Published online Aug 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i23.106140
Revised: March 30, 2025
Accepted: April 22, 2025
Published online: August 16, 2025
Processing time: 107 Days and 14.5 Hours
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare mesenchymal tumors that rarely present with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding due to tumor erosion. GISTs com
A 42-year-old male presented with dark stools and light-headedness over five days. On examination, he was hypotensive, tachycardic, tachypneic, and had pallor. Laboratory tests revealed normocytic normochromic anemia, with a significant one-day drop in hemoglobin (from 7.2 g/dL to 6.4 g/dL). Upper GI endoscopy and colonoscopy were normal, but double-balloon enteroscopy revealed a subepithelial lesion distal to the duodenojejunal flexure, and an overlying ulcer. These findings were suggestive of GIST and were corroborated by a contract-enhanced computed tomography abdomen scan, which revealed a well-defined, homogenously-enhancing solid exophytic lesion (30 mm × 22 mm × 26 mm) arising from the proximal jejunal loops. He underwent resection anastomosis with complete en-bloc surgical removal of the lesion. Histopathological analysis of the resected specimen confirmed a GIST with presence of spindle cells and positive CD117 staining. His hemoglobin levels were stable on regular follow-ups, and there was no documented recurrence six months later.
GISTs should be suspected in cases of unexplained GI bleeding. Early diagnosis and complete surgical resection are key to favorable outcomes.
Core Tip: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare mesenchymal tumors that rarely cause gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. Mucosal ulceration and unfavorable tumor locations are risk factors for tumor progression and malignancy. We present a case of GI bleeding in a 42-year-old man complaining of melena over five days, which was diagnosed as a benign, ulcerated, jejunal GIST on histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Prompt evaluation using specialized diagnostic tools to locate obscure bleeding sources and complete surgical resection are key to favorable outcomes. GI bleeding in GIST is associated with a poor prognosis. Hence, detailed follow-ups are essential to detect and prevent tumor recurrence.
- Citation: Maity R, Rathna RB, Dhali A, Fernandes N, Biswas J, Kapoor GS, Dhali GK. Ulcerated benign jejunal gastrointestinal stromal tumor causing gastrointestinal bleeding: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(23): 106140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i23/106140.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i23.106140
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are generally recognized as spindle cell, epithelioid, or occasionally pleomorphic tumors that usually develop in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Originating from mesenchymal cells of the GI tract, GISTs make up 1%-3% of all GI malignancies and progress to malignancy in approximately 10% to 30% of cases[1,2]. A greater risk of tumor progression is linked to GISTs associated with mucosal ulceration and those that develop outside of the stomach[1,3]. Many GISTs carry mutations in the genes encoding type III receptor tyrosine kinases, particularly KIT or PDGFRA, which is the case in up to 85% of instances. A significant majority, about 95%, of these tumors are positive for the KIT protein when tested with immunohistochemistry[4]. The most common places where GIST arises are the stomach, followed by the small bowel[2]. In 19% of cases, GISTs manifest asymptomatically, particularly in cases of smaller tumors of the intestinal tract. Studies show that around 10% of these cases were caught at autopsy and 20% during abdominal surgery for other conditions, making them a common incidental finding rather than a clinical suspicion[5,6]. Patients who are symptomatic may exhibit non-specific symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, early satiety, abdominal pain, and, in rare cases, a palpable abdominal mass. Obstruction of the GI lumen by endophytic growth or compression of the GI tract by exophytic growth may result in dysphagia, obstructive jaundice, or constipation in larger tumors, contingent upon the mass's specific location[1]. Very rarely do these tumors present as an acute, severe, life-threatening GI bleeding[7]. Herein, we describe a case report of a rather unusual presentation of GIST, i.e., symptomatic GI bleeding caused by an ulcerated jejunal GIST, which was found to be benign in nature. This case report emphasizes the importance of maintaining a high suspicion of this disease when all routine workups for GI bleeding show no obvious findings.
A 42-year-old male with no comorbidities presented with several episodes of black, tarry stools for five days.
