Published online Apr 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1495
Peer-review started: January 23, 2020
First decision: February 26, 2020
Revised: March 29, 2020
Accepted: April 17, 2020
Article in press: April 17, 2020
Published online: April 26, 2020
Processing time: 78 Days and 20.8 Hours
Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney (ASK) is a rare and newly recognized renal neoplasm. The tumor usually is extensive and cystic, characterized by pleomorphic spindle cells with marked atypia and associated with multinucleated cells. To date, only 27 cases have been reported in the literature. The authors present an additional case and summarize the relevant knowledge in the literature.
A 27-year-old previously healthy woman presented with a palpable mass over the abdomen and right flank soreness for one year. After the computed tomography study, the patient underwent right radical nephrectomy obtaining a 1680-g tumor with a size of 18.4 cm × 14.5 cm × 11 cm. The tumor is chiefly composed of anaplastic spindle cells with marked nuclear atypia admixed with multinucleated cells. Immunohistochemical evaluation of tumor cells exhibited diffuse positivity for CD56, p53, and vimentin, and focally positive for desmin. The diagnosis of ASK was established. Unfortunately, a local tumor recurrence followed by a distant metastasis developed within months. The patient died 26 months after the initial surgery. Comparing to the previously 27 cases of ASK, the current case had a relatively worse prognosis, which might be potentially associated with older patient age, larger tumor size, and the lack of en-bloc resection of adjacent organs during the initial radical nephrectomy.
This case points out the featured pathological findings for diagnosing ASK and suggests more aggressive management for patients with ASK.
Core tip: The current case report points out the crucial features to differentiate the rare tumor, anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney (ASK), from other renal malignancies. Besides, the authors summarized the demographic, clinical, and prognostic information of the 28 ASK cases reported in the literature. Based on the lethal outcome in a 5-year old patient and two patients with stage 1 of the disease at presentation, we suggest that all patients with ASK should receive radical nephrectomy, en bloc resection of adjacent organs, chemotherapy, and long-term close follow-up. Further experience is essential to modify this approach in the future.
- Citation: Kao JL, Tsung SH, Shiao CC. Rare anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(8): 1495-1501
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i8/1495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1495
Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney (ASK) is a rare and newly recognized renal neoplasm, first described by Vujanić et al[1] in 2007. The tumor usually is extensive and cystic, characterized by pleomorphic spindle cells with marked atypia and associated with multinucleated cells. To the best of our knowledge, only 27 cases have been reported in the literature[1-8]. Herein, we present an additional case and summarize the relevant knowledge in the literature.
A 27-year-old woman had experienced right flank soreness for around one year.
She did not seek medical help until two months before the admission when she felt increasing painful swelling over the right flank and the right abdomen. There were no gastrointestinal or genitourinary complaints and body weight loss throughout the previous year.
The patient had a free previous medical history.
At presentation, the physical examination disclosed a huge palpable bulging mass over the right abdomen with slight tenderness.
The laboratory tests revealed hemoglobin of 11.4 g/dL, white blood cell count of 7.4 × 109/L, serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL, estimated glomerular filtration rate of 44 mL/min/1.73 m², and urine red blood cell count of 30-50/high power field. Other laboratory biochemistries were unremarkable.
