©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2021; 9(6): 1446-1454
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1446
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1446
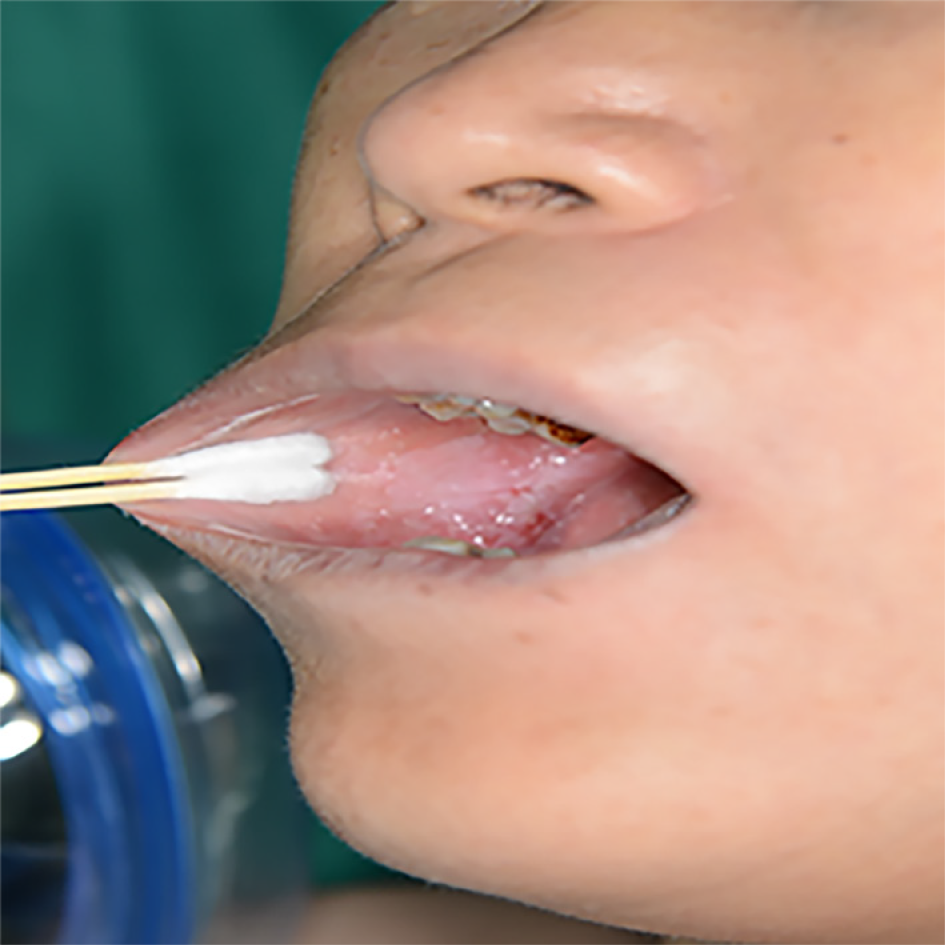
Figure 1 Clinical appearance.
The lesion area of the right buccal lesion was about 4 cm × 3 cm, with white lesions within the area of erosion, congestion, and ulceration.
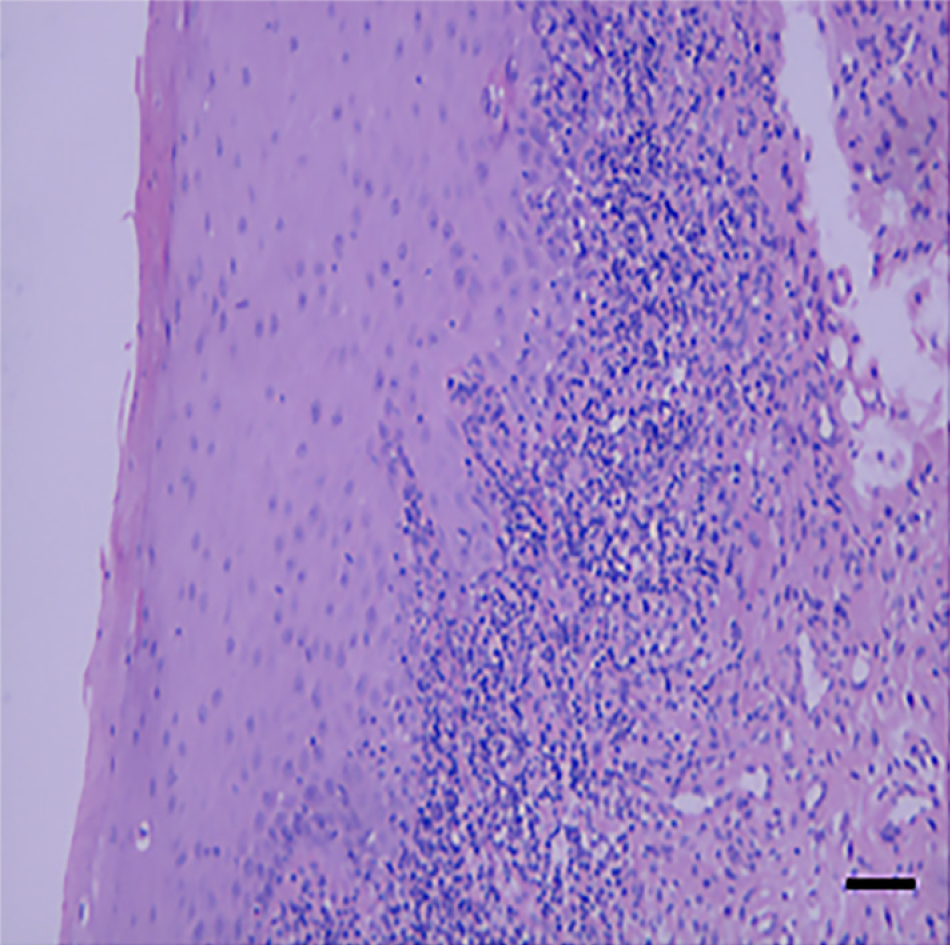
