Published online Jul 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4301
Revised: May 1, 2024
Accepted: May 24, 2024
Published online: July 16, 2024
Processing time: 129 Days and 18.7 Hours
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) poses a significant quandary about public health. It is challenging to study the literature in a particular discipline comprehensively to
To examine the 35-year scientific evolution of articles focused on HCV.
This study examined the 35-year scientific evolution of articles focused on HCV. Our study utilized the Web of Science database. The study encompassed a total of 11930 articles.
Regarding the cumulative count of articles, the leading countries are the United States, Japan, and Italy. Rice CM is the author with the highest recorded H-index and G-index values. The journal with the highest recorded H-index and G-index values is the Journal of Virology. The Journal of Viral Hepatitis contributed 10.94% of the articles, whereas the Journal of Virology published 9.68%. According to the stra
This study provides valuable information about 40 years of academic knowledge on HCV.
Core Tip: In contemporary times, a substantial escalation in the accumulation of knowledge occurs annually. The assi
- Citation: Tok D. Analysis of articles on hepatitis C by scientific mapping: 1989-2022. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(20): 4301-4316
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i20/4301.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4301
Hepatitis C virus (HCV), a constituent of the Flaviviridae family, is characterized as a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus with an enveloped, globular structure measuring approximately 55 nm in diameter. It exerts its influence upon a demographic exceeding 58 million individuals worldwide. Its prevalence within developed nations ranges bet
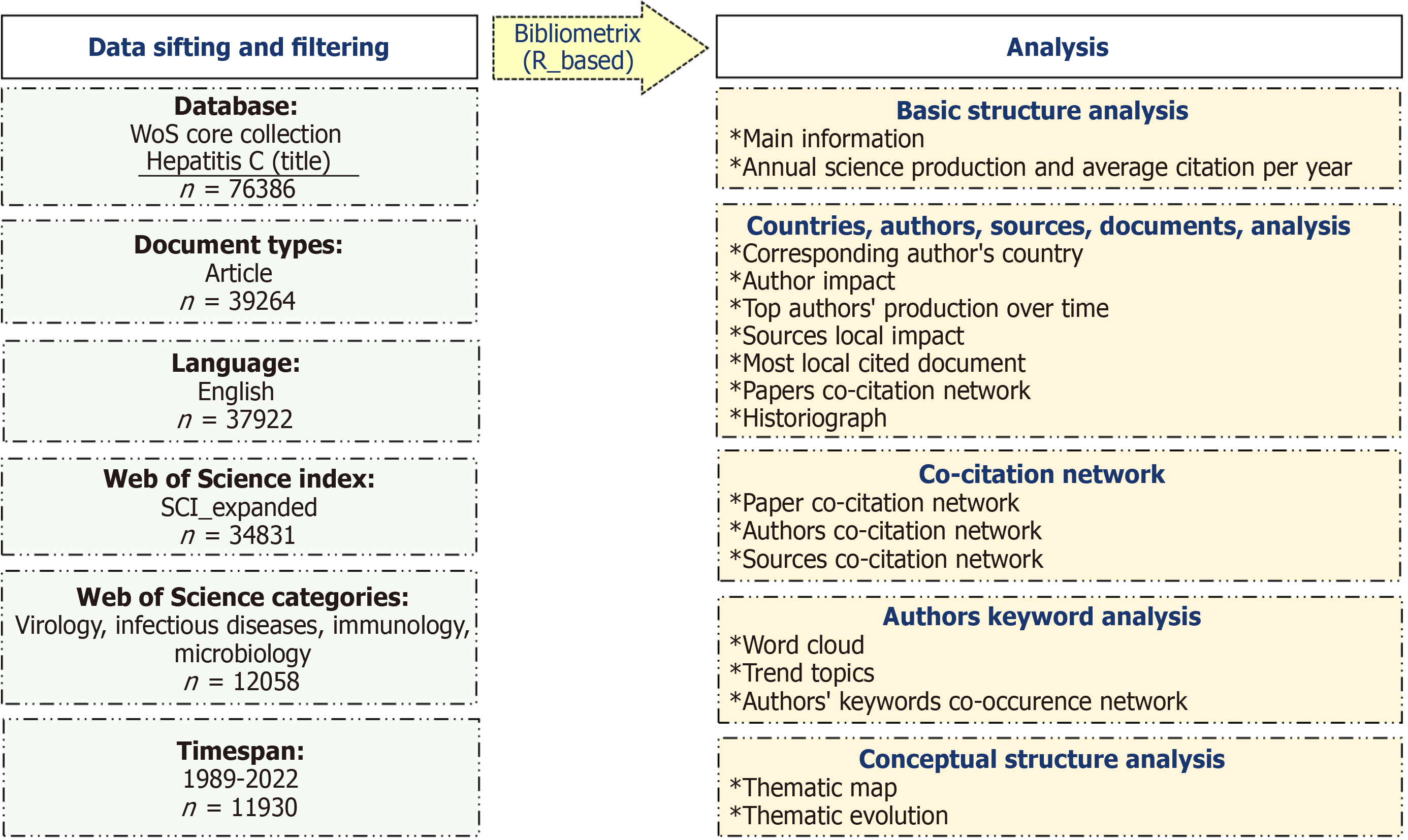
The framework of this study is shown in Figure 1. Our study utilized the Web of Science (WoS) database, renowned for its extensive purview. WoS facilitates access to the complete texts, citation data, or abstracts of scientific articles[9]. The database was searched on May 6, 2023 for our research. The acquired data underwent a meticulous classification and filtration process. The expanse of the ongoing year 2023 was excluded from the scope. The study encompassed a total of 11930 articles. Research and review articles published in English were included in the analysis. For the analysis, the Bi
Basic structure analysis: This section analyzes the annual scientific article production rates and the corresponding yearly average citation counts within the field of HCV. The graph generated has been augmented with the coefficient of determination (R²) as an indicator of reliability, an inclination line depicting trends, and an equation delineating the mathematical relationship.
Countries, authors, sources, and documents analysis: In this section, corresponding author's country, author impact, top-authors’ production over time, source local impact, and most local cited document analyses have been conducted.
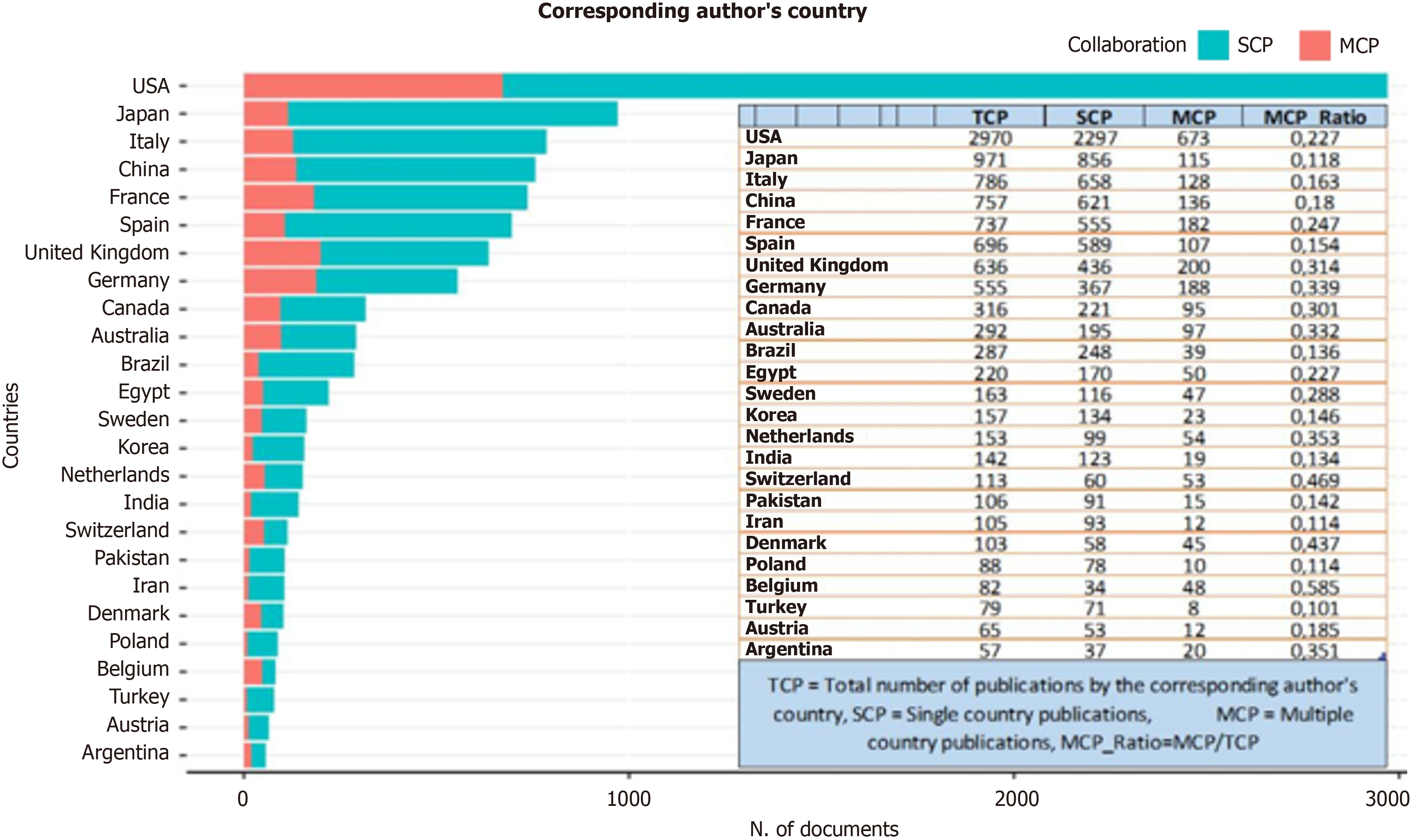
In the analysis of the corresponding author's country, the total number of publications (NP) and the analyses of single- and multiple-country publications (MCP) have been examined. Furthermore, the MCP ratio was calculated. The MCP ratio is derived from the quotient of the count of publications with involvement from multiple countries and the overall count of publications across all countries.
