©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2021; 9(6): 1469-1474
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1469
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1469
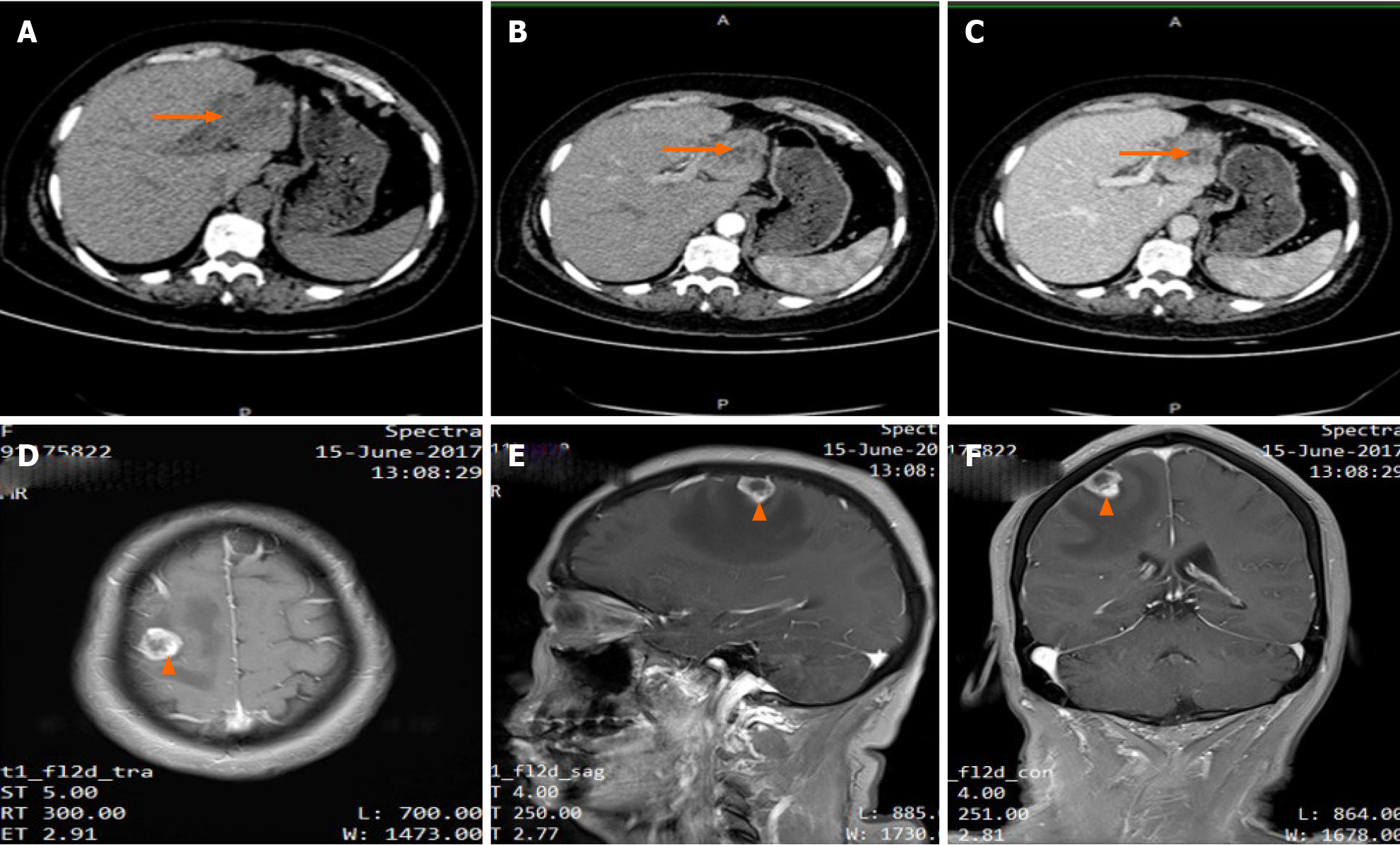
Figure 1 Imaging results of the lesions (Liver: A-C; Brain: D-F).
Abdominal computed tomography showed a mass in the left lobe of the liver (arrow). A: Low density lesions located in the left lateral lobe in unenhanced phase; B: Lesions washed-in and enhanced during hepatic arterial phase; C: Lesions enhanced in portal venous phase. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a single brain metastasis in the right frontal lobe (arrow); D: Axial view; E: Sagittal view; F: Coronal view.