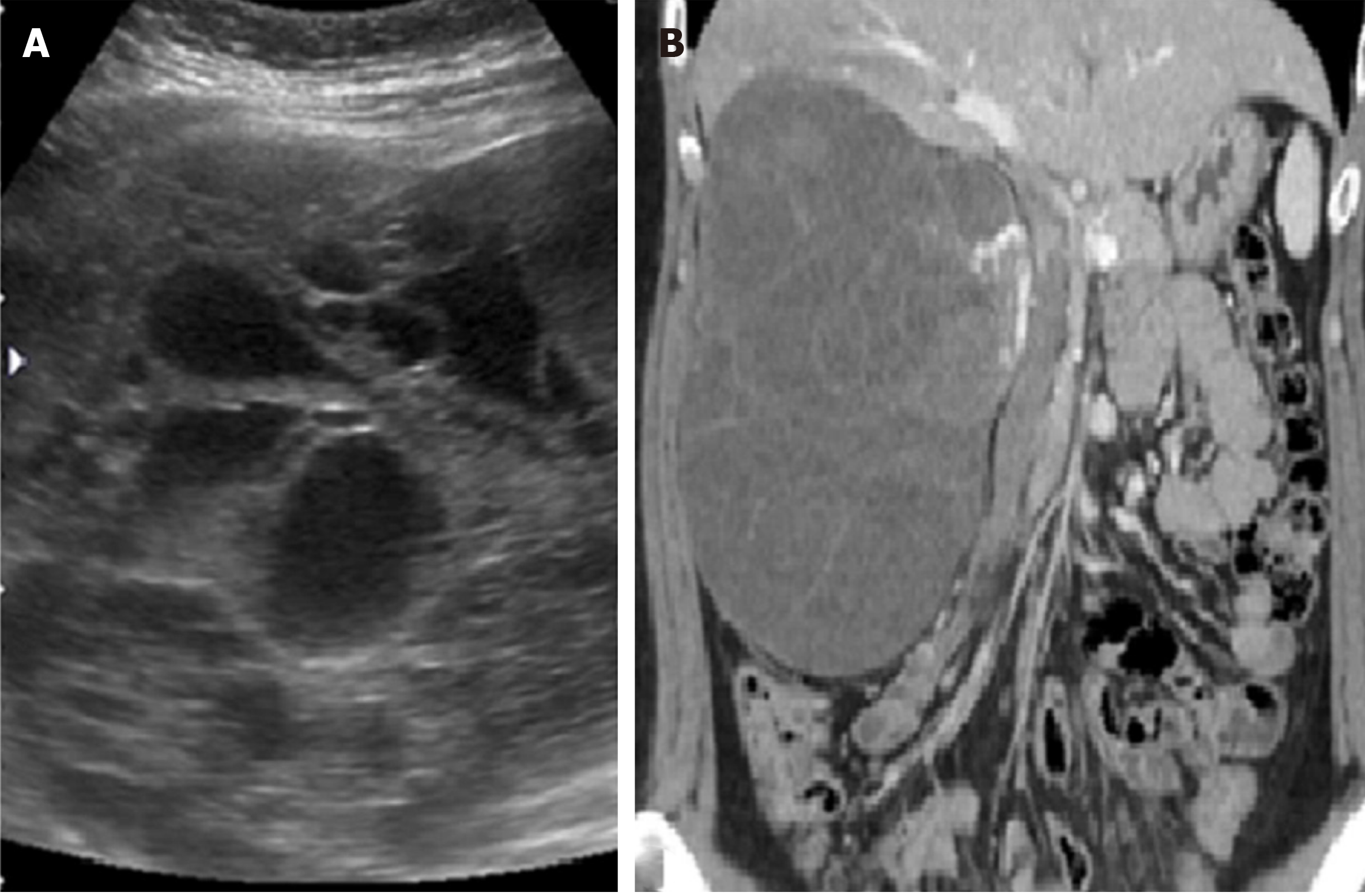
The abdominal sonography revealed a huge well-defined mass measuring about 15 cm in diameter over the right kidney. The tumor was multicystic with the solid component. The subsequent computed tomography (CT) demonstrated a huge, mainly hypodense, multi-loculated cystic tumor measuring about 18 cm × 14 cm × 11 cm (Figure 1).
