©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2021; 9(36): 11467-11474
Published online Dec 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i36.11467
Published online Dec 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i36.11467
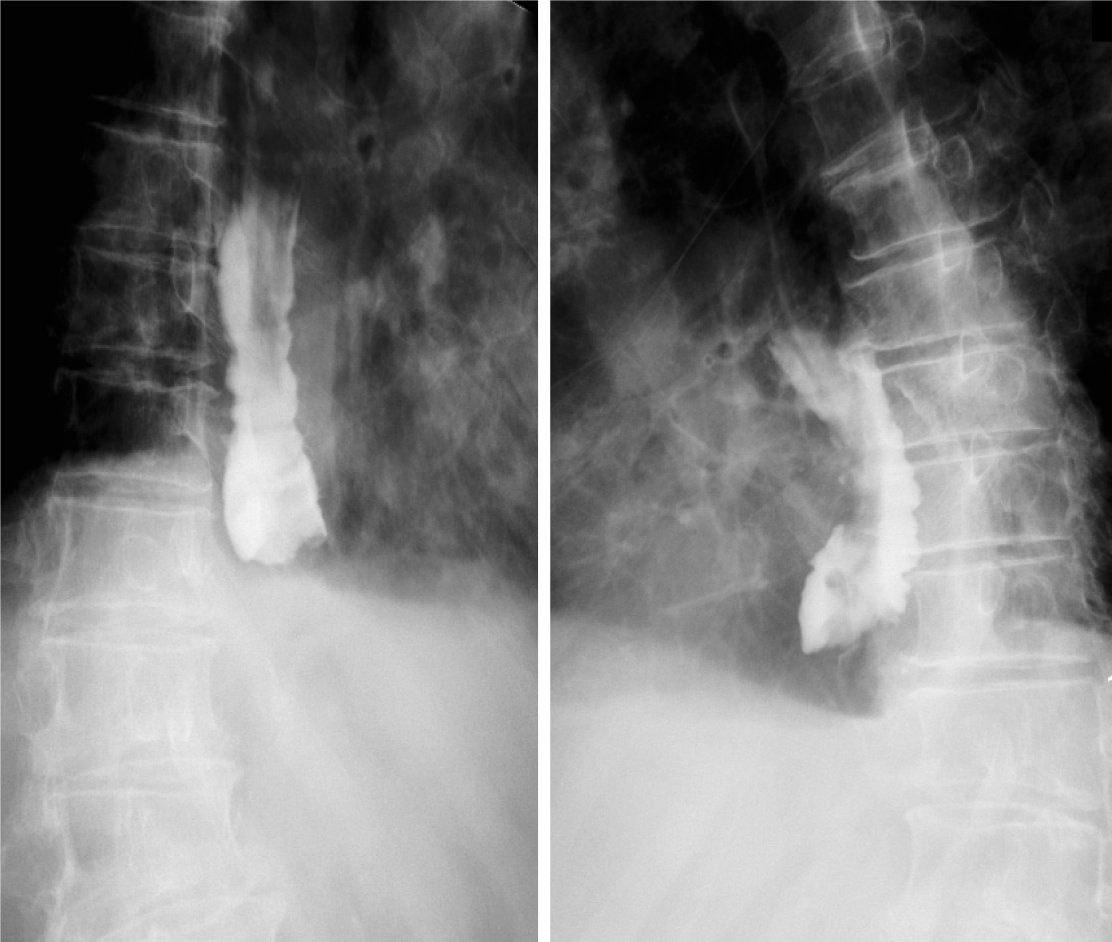
Figure 1 Esophageal X-ray barium meal angiography performed before endoscopic treatment in this case.
The lumen is obviously dilated, and an obstruction can be observed in the lower segment with only a small amount of contrast medium entering the gastric cavity, and there is no obvious extravasation.
