Published online Jan 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.436
Peer-review started: August 25, 2020
First decision: October 27, 2020
Revised: November 7, 2020
Accepted: November 21, 2020
Article in press: November 21, 2020
Published online: January 16, 2021
Processing time: 135 Days and 17.7 Hours
Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is a rare autosomal recessive inherited organic acidemia caused by a genetic deficiency of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD). Its morbidity is low, but mortality is high. There is no effective cure for this disease. Early identification of IVA using clinical features can significantly slow disease progression and reduce mortality. Here we report a Chinese neonate with two mutations of IVD and share valuable information on this disease.
A 12-day-old male neonate with “poor response for 1 d and repeated convulsions accompanied by high muscle tension for 6 h” was hospitalized. The patient was the first child of nonconsanguineous ethnic Chinese parents. He was delivered by cesarean section due to breech position at 39 + 1 wk of gestation with a birth weight of 3.27 kg. Initially, he suffered from dyspnea and rhinobyon, and at 10 d after birth the patient suddenly developed poor feeding, low response, lethargy and seizures. Organic acid analysis of blood and urine by tandem mass spectrometry and gas chromatography mass spectrometry showed extremely high concentrations of isovaleryl glycine. The patient had an acute episode of IVA causing severe metabolic stress and eventually died.
A new case of an IVA patient carrying c.1193G>A (p.Arg398Gln) and c.1208A>G (p.Try403Cys) mutations is reported in China.
Core Tip: Isovaleric acidemia is a rare autosomal recessive inherited organic acidemia caused by a genetic deficiency of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD), with a high mortality. We describe a 12-day-old male neonate diagnosed with IVD after tandem mass spectrometry and gas chromatography mass spectrometry analysis. Organic acid analysis of blood and urine showed extremely high concentrations of isovaleryl glycine. DNA sequencing of the IVD gene in the family revealed c.1193G>A mutation inherited from his mother and c.1208A>G mutation inherited from his father. Furthermore, the clinical characteristics and prognosis were discussed in combination with reported cases over the past 14 years.
- Citation: Wu F, Fan SJ, Zhou XH. Neonatal isovaleric acidemia in China: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(2): 436-444
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i2/436.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.436
Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is a rare inherited organic acidemia caused by a genetic deficiency of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD), an enzyme in the catabolic pathway of leucine, which catalyzes the conversion of isovaleryl-CoA to 3-methyl-crotonyl-CoA[1]. This deficiency leads to abnormally high concentrations of isovaleric acid and its derivatives in cells, blood and urine, which results in severe, life-threatening metabolic encephalopathy.
The clinical presentation of IVA appears to be highly variable ranging from severely affected to asymptomatic patients. Clinical features include poor feeding, vomiting, acidosis, ketosis, progressive alteration of consciousness, seizures and finally deep coma and death without appropriate therapy. The characteristic odor of “sweaty feet” caused by isovaleric acid is often noted during metabolic crisis[2]. The clinical diagnosis of IVA can be confirmed by mutation of the IVD gene. The IVD gene is encoded by the nuclear gene, which is located on chromosome 15q14-15, consisting of 12 exons that span 15 kb of genomic DNA[3]. To date, more than 70 heterogeneous mutations in the IVD gene have been reported in patients with IVA.
Here we report a case of IVA in a Chinese neonate who was compound hetero-zygous for a novel 4-bp duplication together with a missense mutation known to be common in Chinese populations, which has been reported previously. Furthermore, the clinical characteristics and prognosis are discussed in combination with reported cases over the past 14 years.
A 12-day-old male neonate with “poor respond for 1 d and repeated convulsions accompanied by high muscle tension for 6 h” was hospitalized.
On the second day after birth, he was admitted to a local hospital due to dyspnea and rhinobyon and received anti-infection and other symptomatic treatment. The patient suddenly developed poor feeding (mixed feeding of 50-60 mL/time decreased to 20 mL/time at intervals of 3 h), low response, lethargy and seizures at 10 d after birth and was transferred to our hospital.