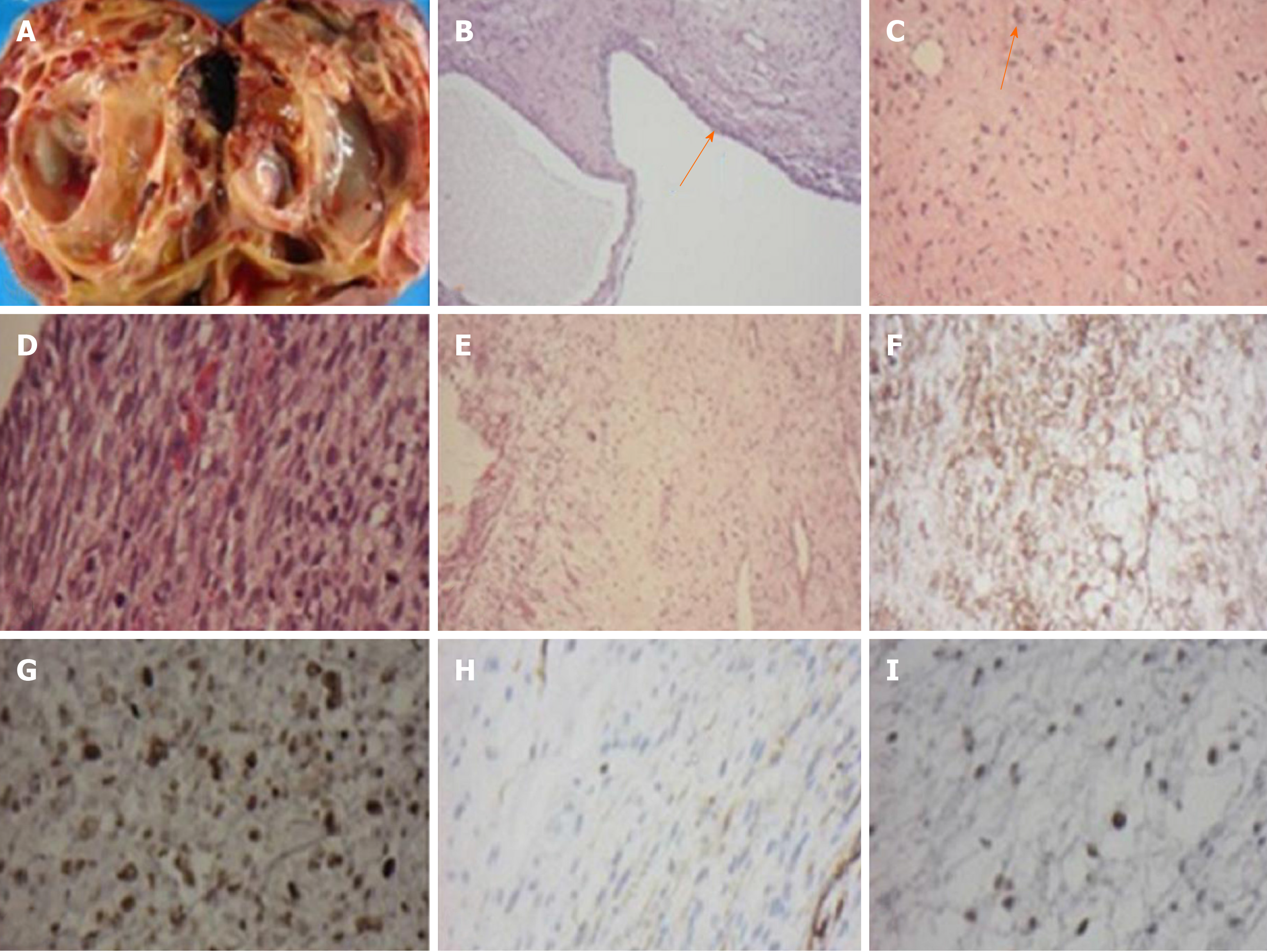
Concerning the probability of malignancy, she underwent a right radical nephrectomy. No lymph node was dissected at the time of surgery. The resected kidney measured 18.4 cm × 14.5 cm × 11.0 cm and weighed 1680 g. The cut surface revealed a variable-size of multi-loculated cystic spaces filled with clear serous fluid. Protruding from the cystic wall was yellowish-gray solid nodules with focal areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. A narrow rim of residual kidney tissue was noted at the edge of the specimen (Figure 2A). Microscopically, the tumor was confined to the kidney and consisted of cystic and solid components. The cystic component was lined by a single layer of benign cuboidal cells (Figure 2B). The solid areas were composed of spindle cells with marked nuclear atypia admixed with multinucleated cells. Mitosis was frequent (Figure 2C and D). Myxoid changes were found (Figure 2E). Neither chondroid differentiation nor blastema-like cells were found in the sections studied. Immunohistochemical evaluation of tumor cells exhibited diffuse positivity for CD56, p53, and vimentin, and focally positive for desmin (Figure 2F-I). The remaining markers, including GFAP, CD34, S-100 protein, and WT-1, were negative. The positivity for P53 could be a reflection of anaplasia. Focal positive staining represented focal muscle differentiation.
