Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4279
Peer-review started: January 15, 2021
First decision: February 11, 2021
Revised: February 15, 2021
Accepted: April 20, 2021
Article in press: April 20, 2021
Published online: June 16, 2021
Processing time: 131 Days and 7.1 Hours
Capecitabine is used in combination with lapatinib as palliative treatment for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 - positive metastatic breast cancer. The most frequently reported adverse events attributed to capecitabine include diarrhea, hyperbilirubinemia, and hand-foot syndrome (HFS). A number of cutaneous adverse events have been attributed to capecitabine, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) as a rare and potentially life-threatening mucocutaneous condition. We report the first case involving concurrent SJS and HFS after capecitabine and lapatinib treatment.
A 70-year-old woman with a history of breast cancer treatment visited our hospital for evaluation of painful skin lesions. Six weeks earlier, she had been prescribed capecitabine plus lapatinib as treatment for metastatic breast cancer. She subsequently developed worsening erythema and bullae on her palms and soles, as well as reddish macules on her back and chest wall. Histopathological evaluation of the chest wall lesions revealed extensive eosinophilic epidermal necrosis and separation of the epidermis from the dermis. The capecitabine plus lapatinib treatment was discontinued immediately and treatment was started using systemic steroids. This treatment resolved most lesions, although the lesions on her palms and soles required Vaseline gauze dressings, which resulted in re-epithelialization. Therefore, we determined that the patient had concurrent SJS and HFS. Although the dermatological problems resolved, the patient ultimately died because of multiple organ failure.
Oral capecitabine treatment carries a risk of both HFS and also life-threatening adverse cutaneous drug reactions, such as SJS.
Core Tip: Hand-foot syndrome (HFS) is a relatively well-known side effect of capecitabine treatment, although Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) is not generally associated with capecitabine treatment. We report a case involving concurrent HFS and SJS. These side effects may decrease the patient's quality of life and delay chemothe
- Citation: Ahn HR, Lee SK, Youn HJ, Yun SK, Lee IJ. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and concurrent hand foot syndrome during treatment with capecitabine: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(17): 4279-4284
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i17/4279.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4279
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) is an acute skin reaction that is characterized by extensive necrosis and detachment of the epidermis and mucosal epithelium[1]. Although SJS is rare, it is a life-threatening disease with a 30% mortality rate[2]. Hand-foot syndrome (HFS), which is also known as palmoplantar erythrodysesthesia, is a well-documented adverse effect of treatment using various chemotherapeutic agents[3].
Capecitabine is a widely used oral antineoplastic agent that is effective and well-tolerated for treating numerous cancers, including breast cancer and gastrointestinal cancers[4]. Common capecitabine-related toxicities include diarrhea and vomiting, which are possibly related to comorbid illness, and dermatitis[5]. Reported cutaneous events have mild to moderate severity, although some patients develop grade 3-4 skin eruptions[5]. Lapatinib can be combined with capecitabine for treating patients who failed trastuzumab treatment for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastatic breast cancer[6], although the combination of capecitabine plus lapatinib leads to adverse events in ≥ 5% of patients. Nevertheless, a comparison of capecitabine monotherapy and lapatinib plus capecitabine revealed no differences in all-grade skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders, with the exception of rash[6], and there are only a few reports of life-threatening cutaneous eruptions, such as SJS, after capecitabine treatment[2,7]. Therefore, we report what we believe is the first case involving concurrent SJS and HFS following capecitabine and lapatinib treatment.
A 70-year-old woman visited our outpatient clinic for subacute painful skin lesions on her trunk, palms, and soles.
The patient had started capecitabine plus lapatinib treatment for breast cancer with multiple metastases. Four weeks after taking capecitabine and lapatinib, erythema was developed on her hands and feet, but she did not visit the clinic. After approximately 6 wk of capecitabine plus lapatinib treatment, she complained of worsening of erythema, edema, and bullae not only her hands and feet but also on her upper arms, trunk, and buttocks. At this point, she visited our clinic for evaluation and treatment. Skin biopsies were performed at the time of admission.
