Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.5119
Peer-review started: January 11, 2022
First decision: February 21, 2022
Revised: March 5, 2022
Accepted: March 26, 2022
Article in press: March 26, 2022
Published online: May 26, 2022
Processing time: 133 Days and 2.5 Hours
Arytenoid cartilage dislocation is a rare and often overlooked complication of tracheal intubation or blunt laryngeal trauma. The most common symptom is persistent hoarseness. Although cases of arytenoid dislocation due to tracheal intubation are reported more frequently in otolaryngology, reports on its occurrence in the intensive care unit (ICU) are lacking. We report a case of delayed diagnosis of arytenoid cartilage dislocation after tracheal intubation in the ICU.
A 20-year-old woman was referred to the ICU following a fall from a height. Her voice was normal; laryngeal computed tomography showed unremarkable findings on admission. However, due to deterioration of the patient’s condition, tracheal intubation, and emergency exploratory laparotomy followed by laparoscopic surgery two d later under general anesthesia were performed. After extubation, the patient was sedated and could not communicate effectively. On the 10th day after extubation, the patient complained of hoarseness and coughing with liquids, which was attributed to laryngeal edema and is common after tracheal intubation. Therefore, specific treatment was not administered. However, the patient’s symptoms did not improve. Five d later, an electronic laryngoscope examination revealed dislocation of the left arytenoid cartilage. The patient underwent arytenoid closed reduction under general anesthesia by an expe
Symptoms of arytenoid cartilage dislocation are difficult to identify in the ICU leading to missed or delayed diagnosis among patients.
Core Tip: We report a case of arytenoid cartilage dislocation in the intensive care unit (ICU). The main reason for delayed diagnosis was difficulty in communicating with the patient, who was under sedation. This resulted in difficulties in early observations of dislocation symptoms. Therefore, patients in the ICU may be at a greater risk for arytenoid cartilage dislocation, and it is difficult to identify these symptoms, leading to missed or delayed diagnosis.
- Citation: Yan WQ, Li C, Chen Z. Delayed diagnosis of arytenoid cartilage dislocation after tracheal intubation in the intensive care unit: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(15): 5119-5123
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i15/5119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.5119
Arytenoid cartilage dislocation refers to the complete separation of the arytenoid cartilage from the cricoarytenoid joint (CAJ). Its clinical manifestations include hoarseness, throat pain, dysphagia, choking cough, and dyspnea in severe cases[1,2]. Arytenoid cartilage dislocation is a rare complication following tracheal intubation or blunt laryngeal trauma[1,3]. Previous reports suggest that the incidence of arytenoid cartilage dislocation is 0.009%-0.097%[2,4,5]. However, the actual incidence could be higher due to missed or misdiagnosed cases[1,5,6]. We report a case of arytenoid cartilage dislocation that was nearly missed due to the unique complexities of critical care settings and critically ill patients.
A 20-year-old woman (163 cm, 50 kg) was referred to the emergency department following a fall from a height.
The patient fell from a height of more than 3 m. On admission, the patient complained of pain and showed marked irritability. The patient was transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU). However, her condition deteriorated shortly after admission. She developed tachypnea, hypotension, and low oxygen saturation due to shock, and progressively aggravated intra-abdominal bleeding. This was addressed by fluid resuscitation and endotracheal tube insertion with mechanical ventilation in the ICU. Endotracheal intubation was performed using a 7.5 mm endotracheal tube by an experienced physician. Subsequently, the patient underwent emergency exploratory laparotomy followed by laparoscopic surgery two d later. The duration of endotracheal intubation was 13 d. Endotracheal intubation and extubation were performed strictly according to the current guidelines for the management of tracheal intubation in critically ill adults[7]. On the 10th day post extubation, the patient complained of hoarseness and reported coughing with liquids.
The patient had no significant medical history.
The patient had no personal family history.
On the 10th day after extubation, oral examination showed swollen and hyperemic pharyngeal mucosa.
Laboratory tests were not conducted.