Based on the histopathology and immunohistochemical profile, the final diagnosis of ASK was established.
The patient received a right radical nephrectomy without chemotherapy before and after the surgery.
Unfortunately, the patient experienced a local tumor recurrence over retroperitoneum about one year after the initial surgery. Despite the immediate resection of the recurrent tumor, distant metastasis to the liver with massive ascites developed within months. Finally, she expired 26 months after the initial radical nephrectomy.
Renal sarcomas are malignant tumors deriving from mesenchymal cells of the kidney, which accounts for 1% of all malignant renal tumors. The renal sarcoma family contains many tumors such as leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, fibrosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, and angiosarcoma, etc. ASK is an extraordinarily rare renal neoplasm characterized by a proliferation of anaplastic spindle cells with bizarre pleomorphic nuclei and atypical mitotic figures.
The cardinal signs at an advanced stage of ASK include flank pain, abdominal mass, and hematuria. The working diagnosis of ASK is processed by history taking, physical examination, and image studies. However, the definitive diagnosis is difficult to make without a pathological examination. In the imaging study, the ASK was highly suggested by the discordant image findings on sonography or CT scan, and the presence of predominant hyperechoic solid components on sonography but a mainly low-density cystic appearance on CT scan. It is postulated that cystic appearance on CT is related to the high-water content in the cyst and the abundant myxoid stroma.
In differential diagnosis, anaplastic Wilms tumor certainly is the most important and challenging one. Certain features help favor ASK when compared with anaplastic Wilms tumor; these features include age, the presence of markedly atypical and numerous anaplastic cells with increased mitotic activity, and the absence of blastema-like cells. Immunohistochemical stains for WT1 was negative. Positivity for CD56 was nonspecific for Wilms tumor. Other tumors to be considered in the differential diagnosis are renal synovial sarcomas[9], malignant mesenchymal[10], and malignant ectomesenchymomas[11].
The optimal treatment is radical nephrectomy with en-bloc resection of adjacent organs such as the spleen, pancreatic tail, or colon. Distant metastasis to lung, bone, and liver is common. Therefore, some patients had been prescribed chemotherapy with the Wilms tumor or Ewing sarcoma protocol[6]. Adjuvant chemotherapy regimen includes a varied combination of vincristine, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, doxorubicin, and carboplatin depending on different risk stratification and protocol[12-14]. However, the patients’ outcomes seem to correlate with tumor staging.
To date, a total of 28 patients, including the current case, have been reported in the literature[1-8]. In these 28 patients, the mean age at tumor diagnosis was 12.6 ± 11.4 [median (minimal, maximal) = 9.4 (0.6, 41.0)] years. Female sex (67.9% of the 28 patients) and the right kidney involvement (68.0% of the 25 patients with a known site) were more frequent in these patients. Female patients were significantly older than male patients at diagnosis (15.6 ± 12.5 years vs 6.3 ± 4.6 years, P = 0.008). At diagnosis, the mean size of the tumor was 13.9 ± 4.5 [15 (4.0, 22.0)] centimeters among the 24 patients with known tumor size, whereas 43.5%, 21.7%, 26.1%, and 8.7% patients were in stage I, II, III and IV, respectively, among the 23 patients with known staging. During the mean follow-up period of 5.5 ± 2.9 [2.9 (0.25, 15)] years, 68.2% patients had no recurrence, 4.5% had local recurrence, and 27.3% had distant metastases among the 22 patients with known results.