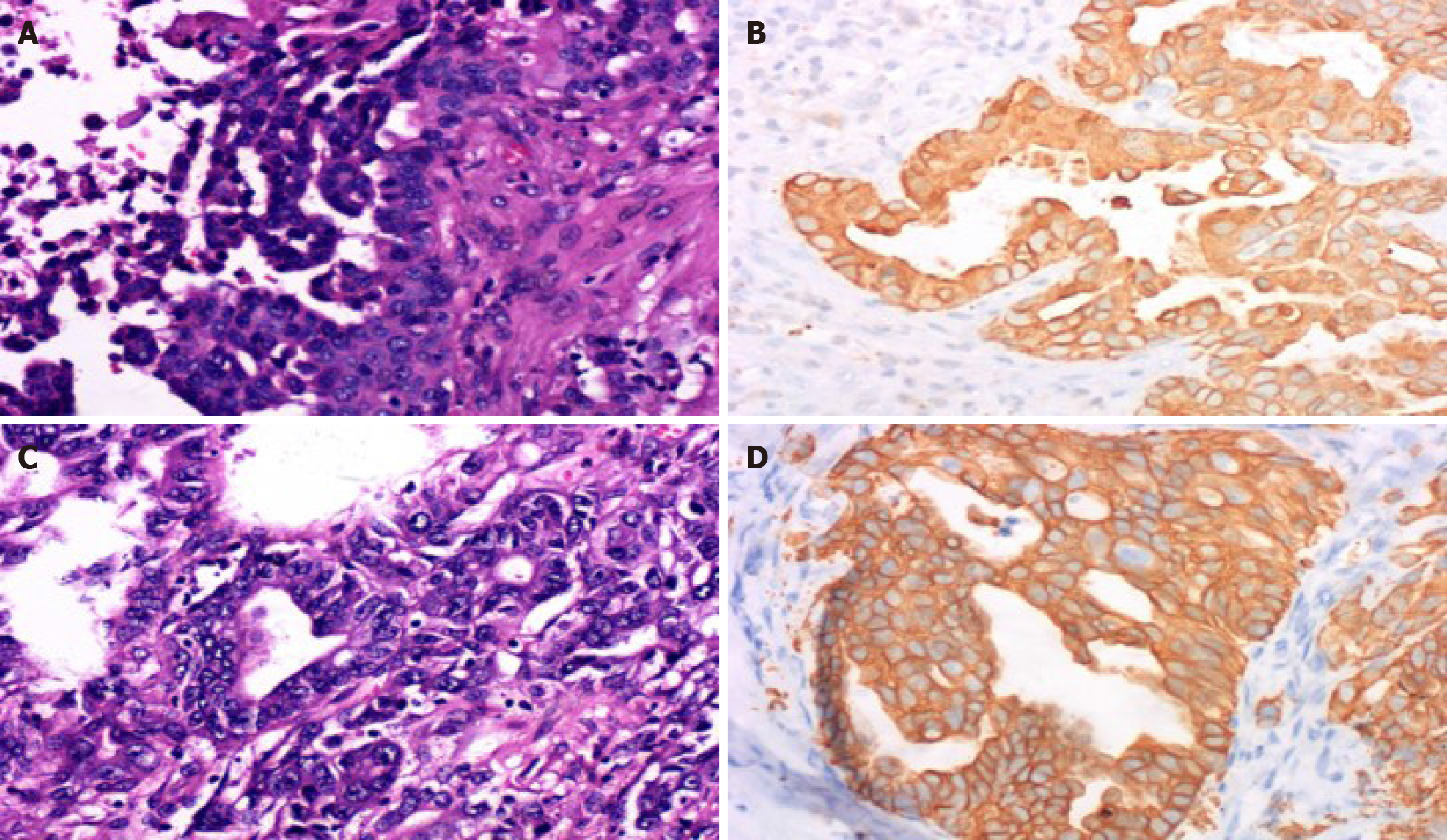
Figure 2 Pathological results of the lesions.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin-stained section of the brain lesion showing abundant eosinophils with large vesicular nuclei and clear cytoplasm (× 400); B: Immunohistochemical staining was positive for cytokeratin 19 (× 400) in the brain tumor cells, which indicated metastasis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; C and D: These findings of the liver lesions were similar to those of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma pathological specimen obtained by hepatectomy (× 400).
- Citation: Zeng JT, Zhang JF, Wang Y, Qing Z, Luo ZH, Zhang YL, Zhang Y, Luo XZ. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is more complex than we thought: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(6): 1469-1474
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i6/1469.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1469