The patient had a 22-year history of medication for treating hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Sixteen years before the current presentation, the patient have undergone modified radical mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy [adriamycin + cyclophosphamide (4 cycles), paclitaxel (4 cycles), and oral 5-fluorourasil] for left-breast triple-negative invasive ductal carcinoma (stage IIb). Eight years after the initial diagnosis, the patient developed recurrence in the contralateral axillary lymph node, although she rejected right modified radical mastectomy and instead underwent axillary lymph node dissection, adjuvant chemotherapy [epirubicin + cyclophosphamide (4 cycles)], and radiotherapy. One year later, she developed right-breast recurrence as stage I invasive ductal carcinoma (estrogen receptor (ER): 3+, progesterone receptor (PR): 3+, HER-2: Negative) and received adjuvant chemotherapy [cyclophosphamide + methotrexate + fluorouracil (6 cycles)]. Five years later, met
There was no family history of malignancy, allergic disease, systemic autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, or other diseases.
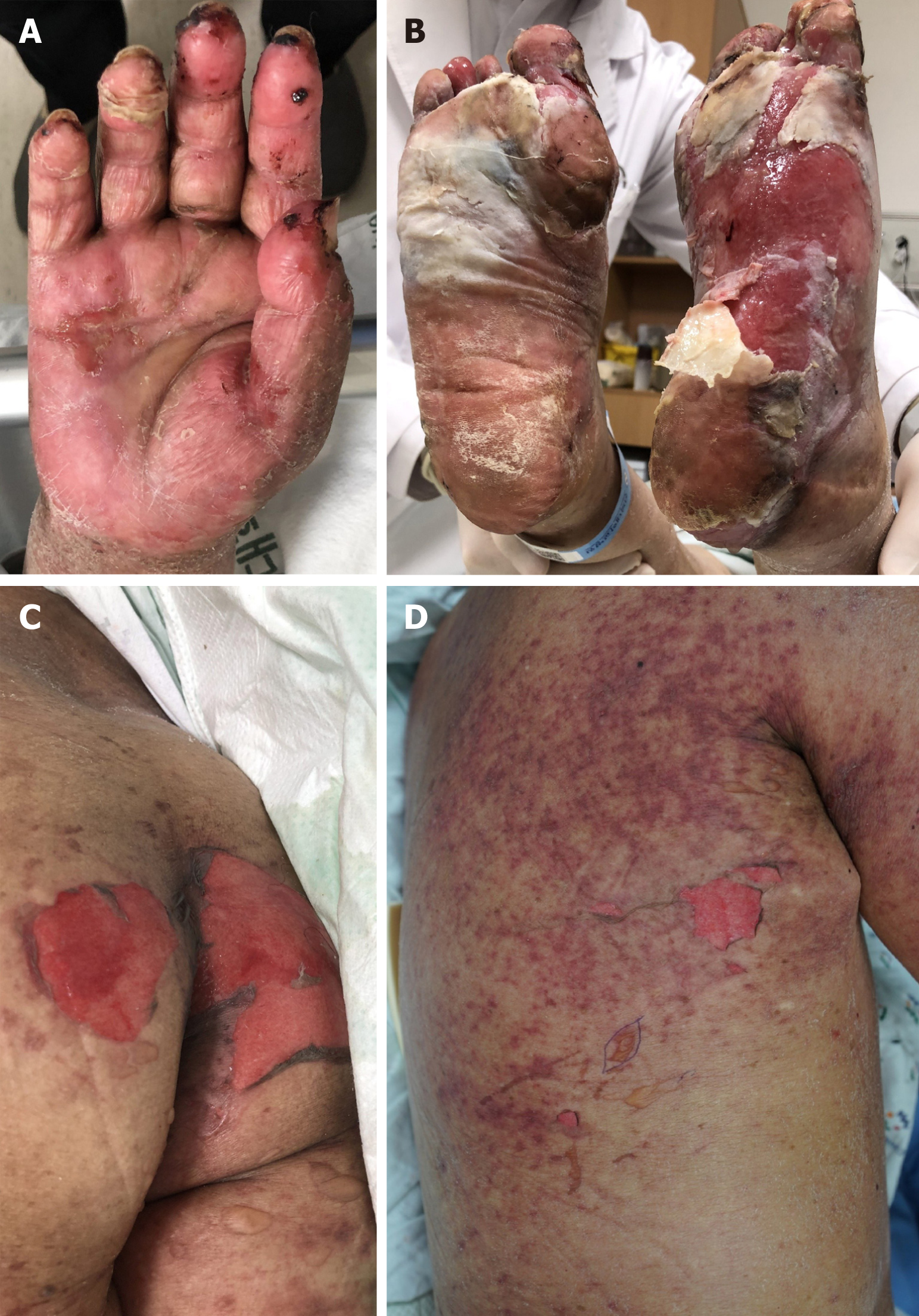
The physical examination revealed erythema, desquamation, and erosions on both palms and soles. We also observed reddish macules with a central non-blanching zone, as well as vesicles and erosions on the trunk and proximal extremities with Nikolsky’s sign (Figure 1). Epidermal detachment developed over approximately 10% of the patient’s body surface area. An intraoral examination revealed ulcerations of the lips and buccal mucosa. The patient had a body temperature of 37.6 °C and no other systemic signs.