During the follow-up periods, five patients expired, 15 survived, and eight had unknown results. The period from diagnosis to the end of follow-up was 5.9 ± 4.2 [6.0 (0.25, 14)] years for the 15 survivors and 4.4 ± 6.0 [2.0 (1.2, 15)] years for the five patients who expired. The 5-year survival rate was 69.2% among the 13 patients who died or who had follow-up periods of more than five years (Table 1). Comparing to other reported cases of ASK, the current case was relatively older and had relatively larger tumor size at diagnosis. The female gender and the right kidney involvement were the same as the majority of the reported cases. Although the tumor stage was very early (stage I), the patient experienced local and distant metastasis, along with subsequent mortality within a relatively shorter period than previously reported cases. The potential reasons for the rapid tumor progression and worse prognoses included older patient age, larger tumor size, and the lack of en-bloc resection of adjacent organs during the initial radical nephrectomy.
| Case | Age | Gender | Side | Size of tumor (diameter/ weight) | Stage | Therapy | Relapse | Outcomes |
| 1[2] | 7 mo | F | L | 18 cm/1620 g | I | N | No recurrence | NED 2 yr |
| 2[1] | 10 mo | F | R | 15 cm/- | - | C + N | Unknown | Unknown |
| 3[1] | 11 mo | M | R | 7.5 cm/250 g | - | N + C | Unknown | Unknown |
| 4[1] | 1.5 yr | M | R | 10 cm/670 g | I | N + C | No recurrence | NED 13 yr |
| 5[1] | 3 yr | F | L | 15 cm/- | I | N + C | No recurrence | NED 14 yr |
| 6[3] | 3 yr | F | R | 19 cm/1420 g | III | N | Unknown | Unknown |
| 7[1] | 3.3 yr | F | R | 16 cm/1400 g | II | C + N + C | No recurrence | NED 9 yr |
| 8[1] | 4 yr | M | L | -/- | II | C + N + C | No recurrence | NED 6 yr |
| 9[1] | 4 yr | F | L | -/- | I | N + C | No recurrence | NED 9 yr |
| 10[1] | 4.3 yr | M | - | 21 cm/1820 g | III | N + C | Abd recurrence, liver metastases | Unknown |
| 11[1] | 4.8 yr | M | R | 11 cm/664 g | II | C + N + C | No recurrence | NED 7 yr |
| 12[1] | 5 yr | M | R | 13 cm/- | III | RT + N + C + RT | Lung and bone metastases | DOD 1.5 yr |
| 13[1] | 8 yr | F | R | 4 cm/115 g | I | C + N + C | No recurrence | NED 8 yr |
| 14[5] | 8.8 yr | F | L | 12.9 cm/- | III | N + R + C | No recurrence | NED 2.8 yr |
| 15[1] | 10 yr | M | L | 17 cm/1210 g | I | N + C | No recurrence | NED 8 yr |
| 16[4] | 12 yr | F | R | 15 cm/- | IV | N + C + RT | Preoperative lung and bone metastases decreased after treatment, no local recurrence | NED 2.3 yr |
| 17[1] | 13 yr | M | - | 17 cm/1750 g | III | C + N + C | No recurrence | NED 2 yr |
| 18[1] | 13 yr | F | - | -/- | II | C+N | Unknown | Unknown |
| 19[6] | 13 yr | M | R | 16 cm/666 g | III | N + C + RT | Abd recurrence, lung and liver metastases | DOD 15y |
| 20[1] | 15 yr | F | R | 10.5 cm/804 g | I | N | Local recurrence | Unknown |
| 21[1] | 17 yr | F | R | -/1100 g | IV | Resection | Lung metastases, renal tumor found postmortem | DOD 1.2 yr |
| 22[7] | 22 yr | F | L | 9.5 cm/- | I | N | No recurrence | NED 3 mo |
| 23[8] | 24 yr | F | R | 22 cm/- | II | N + C + RT | No recurrence | NED 2.5 yr |
| 241 | 27 yr | F | R | 18.4 cm /1680 g | I | N | Local recurrence at retroperitoneum and liver metastases | DOD 26 mo |
| 25[1] | 29 yr | F | R | 10 cm/- | - | N | Unknown | Unknown |
| 26[1] | 30 yr | F | R | 15 cm/409 g | - | N + C | No recurrence | NED 3 yr |
| 27[1] | 35 yr | F | R | 7.5 cm/336 g | - | N | Unknown | Unknown |
| 28[1] | 41 yr | F | L | 14 cm/250 g | I | N + C | Spine, liver and lung metastases | DOD 2 yr |
This case points out the features to differentiate ASK from other renal malignancies. The summary of the 28 reported cases also provided valuable information. Based on the lethal outcome in a 5-year old patient and two patients with stage 1 of the disease at presentation, we suggest that all patients with ASK should receive radical nephrectomy, en bloc resection of adjacent organs, chemotherapy, and long-term close follow-up. Further experience is essential to modify this approach in the future.
