Published online Mar 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1474
Peer-review started: December 8, 2023
First decision: December 18, 2023
Revised: December 29, 2023
Accepted: February 18, 2024
Article in press: February 18, 2024
Published online: March 16, 2024
Processing time: 94 Days and 16.2 Hours
Multilocular thymic cyst (MTC) is a rare mediastinal lesion which is considered to occur in the process of acquired inflammation. It is usually characterized by well-defined cystic density and is filled with transparent liquid.
We report on a 39-year-old male with a cystic-solid mass in the anterior mediastinum. Computer tomography (CT) imaging showed that the mass was irregular with unclear boundaries. After injection of contrast agent, there was a slight enhancement of stripes and nodules. According to CT findings, it was diagnosed as thymic cancer.
After surgery, MTC accompanied by bleeding and infection was confirmed by pathological examination. The main lesson of this case was that malignant thymic tumor and MTC of the anterior mediastinum sometimes exhibit similar CT findings. Caution is necessary in clinical work to avoid misdiagnosis.
Core Tip: Multilocular thymic cyst (MTC) is a rare mediastinal lesion, which is considered to occur in the process of acquired inflammation. It is usually characterized by well-defined cystic density and is filled with transparent liquid. Here we reported on a 39-year-old male with a cystic-solid mass in the anterior mediastinum. Computer tomography (CT) imaging showed that the mass was irregular with unclear boundaries. After injection of contrast agent, there was a slight enhancement of stripes and nodules. According to the CT findings, it was diagnosed as thymic cancer. After surgery, MTC accompanied by bleeding and infection was confirmed by pathological examination.
- Citation: Sun J, Yang QN, Guo Y, Zeng P, Ma LY, Kong LW, Zhao BY, Li CM. Multilocular thymic cysts can be easily misdiagnosed as malignant tumor on computer tomography: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(8): 1474-1480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i8/1474.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1474
Thymic cysts account for about 1%-5% of all mediastinal masses[1-3], mainly located in the anterior mediastinum, with a few cases located in the neck[4]. Most of them are circular, elliptical, and irregular in shape, with or without separation. The clinical symptoms of thymic cysts depend upon the location. If the surrounding tissues and organs of the cyst are compressed, breathing difficulties, coughing, thymic pain, and Horner's syndrome may occur. Most thymic cysts have cystic density, a clear boundary and are easy to be diagnosed by medical imaging[5-8]. Some thymic cysts are difficult to diagnose before surgery and can be misdiagnosed as thymoma based on their location and computer tomography (CT) findings. Here, we reported on a case of multilocular thymic cyst (MTC) with hemorrhage and infection in a 39-year-old patient, which was misdiagnosed as thymic carcinoma.
A 39-year-old man came to our hospital with the symptoms of fever, headache and occasional palpitations.
The patient had the symptoms of fever, headache and occasional palpitations.
There was a history of hyperglycemia and no history of muscle weakness, joint pain, chest trauma or any surgery. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was negative.
The random blood glucose was 21.16 mmol/L. Laboratory tests showed that lactate dehydrogenase was 572 U/L, α-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase was 441 U/L and the leukocyte count was 15.7 × 109/L. Electrocardiogram showed atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and elevated T-waves. All tumor markers were negative (Table 1).