The patient had no history of past illness.
The patient was the first child of nonconsanguineous ethnic Chinese parents. He was delivered by cesarean section due to breech position at 39 + 1 wk of gestation with a birth weight of 3.27 kg and an Apgar score of 9-10-10. His father was 27 years old. His mother was 23 years old. Both were healthy, and his mother underwent an abortion two years ago in early pregnancy.
The patient’s weight was 2580 g, with a significant loss of 690 g since birth, poor response, no frowning and crying after more than 10 times of foot stimulation, characteristic disagreeable “sweaty feet” odor, yellow skin, flat and soft anterior fontanelle, no neck resistance and hypermyotonia of extremities. Both upper limbs were in a state of flexion, his hands were clenched, lower limbs were stiff, grasp reflex was weakened, and rooting reflex, sucking reflex and Moro reflex were not elicited.
Biochemical laboratory examinations indicated pancytopenia (hemoglobin 107 g/L, white blood cells 1.72 × 109/L, platelets 11 × 109/L), increased calcitonin levels (3.180 ng/mL), metabolic acidosis (pH 7.320, bicarbonate 16.50 mmol/L, base excess -9.60 mmol/L), persistent hypocalcemia (1.06-1.24 mmol/L), hyperammonemia (110-543 μmol/L) and positive ketonuria and urinary protein. Cerebrospinal fluid was yellow and limpid, the Pandy test was positive, white blood cells were 3 × 106/L, glucose was 6.55 mmol/L, and protein was 1.80 g/L. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and urine gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS) found isovaleryl glycine.
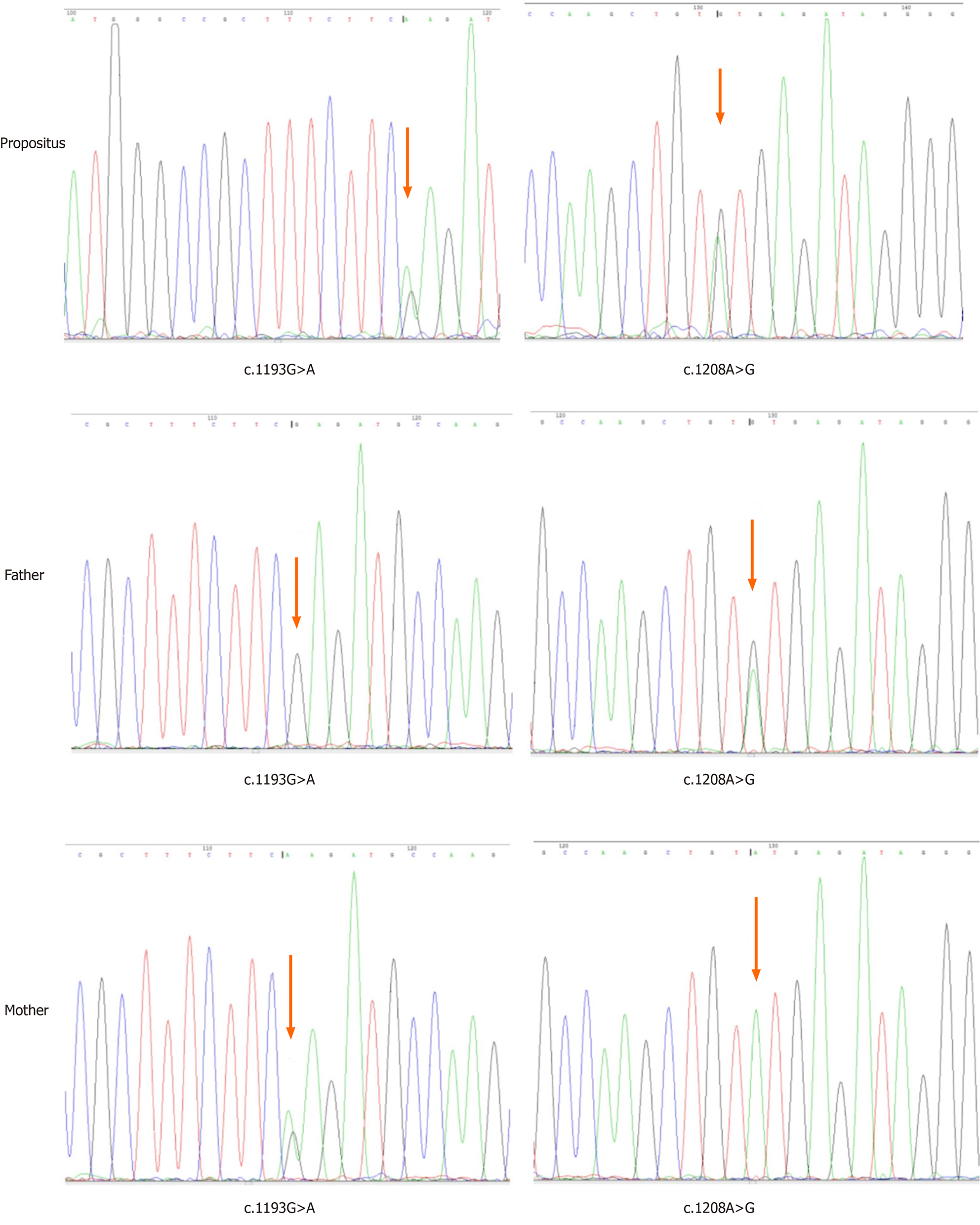
Genetic testing of the IVD gene (NM_002225) was performed using genomic DNA isolated from peripheral leukocytes. The patient had compound heterozygous mutations: c.1193G>A (p.Arg398Gln) and c.1208A>G (p.Try403Cys). The p.Arg398Gln variant was inherited from his mother, whereas p.Try403Cys was inherited from his father (Figure 1). Both variants were missense mutations in accordance with an autosomal recessive inherited disease, which has been previously reported[4,5].