Figure 2 Histopathological analysis revealed hyperepithelialization, hydropic degeneration of the basal cells, unclear basement membrane structure, and infiltration of banded subepithelial lymphocytes and plasma cells.
All pathological diagnoses were inclined to be lichen planus, and the lesions were not malignant. Scale bar: 100 mm.
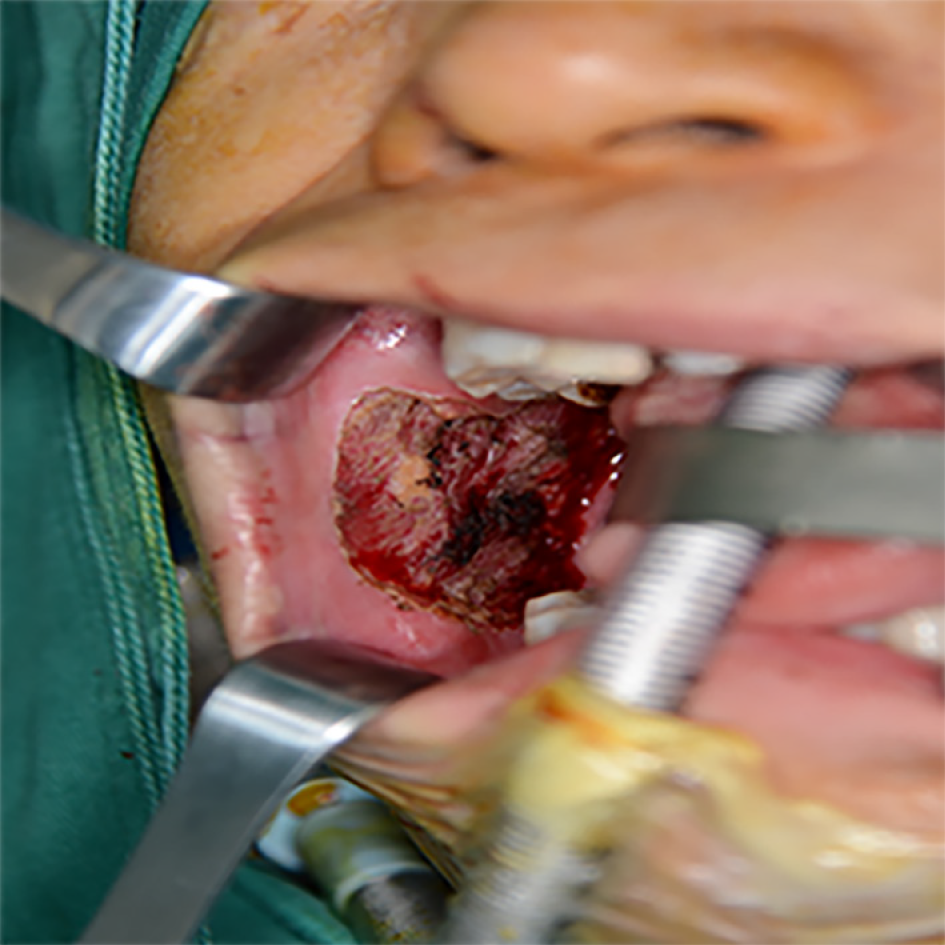
Figure 3 The entire layer of the mucosa lesions was removed, to a depth down to the muscular layer.