In the analyses of author impact and source local impact, the indices H, G, and M have been computed, along with total citations (TC), NP, and publication year starting. The metric citations per paper (TC/NP) has also been calculated. The H-index, introduced to science by Hirsch[11], measures a researcher's productivity and effectiveness[11]. Egghe[12] introduced the G-index, wherein articles garnering more citations hold particular significance[12]. The analysis also en
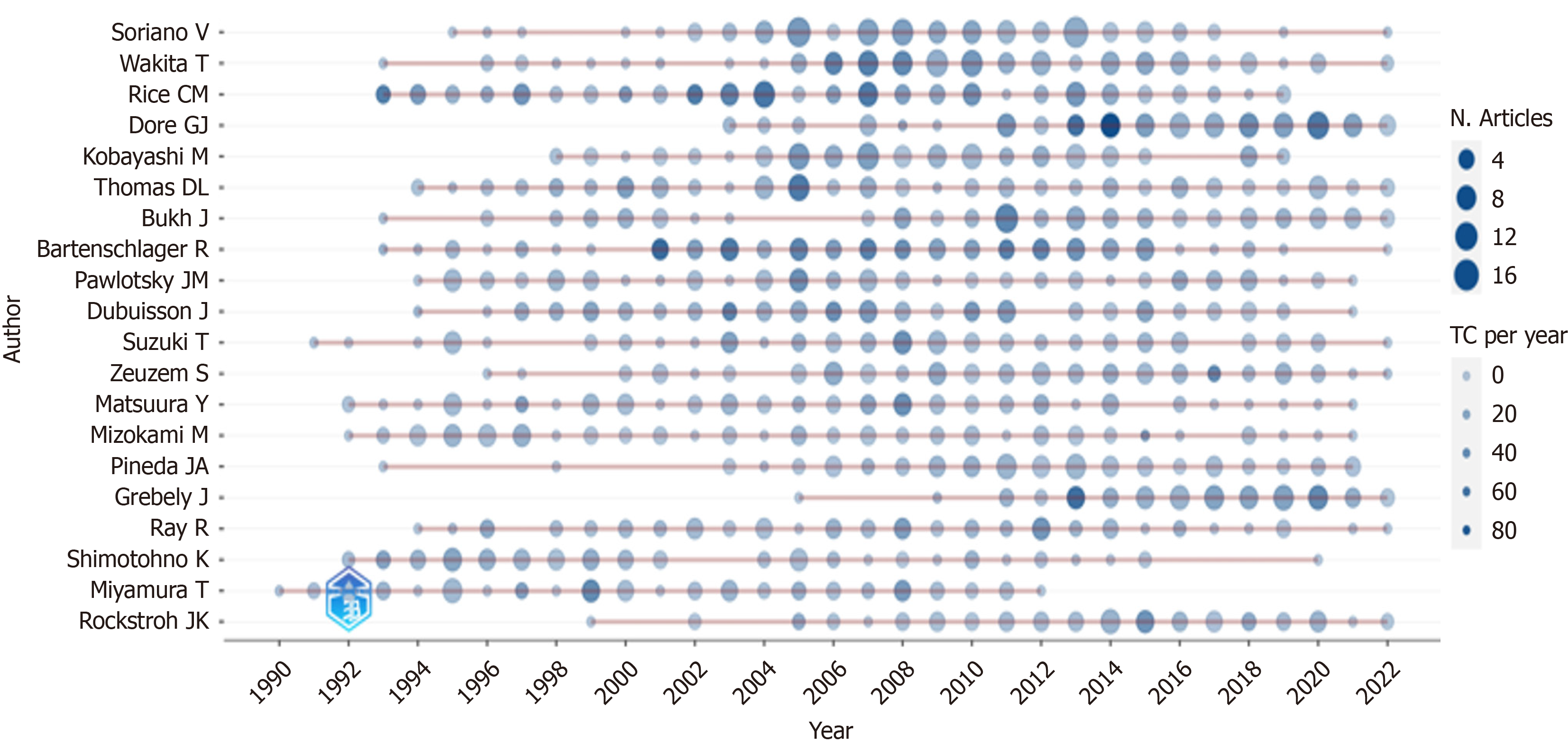
"Top Authors' Production over Time" illustrates the duration during which prominent authors in the field of HCV have contributed to the domain. The magnitudes of the circles correspond to the NP generated in a given year. The intensity of the circle's color signifies the volume of citations accrued by that year's commencement.
The primary objective of analyses about most local cited documents is to scrutinize the intricacies and intellectual framework within the realm of HCV. In the domain of citation analyses, both local (LC) and global citations (GC), the ratio of LC to GC (LC/GC), annual LC [LC/year 2023-year of publication (YYP)], and annual GC (GC/YYP) have been meticulously computed. The YYP value is computed as "2023-Year of Publication" as delineated in its methodology. No
Co-citation network analysis: Co-citation network analysis discusses the development and utilization of shared citations for analysis within the context of medical research. The paper in question has undergone analyses involving co-citation networks of authors and sources. The Louvain algorithm has been employed for the analysis, focusing on examining the initial 30 articles. The outcomes of this analysis are visually represented through clusters distinguished by varying colors. Within these clusters, each circle symbolizes an article, an author, or a source. The size of these circles enlarges proportionally with the escalation of co-citation occurrences. The interconnecting lines amidst these circles delineate relation
Authors’ keyword analysis: Keywords are the defining elements of an article and are determined by the authors. Key
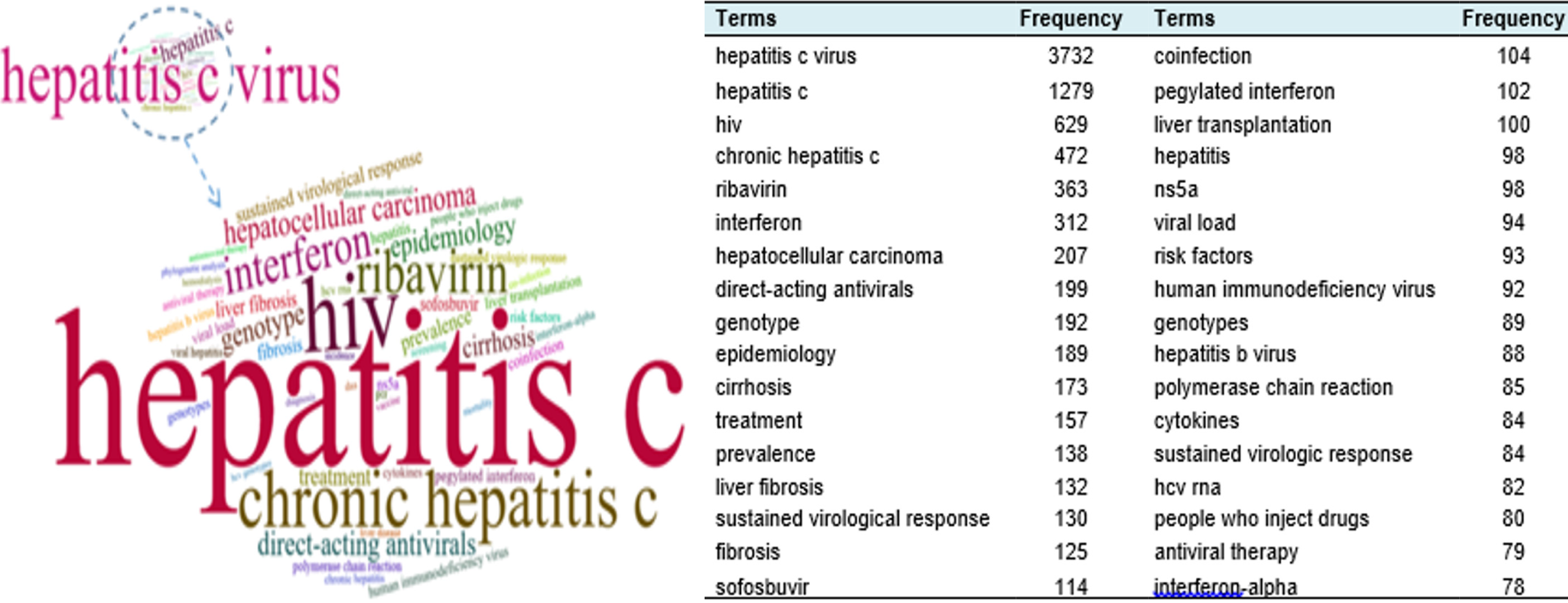
A word cloud was generated during the keyword analysis. This concept represents the graphical depiction of the most frequently investigated subject matters within the HCV domain[15]. The prominence of keywords within the word cloud corresponds to the extent of their investigation frequency. In our study, the first 50 keywords most commonly employed by authors were incorporated into the analysis.
