Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.677
Peer-review started: November 24, 2022
First decision: December 13, 2022
Revised: December 26, 2022
Accepted: January 5, 2023
Article in press: January 5, 2023
Published online: January 26, 2023
Processing time: 63 Days and 3.7 Hours
Brucellosis is the most common zoonosis worldwide and is endemic in the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and Latin America. However, it is uncommon in Central Europe, and periprosthetic infections caused by Brucella are therefore rare. Due to the low prevalence and nonspecific clinical presentation of the disease, accurate diagnosis can be challenging; no gold standard currently exists for treating brucellosis.
Here, we present a 68-year-old Afghan woman living in Austria with a periprosthetic knee infection caused by Brucella melitensis. The interval from total knee arthroplasty to septic loosening was five years. A profound medical history and examinations suggested that the patient had been suffering from unrecognized chronic osteoarticular brucellosis prior to total knee arthroplasty. She was successfully treated by two-stage revision surgery and combined antibiotic therapy over three months.
Clinicians should consider brucellosis as a possible cause of chronic arthralgia and periprosthetic infection in patients originating from countries with a high brucellosis burden.
Core Tip: Periprosthetic infections caused by Brucella species are rare, difficult to diagnose, and challenging to treat. We present here our experience in treating a 68-year-old Afghan woman with a periprosthetic knee joint infection caused by Brucella melitensis. In conclusion we recommend clinicians to consider Brucellosis as a possible cause for chronic arthralgia and periprosthetic infection in patients originating from countries with a high brucellosis burden.
- Citation: Stumpner T, Kuhn R, Hochreiter J, Ortmaier R. Periprosthetic knee joint infection caused by Brucella melitensis which was first -osteoarticular brucellosis or osteoarthrosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(3): 677-683
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i3/677.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.677
Brucellosis is a zoonotic bacterial infection caused by different species of gram-negative coccobacilli Brucellae[1]. While it is the most common zoonosis worldwide and endemic in large parts of the Middle East, Mediterranean, Central Asia, Africa, and Latin America, it is rare in Central Europe and Northern America[2].
Transmission usually occurs through the consumption of unpasteurized milk, and less commonly through direct contact with animals or the inhalation of infected particles[3]. Diagnosis is made by serological tests for antibodies against Brucella and culture of blood, joint aspirates, or other tissue samples. Cultivation of germs may be hampered by the slow-growing nature of Brucella species and therefore culture can require prolonged incubation. Highly sensitive molecular methods (nucleic acid amplification tests) can enable a quick diagnosis; however, they are still under development and no sufficiently validated commercial tests are currently available[4].
The disease itself usually presents with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, and weight loss[3]. Hematogenous spread may affect any organ; however, osteoarticular involvement (arthritis, osteomyelitis) is the most common complication[3,5,6]. Periprosthetic infections due to Brucella are extremely rare, and only 30 cases have been reported in the literature to date[6,7].
In December 2020, a 68-year-old female presented with pain, redness, and swelling in her left knee.
At the time of presentation, the complaints had been present for three months, and antibiotic therapy (oral amoxicillin 1 g twice daily) had already been started by her general practitioner.