Standard laboratory tests only revealed anemia and hyponatremia.
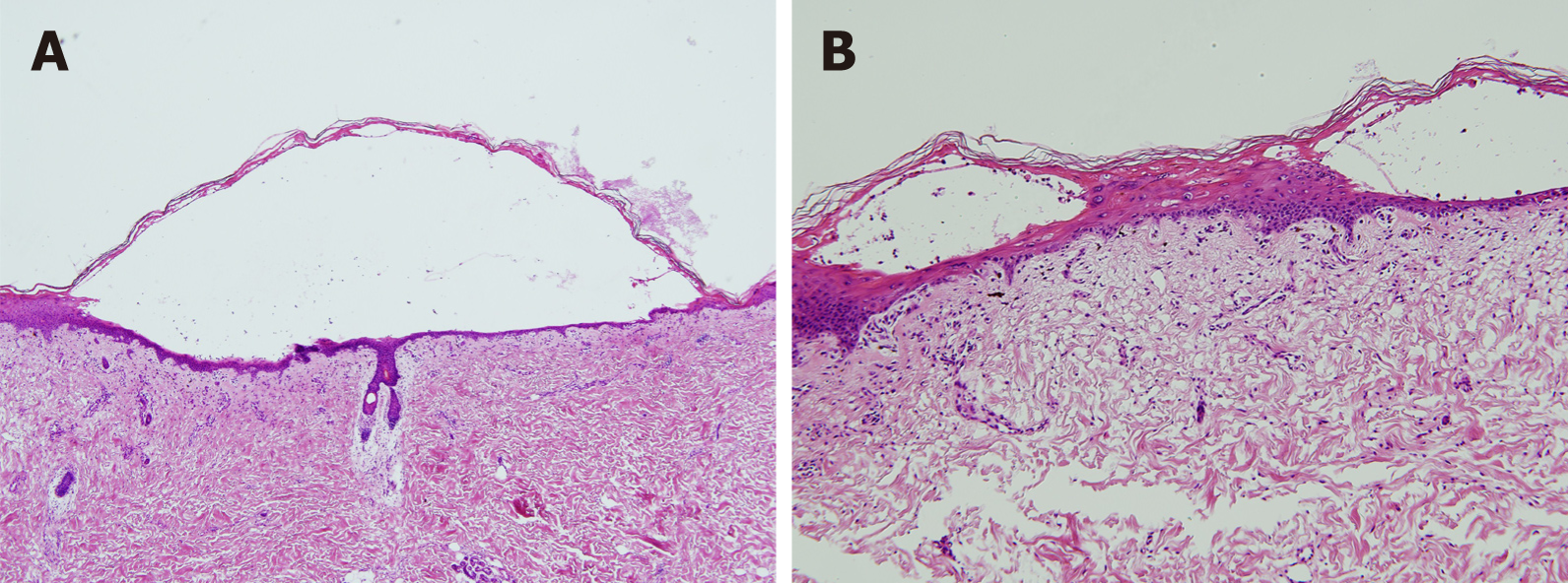
The histopathological findings revealed extensive eosinophilic epidermal necrosis, focal subepidermal blisters, and separation of the epidermis from dermis (Figure 2). Based on the clinical and histopathological findings, the final diagnosis was concurrent SJS and HFS.