The melena was sudden in onset, occurring two to three times per day, and associated with light-headedness. It was not accompanied by abdominal pain, jaundice, altered mentation, altered bowel habits, blood in vomitus, any other bleeding manifestations, early satiety, or weight loss.
The patient denied any history of similar or related complaints in the past. There was no history of any malignancies.
The patient denied any family history of malignant tumors or bleeding disorders. He had no history of recent travel, smoking, or alcohol intake and was not on any regular medications.
On physical examination, he was conscious and oriented to time, place, and person. He was tachycardic with a pulse rate of 132 beats/minute, hypotensive (supine and erect blood pressures 94/60 mmHg and 80/54 mmHg, respectively), and tachypneic with a respiratory rate of 26/minute. Additionally, he showed signs of pallor. There were no signs of icterus or chronic liver disease. The systemic examination was unremarkable. Considering the patient’s history and presentation, the differentials were between peptic ulcer disease and vascular malformations of the gut, like Dieulafoy lesions or angioectasia.
Laboratory investigation revealed normocytic normochromic anemia [hemoglobin (Hb) 7.2 g/dL], with a significant drop in Hb over a day (from 7.2 g/dL to 6.4 g/dL). The liver function test, kidney function test, electrolyte levels, and clotting profile were unremarkable. All his laboratory tests have been summarized in Table 1.
| Parameter (units) | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.2→6.4 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 8.6 |
| Total leukocyte count (cells/cu mm) | 5.1 | 6.6 | 5.1 | - |
| Differential count (neutrophil/lymphocyte) | 77/12 | 80/16 | 82/11 | - |
| Platelet count (cells/cu mm) | 3.3 | 2.7 | 2.2 | - |
| Bilirubin total/Direct (mg/dL) | 0.8 | 0.9/0.1 | - | - |
| SGPT (IU/L)/SGOT (IU/L) | 31 | 28/33 | - | - |
| ALP (IU/L) | - | 118 | - | - |
| Total protein (g/dL) | - | 6.2 | - | - |
| Serum albumin (g/dL)/globulin (g/dL) | 3.8 | 4.0/2.2 | - | - |
| PT (seconds)/INR | 0.98 | 1.11 | - | - |
| Serum urea (mg/dL)/creatinine (mg/dL) | 31/0.9 | 27/0.7 | 20/0.8 | - |
| Na+ (mEq/L)/K+ (mEq/L) | 141/3.7 | 139/4.1 | 139/3.9 | - |
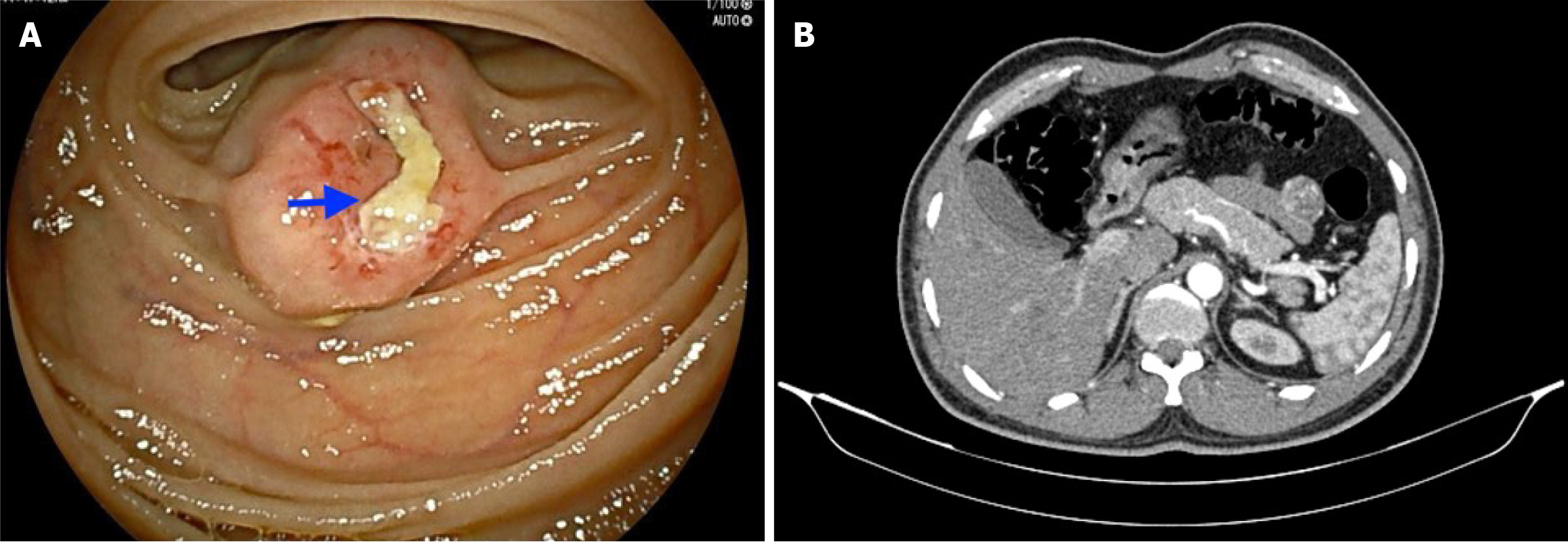