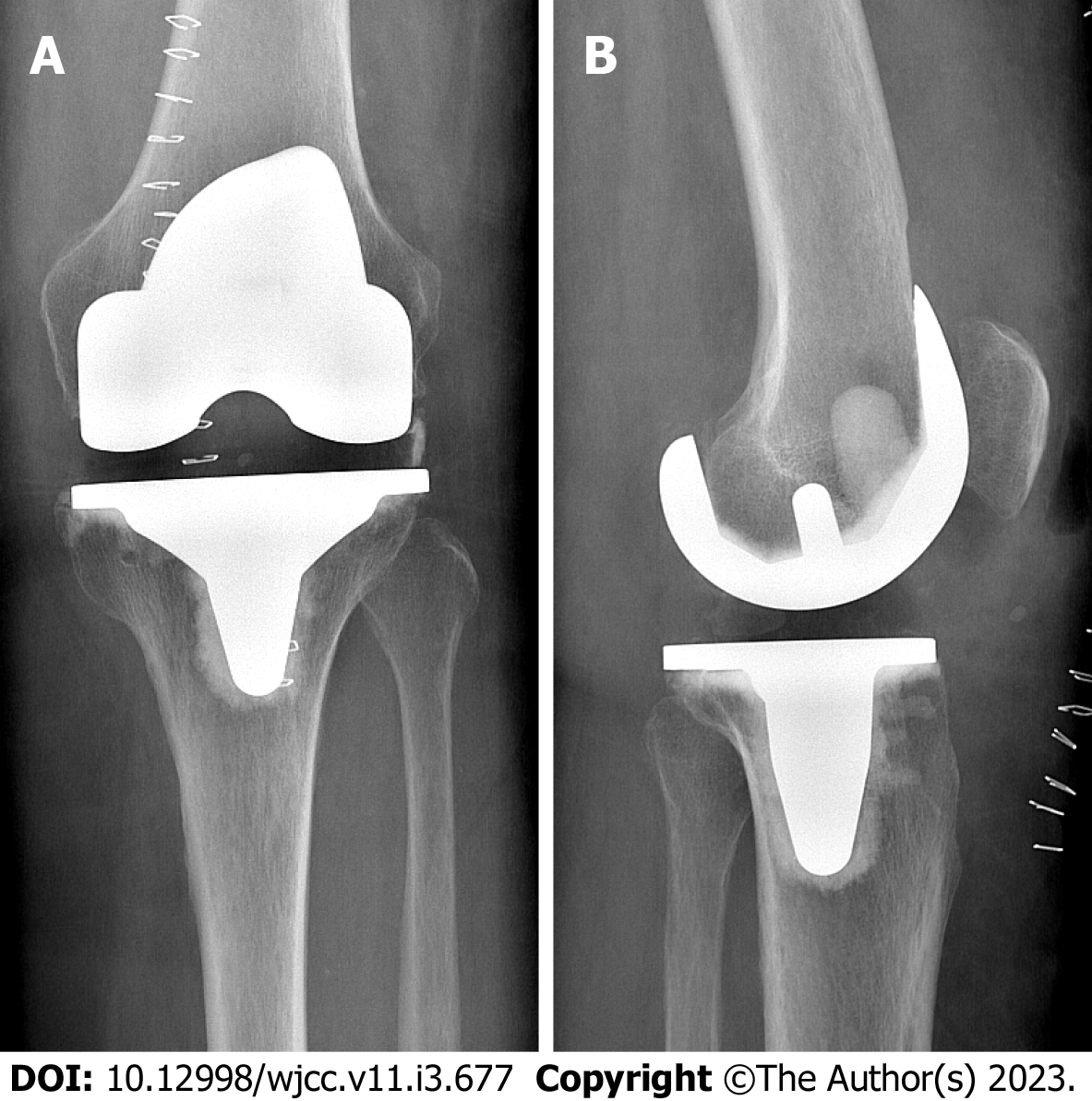
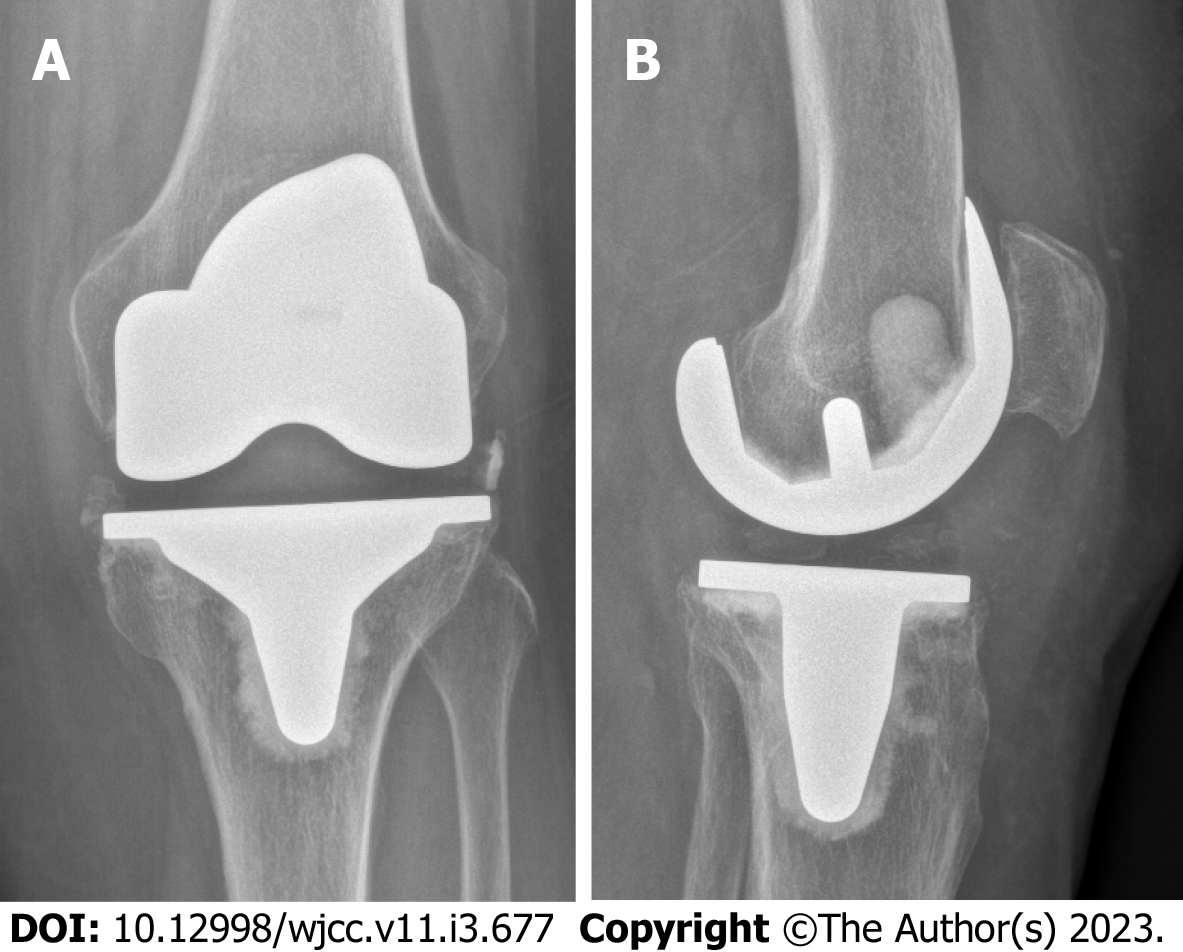
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in the affected joint had been performed five years prior due to osteoarthritis (Figure 1). The initial postoperative course was uneventful. In the following years however the patient repeatedly presented to our outpatient clinic with pain in the operated knee and lumbar spine. Complaints always improved with physiotherapy, oral pain medication, and local cryotherapy to the knee.
Neither the patient nor her family members had previous episodes of similar symptoms.
There was marked effusion, warming, and swelling in the left knee. The range of motion was quite limited due to pain. The patient was afebrile without any feeling of illness.
The C-reactive protein (CRP) level was 2 mg/dL (norm < 1 mg/dL), and the leukocyte count was within the normal range. No aspirate could be withdrawn by intraarticular puncture.
X-ray imaging showed a tilt of the tibial plateau and radiolucent lines around the femoral component (Figure 2).
Despite suspicion of septic loosening, an outpatient procedure was initially agreed upon because the patient refused surgical intervention. Therefore, she was fitted with a rigid knee brace and antibiotic therapy with amoxicillin was continued. We scheduled her for a check-up in our orthopedic outpatient clinic.
