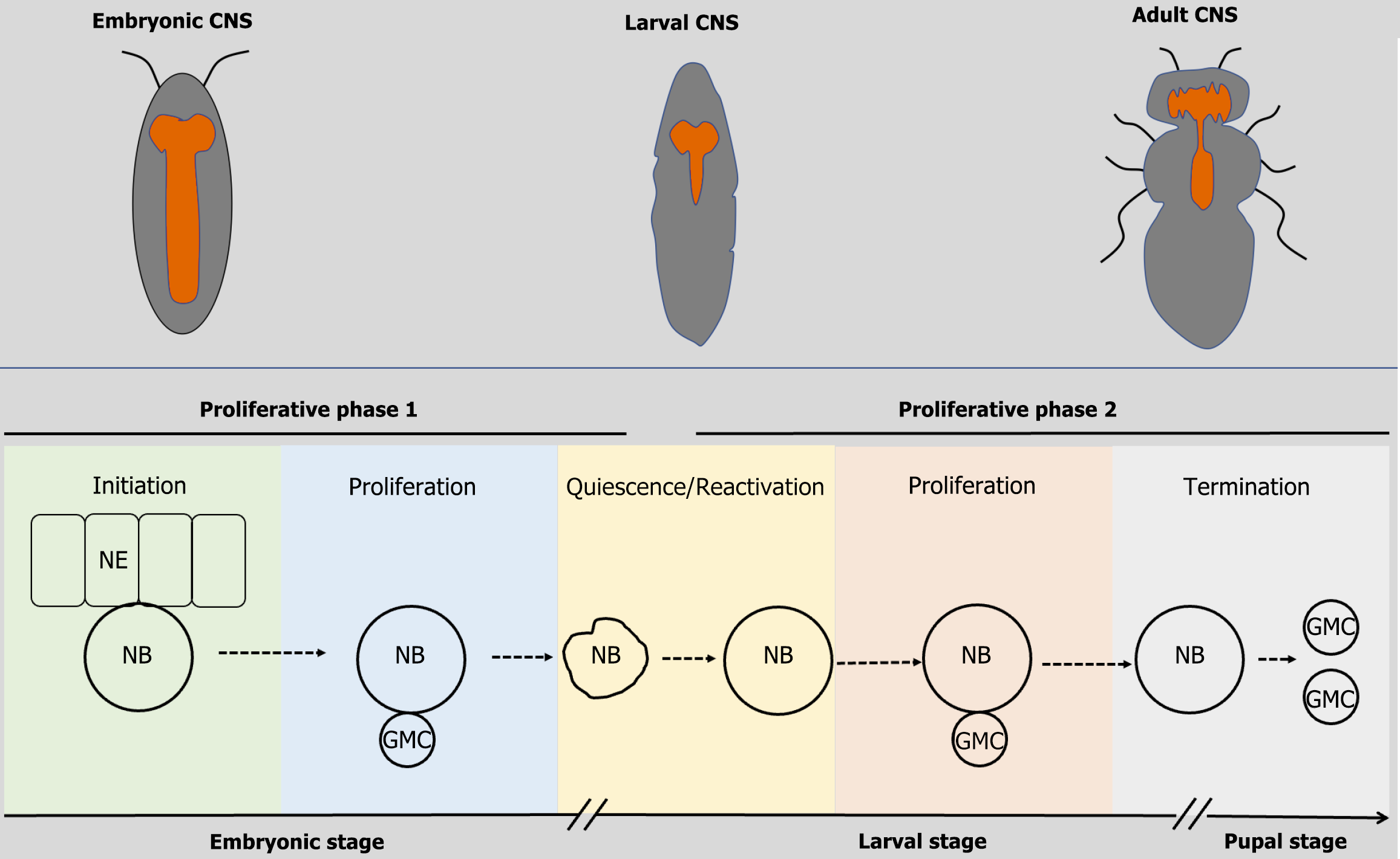
Figure 1 Developmental timeline of the Drosophila central nervous system and neural stem cell activity.