| Tumor marker | ng/mL |
| Alpha-fetoprotein | 1.5 |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen | 3 |
| Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 | 48.4 |
| Neuro-specific enolase | 24.8 |
| Ferritin | 1000 |
| Tumor specific factors | 66.2 |
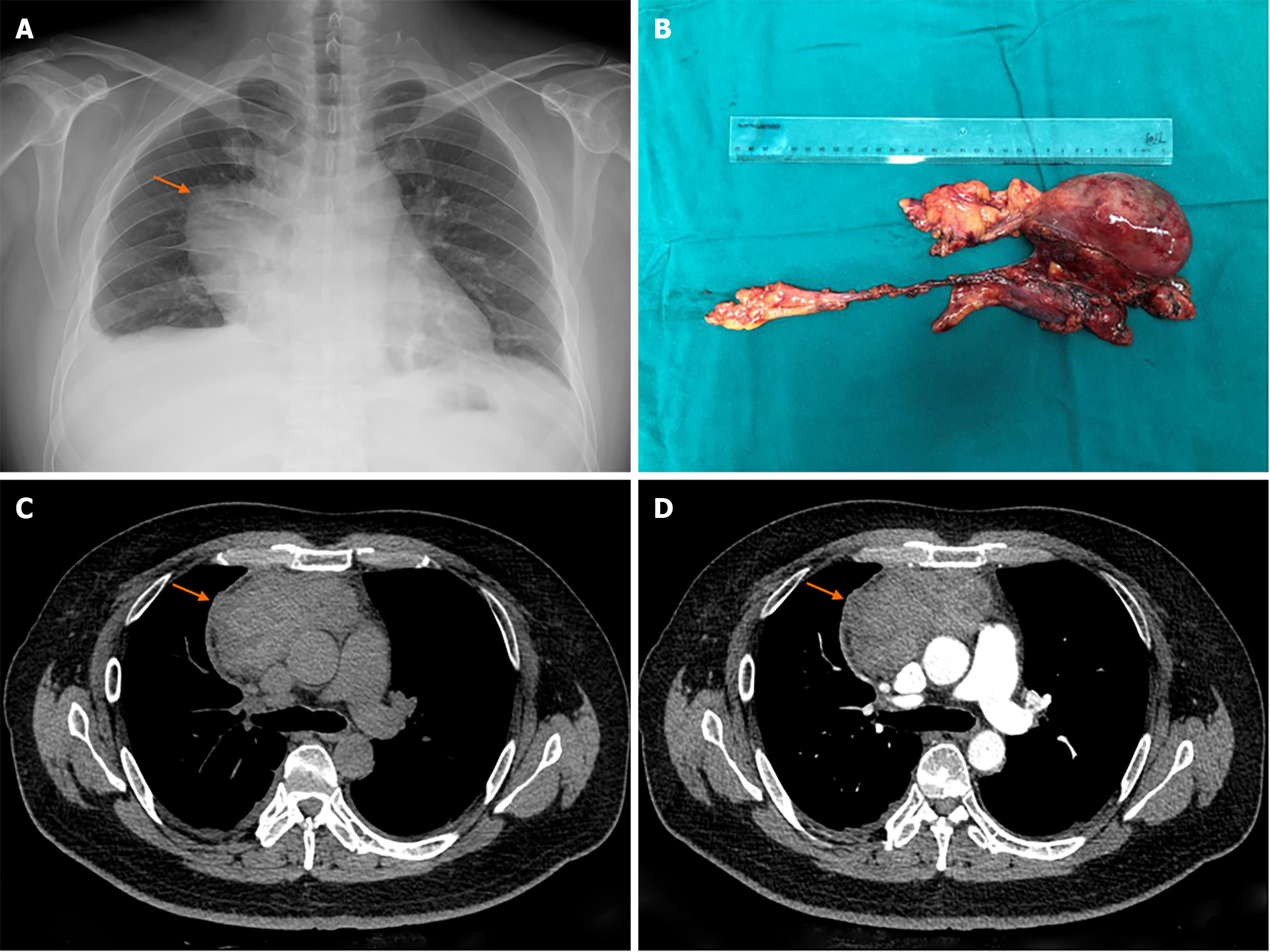
After chest X-ray examination, a mediastinal mass was found (Figure 1). CT examination showed a mass in the anterior mediastinum, with a size of 5.6 cm × 11.3 cm × 10.2 cm. It had uneven density, showing a mixture of cystic density and solid density, with CT values ranging from 30 to 50 HU. Its shape was irregular and the boundary was unclear. No calcifications were observed. After contrast agent injection, a slight enhancement of stripe and nodular shape were found. The mass was adjacent to the ascending aorta, superior vena cava and left brachial vein. The boundary with the above structure was unclear, but the vascular lumen was not invaded. Bilateral pleural effusion was found (Figure 1). According to CT findings, it was diagnosed as a thymic cancer.