Cerebral ultrasound showed that the cerebral parenchyma and white matter of the periventricular were damaged with intraventricular hemorrhage (grade I-II), and encephaledema.
He was diagnosed with IVA 7 d later.
The patient was treated with anti-infection, granulocyte stimulating factor, human immunoglobulin to enhance immunity, correcting electrolyte disorders and fasting and parenteral nutrition to supply calories. He also received several transfusions of blood products.
The patient developed a persistent poor response and internal environment disturbance. His parents gave up treatment after 4 d, and he was discharged from hospital. He subsequently died.
IVA is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a defect in IVD, a mitochondrial matrix enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of isovaleryl-CoA to 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA in the leucine degradation pathway[1]. It was first reported by Tanaka et al[6] and diagnosed by GC/MS and urine organic acid analysis technology in 1966. Neonatal screening studies of IVA have been conducted in many countries and regions, and the incidence of IVA in Germany is 1 in 62500[7] and in the United States is 1 in 250000[8]. The incidence in China is about 1 in 190000 diagnosed by neonatal MS/MS[9]. We performed a literature review by searching the Wanfang database, CNKI and the VIP database using the terms “isovaleric acidemia,” “isovaleric aciduria,” “organic acidemia” and “organic aciduria” in order to obtain comprehensive information on the clinical course of IVA from a larger number of patients. The clinical features are summarized in Table 1[10-29].