One week later, the pain and redness were reduced and the CRP level and leukocyte count remained unchanged. However, considerable effusion remained. Ten milliliters of intraarticular serohemorrhagic fluid were aspirated, and qualitative determination of alpha-defensin (Synovasure®, Zimmer Biomet) was positive. The cell count in the aspirate was 9800: 76% of these cells were granulocytes, thus confirming a periprosthetic joint infection. Revision surgery was agreed upon with the patient.
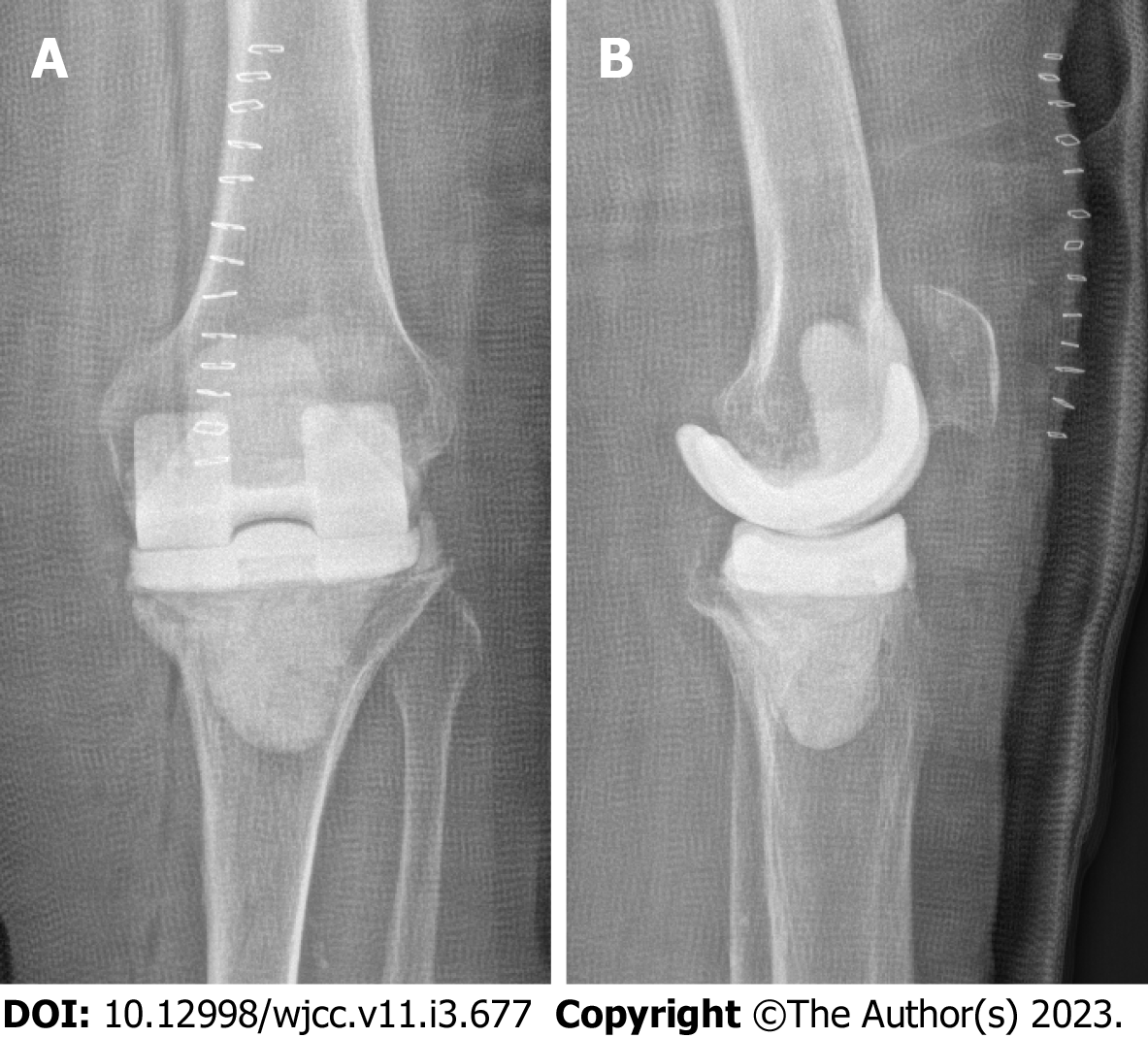
After removal of the prosthesis, a mobile vancomycin- and gentamicin-loaded spacer (VancoGenx™ SPACE Knee,Medix Medical) was implanted (Figure 3). Seven tissue samples were taken intraoperatively for culture and histopathology, and the prosthesis was sent for sonication. The antibiotic regimen was changed to intravenous (i.v.) cefuroxime.