This patient was finally diagnosed with acute myocarditis, acute upper respiratory tract infection, MTC with infection in the anterior mediastinum, and diabetes.
Myocarditis was diagnosed based on the abnormal electrocardiogram, high levels of lactate dehydrogenase and α-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, and the clinical symptoms of fever and palpitations. After treatment with cefuroxime, fructose, sodium diphosphate, betaloc, insulin and acarbose, the lactate dehydrogenase and α-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase levels decreased and the leukocytes returned to normal. The mediastinal mass resection was performed 13 d after admission. The mass consisted of a cystic part and a solid part, attached to the adjacent tissues and surrounded the right brachiocephalic vein.
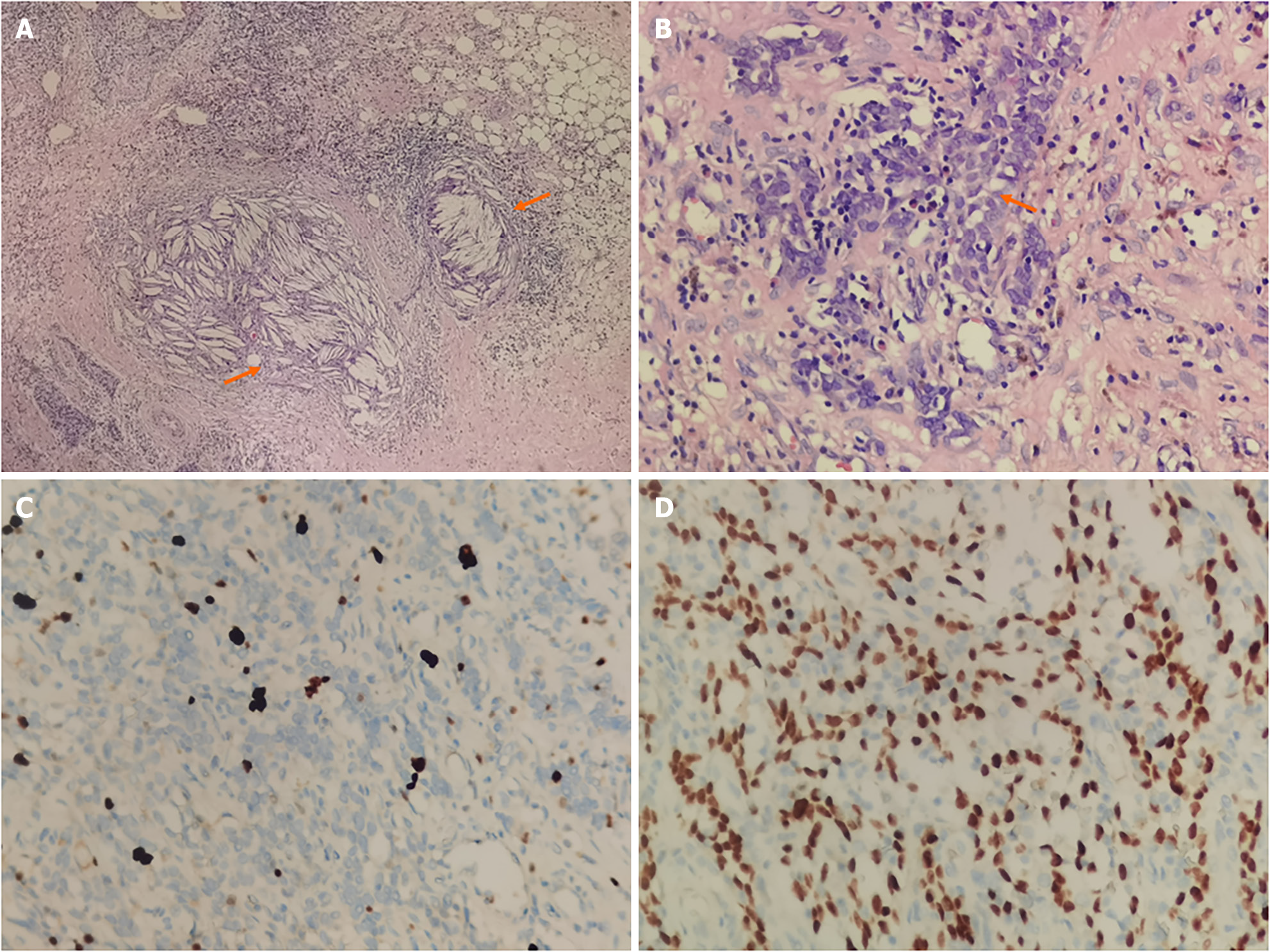
After surgery, histopathological examination was performed. Squamous epithelium, cholesterol crystals, bleeding and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia with CD1 α (-), CD20 (partially positive), CD3 (partially positive), CD5 (partially positive), CD99 (+), CK (+), CK7 (partially positive), CK19 (+), CK5/6 (+), EMA (+), Ki-67 (5% +), p63 (+), CD117 (-) were found and MTC was diagnosed (Figure 2).