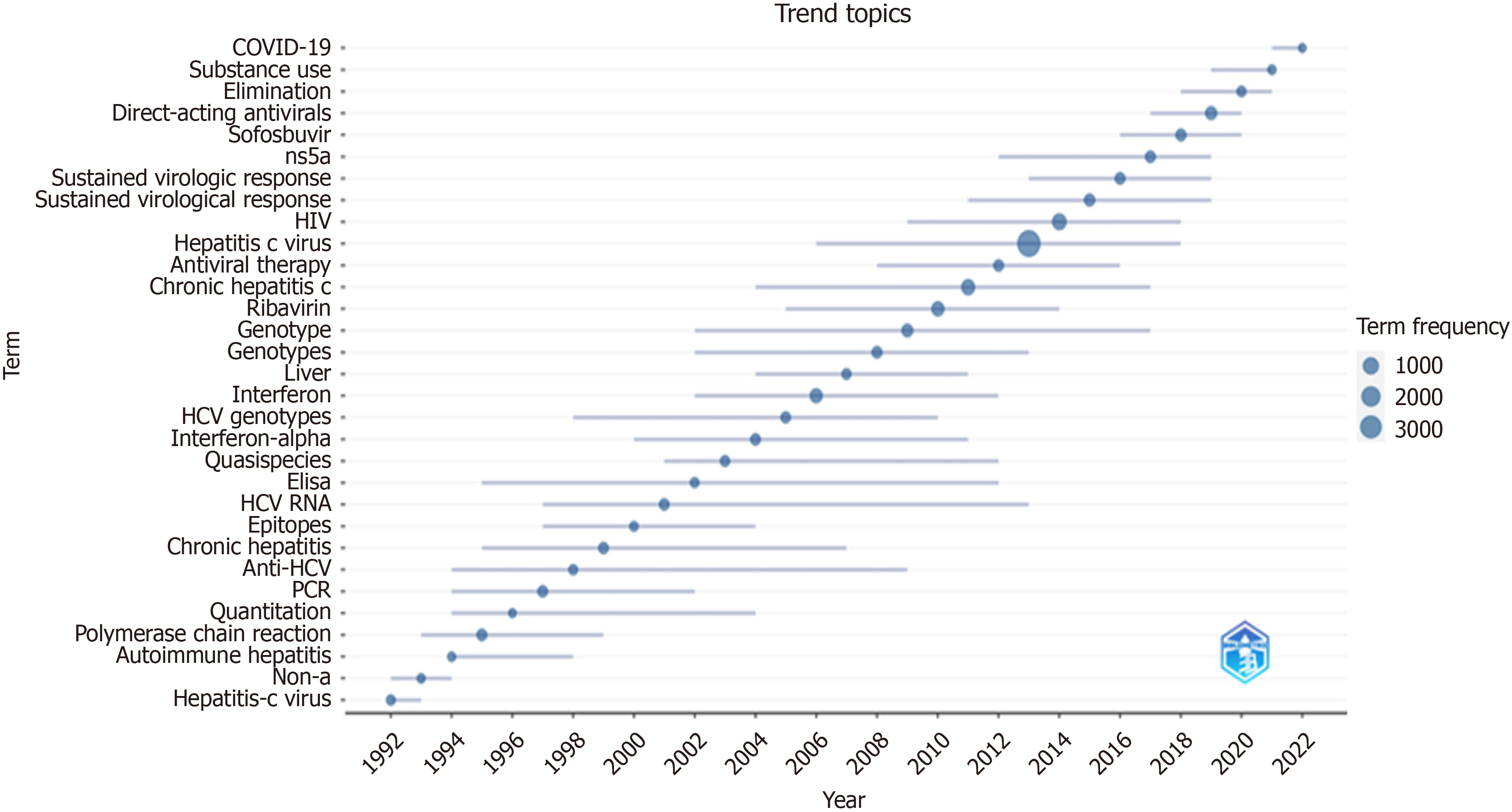
Trend topic analysis was performed to ascertain the years in which keywords began to be utilized and reached their peak frequency. Keywords employed at least five times each year were included in the analysis.
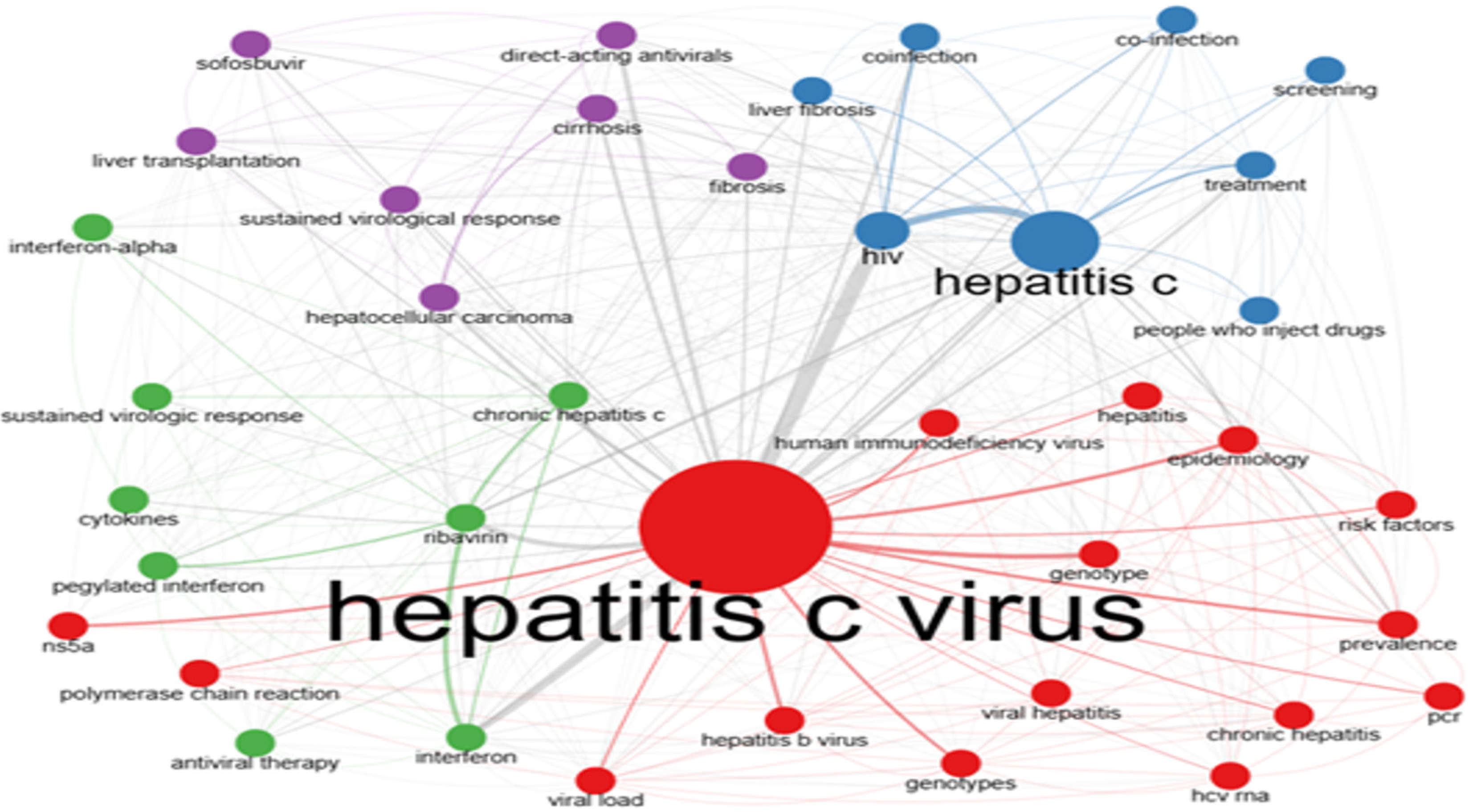
An analysis of the co-occurrence network of authors' keywords was conducted. This analysis encompassed 39 key
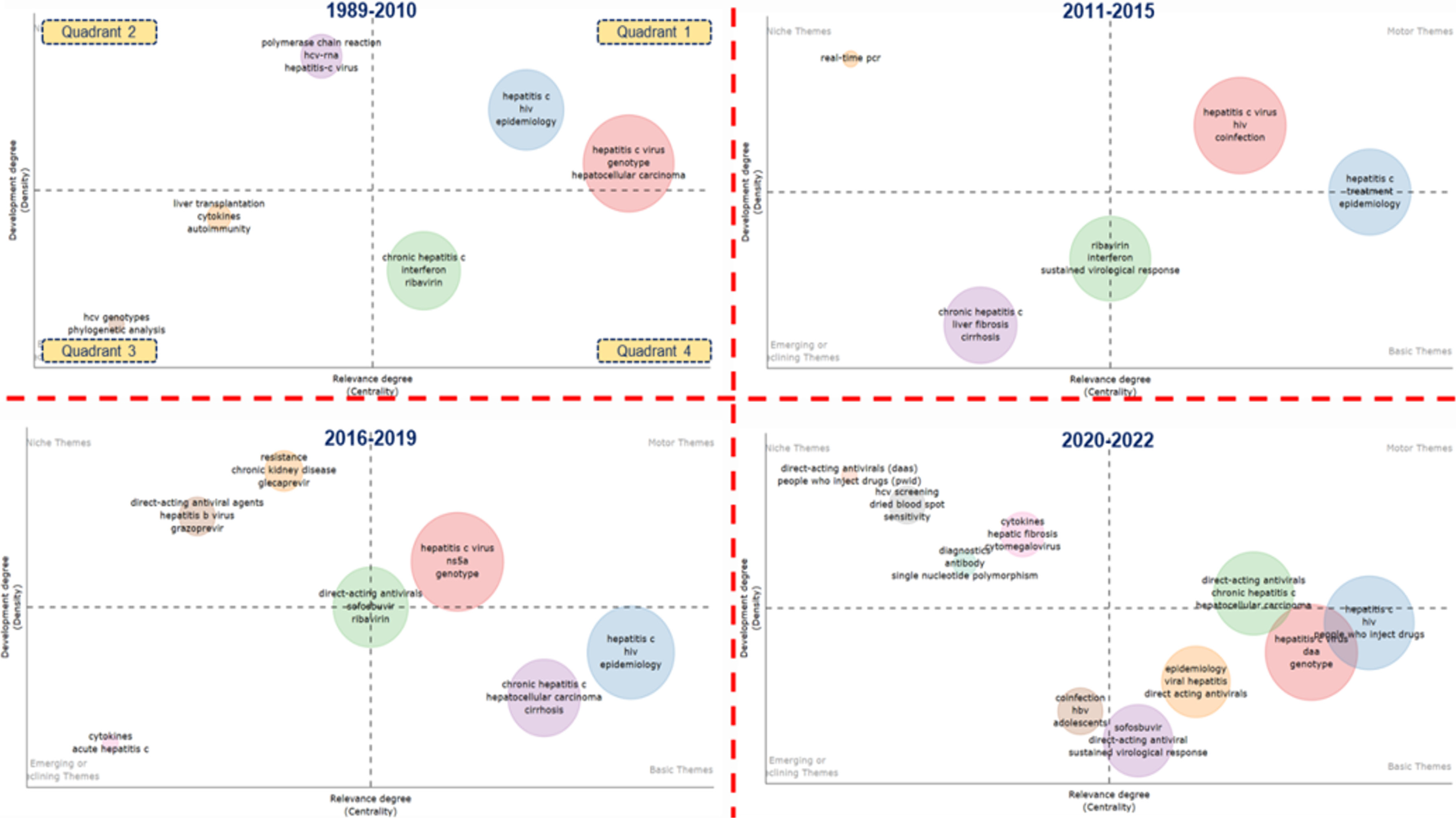
Conceptual structure analysis: A thematic map or strategic diagram has been devised using the most frequently em
A four-period Thematic Evolution Map has been constructed to analyze the themes' transformation and progression over the years. The Thematic Evolution Map consists of diverse nodes, distinguished by colors and sizes, formed by the keywords. The size of the nodes is directly proportional to the number of keywords. Interconnecting lines among the nodes illustrate the direction of thematic cluster evolution[18].