The authors thank Simone Yu for her professional English-editing and assisting in making the “audio core tip”.
| 1. | Vujanić GM, Kelsey A, Perlman EJ, Sandstedt B, Beckwith JB. Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney: a clinicopathologic study of 20 cases of a new entity with polyphenotypic features. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1459-1468. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Wu MK, Cotter MB, Pears J, McDermott MB, Fabian MR, Foulkes WD, O'Sullivan MJ. Tumor progression in DICER1-mutated cystic nephroma-witnessing the genesis of anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney. Hum Pathol. 2016;53:114-120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Arabi H, Al-Maghraby H, Yamani A, Yousef Y, Huwait H. Anaplastic Sarcoma of the Kidney: A Rare Unique Renal Neoplasm. Int J Surg Pathol. 2016;24:556-561. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Gomi K, Hamanoue S, Tanaka M, Matsumoto M, Kitagawa N, Niwa T, Aida N, Kigasawa H, Tanaka Y. Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney with chromosomal abnormality: first report on cytogenetic findings. Hum Pathol. 2010;41:1495-1499. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Wu MK, Goudie C, Druker H, Thorner P, Traubici J, Grant R, Albrecht S, Weber E, Charles A, Priest JR, Fabian MR, Foulkes WD. Evolution of Renal Cysts to Anaplastic Sarcoma of Kidney in a Child With DICER1 Syndrome. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63:1272-1275. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Watanabe N, Omagari D, Yamada T, Nemoto N, Furuya T, Sugito K, Koshinaga T, Yagasaki H, Sugitani M. Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney: case report and literature review. Pediatr Int. 2013;55:e129-e132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Chen CC, Liao KS. Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney: Case report and literature review. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;31:129-132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Labanaris A, Zugor V, Smiszek R, Nützel R, Kühn R. Anaplastic sarcoma of the kidney. ScientificWorldJournal. 2009;9:97-101. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Argani P, Faria PA, Epstein JI, Reuter VE, Perlman EJ, Beckwith JB, Ladanyi M. Primary renal synovial sarcoma: molecular and morphologic delineation of an entity previously included among embryonal sarcomas of the kidney. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1087-1096. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 183] [Cited by in RCA: 168] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Reed HM, Poppiti R, Sivina M. Malignant mesenchymoma of kidney and inferior vena cava. Urology. 1983;22:297-299. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Goldsby RE, Bruggers CS, Brothman AR, Sorensen PH, Beckwith JB, Pysher TJ. Spindle cell sarcoma of the kidney with ganglionic elements (malignant ectomesenchymoma) associated with chromosomal abnormalities and a review of the literature. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998;20:160-164. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Oostveen RM, Pritchard-Jones K. Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Wilms Tumor: An Update. Paediatr Drugs. 2019;21:1-13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Hol JA, Pritchard-Jones K, van Tinteren H, Furtwängler R, Verschuur AC, Vujanic GM, Leuschner I, Brok J, Rübe C, Smets AM, Janssens GO, Godzinski J, Ramírez-Villar GL, de Camargo B, Segers H, Collini P, Gessler M, Bergeron C, Spreafico F, Graf N; International Society of Paediatric Oncology – Renal Tumour Study Group (SIOP–RTSG). Position paper: Rationale for the treatment of Wilms tumour in the UMBRELLA SIOP-RTSG 2016 protocol. Nat Rev Urol. 2017;14:743-752. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 313] [Cited by in RCA: 244] [Article Influence: 27.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Doroudinia A, Ahmadi S, Mehrian P, Pourabdollah M. Primary Ewing sarcoma of the kidney. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See:
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Corresponding Author's Membership in Professional Societies: Taiwan Society of Nephrology (TSNS0874).
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: Taiwan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Hu X, Kamimura K, Tzamaloukas AHH S-Editor: Dou Y L-Editor: A E-Editor: Ma YJ