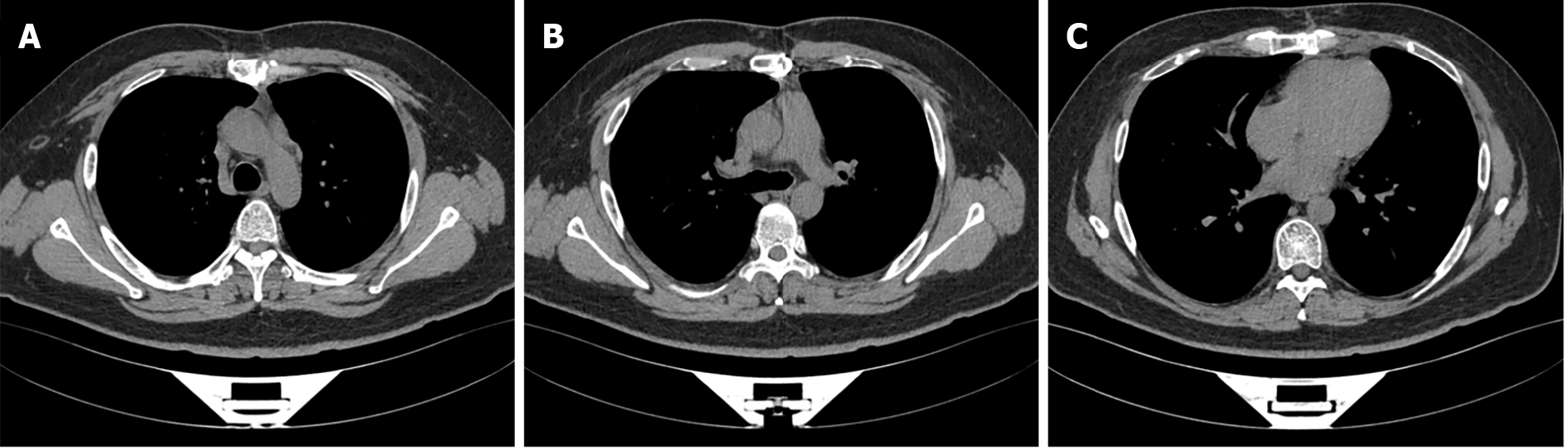
After treatment, all symptoms were improved and the patient was discharged successfully. The patient was tracked for 9 months and no signs of recurrence was found (Figure 3).