Eight days after surgery Brucella melitensis was successfully cultivated in synovial fluid. Serological tests were positive for antibodies against Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus.
The final diagnosis was a periprosthetic knee joint infection caused by Brucella melitensis.
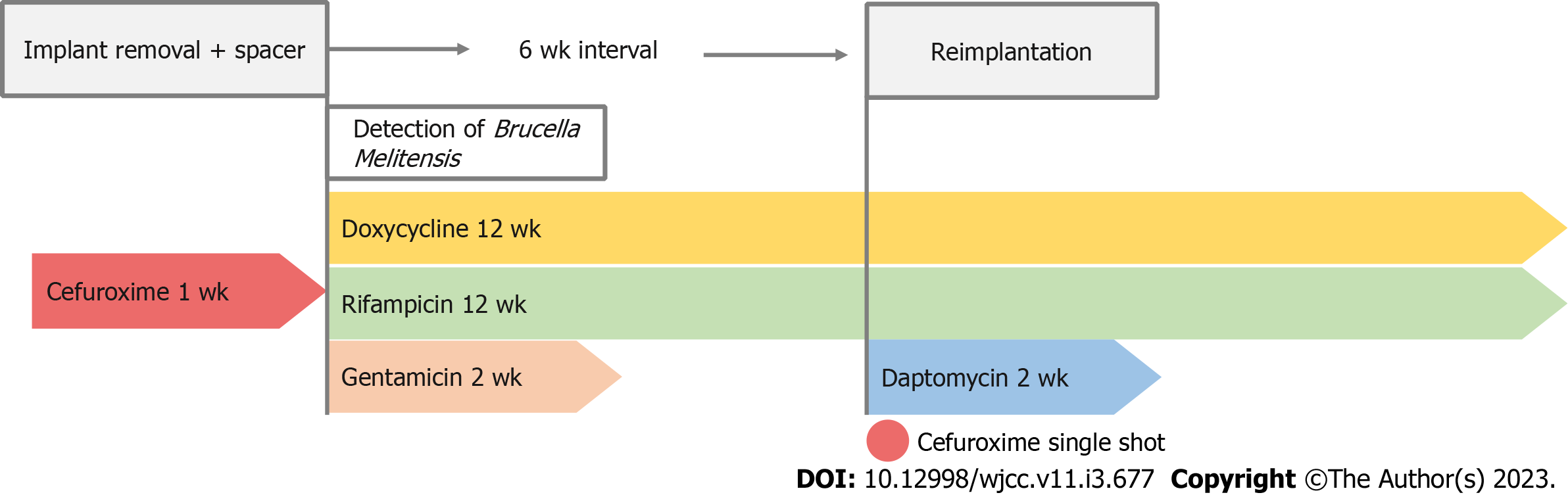
Antibiotic therapy was adapted to oral doxycycline 200 mg daily plus oral rifampicin 450 mg twice daily for 12 wk, and i.v. gentamicin was administered for two weeks under the close monitoring of serum levels due to severe renal insufficiency. Six weeks after implant removal a revision TKA was performed. To protect the new prosthesis from superinfection with rifampicin-resistant staphylococci, our patient received a single 1.5 g shot of i.v. cefuroxime preoperatively and i.v. daptomycin 500 mg for 14 d after reimplantation. After a total of 12 wk targeted antibiotic therapy was terminated (Figure 4).