After initial fluid resuscitation and two units of packed red cell transfusion, he underwent an upper GI endoscopy, which was unremarkable. A colonoscopy showed fresh and altered blood clots all along the entire length of mucosa, which was normal and did not reveal any source of bleeding. He underwent a double-balloon enteroscopy (DBE), which revealed a subepithelial lesion (2 cm × 1.5 cm) approximately 150 cm distal to the duodenojejunal flexure and an overlying ulcer that was not actively bleeding (Figure 1A). A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan of the whole abdomen corroborated the above findings, revealing a well-defined, round-shaped, homogenously enhancing solid exophytic lesion (30 mm × 22 mm × 26 mm) arising from the proximal jejunal loops, without any obvious adjacent organ invol
Combined with the endoscopic and postoperative histopathological findings, the final diagnosis was a benign jejunal GIST, which was confirmed by histopathological examination of the postoperative specimen.
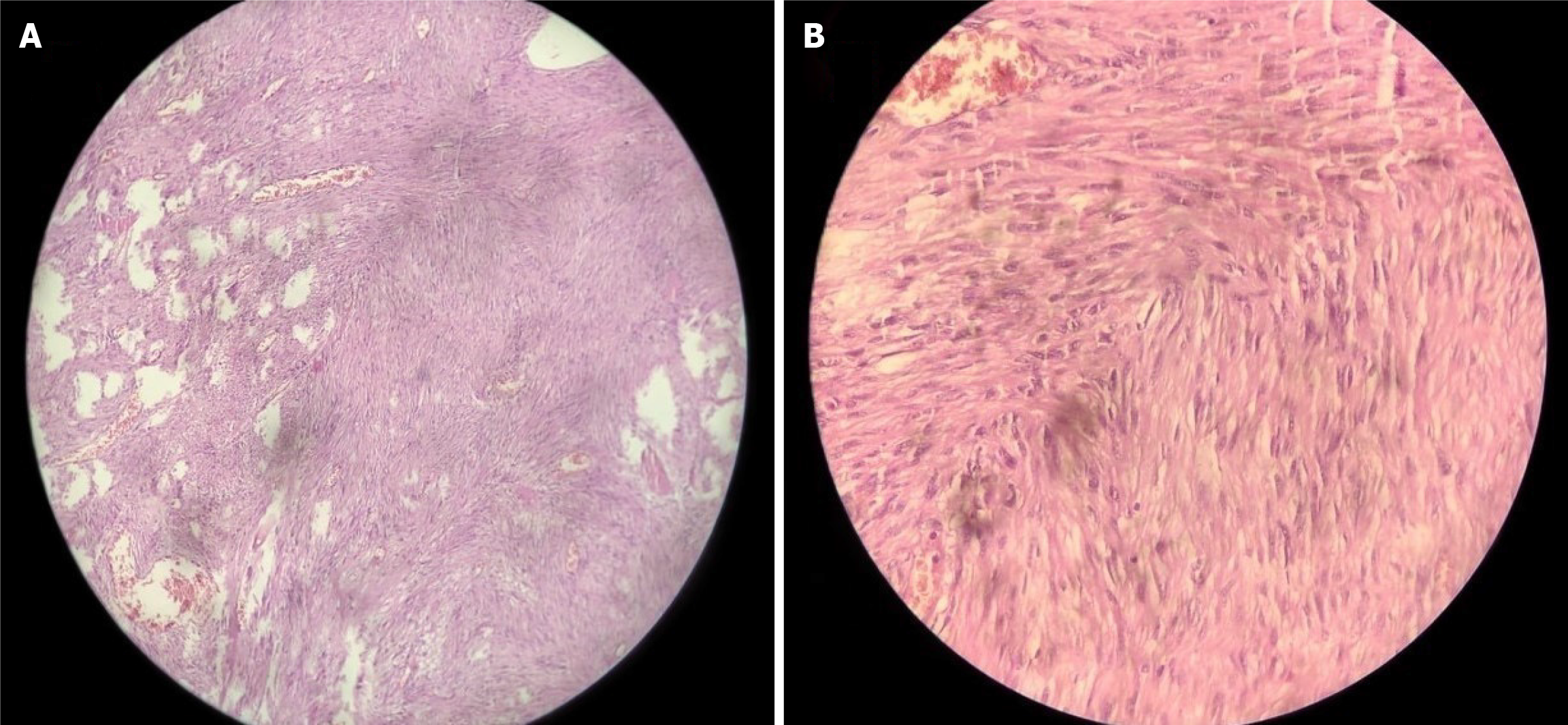
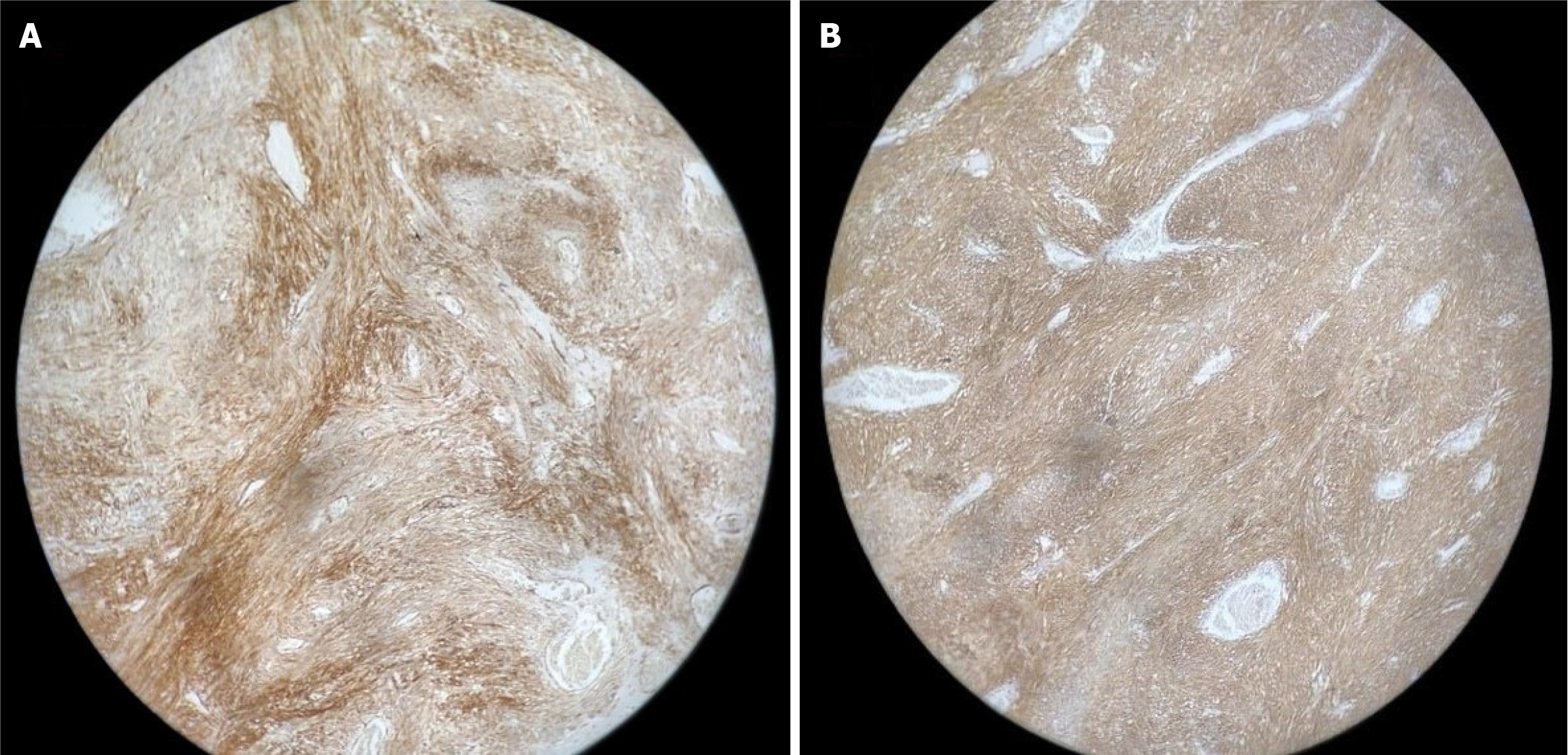
He underwent resection anastomosis with complete en-bloc surgical removal of the suspicious lesion with a reasonable tumor-free margin. The post-operative recovery period was uneventful. Histopathology identified a submucosal tumor with spindle cells, mild hyperchromasia with a low mitotic index, and no necrosis or epithelioid cells (Figure 2). The cells were diffusely immunopositive for CD117 and DOG1, which confirmed GIST (Figure 3).
Our patient was postoperatively well and followed up for six months thereafter. His Hb level was stable on regular follow-ups, and there was no documented recurrence six months later.
GISTs usually occur as solitary lesions and are thought to originate from the interstitial cells of Cajal, a complex cellular network that regulates peristalsis[1]. These are rare tumors, having a reported incidence ranging from 0.4 cases to 2 cases per 100000 annually. Males have a slightly higher incidence of GIST, and the median age of presentation is approximately 60 years to 65 years[8]. GISTs can originate anywhere in the GI tract; however, the most common locations are the stomach, followed by the small bowel[6]. Less than 3% of all GI tumors are jejunal GISTs[9]. GISTs can rarely occur even outside the GI tract in the retroperitoneum or mesentery[2]. The presentation of GIST varies, ranging from non-specific symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distension to a palpable abdominal mass. While symptoms due to large tumors are usually attributed to mass effect, perforated neoplasms may present with peritonitis or GI bleeding[1]. Ongoing active acute blood loss, as in the above patient with no comorbidities, warrants a complete visualization of the GI tract to look for any bleeders, which includes visualization of the small intestine. Most