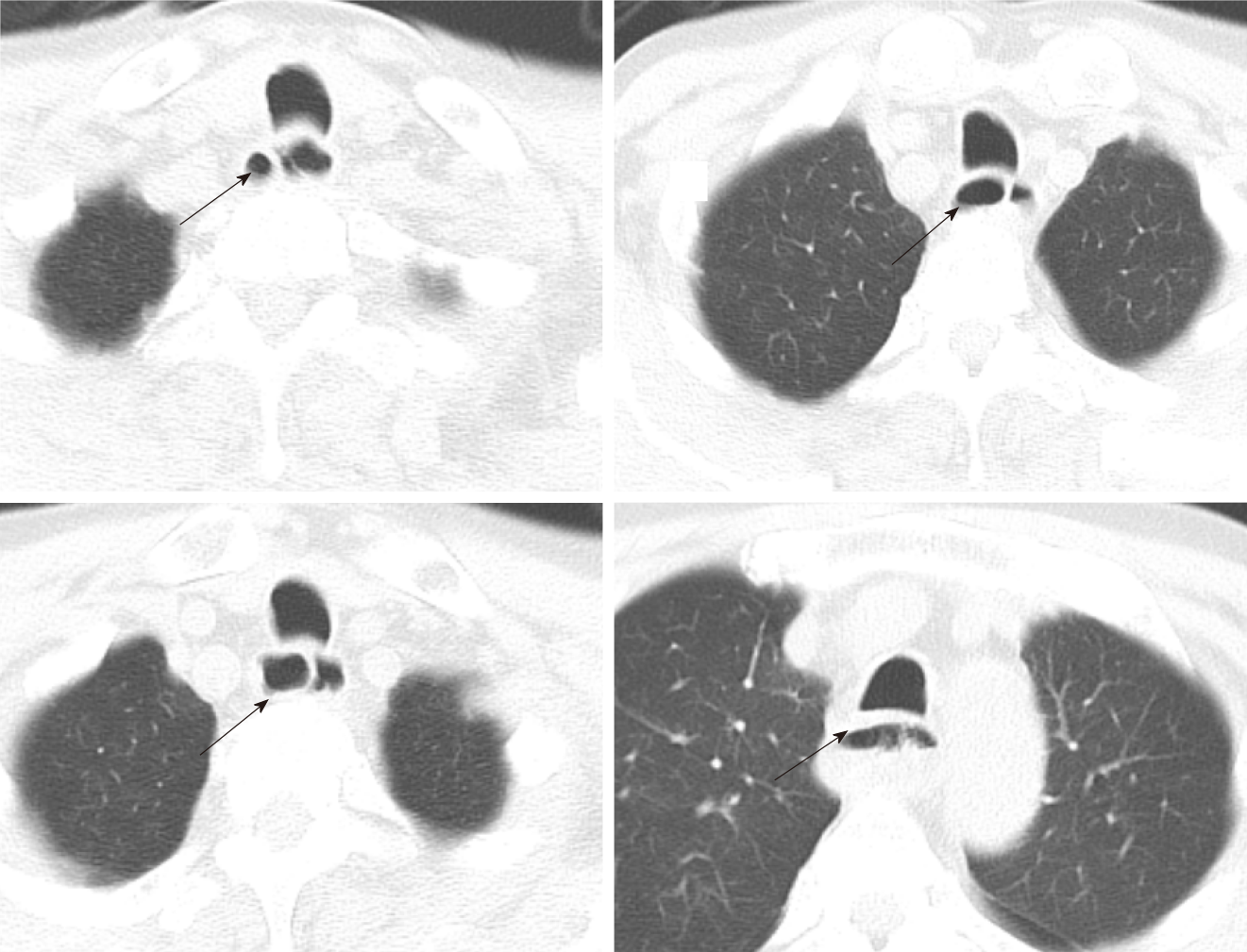
Figure 2 Computed tomography of the esophagus before endoscopic treatment in this patient.
The esophageal cavity was dilated with an irregular diaphragmatic shadow, linear-enhancement is observed in the mucosa after contrast enhancement and some segments of the esophagus have a “double-barreled” appearance. The arrow indicates a “double-barreled” appearance on computed tomography scan.
Figure 3 Gastroscopy was a performed before endoscopic treatment for this patient.
A and B: Endoscopic picture of the middle level of the esophagus. A thin mucosal bridge connects the proximal and distal mucosal tubes. Note the large mucosal defect with numerous small depressions around the mucosal bridge; Gastroscopic manifestations of the patient during endoscopic treatment; C-E: The esophageal mucosa was completely stripped and dissociated in the esophageal cavity, the lower end was narrow, and the gastroscope could not pass through. The blind end of the mucosa was cut with an L-knife. Subsequently, a disposable polypectomy device was used to remove a part of the mucosal strip so that the blind end was unobstructed, after which the gastroscope entered the gastric cavity smoothly.