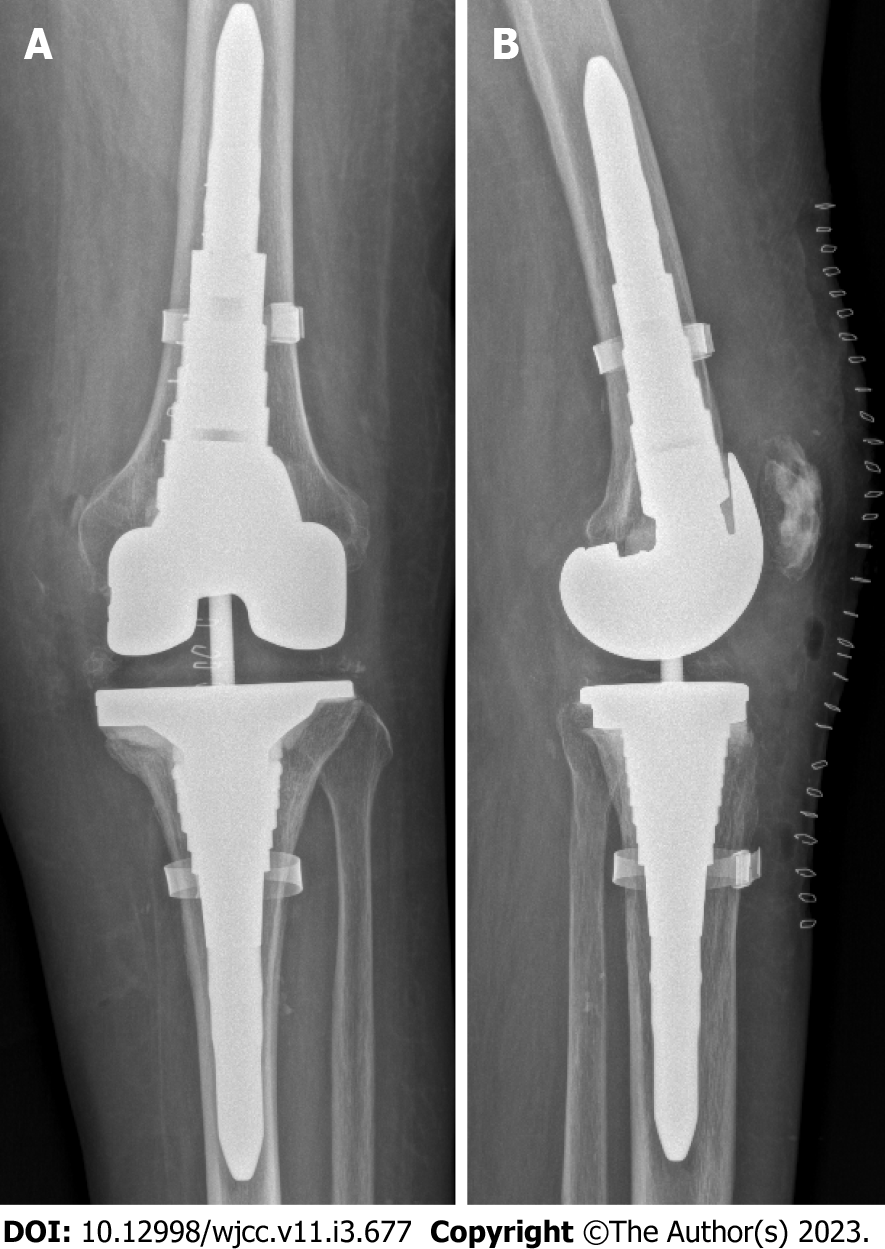
Nineteen months after reimplantation, the patient was free of pain and walked without crutches. The affected joint showed no swelling, and the active range of motion was 115 degrees without a fixed flexion deformity or extensor lag. Inflammatory markers were within the normal range, and the levels of anti-Brucella antibodies had decreased. X-ray imaging showed no signs of loosening (Figure 5).