According to the morphology, thymic cysts could be divided into two subtypes: monocular thymic cyst and MTC. Monocular thymic cysts are common, while MTC is rare. MTC is generally considered to be formed during inflammation and usually accompanied by immune deficiency diseases (such as HIV), autoimmune diseases (such as arthritis or Sjögren syndrome[9,10]) or thymic trauma[11]. Therefore, MTC is also called an acquired thymic cyst. It is usually filled with transparent liquids, and sometimes may contain cloudy liquids or gelatinous substances due to bleeding. The main histologic features of MTC included the following: multiple cystic cavities, the wall of which was composed of fibrous wall, squamous epithelium, columnar epithelium or cubic epithelium; acute and chronic inflammation with fibrovascular proliferation; necrosis, hemorrhage, cholesterol granuloma and reactive lymphoproliferative[9]. The pathological diagnostic criteria of the World Health Organization are the gold standard for diagnosing MTC. If MTC is small and asymptomatic, surgery is not necessary, which can protect patients from surgical trauma and reduce psychological stress. Imaging evaluation plays an important role in the diagnosis, treatment and decision-making with MTC.
Most MTCs showed cystic density with separation, no enhancement, and no complicated pleural effusion. The CT manifestation of this case was a mixed density mass with cystic and solid components. After injection of contrast agent, there was a slight enhancement of striped and nodular shape. It is very difficult to differentiate it from other mediastinal tumors, especially thymoma. According to the surgical and pathological results, the solid density was formed by bleeding, turbid liquid or colloidal material. The striped and nodular enhancement were caused by cyst wall, septum and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia. Previously, Jin et al[12] has reported 13 cases of thymic cyst with solid density which were misdiagnosed as thymoma. Marvasti et al[13] have reported five mediastinal cysts containing viscous liquid, which showed solid density on CT. The solid density in thymic cysts may be caused by bleeding, lymphoid tissue, viscous liquid containing high levels of protein and hyperplastic thymic tissue at different stages. The solid density has also been reported as cholesterol granuloma and calcification[1,7,14-20] (Table 2). In this case, the boundary of the lesion was not clear, which was easy to be misdiagnosed as a malignant tumor. Usually, unclear boundary was considered as an invasive marker of malignant tumors. According to the histopathological results, there was bleeding, inflammation and reactive lymphoproliferation in this lesion. The unclear boundary might be caused by these factors, which also explains the significant increase of leukocytes. Pleural effusion is also a sign of malignant tumor, which misleads the diagnosis of this disease to a certain extent. Previously, there was no report of MTC complicated with pleural effusion. In this case, the bilateral pleural effusion may be caused by acute myocarditis. However, due to the lack of pleural fluid cytology results, the cause of pleural effusion was not clear.
| Ref. | Number of cases | CT value | Histopathologic of solid density |
| Jin et al [12] | 28 | 38.61 ± 15.01 HU | N |
| Matsumoto et al[14] | 1 | NA | Lymphoid hyperplasia |
| Chalaoui et al[15] | 1 | 35 HU | Hemorrhage |
| Kim et al[16] | 1 | NA | Lymphoid hyperplasia and fibrous septa |
| Mohakud et al[17] | 1 | 60-80 HU (high density areas) | Hemorrhage |
| Nagata et al[19] | 1 | NA | Cholesterol granuloma |
| Choi et al[18] | 8 | Ranged -20 to 17 HU | Thick inflammatory thymic tissue, thymic hyperplasia and calcification |
| Izumi et al[7] | 4 | NA | Foreign body granulomas |
| Ridder et al[20] | 2 | NA | Hemorrhage and cholesterol granuloma |
| Damaskos et al[1] | 1 | NA | Calcification and fragments of thymic tissue |
Through this case, we found that MTC can have both cystic density and solid density simultaneously. Sometimes, due to combined inflammation, bleeding and other reasons, the edge may be unclear and pleural effusion may occur. In these conditions, it is easy to be misdiagnosed with malignant tumors. Full understanding of the special manifestations of the disease, combined with clinical and laboratory examination, is very important for accurate diagnosis.