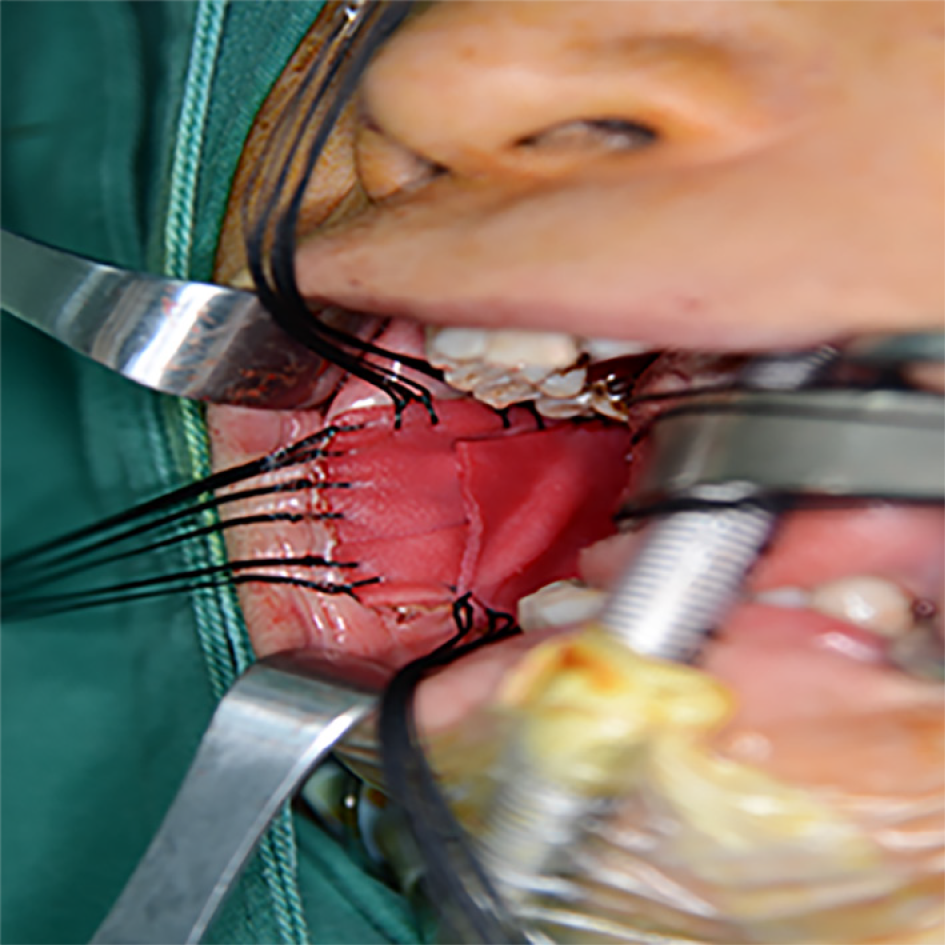
Figure 4 Acellular dermal matrix was sutured to the edges of the mucosa with 3-0 Vicryl after local excision.
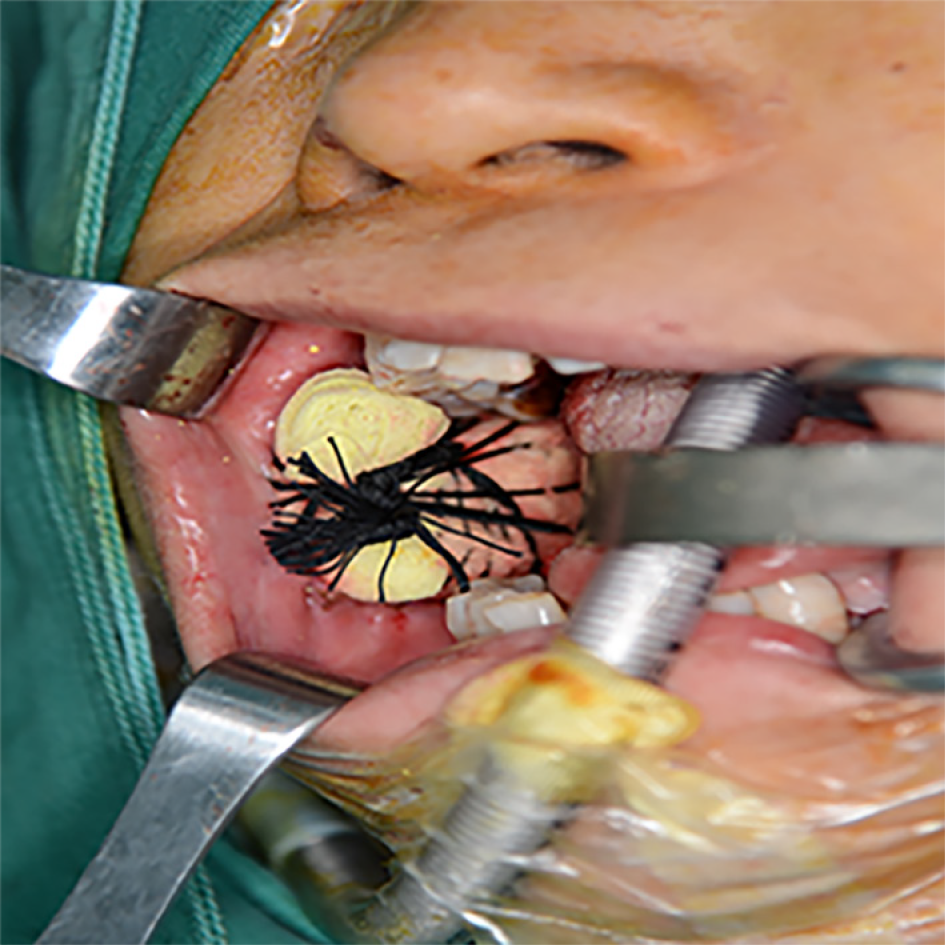
Figure 5 The iodoform yarn strips were packed and placed above the acellular dermal matrix, and the wound sutures were divided into four anti-wrapping and pressurizing strands.