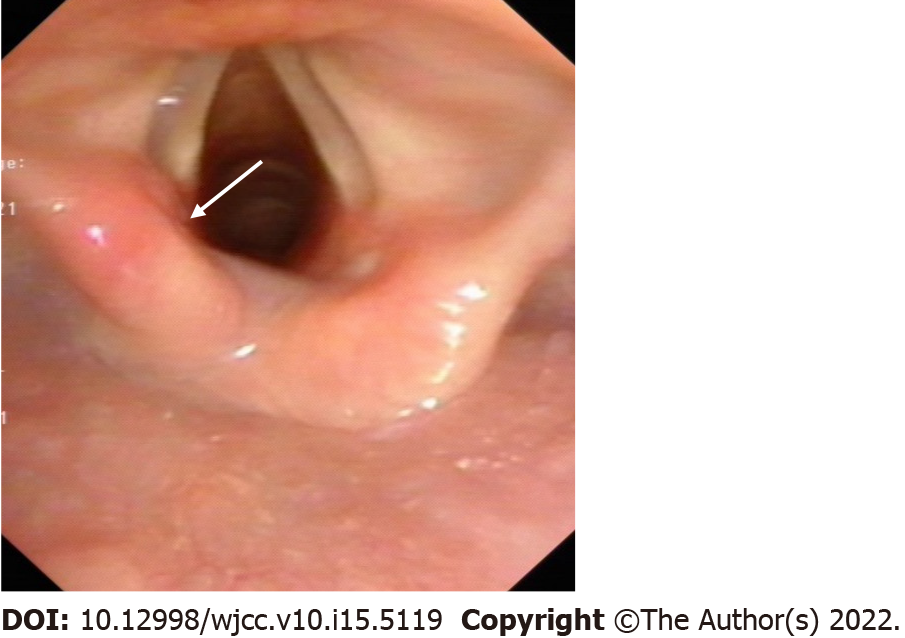
On admission, laryngeal computed tomography (CT) before the tracheal intubation revealed unremarkable findings. On the 15th day post extubation, an electronic laryngoscope revealed dislocation of the left arytenoid cartilage (Figure 1). The patient was recommended a CAJ three-dimensional CT and laryngeal electromyography (EMG). These examinations would facilitate the diagnosis. However, the patient and her family refused to conduct this imaging test as it would result in out-of-pocket expenses, and they lacked funds for these expenses.
The final diagnosis for this patient with hoarseness was left arytenoid cartilage dislocation secondary to tracheal intubation.
The patient underwent an arytenoid closed reduction procedure under general anesthesia that was carried out by an experienced otolaryngologist.
After surgery, the hoarseness improved and coughing with liquids resolved. We recommend that CAJ three-dimensional CT and laryngeal EMG should be performed after a successful arytenoid closed reduction procedure. However, the patient refused this imaging test as she had regained her normal voice. The 6-month follow up indicated that the hoarseness gradually reduced within 4 wk post reduction procedure.
The CAJ is important for laryngeal function, particularly in supporting optimal phonation and airway protection. However, the pathogenesis of arytenoid cartilage dislocation remains unclear. The original theory[8] was that direct trauma by a laryngoscope or intubation tube is responsible for dislocation of the CAJ. However, a cadaveric study argued that high-force simulated intubation was unlikely to cause arytenoid dislocation[9]. Recently, Gallet et al[10] suggested that arytenoid cartilage dislocation might be due to cricoarytenoid instability rather than the forces exerted on the articulation. A review[1] reported that risk factors that weaken the CAJ include anemia, laryngomalacia, acromegaly, chronic steroid use, low body mass index (BMI)[11], Marfan syndrome, renal failure, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), CHARGE (coloboma of the eye, heart defects, atresia of the choanae, retardation of growth, genital abnormalities, and ear abnormalities) syndrome[12]. The review also reported that the type and difficulty of intubation, operation time, type of intervention, use of transesophageal echocardiography during surgery[13], and insertion of a calibrating orogastric tube in bariatric surgery[14] were associated with a significant incidence of arytenoid cartilage dislocation.
In the ICU setting, many additional risk factors such as prolonged endotracheal intubation, difficult intubation, nasogastric tube insertion, anemia, chronic steroid use, and low BMI exist. In our case, a young patient without a history of anemia, chronic steroid use, or persistent hoarseness required tracheal intubation; it was successfully performed by an experienced emergency department physician. Longer tracheal intubation duration and the presence of a nasogastric feeding tube were key risk factors for this patient. In addition, the patient had injuries due to a fall from considerable height. We had ruled out neck injury resulting in arytenoid cartilage dislocation because her voice was normal, and laryngeal CT showed unremarkable findings at the time of admission. However this does not preclude the fact that a fall from height might make the CAJ unstable and increase the likelihood of arytenoid cartilage dislocation.