| Patient No. | Ref. | Sex | Age of symptom onset | Age at diagnosis | Clinical presentation | Urine isovaleryl-glycine | IVD gene mutations | Prognosis |
| 1 | Zhou et al[10] | Male | 4 d | After death | Poor feeding, sweaty feet odor, thrombocytopenia, acidosis, coma, hypocalcemia | Increased | - | Died at 13 d after birth |
| 2 | Qiu et al[11] | Male | 3 d | 31 mo | Vomiting, acidosis, hyperglycemia, hypocalcemia | Increased | c.149G>A, c.466G>C | Intelligence and development retardation |
| 3 | Ren et al[12] | Female | 3 d | After death | Poor feeding, low response, acidosis, hypoglycemia, coma, shock | Increased | - | Died at 7 d after birth |
| 4 | Wang et al[13] | Male | 7 d | After death | Poor feeding, low response, acidosis, thrombocytopenia, anemia, lethargy | Increased | - | Died at 1 mo after birth |
| 5 | Wu et al[14] | Female | 7 d | 10 d | Rhinobyon, poor feeding, sweaty feet odor, coma, poor response, convulsion, hyperammonemia, thrombocytopenia | 25.73 | - | The patient showed normal growth and development after follow-up for 3 mo |
| 6 | Zhao et al[15] | Male | 6 d | After death | Poor response, lethargy, sweaty feet odor, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, shock | Increased | - | Died at 12 d after birth |
| 7 | Teng et al[16] | Male | 3 mo | 11 yr | Poor feeding, low response, lethargy, sweaty feet odor | 1192.54 | - | Delayed development after 2.5 yr follow-up |
| 8 | Long et al[17] | Female | 68 d | 70 d | Poor response, sweaty feet odor, anemia, thrombocytopenia, lethargy | Increased | - | Died at 78 d after birth |
| 9 | Shang et al[18] | Female | 7 d | 11 d | Lethargy, rhinobyon, convulsion, hyperammonemia, hypocalcemia, thrombocytopenia, sweaty feet odor | Increased | - | After treatment for 7 d, the patient was better and was discharged, reviewed urine isovaleryl-glycine decreased to 25.12 |
| 10 | Shang et al[18] | Male (the older of twins) | 5 d | After death | Lethargy, sweaty feet odor, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, poor response, coma, shock, hyperammonemia | 25.13 | - | Died at 10 d after birth |
| 11 | Shang et al[18] | Male (the younger of twins) | 5 d | 10 d | Lethargy, sweaty feet odor, thrombocytopenia, poor response, hyperammonemia | 25.73 | - | Leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and hyperammonemia after follow-up for 1 wk, reviewed urine isovaleryl-glycine was slightly elevated |
| 12 | Zhu et al[19] | Male | 6 d | After death | Poor feeding, poor response, lethargy, acidosis, hypocalcemia, urine ketone | Increased | - | Died at 12 d after birth |
| 13 | Xu et al[20] | Male | 5 d | 14 d | Poor response, poor feeding, sweaty feet odor, thrombocytopenia | 1989.67 | - | Better after treatment, sweaty feet odor disappeared |
| 14 | Xu et al[21] | Male | 4 d | After death | Poor feeding, poor response, sweaty feet odor, thrombocytopenia, acidosis, hypocalcemia, ecchymosis | Increased | - | Died at 13 d after birth |
| 15 | Xu et al[21] | Male | 4 d | After death | Lethargy, poor feeding, sweaty feet odor, acidosis, hypoxemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia | Increased | - | Died at 13 d after birth |
| 16 | Bei et al[22] | Female | 4 d | 11 d | Poor response, poor feeding, dyspnea, sweaty feet odor, shock, acidosis, hyperammonemia | 1488.78 | c.39G>A, c.597C>G | Died at 12 d after birth |
| 17 | Fu et al[23] | Male | 7 d | 11 d | Lethargy, sweaty feet odor, poor response, poor feeding, hyperammonemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, urine ketones, urine protein | Increased | c.1016G>A | Died at 14 d after birth |
| 18 | Fu et al[23] | Male | 2 mo | 7 d | Hyperammonemia, sweaty feet odor | Increased | c.1016G>A | Due to timely detection and treatment, the patient’s growth and development were normal after follow-up of 2 yr |
| 19 | Li et al[24] | Female | 4 d | 20 mo | Vomiting, coma, thrombocytopenia, acidosis, hyperammonemia | 2535.76 | c.1193G>A, c.1208A>G | Normal development after follow-up of 3 yr |