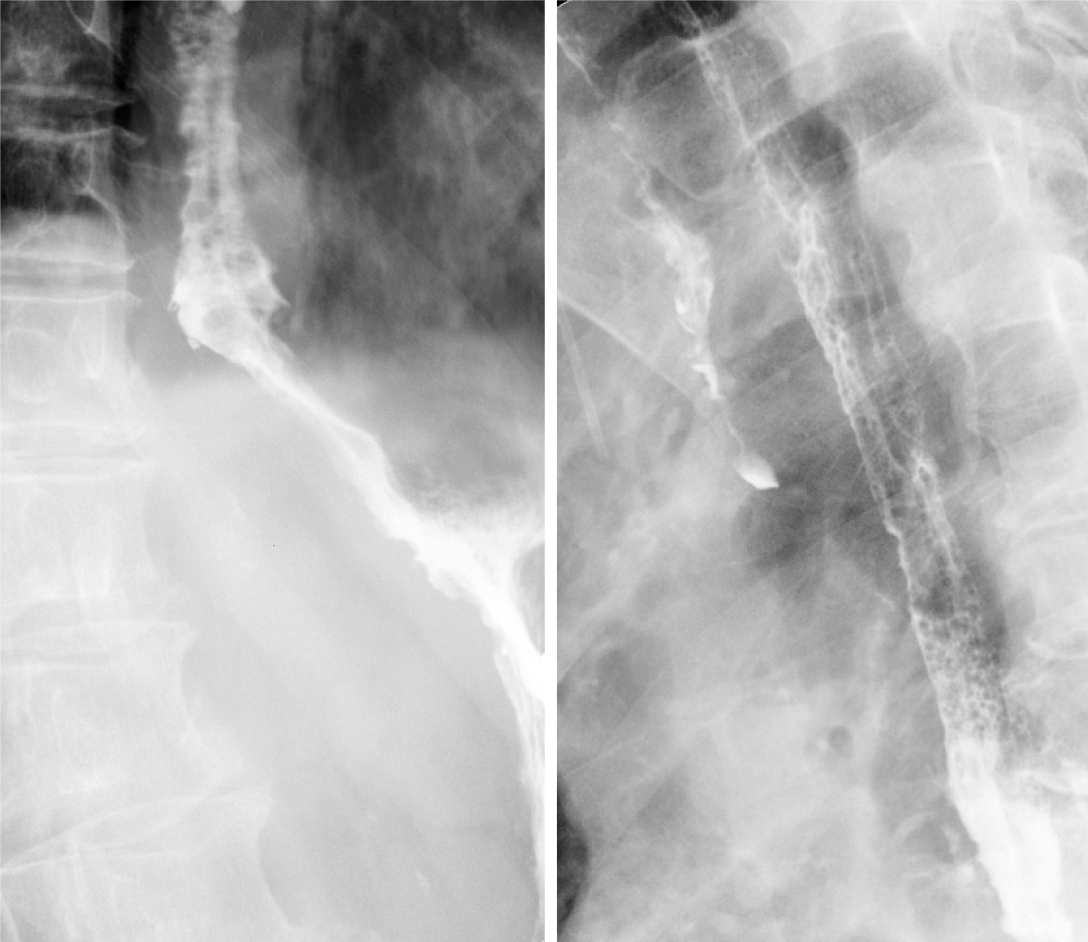
Figure 4 Reexamination with esophageal X-ray barium meal angiography after endoscopic treatment.
It revealed smooth passage of the contrast agent without obstruction, and the lumen of the esophageal wall was observed to be widened.
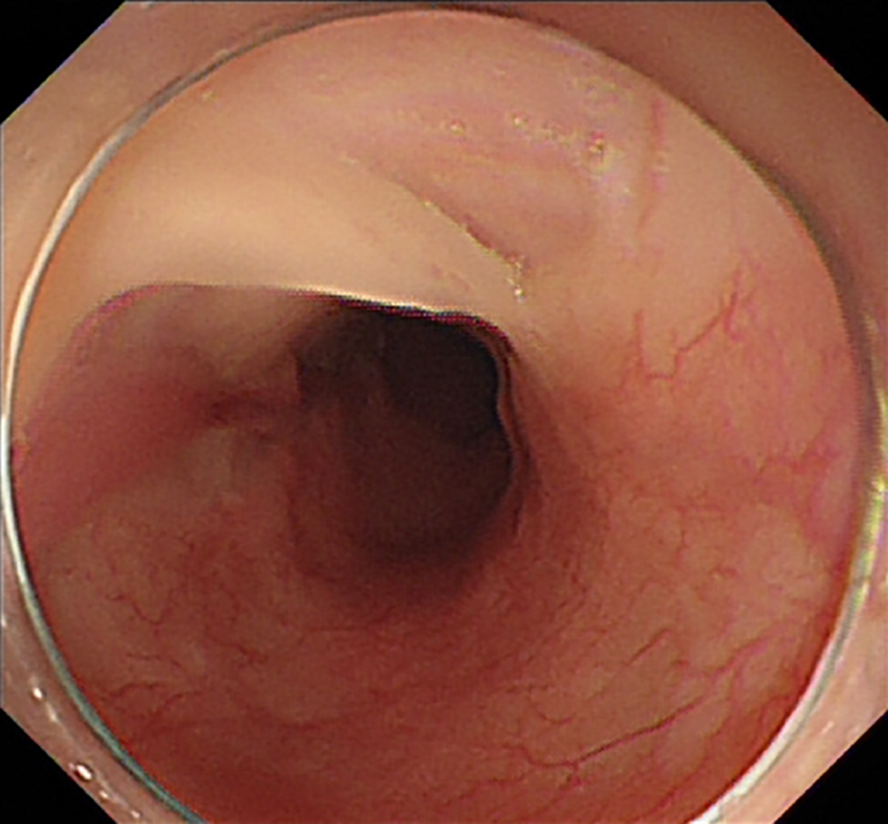
Figure 5 Follow-up gastroscopy performed after 2 mo.
Gastroscopy revealed that most of the regenerated esophageal mucosa had covered the surface of the esophageal muscle layer again.
- Citation: Hu JW, Zhao Q, Hu CY, Wu J, Lv XY, Jin XH. Rare spontaneous extensive annular intramural esophageal dissection with endoscopic treatment: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(36): 11467-11474
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i36/11467.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i36.11467