The Drosophila central nervous system (CNS) arises from neural stem cells (NSCs) across developmental stages (embryonic, larval, and adult). NSC development progresses through five phases: Initiation, proliferation, quiescence/reactivation, secondary proliferation and termination. During embryogenesis, CNS NSCs delaminate from the neuroepithelium and undergo asymmetric divisions. Quiescent NSCs (smaller in size) reactivate during the larval stage, leading to glial niche remodeling. Terminating NSCs shift to symmetric divisions. GMC: Ganglion mother cell; NB: Neuroblast.
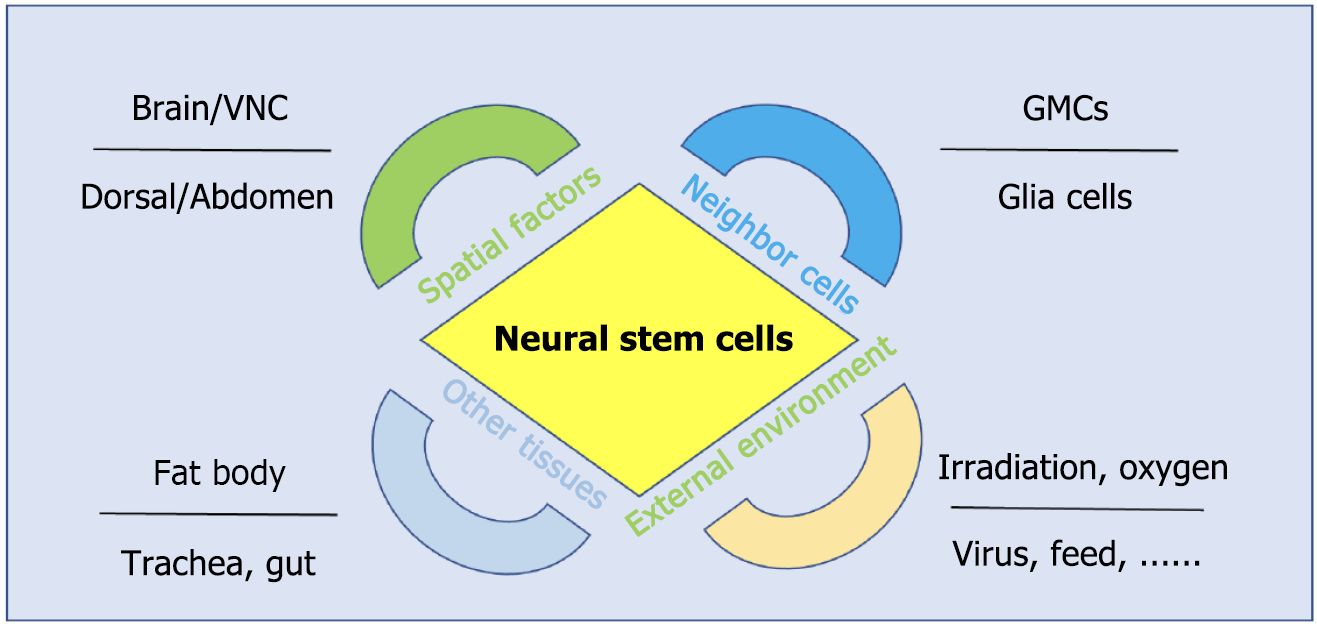
Figure 2 Ambient cues regulating neural stem cells in Drosophila.
Four major extrinsic regulatory categories influence neural stem cell development: Spatial patterning, niche interactions, intertissue signaling, and external environmental inputs. GMCs: Ganglion mother cells; VNC: Ventral nerve cord.