| 20 | Li et al[24] | Male | 1 d | 25 d | Vomiting, poor feeding, hypothermia, coma, acidosis, hyperammonemia | 1537.94 | c.145C>T | Mild development retardation after follow-up of more than 3 yr |
| 21 | Li et al[24] | Female | 3 d | 4 yr | Vomiting, acidosis | 858.51 | c.611A>G, c.1183C>T | Normal development after follow-up of 10 yr |
| 22 | Li et al[24] | Male | 2 d | After death | Vomiting, poor feeding, coma, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hyperammonemia | 258.30 | c.158G>A, c.676-677insA | Died at 15 d after birth |
| 23 | Zhang et al[25] | Male | 6 d | After death | Tachypnea, hypothermia, leukopenia, acidosis, poor response, hypocalcemia, hyperammonemia, septicemia | Increased | - | Died at 11 d after birth |
| 24 | Wang et al[26] | Male | 1 d | 33 mo | Recurrent vomiting, acidosis, leukopenia, elevated urine ketones and urine acid, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, thrombocytopenia | 576.181 | - | Severe mental retardation |
| 25 | Tan et al[27] | Male | 1 d | 9 d | Cough, somnolent, delirious, pneumonia, sweaty feet odor, acidosis, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hyperglycemia | 2122.18 | c.1208A>G | Died at 16 d after birth |
| 26 | Mei et al[28] | Male | 5 d | 8 d | Poor response, sweaty feet odor, leukopenia, hypoglycemia, hyperammonemia, acidosis, hypocalcemia | Increased | c.1195G>C, c.466-3_466-2delinsGG | Died at 14 d after birth |
| 27 | Sun et al[29] | Male | 1 d | 5 d | Poor response, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, sweaty feet odor, hyperammonemia, urinary ketones and protein, hypermyotonia | 623.4 | c.158G>A, c.1195G>C | The patient’s growth and development were normal after follow-up of 1 yr |
| 28 | Sun et al[29] | Female | 20 d | 3 d | Hyperammonemia | 58.73 | c.214G>T | Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain showed abnormal signals at the right parietal lobe and left thalamus at 21 mo old, intelligence retardation after follow-up of 26 mo |
| 29 | Sun et al[29] | Female | 1 mo | 1 mo | No obvious abnormalities were found in routine blood work, biochemistry and blood ammonia | 41.32 | - | Normal development after follow-up of 6 mo |
As shown in Table 1, 29 cases of clinically diagnosed IVA published between 2007 and 2020 were identified and reviewed, specifically focusing on patient age at disease onset, mortality and neurocognitive outcome. The clinical features included neonatal onset (25 cases), acute episode (24 cases), sweaty feet odor (17 cases), pancytopenia (19 cases) and hyperammonemia (14 cases), and 15 deaths were reported. Through the literature review, we found that most cases occurred during the neonatal period, and the mortality rate was high. Thus, it is important for clinicians to be aware of this disease.
The clinical manifestations vary, and disease onset can range from the neonatal period to the adult period. The clinical presentation of IVA is classified into two types: classic acute neonatal episodes and chronic intermittent episodes[30]. The typical clinical manifestations are severe metabolic acidosis and encephalopathy, often accompanied by leukopenia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia due to bone marrow suppression and other abnormal blood systems in the neonatal period, and hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia, coma and death may occur if appropriate treatment is not initiated. Therefore, the fatality rate is very high[5]. These clinical manifestations often lack specificity, and the symptoms are similar to feeding intolerance and neonatal infection, which often cause diagnostic difficulties. Patients with the chronic intermittent form develop intermittent metabolic derangement during episodes of stress, such as infections and developmental delays. Due to the accumulation of isovaleric acid in the body, the patient’s body and urine will have an odor similar to sweaty feet, which is an important clue for clinical diagnosis. Our patient demonstrated classical IVA features: Pancytopenia, hypocalcemia, acidosis and hyperammonemia. The characteristic “sweaty feet odor” should enable this condition to be easily recognized clinically.