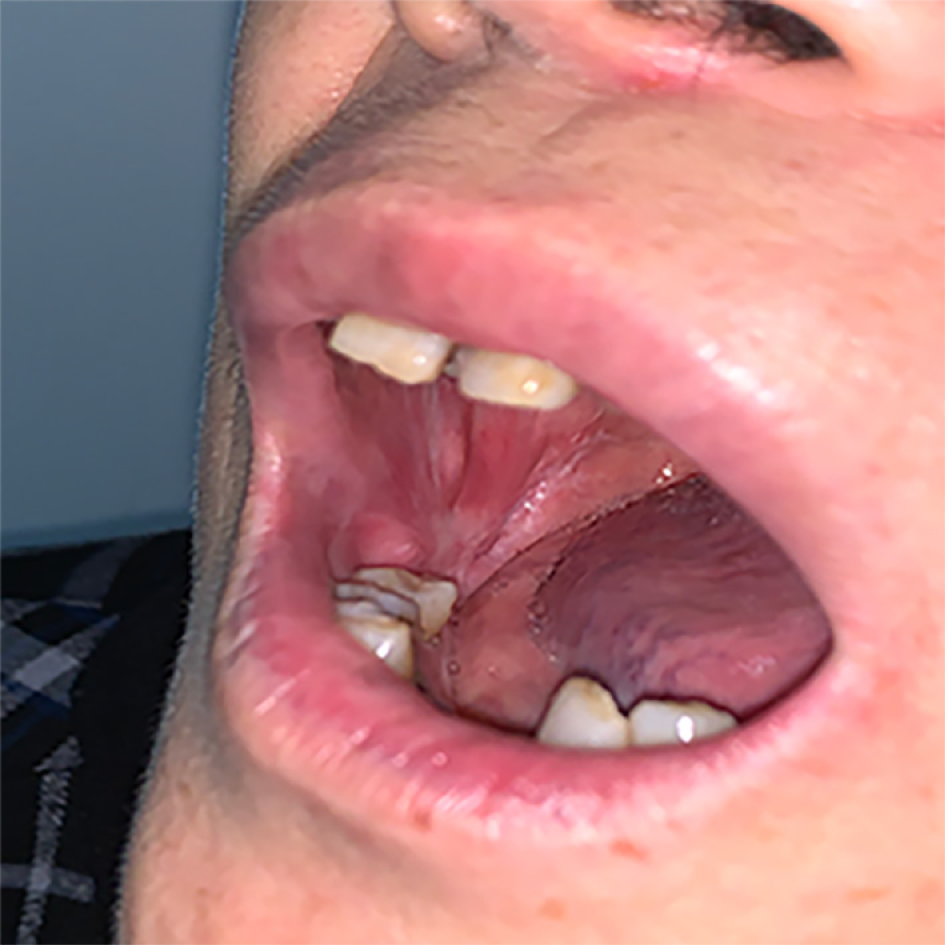
Figure 6 The surgical area was flat with similar mucosal tissue covering and local scar formation.
The degree of mouth opening returned to normal. The transplanted area remained stable.
- Citation: Fu ZZ, Chen LQ, Xu YX, Yue J, Ding Q, Xiao WL. Treatment of oral lichen planus by surgical excision and acellular dermal matrix grafting: Eleven case reports and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(6): 1446-1454
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i6/1446.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1446