Periprosthetic infections with Brucella species are rare; therefore, diagnosis can be a challenge especially in nonendemic countries such as Austria. Our patient is originally from Afghanistan and had been living in Austria since 2013. The pain in her left knee started years before she emigrated to Austria, but no cause could be found in Afghanistan. TKA was performed in our department in 2015 after several attempts of conservative treatment for osteoarthritis.
When asked about the possible transmission of Brucella species, the patient denied consumption of unpasteurized milk or raw meat, but she reported that she had kept livestock in Afghanistan. The fact that the periprosthetic infection occurred five years after implantation but seven years after the last contact with livestock suggests that the patient had a latent infection with Brucella melitensis prior to TKA. Brucellosis has a tendency towards chronicity similar to tuberculosis. By evading the host immune defense, it can persist for long periods in practically any organ system, thus causing chronic granulomatous infections[5,8]. It is debatable whether the real cause of knee pain eventually leading to TKA in 2015 was chronic osteoarticular brucellosis rather than osteoarthrosis. In fact, our patient complained of recurrent load-dependent knee pain after her initial surgery. Minimal effusion was observed in various visits to our department. There was no warming or redness, and the pain always improved with cryotherapy and oral analgesics. Minor radiolucent lines at the anterior and posterior flanges of the femoral component were already evident one year postoperatively (Figure 6). However, such ra
After the diagnosis of brucellosis was confirmed we performed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine due to the patient’s history of chronic lower back pain. The MRI showed depleted intervertebral space in L4/L5 and post-inflammatory alterations indicating a residual state after spondylodiscitis. In conclusion, the history and clinical findings retrospectively and strongly suggest that the patient had suffered from chronic brucellosis with involvement of the knee and lumbar spine for years.
Our case also demonstrates the difficulty in detecting brucellosis especially because the patient was already receiving broad-spectrum penicillin when the diagnostic testing began. Culture was positive in one out of two synovial fluid samples and only one in seven intraoperative tissue samples. It took two weeks of culture until bacterial growth was noted. Sonication was negative. Antibody detection was performed after receiving the microbiological findings and was positive for Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus; the latter, however, was considered a serological cross-reaction. Our diagnostic experience is consistent with reports in the literature stating that the detection of brucellosis can be challenging and complicated by the long cultivation required due to slow bacterial growth[4,6,7]. We therefore concur with recommendations suggesting screening for anti-Brucella antibodies early in patients from endemic countries or in close contact with livestock[6,7]. When serology is positive, invasive procedures such as joint aspiration or surgery should be performed using special protection including an apron, eye protection, and filtering face piece-3 mask to prevent transmission via aerosols. Laboratory staff must be informed about special hazards when handling samples[6,7,11].
Treatment of systemic brucellosis requires antibiotic combination therapy for at least six weeks. Monotherapy or a shorter duration of therapy carries a high risk of treatment failure and relapse[3,7,8]. The most common antibiotic combinations are doxycycline plus rifampicin or doxycycline plus streptomycin. Fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, or gentamicin are also used. To date, no gold standard in antibiotic combination and duration of therapy has been established[3,7].
Antibiotic therapy for at least 12 wk is recommended in osteoarticular brucellosis[7,12]. Antimicrobial therapy without surgical intervention may be feasible in cases of periprosthetic infection and the absence of radiological loosening[6,13,14]. Thus, successful outcomes have been reported in eight out of nine joints with periprosthetic infections due to Brucella and with well-fixed implants when treated solely with antibiotics over six to 52 wk[6]. However, the sample number of patients described is too small to derive firm recommendations. Revision surgery is mandatory in cases of loose implants. Good results have been described for both one-stage and two-stage revision surgery with short or long intervals[6,7]. The prognosis of brucellosis, whether local or systemic, is generally good: Mortality is low but with high morbidity due to the multilocular and often protracted course of disease[3].