For the analysis in the article, ultimately, open sources were used. The article does not contain any human or animal elements. Therefore, ethics committee permission is not required.
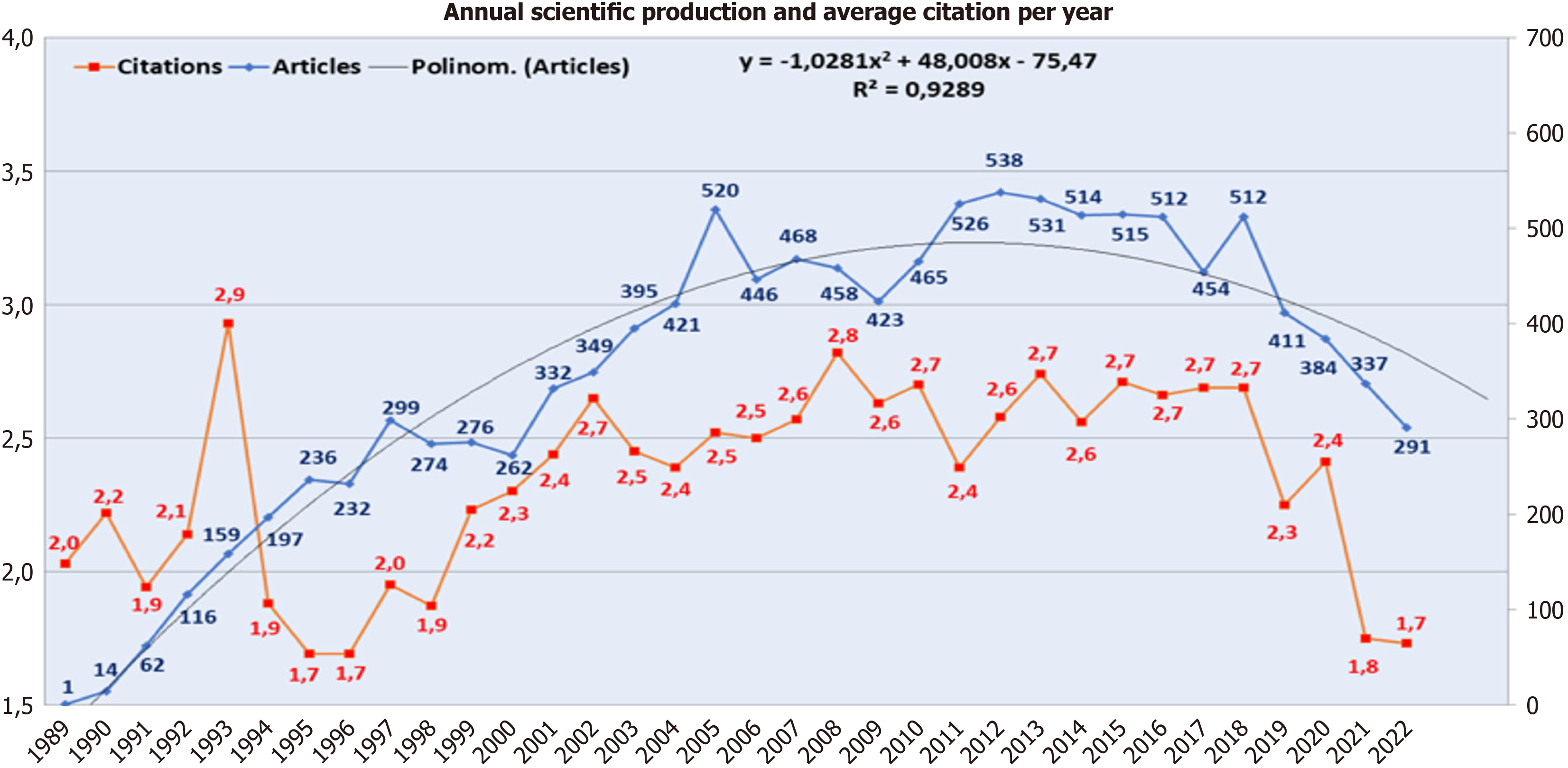
The included corpus comprises 11930 articles generated between 1989 and 2022. These articles have been disseminated across 292 distinct journals. The cumulative assembly of authors exceeds a staggering 43000 individuals. Manifesting a noteworthy annual escalation at 18.76%, the per-article citation quotient nearly approximates 35 (Figure 2).
The number of published articles has shown an ascending trajectory until 2018. The zenith in terms of article count was reached in the year 2012. The year 1993 stands as the epoch in which these articles garnered the highest citation fre
The countries of origin of the corresponding authors of the articles are delineated for the top 25 nations, as illustrated in Figure 4. Concerning the cumulative count of articles, the leading three countries are the United States, Japan, and Italy. In the case of articles featuring authors from multiple countries, the sequence is as follows: United States, United King
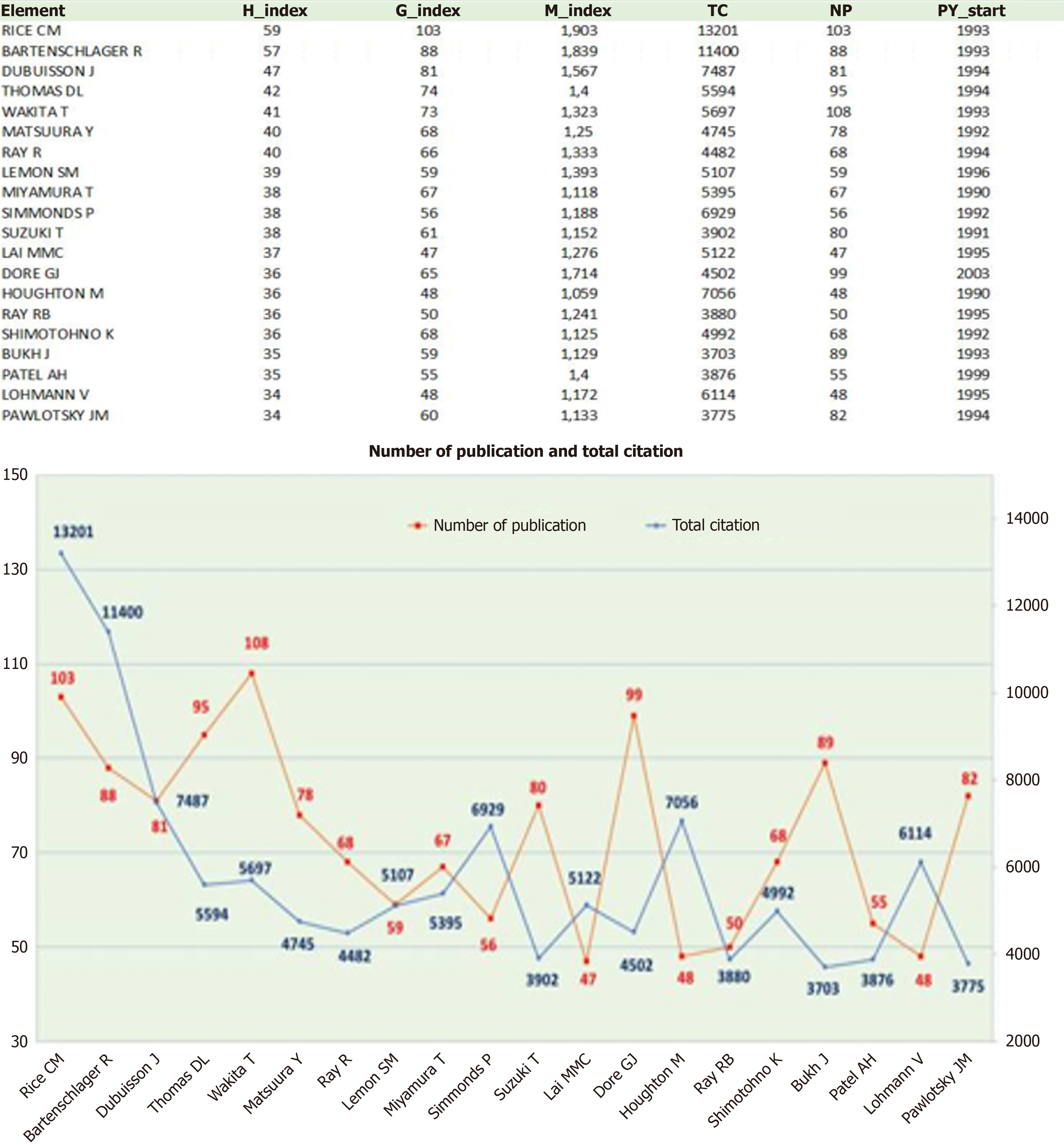
Figure 5 presents statistics about the most influential top 20 authors based on their H-index values. Within the scope of our study, Rice CM is the author with the highest recorded H-index and G-index values. The respective H and G-index values attributed to this author are 59 and 103. It is essential to underscore that Bartenschlager R. and Dubuisson J. closely trail this author across both indices.