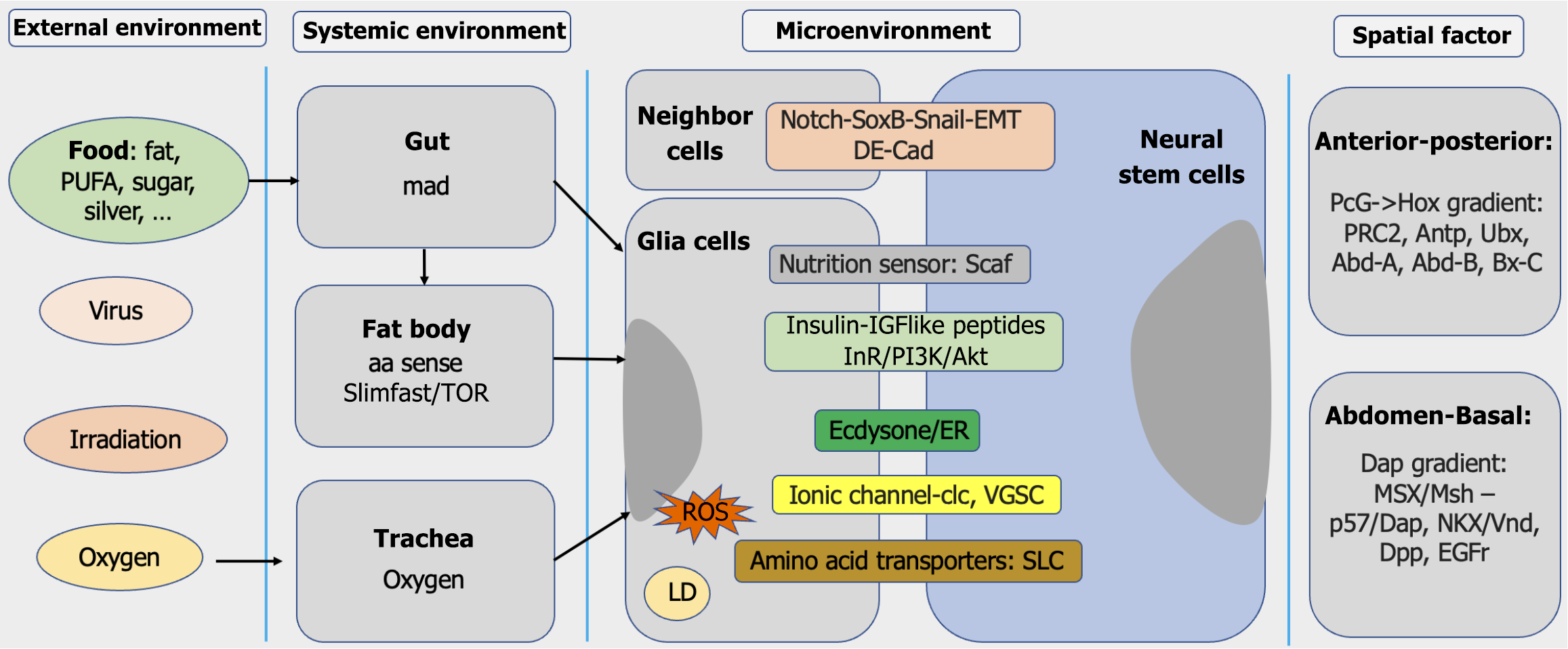
Figure 3 Ambient factors regulating neural stem cells in Drosophila.
Key extrinsic regulators include external environment (e.g., diet, virus infections, irradiation and oxygen tension), systemic environment (e.g., gut, fat body, trachea), microenvironment (e.g., neighboring cells, glia and lipid droplets), and spatial factors (e.g., anteroposterior and abdomen-basal positioning). aa: Amino acid; Abd: Abdominal; Antp: Antennapedia; CLC: Chloride channel; Dap: Dapaco; DE-Cad: Drosophila E-cadherin; Dpp: Decapentaplegic; EGFr: Epidermal growth factor receptor; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ER: Ecdysone receptor; Hox: Homeobox gene; LD: Lipid droplet; Msh: Muscle segment homeobox; PcG: Polycomb group; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PRC2: Polycomb-repressive complex 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SLC: Solute carrier transporter; TOR: Target of rapamycin; Ubx: Ubiquitination regulatory x; VGSC: Voltage-gated sodium channel; Vnd: Ventral nervous system defective.
- Citation: Ren XM, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Zhang LJ, Yu Y, Chen QJ, An HP. Ambient effects on neural stem cells: Insights from Drosophila. World J Meta-Anal 2025; 13(3): 107588
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2308-3840/full/v13/i3/107588.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.13105/wjma.v13.i3.107588