Plasma isovaleryl carnitine and urine isovaleryl glycine are IVA biomarkers, and the levels of these biomarkers can increase several hundred-fold during acute episodes. Since the implementation of expanded newborn screening by MS/MS in many countries, IVA can be diagnosed presymptomatically[31]. Molecular genetic analysis helps to further confirm the clinical diagnosis of IVA. To date, more than 70 heterogeneous mutations in the IVD gene have been reported in patients with IVA, including point mutations, frameshift mutations and slice-site mutations (http://www.hgmd.org/). Missense and splicing mutations are the most common, but a small number of frameshift mutations have been reported[3]. Recently, a novel mild and potentially asymptomatic form of IVA and its association with a common missense mutation, c.932C>T (p.A282V) was identified in two-thirds of patients[32]. The missense mutations, c.149G>A (p.R21H) and c.1199A>G (p.Y371C), are common in Han Chinese subjects, especially the latter[11,33,34]. In the present study, the patient had compound heterozygous mutations: c.1193G>A (p.Arg398Gln) and c.1208A>G (p.Try403Cys), and both were missense mutations in accordance with an autosomal recessive inherited disease, which have been previously reported[4,5].
Early diagnosis and treatment are necessary to prevent neonatal mortality and improve the neurologic and cognitive outcomes. Grünert et al[8] investigated 155 IVA patients and found that the survival rate was higher in the group diagnosed early (i.e. diagnosed in the first 5 wk) than in the group diagnosed later (33% and 3%, respectively), and the rate of normal cognitive outcome followed a similar pattern (85% vs 45%, respectively). These data emphasize that early diagnosis and treatment play a vital role in the outcome of IVA. Therefore, early diagnosis is crucial, and asymptomatic detection is possible with expanded neonatal screening. In newborns or older babies who present with multiple symptoms such as poor feeding, vomiting, drowsiness, coma, metabolic acidosis, ketosis, hyperammonemia, hypocalcemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and a decrease in whole blood cells at the same time, or other diseases of unknown causes, IVA should be considered. Relevant examinations should be carried out to establish a diagnosis as early as possible. We summarized characteristics of the IVA cases reported over a 14-year period using the Wanfang database, CNKI and the VIP database and found that neonatal morbidity was prevalent in the vast majority of cases. The patient’s clinical symptoms and laboratory examinations were typical in the acute type, and the chronic intermittent type was not easily identified at an early age. When certain clinical manifestations occur in children, the disease can be diagnosed by blood and urinary organic acid or acyl carnitine analysis. However, there are few reported gene mutations related to this disease in China, and there is also a lack of long-term follow-up study data on IVA children.
An early diagnosis leads to early treatment and subsequently results in normal development of the children. Mild protein restriction and glycine and carnitine are recommended to remove toxic metabolites, in addition to antibiotics and supportive care. If untreated, patients may die or show significant developmental delay. The use of glycine has been effective in the treatment of IVA, and it has been shown that glycine administration reduced the rise in serum isovaleric acid produced by a leucine load[35]. The measurement of disease-specific metabolites in the amniotic fluid and [14C] IVA incorporation in cultured amniocytes could help prenatal diagnosis[36]. It is also important for the mother to undergo detection of metabolites in amniotic fluid during future pregnancies for prenatal diagnosis of IVA.