From the perspective of the M-index, Rice CM is the most influential author, akin to other indices. Bartenschlager R, Dore GJ, and Dubuisson J. Rice CM follow this author with the highest aggregate citation count. Wakita T holds the record for the most prolific article publications. Noteworthy is Dore GJ, who embarked on their publishing journey later than other researchers yet has garnered attention with 99 articles and 4502 citations.
Having authored 48 articles, Houghton M has achieved 147 citations per article citation-to-article ratio, bolstered by a substantial 7056 citations. Bartenschlager R and Rice CM follow this trend.
Suzuki T emerges as the author with the most extended duration of article production in the field of HCV. Since 1991, Suzuki T's publishing activities have remained active (Figure 6). Among the foremost 20 authors, 11 maintain their scholarly output. Notably in 2013, Soriano V produced 16 articles, earning the accolade of the most prolific author within a year. Furthermore, in 2014, Dore GJ acquired 87 citations, establishing their prominence as the most referenced author within a year.
According to the H-index ranking, the first 20 journals are listed in Table 1. These journals have a collective publication share of 61.09% of the total articles. The Journal of Virology claims the highest H- and G-index values. The Journal of Viral Hepatitis contributed 10.94% of the articles, whereas the Journal of Virology published 9.68%. The Journal of Virology boasts the highest citation frequency, followed by the Journal of Viral Hepatitis. The Journal of Immunology holds the pinnacle regarding the average citation per article. Plos Pathogens, a journal that commenced its publication trajectory later than its counterparts, has rapidly garnered a substantial impact. Despite its delayed inception in 2007, the journal's H- and G-index values stand at 53 and 89, respectively.
| Journal | H-index | G-index | TC | NP | TC/NP | PY_start |
| Journal of Virology | 159 | 233 | 100986 | 1155 | 87.4 | 1991 |
| Clinical Infectious Diseases | 80 | 121 | 21782 | 441 | 49.4 | 1992 |
| Journal of Infectious Diseases | 80 | 122 | 23751 | 465 | 51.1 | 1990 |
| Journal of General Virology | 76 | 130 | 22469 | 423 | 53.1 | 1990 |
| Journal of viral hepatitis | 72 | 101 | 30726 | 1305 | 23.5 | 1995 |
| Journal of Medical Virology | 66 | 90 | 23289 | 895 | 26.0 | 1990 |
| Virology | 66 | 107 | 15059 | 271 | 55.6 | 1992 |
| Journal of Clinical Microbiology | 62 | 94 | 14249 | 349 | 40.8 | 1991 |
| Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy | 59 | 91 | 11924 | 281 | 42.4 | 1996 |
| Transplantation | 59 | 83 | 9569 | 221 | 43.3 | 1991 |
| Journal of Immunology | 53 | 92 | 8595 | 98 | 87.7 | 1991 |
| Plos Pathogens | 53 | 89 | 8234 | 114 | 72.2 | 2007 |
| AIDS | 52 | 85 | 9838 | 263 | 37.4 | 1995 |
| Antiviral Therapy | 35 | 46 | 3501 | 173 | 20.2 | 1998 |
| Journal of Clinical Virology | 34 | 49 | 3665 | 184 | 19.9 | 1999 |
| JAIDS-Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome | 33 | 51 | 3092 | 99 | 31.2 | 2002 |
| Antiviral Research | 32 | 51 | 3715 | 158 | 23.5 | 1994 |
| Clinical and Experimental Immunology | 32 | 50 | 2983 | 88 | 33.9 | 1992 |
| International Virology | 32 | 46 | 2921 | 144 | 20.3 | 1994 |
| Journal of Virology Methods | 30 | 48 | 3310 | 162 | 20.4 | 1991 |
The most extensively referenced 20 articles based on LC values are presented in Table 2. Notably, the works authored by Simmonds P (1993), Takamizawa A (1991), and Blight KJ (2002) exhibit the highest LC values within this compilation. Conversely, concerning GC values, the articles authored by Okamoto H (1992), Simmonds P (1993), and Lechner F (2000) manifest as prominently significant. The pinnacle LC/YYP value resides within the work of Blight KJ (2002), whereas the highest GC/YYP value finds its place within the discourse of Lechner F (2000). Demonstrating utmost contemporary influence, the article authored by Bartosch B (2003) distinguishes itself. The LC and GC values stand at 264 and 888, respectively.
| Author | Journal | Year | LC | LC/YYP | GC | GC/YYP | LC/GC ratio |
| Simmonds P | Journal of General Virology | 1993 | 419 | 13.967 | 1248 | 41.600 | 33.57 |
| Takamizawa A | Journal of Virology | 1991 | 353 | 11.031 | 921 | 28.781 | 38.33 |
| Blight KJ | Journal of Virology | 2002 | 346 | 16.476 | 950 | 45.238 | 36.42 |
| Grarakoul A | Journal of Virology | 1993 | 331 | 11.033 | 801 | 26.700 | 41.32 |
| Okamoto H | Journal of Experimental Medicine | 1992 | 323 | 10.419 | 1262 | 40.710 | 25.59 |
| Lechner F | Journal of Experimental Medicine | 2000 | 288 | 12.522 | 1066 | 46.348 | 27.02 |
| Bartosch B | Journal of Experimental Medicine | 2003 | 264 | 13.200 | 888 | 44.400 | 29.73 |
| Thimme R | Journal of Experimental Medicine | 2001 | 253 | 11.500 | 952 | 43.273 | 26.58 |
| Grarakoul A | Journal of Virology | 1993 | 217 | 7.233 | 543 | 18.100 | 39.96 |
| Stuyver L | Journal of General Virology | 1993 | 215 | 7.167 | 695 | 23.167 | 30.94 |
| Okamoto H | Virology | 1992 | 205 | 6.613 | 551 | 17.774 | 37.21 |
| Okamoto H | Journal of General Virology | 1991 | 197 | 6.156 | 434 | 13.563 | 45.39 |
| Tsukiyamakoha K | Journal of Virology | 1992 | 195 | 6.290 | 777 | 25.065 | 25.10 |
| Gale MJ | Virology | 1997 | 195 | 7.500 | 675 | 25.962 | 28.89 |
| Graham CS | Clinical Infectious Diseases | 2001 | 195 | 8.864 | 734 | 33.364 | 26.57 |
| Egger D | Journal of Virology | 2002 | 193 | 9.190 | 644 | 30.667 | 29.97 |
| Cooper S | Immunity | 1999 | 190 | 7.917 | 675 | 28.125 | 28.15 |
| Chan SW | Journal of General Virology | 1992 | 180 | 5.806 | 407 | 13.129 | 44.23 |
| Dubuisson J | Journal of Virology | 1994 | 179 | 6.172 | 350 | 12.069 | 51.14 |
| Krieger N | Journal of Virology | 2001 | 179 | 8.136 | 431 | 19.591 | 41.53 |
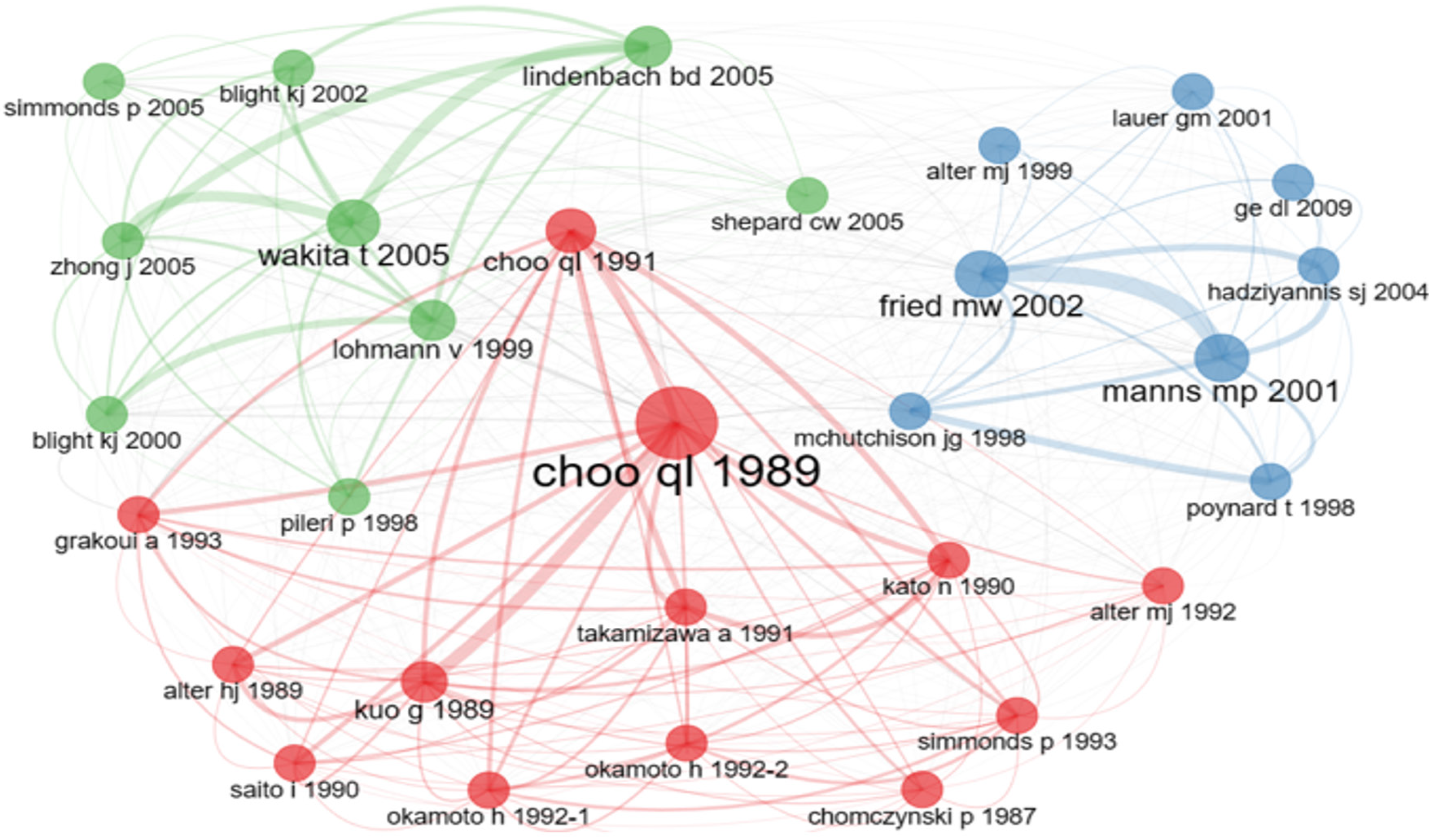
The initial 30 articles were analyzed (Figure 7). The co-citation network is comprised of three distinct clusters denoted by chromatic circles. These clusters consist of 13, 9, and 8 articles, respectively, with each circle serving as a graphical representation of an individual article. Foremost among these is the article authored by Choo QL (1989), distinguished by the highest frequency of shared citations. Subsequently, in prominence, the articles authored by Fried MW (2002) and Manns MP (2001) follow. The thickness of the interconnecting lines signifies the preeminence of the article dyad composed of Fried MW (2002) and Manns MP (2001), the most prominently referenced pair within the network.