In this case, the diagnosis of arytenoid cartilage dislocation was delayed primarily due to the difficulty in communicating with the patient. After extubation, the patient remained in a state of sedation and analgesia and could not communicate effectively. After 10 d, hoarseness and coughing with liquid were observed. We considered these symptoms to be a result of common laryngeal edema after tracheal intubation. Therefore, specific treatment was not administered. Until the symptoms did not improve, we considered the possibility of arytenoid cartilage dislocation, and examination using an electronic laryngoscope confirmed our diagnosis. A definitive diagnosis was made on the 15th day after extubation. If not treated or treatment fails due to missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis, arytenoid cartilage dislocation could lead to hypermobile joint or ankylosis of the affected CAJ[12]. Fortunately, this was not observed in this case. It is difficult for critically ill patients to communicate effectively, making early observation of dislocation symptoms difficult. If a patient has cognitive or language impairments, diagnosis is particularly difficult. In addition, a large number of patients have died in the ICU, after extubation, which may have resulted in missing some patients with dislocations. Therefore, the actual incidence of arytenoid cartilage dislocation could be underestimated.
Patients in the ICU may be at a greater risk for arytenoid cartilage dislocation, and hoarseness and/or other symptoms that are difficult to identify especially by untrained physicians, resulting in missed or delayed diagnosis. This case report could be of value for intensivists and young doctors and aid them in diagnosing this condition effectively.
The authors would like to thank the patient and all the doctors and nurses participated in the case.
| 1. | Frosolini A, Marioni G, Maiolino L, de Filippis C, Lovato A. Current management of arytenoid sub-luxation and dislocation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;277:2977-2986. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Gauss A, Treiber HS, Haehnel J, Johannsen HS. Spontaneous reposition of a dislocated arytenoid cartilage. Br J Anaesth. 1993;70:591-592. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Rubin AD, Hawkshaw MJ, Moyer CA, Dean CM, Sataloff RT. Arytenoid cartilage dislocation: a 20-year experience. J Voice. 2005;19:687-701. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Wu L, Shen L, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Huang Y. Association between the use of a stylet in endotracheal intubation and postoperative arytenoid dislocation: a case-control study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018;18:59. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Yamanaka H, Hayashi Y, Watanabe Y, Uematu H, Mashimo T. Prolonged hoarseness and arytenoid cartilage dislocation after tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:452-455. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Shen L, Wang WT, Yu XR, Zhang XH, Huang YG. Evaluation of risk factors for arytenoid dislocation after endotracheal intubation: a retrospective case-control study. Chin Med Sci J. 2014;29:221-224. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Higgs A, McGrath BA, Goddard C, Rangasami J, Suntharalingam G, Gale R, Cook TM; Difficult Airway Society; Intensive Care Society; Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine; Royal College of Anaesthetists. Guidelines for the management of tracheal intubation in critically ill adults. Br J Anaesth. 2018;120:323-352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 392] [Cited by in RCA: 546] [Article Influence: 60.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Wang RC. Three-dimensional analysis of cricoarytenoid joint motion. Laryngoscope. 1998;108:1-17. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Friedman AD, Kobler JB, Landau-Zemer T, Barbu AM, Burns JA. High-force simulated intubation fails to dislocate cricoarytenoid joint in ex vivo human larynges. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2012;121:746-753. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Gallet P, Nguyen DT, Toussaint B, Rumeau C. Spontaneous arytenoid dislocation and crico-arytenoid instability. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2019;136:307-308. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Lou Z, Yu X, Li Y, Duan H, Zhang P, Lin Z. BMI May Be the Risk Factor for Arytenoid Dislocation Caused by Endotracheal Intubation: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. J Voice. 2018;32:221-225. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Mallon AS, Portnoy JE, Landrum T, Sataloff RT. Pediatric arytenoid dislocation: diagnosis and treatment. J Voice. 2014;28:115-122. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | Tsuru S, Wakimoto M, Iritakenishi T, Ogawa M, Hayashi Y. Cardiovascular operation: A significant risk factor of arytenoid cartilage dislocation/subluxation after anesthesia. Ann Card Anaesth. 2017;20:309-312. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Hung KC, Chen YT, Chen JY, Kuo CY, Wu SC, Chiang MH, Lan KM, Wang LK, Sun CK. Clinical characteristics of arytenoid dislocation in patients undergoing bariatric/metabolic surgery: A STROBE-complaint retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98:e15318. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Chen S, China; Seifu A, Ethiopia S-Editor: Wang LL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang LL