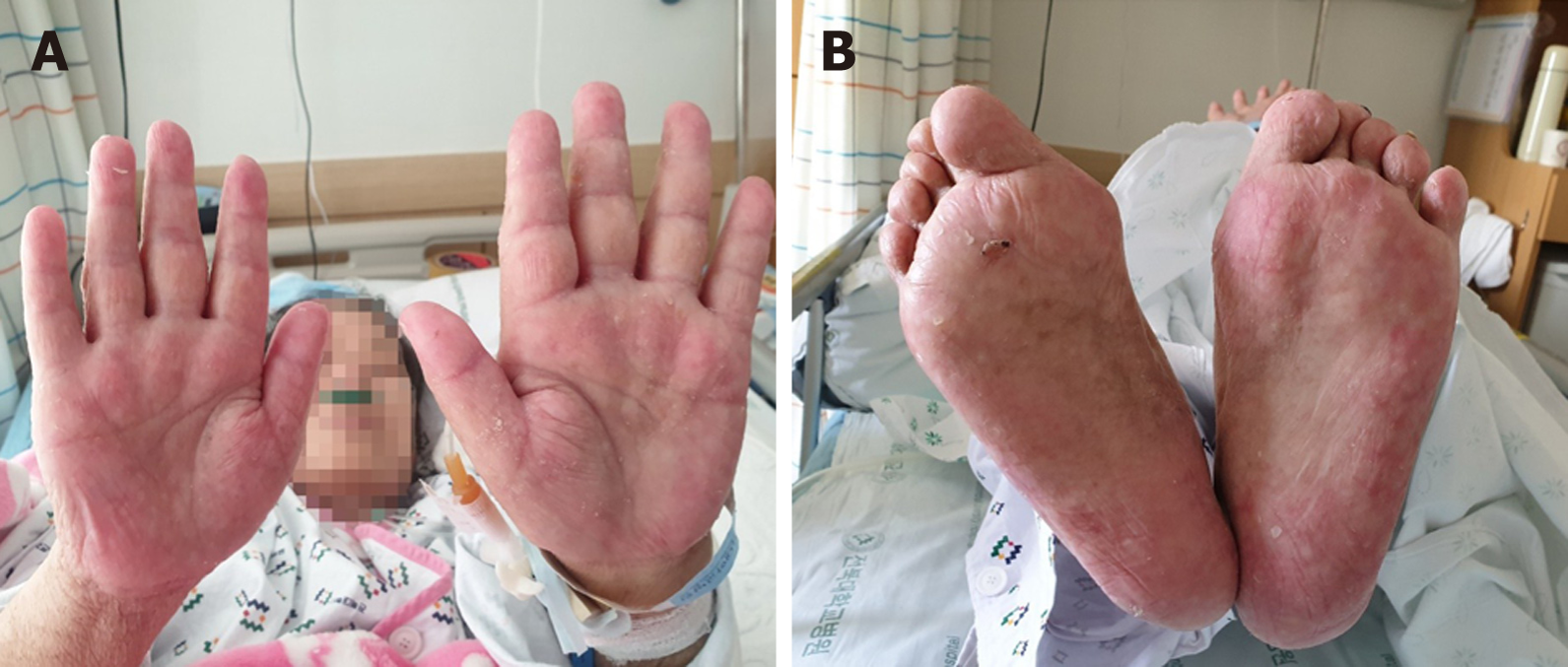
The capecitabine plus lapatinib treatment was discontinued immediately. Intravenous high-dose methylprednisolone (250 mg/d) was administered for 2 d and then gradually tapered to a dose of 62.5 mg/d for 5 d. The treatment was then changed to oral prednisolone (30 mg/d), which was tapered slowly (50% reduction every 7 d) to reach a dose of 2.5 mg/d. Most skin lesions, with the exception of the lesions on the palms and soles, healed within 3 wk after starting systemic steroid therapy. The palms and soles were treated using daily Vaseline gauze dressing for an additional 3 wk, which resulted in re-epithelialization with residual hypopigmented scarring (Figure 3).
The SCORTEN system can be used to predict the prognosis of patients with epidermal necrosis, including SJS[1]. The patient’s SCORTEN score was 3 points, which cor
As an acute life-threatening mucocutaneous reaction, SJS is characterized by extensive necrosis and detachment of the epidermis and mucosal epithelium. The exact pathophysiology of SJS remains unclear, although drug treatment is considered the most important etiological factor[1]. More than 100 different drugs may potentially cause SJS[1], which is histologically characterized by subepidermal vesiculation secondary to extensive vacuolar alteration and confluent necrosis of keratinocytes[1]. The diagnosis of SJS in the present case was based on the patient’s clinical and his
As a localized skin eruption, HFS (also known as palmoplantar erythrodysesthesia or acral erythema) is characterized by painful, symmetric, well-defined erythema, edema, bullae, and desquamation with burning pain[3]. Furthermore, HFS occurs in approximately 50%-60% of cases with capecitabine treatment[3], and the diagnosis of HFS is made clinically[3]. In the present case, the patient presented with palmoplantar erythema, blisters, and edema with burning pain approximately 6 wk after starting capecitabine and lapatinib treatment. We diagnosed concurrent HFS and SJS because of the atypical distribution of the SJS, as well as the differences in the time needed for re-epithelialization at the distal extremities and the other affected sites.
Lapatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets HER2 and epidermal growth factor receptor, and is used in combination with capecitabine for treating HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer[6]. Rash is one of the most frequently reported adverse events related to lapatinib treatment[6,8], which generally involves mild-to-moderate rash (grade 1-2) that may resemble folliculitis or an acneiform drug eruption[8]. A phase III randomized trial revealed that capecitabine plus lapatinib was associated with a higher risk of rash (vs capecitabine monotherapy), although the combination therapy was not associated with increases in the rates of serious toxic effects or treatment discontinuation related to adverse events[6]. Therefore, we believe that capecitabine was the causative drug in this case, although we cannot completely exclude the possibility that lapatinib was involved in the development of SJS.
The management of SJS has three stages: Withdrawal of the causative drug(s), rapidly initiating supportive care, and specific drug therapy. Supportive care includes monitoring fluids and electrolyte levels, barrier nursing care, nutritional support, and infection control. Because SJS is rare and has a high mortality rate, there is insufficient evidence to support treatment using steroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, tumor necrosis factor, or even cyclosporine[1]. However, a recent systemic review suggested that corticosteroids were useful for treating SJS[9]. Thus, we treated our patient using systemic corticosteroids, which resulted in re-epithelialization at most skin lesions.
Physicians who prescribe oral capecitabine should be aware of the risks of focal HFS and other less common life-threatening adverse cutaneous drug reactions, such as SJS. Although capecitabine-induced SJS has not been frequently reported, the adverse events associated with this treatment suggest that caution is warranted when prescribing it, and that mandatory education regarding cutaneous adverse events might be beneficial.
| 1. | Maja M, Jean-Claude R. Epidermal necrolysis (Stevens-johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal necrolysis). In: Kang SW, Amagai M, Anna LB, Alexander HE, David JM, Amy JM, Jeffrey SO. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2019: 734-748. |
| 2. | Jadhav P, Rogers JE, Shroff R. A Case Report-Stevens-Johnson Syndrome as an Adverse Effect of Capecitabine. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2018;49:349-350. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Miller KK, Gorcey L, McLellan BN. Chemotherapy-induced hand-foot syndrome and nail changes: a review of clinical presentation, etiology, pathogenesis, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:787-794. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 145] [Article Influence: 12.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Milano G, Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Mari M, Lassalle S, Formento JL, Francoual M, Lacour JP, Hofman P. Candidate mechanisms for capecitabine-related hand-foot syndrome. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;66:88-95. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Blum JL, Jones SE, Buzdar AU, LoRusso PM, Kuter I, Vogel C, Osterwalder B, Burger HU, Brown CS, Griffin T. Multicenter phase II study of capecitabine in paclitaxel-refractory metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:485-493. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 579] [Cited by in RCA: 597] [Article Influence: 22.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Geyer CE, Forster J, Lindquist D, Chan S, Romieu CG, Pienkowski T, Jagiello-Gruszfeld A, Crown J, Chan A, Kaufman B, Skarlos D, Campone M, Davidson N, Berger M, Oliva C, Rubin SD, Stein S, Cameron D. Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2733-2743. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2515] [Cited by in RCA: 2491] [Article Influence: 124.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Sendur MA, Kilickap S. Stevens-Johnson syndrome after treatment with capecitabine. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2008;20:202-203. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Moy B, Goss PE. Lapatinib-associated toxicity and practical management recommendations. Oncologist. 2007;12:756-765. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Zimmermann S, Sekula P, Venhoff M, Motschall E, Knaus J, Schumacher M, Mockenhaupt M. Systemic Immunomodulating Therapies for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:514-522. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 203] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 25.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Oncology
Country/Territory of origin: South Korea
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Han JG, Hu XS, Qiao ZG S-Editor: Liu M L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhang YL