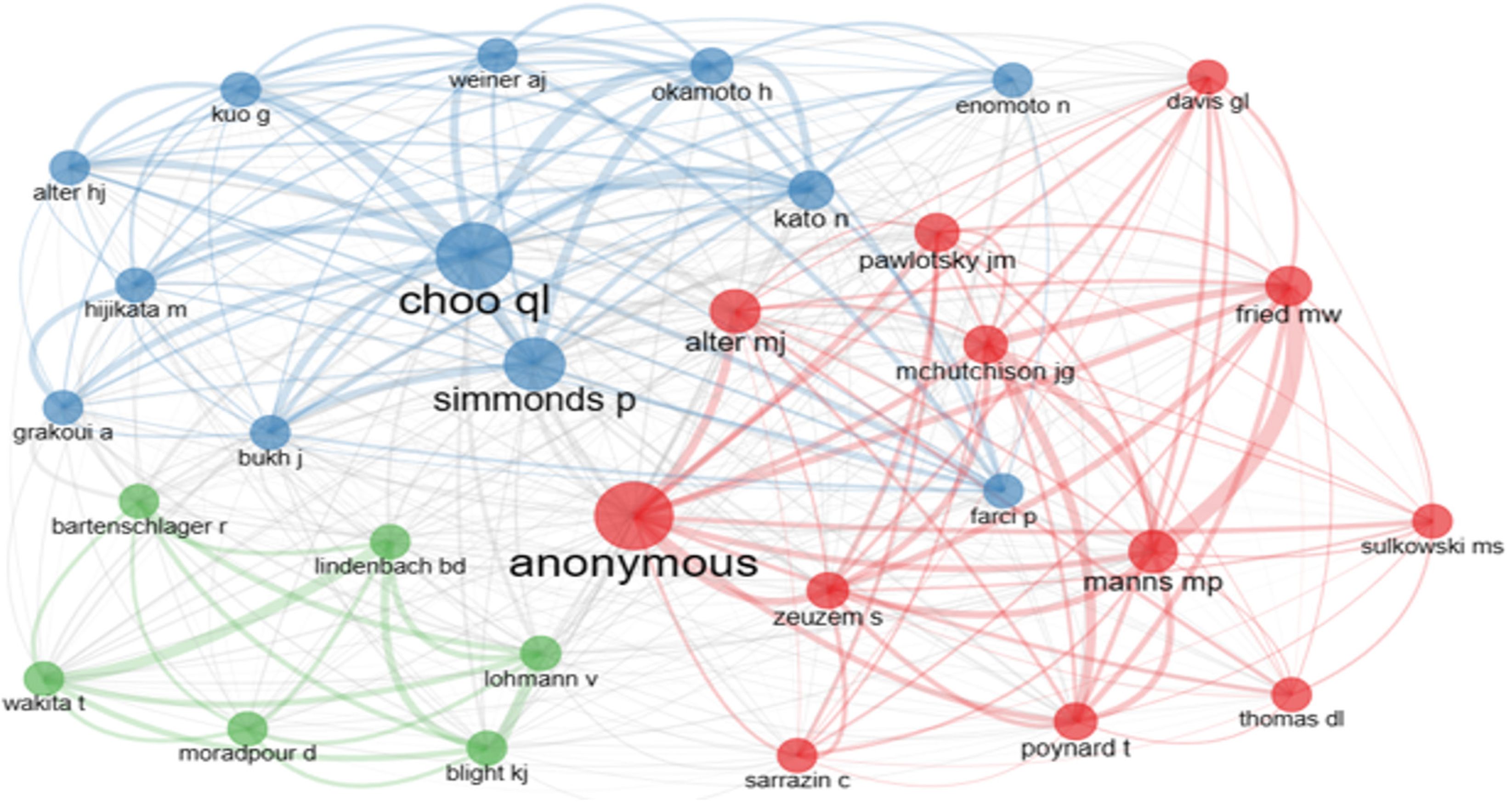
The co-citation network is partitioned into three clusters of colored circles (Figure 8). The red, blue, and green clusters have 12, 12, and 6 authors, respectively. Within the red cluster, the preeminent recipient of citations is the entity denoted as Anonymous, symbolizing institutional publications. The dominant author within the blue cluster is Choo QL. Authors with the highest shared citation incidences include Choo QL, Simmonds P, and Manns MP. By line thicknesses, the most heavily co-cited authors are Manns MP–Fried MW, Choo QL–Kuo G, and Wakita T–Lindenbach BD.
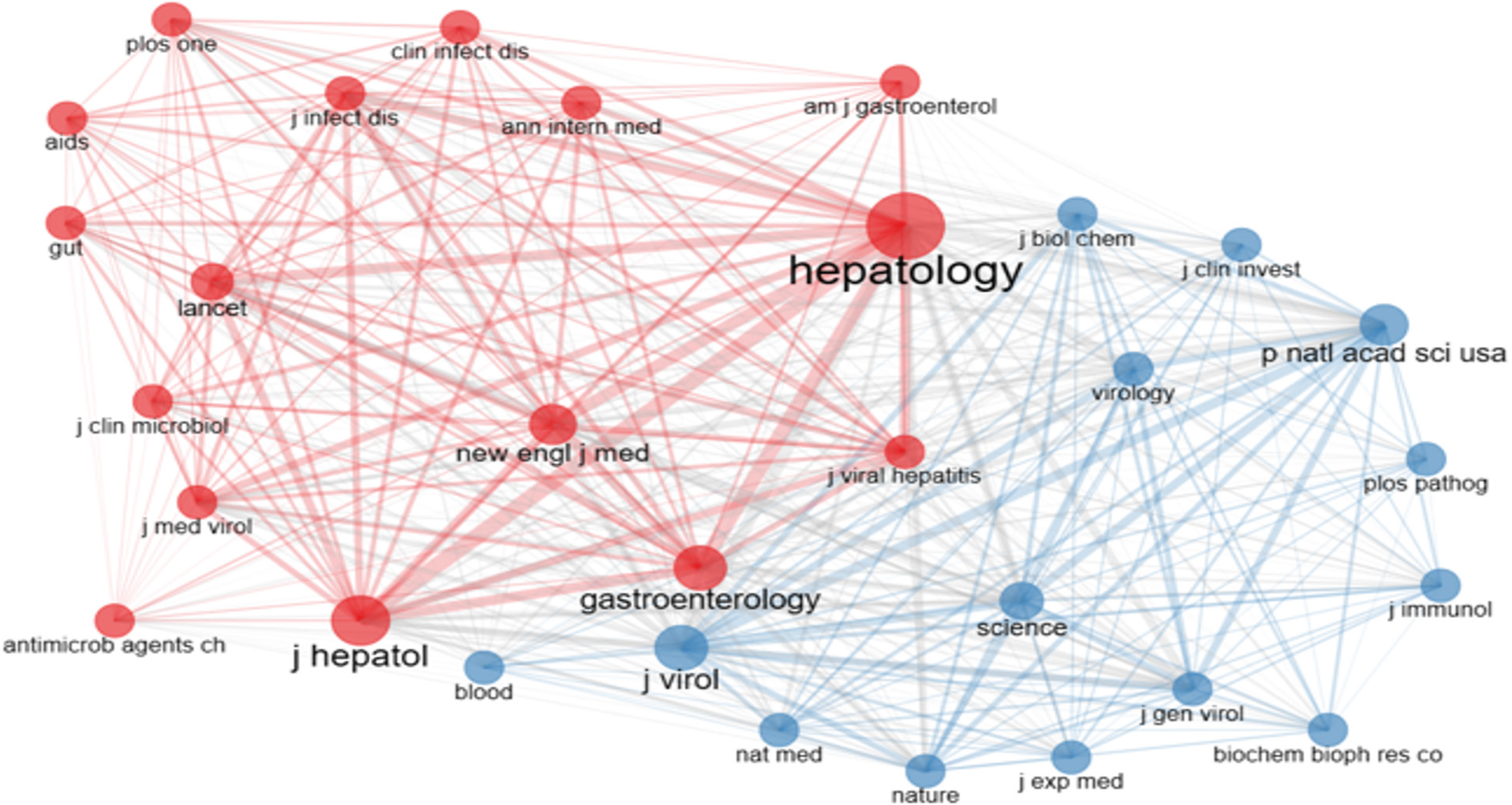
Sources co-citation network analysis is shown in Figure 9. It reveals the presence of two distinct clusters of nodes. Each node assumes the representation of a journal. The cluster denoted by red exhibits a heightened degree of centrality and encompasses 16 distinct journals. Notably, the journal "Hepatology" is central to this cluster. Among the journals encom
Figures 10 and 11 present the first 50 of the most frequently employed keywords and trend topics. The word cloud and frequency table discern the most recurrent keywords.