GIST cases are attributed to oncogenic mutations in KIT or PDGFRA that result in gain-of-function of tyrosine kinases; these mutations are found in approximately 85% of GISTs. A subset of cases is associated with alternative mechanisms, including the inactivation of NF14 or genes that encode subunits of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH). SDH-deficient GISTs have a slower clinical progression than KIT/PDGFRA-mutant GISTs. Although most cases occur sporadically among adults, a few of them may occur in children and young adults as part of the non-hereditary Carney triad syndrome (comprising multifocal gastric GISTs, paraganglioma, and pulmonary chondroma) or autosomal-dominant Carney-Stratakis syndrome (comprising multifocal gastric GIST and paragangliomas)[4]. GISTs can be detected using abdominal ultrasound, CT, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography. CT enterography is the most effective modality for identifying the location of tumors, assessing any perforation, evaluating invasion into adjacent structures, and detecting metastasis. Small tumors display homogenous densities on radiological investigations, but large tumors reveal heterogeneous enhancement, mucosal ulceration, central and coagulative necrosis, and irregular lobulated borders[1]. Histologically, GISTs are of three types: Spindle cell, epithelioid, and mixed type. Since they are often misdiagnosed as leiomyoma or leiomyosarcoma, immunohistochemical analysis is essential. 95% of GISTs are positive for CD117, while DOG1 is expressed in 98% of cases. Additionally, PDGFRA and CD34 are expressed in 80% and 70%-80% tumors, respectively. The diagnosis is confirmed when CD117 and/or DOG1 are present. Furthermore, there is loss of SDH-B expression in SDH-deficient tumors, making it an important diagnostic test in SDH-deficient GIST[4]. Schwannoma, along with leiomyoma and leiomyosarcoma, are some notable differentials of GIST. While almost all GISTs are negative for desmin (marker for mature smooth muscle cells) and S100 protein (Schwann cell marker), they are positive in the above-mentioned differentials, i.e., smooth muscle tumors (leiomyoma and leiomyosarcoma), and Schwannomas express desmin and S100 protein positivity, respectively[10]. The most important and life-threatening complication of GIST is GI hemorrhage[11,12]. Tumor growth may cause digestive tract mucosa to become restricted, altering the local mucosal blood supply. Consequently, cell necrosis damages the barrier, which when combined with digestive fluids, can lead to ulcerative bleeding[11]. Tumors larger than 4 cm are likely to cause life-threatening GI bleed due to overlying mucosal and sub