| 1. | Damaskos C, Garmpis N, Garmpi A, Georgakopoulou VE, Tomos P. Multilocular Thymic Cyst in a Young, Otherwise Healthy Woman: A Case Report. Cureus. 2020;12:e11210. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Kondov G, Kondov B, Srceva MJ, Damjanovski G, Ferati I, Karapetrov I, Topuzovska IK, Tanevska N, Kokareva A. Giant Mediastinal Thymic Cyst. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2017;38:139-145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Araki T, Nishino M, Gao W, Dupuis J, Washko GR, Hunninghake GM, Murakami T, O'Connor GT, Hatabu H. Anterior Mediastinal Masses in the Framingham Heart Study: Prevalence and CT Image Characteristics. Eur J Radiol Open. 2015;2:26-31. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Queralt Martín R, Ibáñez Belenguer M, Martínez Hernández A, Menor Durán PD, Laguna Sastre JM. Thymic Cysts: A Rare Entity in Adults. Cir Esp (Engl Ed). 2021;99:71-73. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Gorospe L, García-Villanueva MJ, García-Cosío-Piqueras M, García-Gómez-Muriel I. Multilocular thymic cyst in a patient with Sjögren syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58:369. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Gill D, Cox T, Bhatia K, Stanbridge R, Layton M. Multilocular thymic cyst presenting with apparent cardiac enlargement on chest radiograph. Postgrad Med J. 2016;92:686. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Izumi H, Nobukawa B, Takahashi K, Kumasaka T, Miyamoto H, Yamazaki A, Sonobe S, Uekusa T, Suda K. Multilocular thymic cyst associated with follicular hyperplasia: clinicopathologic study of 4 resected cases. Hum Pathol. 2005;36:841-844. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Tamagno M, Bibas BJ, Bernardi F, Lian YC, Bammann RH, Fernandez A, Jatene FB. Giant multilocular thymic cyst in an HIV-infected adolescent. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46:1842-1845. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Kawamoto N, Okita R, Inokawa H, Murakami T, Okabe K. Multilocular thymic cyst in a patient with preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;74:136-139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Kondo K, Miyoshi T, Sakiyama S, Shimosato Y, Monden Y. Multilocular thymic cyst associated with Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72:1367-1369. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Jaramillo D, Perez-Atayde A, Griscom NT. Apparent association between thymic cysts and prior thoracotomy. Radiology. 1989;172:207-209. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Jin Z, Wu Y, Wang Y, Pu Z, Wang J, Li D, Hu B, Jin Y, Zheng J. Multislice computed tomography performance in differential diagnosis of high-density thymic cyst and thymoma in lesions less than 3 cm. Thorac Cancer. 2018;9:1300-1304. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Marvasti MA, Mitchell GE, Burke WA, Meyer JA. Misleading density of mediastinal cysts on computerized tomography. Ann Thorac Surg. 1981;31:167-170. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Matsumoto S, Mori Y, Takiya H, Iwata H, Shirahashi K. [Multilocular thymic cyst associated with rheumatoid arthritis]. Kyobu Geka. 2012;65:205-208. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Chalaoui J, Samson L, Robillard P, Constantin A, Dussault RG. Cases of the day. General. Benign thymic cyst complicated by hemorrhage. Radiographics. 1990;10:957-958. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Kim JS, Cha EJ. A Rare Case of Multilocular Thymic Cyst with Follicular Lymphoid Hyperplasia: Radiologic and Histopathologic Features. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;50:161-163. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Mohakud S, Sethy M, Naik S, Mohapatra PR. Giant cervicomediastinal thymic cyst in an elderly: diagnosis by multimodality imaging and fine-needle aspiration cytology with immunocytochemistry. BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13:e235425. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Choi YW, McAdams HP, Jeon SC, Hong EK, Kim YH, Im JG, Lee SR. Idiopathic multilocular thymic cyst: CT features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:881-885. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Nagata S, Ishihara M, Omasa M, Nakanishi T, Motoyama H. Multifocal thymic cysts with cholesterol granuloma. Respirol Case Rep. 2018;6:e00361. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Ridder GJ, Boedeker CC, Kersten AC. Multilocular cervical thymic cysts in adults. A report of two cases and review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2003;260:261-265. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Routray C, United States S-Editor: Zhang H L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Yu HG