Within the scrutinized analyses, between 1992 and 2000, terms such as HCV, non-a autoimmune hepatitis, and poly
Figure 12 depicts a network of co-occurrences among the keywords. The keywords are categorized into four clusters, distinguished by different colors. The red cluster represents HCV, while the blue one signifies hepatitis C-related key
The thematic map or strategic diagram is shown in Figure 13.
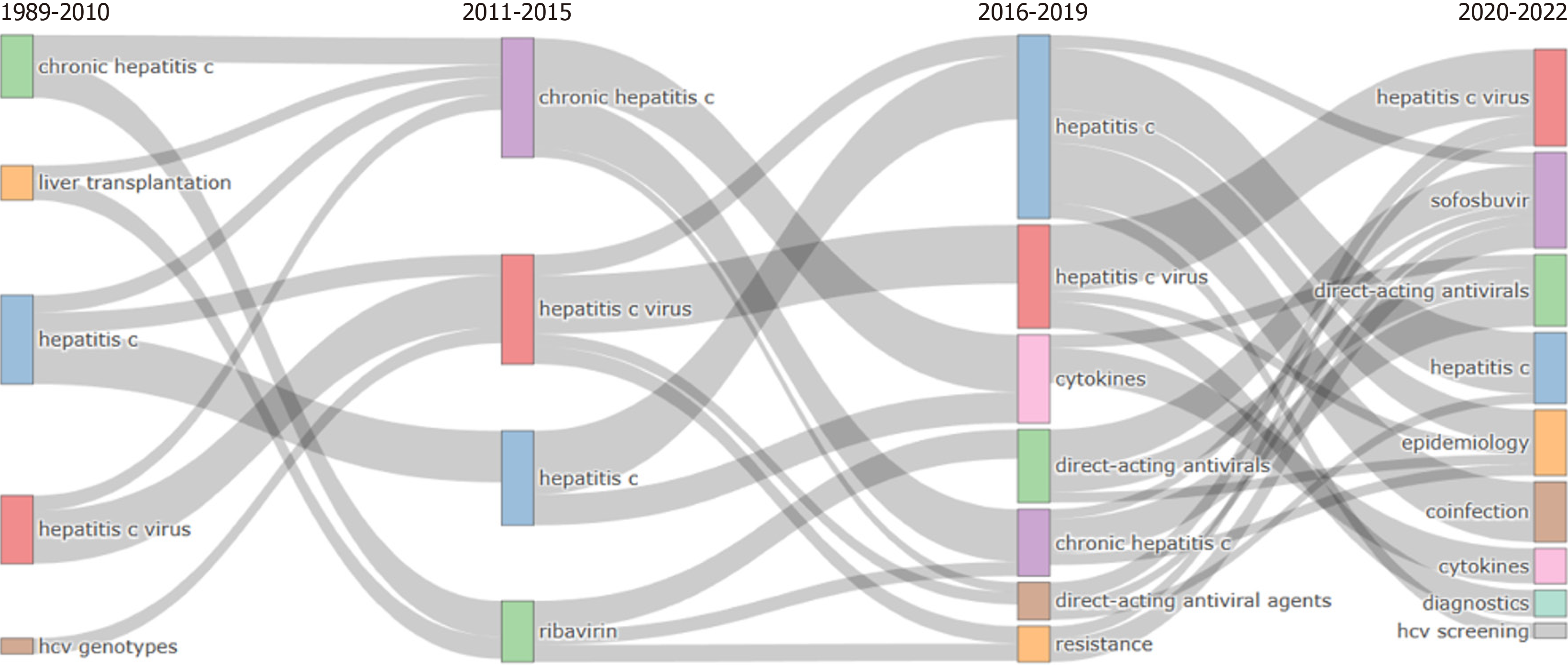
Keywords are chronic hepatitis C in 1989-2010, hepatitis C and ribavirin in 2011-2015, chronic hepatitis C, hepatitis C, and direct-acting antivirals in 2016-2019, and HCV, epidemiology, and sofosbuvir in 2020-2022.
In this case, the main themes between 2020-2022, which is the last period and represents our day in the best way, are examined in more detail: (1) HCV and genotype; (2) viral hepatitis, direct acting antivirals, and epidemiology; (3) direct-acting antiviral, sustained virological response, and sofosbuvir; and (4) hepatitis C, HIV, and people who inject drug.
In order to examine the change and development of HCV themes over the years, the four-period thematic evolution mapping in Figure 14 was created.
Upon scrutinizing the diagram, it becomes evident that the theme of hepatitis C is consistently present throughout each defined time interval. Within the timeframe spanning from 2020 to 2022, the thematic cluster encompassing hepatitis C is intricately associated with subjects including sofosbuvir, direct acting antivirals, epidemiology, coinfection, cytokines, diagnostics, and HCV screening. During this identical period, the thematic prominence of hepatitis C is notably in
Scientific data is undergoing an exponential surge today, and researchers need help accessing this voluminous infor
Scientific mapping analysis visualizes and examines information. It leverages advanced computational techniques and bibliometric data for analysis. Through this means, fundamental scientific trends are delineated, and scholarly works are scrutinized. Relationships among authors, institutions, and research topics are analyzed. This analysis is sought after to comprehend the dynamics of scientific domains[8].
The foundation of scientific mapping rests upon an exhaustive perusal of the scientific literature from comprehensive databases. Bibliometric data such as citations and publication dates from diverse networks and diagrams. These networks and diagrams constitute the backbone for identifying impactful works and trends. Scientific mapping can also be characterized as text mining, wherein algorithms are used to analyze scientific content and keywords. The program's corner
Bibliometrics, an R-based software package, has become a significant tool in science mapping. This software has been effectively employed in our study. Within our research, utilizing Bibliometrix allows for analyzing H-, G-, and M-indices and authorship and citation networks. Moreover, the outcomes of these analyses can be aptly visualized[21].
Scholars hold paramount importance in the systematic examination of knowledge dissemination. In this domain, Bi
The overarching findings of our study have been presented in a tabular format. Within the scope of the analysis, 11930 documents, 43207 authors, and 292 sources were scrutinized. The year 2012 has the highest NP concerning HCV. In 1989, Houghton et al[23] successfully cloned the viral genome, coining the term HCV[23]. Subsequently, assays for HCV de
In our study, it has been determined that the researcher with the highest H-index and G-index values is Charles M. Rice. This researcher, holding the title of professor, is affiliated with Rockefeller University. He was honored with the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2020. His primary field of expertise lies within virology. Professor Rice is also a member of the National Academy of Sciences. Following Charles M. Rice, the researcher with the highest H- and g-index values is Ralf Bartenschlager. Professor Bartenschlager conducts research in the domain of molecular virology at Heidelberg University. His fundamental area of interest is the HCV replication cycle's molecular and cellular underpinnings. Simultaneously, he is associated with the German Cancer Research Center[29]. Charles M. Rice and Ralf Bartenschlager are globally acknowledged for their contributions to HCV research. The most prolific author in terms of publication volume is Takaji Wakita. This Japanese virologist collaborated with Bartenschlager. Their collaborative efforts revolutionized the isolation of HCV[30]. Wakita holds the position of the director at the Japan National Institute of Infectious Diseases. He boasts a long
9.68% of all articles have been published in the Journal of Virology, which holds the highest H and G-index values. The Journal of Viral Hepatitis has published 10.94% of all articles. Regarding H and G-index values, the Journal of Virology is followed by the Journal of Infectious Diseases. The Journal of Virology, a monthly peer-reviewed publication, serves as the official journal of the American Society for Microbiology and has been circulating since 1967[32]. The Journal of Viral Hepatitis has been published since 1994 as a monthly peer-reviewed journal under the aegis of Wiley-Blackwell Publish
The article with the highest LC value was authored by Simmonds et al[35] in 1993. This article established classifications of HCV variants, and criteria for the classification of yet-to-be-discovered variants were delineated[35]. The 1991 publication by Takamizawa et al[36], which delved into the structure and organization of the HCV genome, ranks second in terms of LC values[36]. Notably, a recent impactful work by Bartosch et al[37], published in 2003, discusses pseudo-particles, suggesting their suitability as targets for antiviral treatments[37]. The significance of examining pivotal topics of their respective eras is a pivotal factor contributing to the substantial citations garnered by these articles.