The case of IVA reported herein showed that the mutations were not polymorphic. The frequency of occurrence in the population is extremely low. The clinical and genetic features of this patient help to further expand our knowledge of IVA. Moreover, most cases occur during the neonatal period, and the mortality rate is high. Thus, clinicians should be aware of this disease. Early diagnosis as well as the detection of genetic metabolic diseases may improve patient outcomes.
| 1. | Budd MA, Tanaka K, Holmes LB, Efron ML, Crawford JD, Isselbacher KJ. Isovaleric acidemia. Clinical features of a new genetic defect of leucine metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1967;277:321-327. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 94] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Sweetman L, Williams JD. Branched chain organic acidurias. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly W, Valle D. The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease, 8th ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2001: 2125-2164. |
| 3. | Parimoo B, Tanaka K. Structural organization of the human isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase gene. Genomics. 1993;15:582-590. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 4. | Al-Shamsi A, Hertecant JL, Al-Hamad S, Souid AK, Al-Jasmi F. Mutation Spectrum and Birth Prevalence of Inborn Errors of Metabolism among Emiratis: A study from Tawam Hospital Metabolic Center, United Arab Emirates. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2014;14:e42-e49. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Lin WD, Wang CH, Lee CC, Lai CC, Tsai Y, Tsai FJ. Genetic mutation profile of isovaleric acidemia patients in Taiwan. Mol Genet Metab. 2007;90:134-139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Tanaka K, Budd MA, Efron ML, Isselbacher KJ. Isovaleric acidemia: a new genetic defect of leucine metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1966;56:236-242. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 242] [Cited by in RCA: 226] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Schulze A, Lindner M, Kohlmüller D, Olgemöller K, Mayatepek E, Hoffmann GF. Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry: results, outcome, and implications. Pediatrics. 2003;111:1399-1406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 341] [Cited by in RCA: 349] [Article Influence: 15.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Grünert SC, Wendel U, Lindner M, Leichsenring M, Schwab KO, Vockley J, Lehnert W, Ensenauer R. Clinical and neurocognitive outcome in symptomatic isovaleric acidemia. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7:9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Zhou W, Li HZ, Wang CX, Gu MS. Clinical study of abnormal conditions of isovaleric acidemia in NICU neonate by tandem mass spectrometry. Zhongguo Yousheng Yu Yichuan Zazhi. 2018;26:82-84. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 10. | Tang JM. Neonatal isovaleric acidemia in a case. Zhonghua Erke Zazhi. 2007;45:720. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 11. | Qiu WJ, Gu XF, Ye J, Han LS, Bai HT, Wang X, Gao XL, Wang Y, Jin J, Zhang HW. Clinical and mutational study of a Chinese infant with isovaleric acidemia. Zhonghua Erke Zazhi. 2008;6:526-530. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 12. | Ren CJ, Li YM, Chen BC, Er EDGW, Han XM. Case report of a patient with isovaleric acidemia. Linchuang Erke Zazhi. 2009;27:1185. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 13. | Wang F, Ding XC. One case of isovaleric acidemia. Zhonghua Fuyou Linchuang Yixue Zazhi (Electron Ed). 2011;7:74. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 14. | Wu XL, Shang CL, Liu XH, Liu Y, Chen MQ. One case of neonatal isovaleric acidemia was reported. Zhonghua Xinsheng Erke Zazhi. 2011;26:48. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 15. | Zhao FP, Shi JY, Yi B. One case of neonatal isovaleric acidemia was reported. Zhongguo Yousheng Youyu Zazhi. 2011;17:359-360. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 16. | Teng AL, Zhang HY, Li JH, Ma RQ, Xu Q. One case of isovaleric acidemia was reported. J Clin Pediatr 2012; 30: 988,993. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 17. | H. One case of isovaleric acidemia. Youjiang Yixue Zazhi. 2012;40:452-453. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 18. | Shang Y, Yin LF, Liu XH, Wen PQ, Feng JX. Three cases of neonatal isovaleric acidemia were reported. Zhongguo Shiyong Erke Zazhi. 2012;27:399-400. |