We opted for a two-stage revision with a six-week interval given the long history of pain over three months and the profound radiological changes in our case. The antibiotic regimen consisted of doxycycline and rifampicin for 12 wk, gentamicin for two weeks after implant removal, and daptomycin for two weeks after reimplantation. No side effects (changes in blood count or transaminases) were encountered. The treatment of our patient with multiple comorbidities was an interdisciplinary challenge involving orthopedics, internal medicine, and microbiology, and we would like to thank all the disciplines for their contribution to the good outcome.
Brucellosis can be easily missed given the low prevalence in nonendemic countries. We recommend that clinicians consider brucellosis as a possible cause for chronic arthralgia, backache, and periprosthetic infection in patients from countries with a high brucellosis burden. If brucellosis is considered, then serological tests should be performed prior to joint aspiration or surgery because those procedures pose a risk of transmission via aerosols and therefore require special safety precautions. There is currently no uniform treatment concept in surgical intervention or choice and duration of antibiotic therapy for periprosthetic joint infections caused by Brucella; however, our antibiotic regimen was successful and can be used to guide future cases.
| 1. | González-Espinoza G, Arce-Gorvel V, Mémet S, Gorvel JP. Brucella: Reservoirs and Niches in Animals and Humans. Pathogens. 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, Christou L, Tsianos EV. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:91-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1203] [Cited by in RCA: 1385] [Article Influence: 69.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Yousefi-Nooraie R, Mortaz-Hejri S, Mehrani M, Sadeghipour P. Antibiotics for treating human brucellosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD007179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Yagupsky P, Morata P, Colmenero JD. Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;33. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in RCA: 245] [Article Influence: 35.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Franco MP, Mulder M, Gilman RH, Smits HL. Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:775-786. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 606] [Cited by in RCA: 747] [Article Influence: 41.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Lewis JM, Folb J, Kalra S, Squire SB, Taegtmeyer M, Beeching NJ. Brucella melitensis prosthetic joint infection in a traveller returning to the UK from Thailand: Case report and review of the literature. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2016;14:444-450. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Flury D, Behrend H, Sendi P, von Kietzell M, Strahm C. Brucella melitensis prosthetic joint infection. J Bone Jt Infect. 2017;2:136-142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E. Brucellosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2325-2336. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 878] [Cited by in RCA: 915] [Article Influence: 43.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Behrend H, Hochreiter B, Potocnik P, El Baz Y, Zdravkovic V, Tomazi T. No difference in radiolucent lines after TKA: a matched-pair analysis of the classic implant and its evolutional design. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28:3962-3968. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Staats K, Wannmacher T, Weihs V, Koller U, Kubista B, Windhager R. Modern cemented total knee arthroplasty design shows a higher incidence of radiolucent lines compared to its predecessor. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27:1148-1155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Traxler RM, Lehman MW, Bosserman EA, Guerra MA, Smith TL. A literature review of laboratory-acquired brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:3055-3062. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Unuvar GK, Kilic AU, Doganay M. Current therapeutic strategy in osteoarticular brucellosis. North Clin Istanb. 2019;6:415-420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kim SJ, Park HS, Lee DW, Kim JH. Brucella infection following total joint arthroplasty: A systematic review of the literature. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018;52:148-153. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Balkhair A, Al Maskari S, Ibrahim S, Al Busaidi I, Al Amin M, Ba Taher H. Brucella Periprosthetic Joint Infection Involving Bilateral Knees with Negative Synovial Fluid Alpha-Defensin. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2019;2019:9423946. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: Austria
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Li M, China; Ye YP, China S-Editor: Wang LL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang LL