GISTs can present with GI hemorrhage due to erosion of the epithelial layers. It is important to recognize this and evaluate the possible causes of GI hemorrhage, one of which is likely a GIST. The surgical resection in cases of small tumors with tumor-free margins and histopathological analysis for molecular subtyping and confirmation of GIST should be mainstream. Physicians should be aware of the increased risk of GIST recurrence following GI bleeding and should carry out a close follow-up of such patients. Assessment of further need for adjuvant imatinib based on molecular studies and risk assessment criteria for recurrence is also essential.
| 1. | Parab TM, DeRogatis MJ, Boaz AM, Grasso SA, Issack PS, Duarte DA, Urayeneza O, Vahdat S, Qiao JH, Hinika GS. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a comprehensive review. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019;10:144-154. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 198] [Article Influence: 24.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 2. | Sorour MA, Kassem MI, Ghazal Ael-H, El-Riwini MT, Abu Nasr A. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) related emergencies. Int J Surg. 2014;12:269-280. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Carter BM, Bronsert MR, Wilky BA, McCarter MD. Mucosal Ulceration in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor is an Independent Predictor of Progression-Free Survival. J Surg Res. 2023;284:221-229. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Schaefer IM, DeMatteo RP, Serrano C. The GIST of Advances in Treatment of Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2022;42:1-15. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 11.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Sanchez-Hidalgo JM, Duran-Martinez M, Molero-Payan R, Rufian-Peña S, Arjona-Sanchez A, Casado-Adam A, Cosano-Alvarez A, Briceño-Delgado J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A multidisciplinary challenge. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:1925-1941. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Søreide K, Sandvik OM, Søreide JA, Giljaca V, Jureckova A, Bulusu VR. Global epidemiology of gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST): A systematic review of population-based cohort studies. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016;40:39-46. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 579] [Cited by in RCA: 558] [Article Influence: 55.