| 19. | Zhu CL. Case discussion of neonatal isovaleric acidemia. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2012;35:76-78. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 20. | Xu XM, Huang P, Zhang GQ, Sun JH, Bei F. One case of neonatal isovaleric acidemia was reported. Gansu Yiyao Zazhi. 2013;32:239-240. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 21. | Xu RF, Wu ZM, Wang WK. Two cases of neonatal isovaleric acidemia and literature analysis. Guoji Erke Xue Zazhi. 2014;41:215-216. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 22. | Bei F, Jia J, Sun JH. Two isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase gene mutations in a newborn with isovaleric acidemia. Zhonghua Weichan Yixue Zazhi. 2014;17:632-635. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 23. | Fu X, Gao HJ, Wu TT, Zhang WD, Liao LH, Luo XP. Clinical and genetic analysis of two Chinese patients with neonatal isovaleric acidemia and review of literature. Zhonghua Shiyong Erke Linchuang Zazhi. 2014;29:599-604. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 24. | Li XY, Hua Y, Ding Y, Liu YP, Song JQ, Wang Q, Wu TF, Zhang Y, Hou XL, Li MQ, Qin YP, Yang YL. Analysis of 4 cases of typical isovaleric acidemia in neonates. Zhonghua Weichan Yixue Zazhi. 2015;18:188-194. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 25. | Zhang EQ, Xu XJ, Wang JY. A case of isovaleric acidemia during neonatal period. Zhonghua Weichan Yixue Zazhi. 2015;18:700-701. |
| 26. | Wang X, Wang ZH, Shang J, Li HB. Analysis of clinical characteristics of children with isovaleric acidaemia. Zhongguo Dangdai Yiyao Zazhi. 2016;23:101-103. |
| 27. | Tan JQ, Chen DY, Mo ZQ, Li ZT, Huang JW, Cai R, Yan TZ. Pancytopenia and metabolic decompensation in a neonate. Zhongguo Dangdai Erke Zazhi. 2016;18:1150-1153. |
| 28. | Mei SY, Bai N, Hu S, Liu N, Liu LN, Kong XD. Analysis of two cases of genetic variation in isovaleric acidemia and one case of prenatal diagnosis. Zhonghua Weichan Yixue Zazhi. 2018;21:31-35. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 29. | Sun M, Li YL, Zou H. Diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of 3 cases wih neonatal isovaleric acidemia. Fayu Yixue Dianzi Zazhi. 2020;8:77-80. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 30. | Tanaka K. Isovaleric acidemia: personal history, clinical survey and study of the molecular basis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;321:273-290. [PubMed] |
| 31. | Vockley J, Ensenauer R. Isovaleric acidemia: new aspects of genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2006;142C:95-103. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 175] [Cited by in RCA: 138] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Ensenauer R, Vockley J, Willard JM, Huey JC, Sass JO, Edland SD, Burton BK, Berry SA, Santer R, Grünert S, Koch HG, Marquardt I, Rinaldo P, Hahn S, Matern D. A common mutation is associated with a mild, potentially asymptomatic phenotype in patients with isovaleric acidemia diagnosed by newborn screening. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75:1136-1142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 127] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Lee HH, Lee RS, Lai CK, Yuen YP, Siu TS, Chan AY, Lam CW. A novel duplication at the putative DNA polymerase alpha arrest site and a founder mutation in Chinese in the IVD gene underlie isovaleric acidaemia. Hong Kong Med J. 2010;16:219-222. [PubMed] |
| 34. | Lee YW, Lee DH, Vockley J, Kim ND, Lee YK, Ki CS. Different spectrum of mutations of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD) gene in Korean patients with isovaleric acidemia. Mol Genet Metab. 2007;92:71-77. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Krieger I, Tanaka K. Therapeutic effects of glycine in isovaleric acidemia. Pediatr Res. 1976;10:25-29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Hine DG, Hack AM, Goodman SI, Tanaka K. Stable isotope dilution analysis of isovalerylglycine in amniotic fluid and urine and its application for the prenatal diagnosis of isovaleric acidemia. Pediatr Res. 1986;20:222-226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Slomiany BL S-Editor: Gao CC L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Xing YX