Keyword analysis reveals that between 1992 and 2000, the terms "Hepatitis C Virus" "Non-A Autoimmune Hepatitis", and "PCR" demonstrated pronounced trends. Diagnosis of HCV relies on analyses of HCV RNA and recombinant HCV polyprotein antibodies. Antibodies targeting the core, NS4, NS3, and NS5 sequences are pursued[38]. The preeminence of PCR analysis as the foundational diagnostic method underscores its enduring trend.
COVID-19, substance use, elimination, direct-acting antivirals, and sofosbuvir have emerged as trends in contemporary times. Numerous studies have been conducted on the impact of COVID-19 on HCV-infected patients during the pan
Our study exhibits several strengths and limitations. Primarily, its robust construction stands out as a significant strength. Advanced statistical analyses have been employed in the research. Among the limitations, the reliance solely on the WoS database is notable. Including diverse databases in the analyses might enhance the reliability of the outcomes.
| 1. | Mukhtar NA, Ness EM, Jhaveri M, Fix OK, Hart M, Dale C, Pratt C, Kowdley KV. Epidemiologic features of a large hepatitis C cohort evaluated in a major health system in the western United States. Ann Hepatol. 2019;18:360-365. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Catanese MT, Uryu K, Kopp M, Edwards TJ, Andrus L, Rice WJ, Silvestry M, Kuhn RJ, Rice CM. Ultrastructural analysis of hepatitis C virus particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:9505-9510. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 208] [Cited by in RCA: 212] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Bauer PJ. We Know More Than We Ever Learned: Processes Involved in the Accumulation of World Knowledge. Child Dev Perspect. 2021;15:220-227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Dhudasia MB, Grundmeier RW, Mukhopadhyay S. Essentials of data management: an overview. Pediatr Res. 2023;93:2-3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Aboelkhir HAB, Elomri A, ElMekkawy TY, Kerbache L, Elakkad MS, Al-Ansari A, Aboumarzouk OM, El Omri A. A Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization of Decision Support Systems for Healthcare Referral Strategies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Small H. Visualizing science by citation mapping. J Am Soc Inf Sci. 1999;50:799-813. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 7. | Manoj Kumar L, George RJ, P S A. Bibliometric Analysis for Medical Research. Indian J Psychol Med. 2023;45:277-282. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Ullah R, Asghar I, Griffiths MG. An Integrated Methodology for Bibliometric Analysis: A Case Study of Internet of Things in Healthcare Applications. Sensors (Basel). 2022;23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Mingers J, Leydesdorff L. A review of theory and practice in scientometrics. Eur J Oper Res. 2015;246:1-19. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 10. | Aria M, Cuccurullo C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr. 2017;11:959-75. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1736] [Cited by in RCA: 2619] [Article Influence: 291.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 11. | Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:16569-16572. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5772] [Cited by in RCA: 4544] [Article Influence: 216.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 12. | Egghe L. Theory and practise of the g-index. Scientometrics. 2006;69:131-152. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1196] [Cited by in RCA: 891] [Article Influence: 68.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Harzing A. Reflections On The H-Index. Bus Leadership. 2012;1:101-6. |
| 14. | Zheng X, Le Y, Chan AP, Hu Y, Li Y. Review of the application of social network analysis (SNA) in construction project management research. Int J Proj Manage. 2016;34:1214-1225. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 152] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Orimoloye IR, Ololade OO. Potential implications of gold-mining activities on some environmental components: A global assessment (1990 to 2018). J King Saud Univ Sci. 2020;32:2432-2438. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 16. | Schöggl J, Stumpf L, Baumgartner RJ. The narrative of sustainability and circular economy - A longitudinal review of two decades of research. Resour, Conserv and Recycl. 2020;163:105073. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 17. | Nasir A, Shaukat K, Hameed IA, Luo S, Alam TM, Iqbal F. A Bibliometric Analysis of Corona Pandemic in Social Sciences: A Review of Influential Aspects and Conceptual Structure. IEEE Access. 2020;8:133377-133402. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Shi J, Duan K, Wu G, Zhang R, Feng X. Comprehensive metrological and content analysis of the public–private partnerships (PPPs) research field: a new bibliometric journey. Vol. 124, Scientometrics. Springer International Publishing; 2020. 2145–2184 p.. |
| 19. | Lafia S, Kuhn W, Caylor K, Hemphill L. Mapping research topics at multiple levels of detail. Patterns (N Y). 2021;2:100210. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | O'Keefe H, Rankin J, Wallace SA, Beyer F. Investigation of text-mining methodologies to aid the construction of search strategies in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy-a case study. Res Synth Methods. 2023;14:79-98. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Arruda H, Silva ER, Lessa M, Proença D Jr, Bartholo R. VOSviewer and Bibliometrix. J Med Libr Assoc. 2022;110:392-395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 230] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 22. | Waaijer CJF, Teelken C, Wouters PF, van der Weijden ICM. Competition in Science: Links Between Publication Pressure, Grant Pressure and the Academic Job Market. High Educ Policy. 2018;31:225-243.. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 23. | Houghton M. Discovery of the hepatitis C virus. Liver Int. 2009;29 Suppl 1:82-88. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 24. | Oancea CN, Butaru AE, Streba CT, Pirici D, Rogoveanu I, Diculescu MM, Gheonea DI. Global hepatitis C elimination: history, evolution, revolutionary changes and barriers to overcome. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2020;61:643-653. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report, 2017. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565455. |
| 26. | Di Bisceglie AM, Martin P, Kassianides C, Lisker-Melman M, Murray L, Waggoner J, Goodman Z, Banks SM, Hoofnagle JH. Recombinant interferon alfa therapy for chronic hepatitis C. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1506-1510. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 900] [Cited by in RCA: 863] [Article Influence: 23.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Reichard O, Andersson J, Schvarcz R, Weiland O. Ribavirin treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Lancet. 1991;337:1058-1061. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 206] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Jhaveri R. Screening for Hepatitis C Virus: How Universal Is Universal? Clin Ther. 2020;42:1434-1441. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Williams CL. Ralf Bartenschlager, Charles Rice, and Michael Sofia are honored with the 2016 Lasker~DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3639-3644. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Nair P. Profile of Charles M. Rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:8541-8543. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | WAKITA Takaji. National Institute of Infectious Diseases 2023. Available from: https://nrid.nii.ac.jp/nrid/1000040280789/. |
| 32. | Journal of Virology. American Society for Microbiology 2023. Available from: https://journals.asm.org/journal/jvi. |
| 33. | John Wiley and Sons. Overview. 2023. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/page/journal/13652893/homepage/productinformation.html. |
| 34. | Oxford University Press. About the Journal 2023. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jid/pages/About. |
| 35. | Simmonds P, Holmes EC, Cha TA, Chan SW, McOmish F, Irvine B, Beall E, Yap PL, Kolberg J, Urdea MS. Classification of hepatitis C virus into six major genotypes and a series of subtypes by phylogenetic analysis of the NS-5 region. J Gen Virol. 1993;74 (Pt 11):2391-2399. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 931] [Cited by in RCA: 930] [Article Influence: 28.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Takamizawa A, Mori C, Fuke I, Manabe S, Murakami S, Fujita J, Onishi E, Andoh T, Yoshida I, Okayama H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J Virol. 1991;65:1105-1113. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 694] [Cited by in RCA: 684] [Article Influence: 19.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Bartosch B, Dubuisson J, Cosset FL. Infectious hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles containing functional E1-E2 envelope protein complexes. J Exp Med. 2003;197:633-642. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 885] [Cited by in RCA: 880] [Article Influence: 38.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Feld JJ. Hepatitis C Virus Diagnostics: The Road to Simplification. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2018;12:125-129. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Yeo YH, Gao X, Wang J, Li Q, Su X, Geng Y, Huang R, Wu C, Ji F, Sundaram V, Noureddin M, Buti M, Ayoub WS. The impact of COVID-19 on the cascade of care of HCV in the US and China. Ann Hepatol. 2022;27:100685. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Ronderos D, Omar AMS, Abbas H, Makker J, Baiomi A, Sun H, Mantri N, Choi Y, Fortuzi K, Shin D, Patel H, Chilimuri S. Chronic hepatitis-C infection in COVID-19 patients is associated with in-hospital mortality. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9:8749-8762. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Cooper MP, Foley H, Damico D, Wright M, Rhudy C, Schadler A, Platt T. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on hepatitis C outcomes at a health-system specialty pharmacy. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2022;28:667-672. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Jacobson MA, Blanc PD, Tulsky J, Tilly M, Meister R, Huen W, McNicholas JE Jr. Risk of subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection among vaccinated employees with or without hybrid immunity acquired early in the Omicron-predominant era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Am J Ind Med. 2024;67:334-340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Liang TJ, Ward JW. Hepatitis C in Injection-Drug Users - A Hidden Danger of the Opioid Epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1169-1171. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 10.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Saviano A, Heroin L, Mayer P, Baumert TF. Hepatitis C treatment in patients with substance use disorder: the faster the better. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022;11:129-31. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Dhiman RK, Premkumar M. Hepatitis C Virus Elimination by 2030: Conquering Mount Improbable. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020;16:254-261. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Geddawy A, Ibrahim YF, Elbahie NM, Ibrahim MA. Direct Acting Anti-hepatitis C Virus Drugs: Clinical Pharmacology and Future Direction. J Transl Int Med. 2017;5:8-17. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 138] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Tsai WL, Wang CF, Cheng JS, Chen WC, Bair MJ, Lo CC. Sofosbuvir-based regimen for genotype 2 HCV infected patients in Taiwan: A real world experience. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0227424. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/