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 7. | Saeidi N, AlAli Y, Boushehry R, Al Safi S. An unusual and life-threatening presentation of a large GIST. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022;99:107666. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Casali PG, Blay JY, Abecassis N, Bajpai J, Bauer S, Biagini R, Bielack S, Bonvalot S, Boukovinas I, Bovee JVMG, Boye K, Brodowicz T, Buonadonna A, De Álava E, Dei Tos AP, Del Muro XG, Dufresne A, Eriksson M, Fedenko A, Ferraresi V, Ferrari A, Frezza AM, Gasperoni S, Gelderblom H, Gouin F, Grignani G, Haas R, Hassan AB, Hindi N, Hohenberger P, Joensuu H, Jones RL, Jungels C, Jutte P, Kasper B, Kawai A, Kopeckova K, Krákorová DA, Le Cesne A, Le Grange F, Legius E, Leithner A, Lopez-Pousa A, Martin-Broto J, Merimsky O, Messiou C, Miah AB, Mir O, Montemurro M, Morosi C, Palmerini E, Pantaleo MA, Piana R, Piperno-Neumann S, Reichardt P, Rutkowski P, Safwat AA, Sangalli C, Sbaraglia M, Scheipl S, Schöffski P, Sleijfer S, Strauss D, Strauss SJ, Hall KS, Trama A, Unk M, van de Sande MAJ, van der Graaf WTA, van Houdt WJ, Frebourg T, Gronchi A, Stacchiotti S; ESMO Guidelines Committee, EURACAN and GENTURIS. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2022;33:20-33. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 152] [Cited by in RCA: 386] [Article Influence: 96.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 9. | Martins D, Costa P, Guidi G, Pinheiro P, Pinto-de-Sousa JA. Jejunal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: A Strange Cause of Massive Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Cureus. 2023;15:e43229. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Hirota S. Differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor by histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:27. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Liu Q, Li Y, Dong M, Kong F, Dong Q. Gastrointestinal Bleeding Is an Independent Risk Factor for Poor Prognosis in GIST Patients. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7152406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Liu Q, Kong F, Zhou J, Dong M, Dong Q. Management of hemorrhage in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a review. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:735-743. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Jabłońska B, Szmigiel P, Wosiewicz P, Baron J, Szczęsny-Karczewska W, Mrowiec S. A jejunal gastrointestinal stromal tumor with massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage treated by emergency surgery: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101:e30098. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Mahmoud S, Salman H. Massive bleeding of a jejunal gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a rare case of a life-threatening presentation. J Surg Case Rep. 2020;2020:rjaa355. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Dualim DM, Loo GH, Rajan R, Nik Mahmood NRK. Jejunal GIST: Hunting down an unusual cause of gastrointestinal bleed using double balloon enteroscopy. A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;60:303-306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Zhou L, Liao Y, Wu J, Yang J, Zhang H, Wang X, Sun S. Small bowel gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a retrospective study of 32 cases at a single center and review of the literature. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14:1467-1481. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Wadhwa M, Nagra N, Singh N, Kumar S, Omer E. Jejunal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Presenting as Hemorrhagic Shock. Cureus. 2024;16:e62155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Neppala S, Caravella J, Chigurupati H, Santos H, Camero A, Canales E. S3597 Jejunal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: A Case Report Presenting With Recurrent Episodes of Melena for 2 Years. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116:S1474-S1475. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 19. | Singh AS, Hecht JR, Rosen L, Wainberg ZA, Wang X, Douek M, Hagopian A, Andes R, Sauer L, Brackert SR, Chow W, DeMatteo R, Eilber FC, Glaspy JA, Chmielowski B. A Randomized Phase II Study of Nivolumab Monotherapy or Nivolumab Combined with Ipilimumab in Patients with Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:84-94. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2006;23:70-83. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1244] [Cited by in RCA: 1336] [Article Influence: 70.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (33)] |
| 21. | Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ, Miettinen M, O'Leary TJ, Remotti H, Rubin BP, Shmookler B, Sobin LH, Weiss SW. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002;33:459-465. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2231] [Cited by in RCA: 2170] [Article Influence: 90.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 22. | Bai S, Sun Y, Xu H. Impact of Gastrointestinal Bleeding on Prognosis and Associated Risk Factors in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am Surg. 2025;91:434-443. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/