©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2021; 9(33): 10382-10391
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10382
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10382
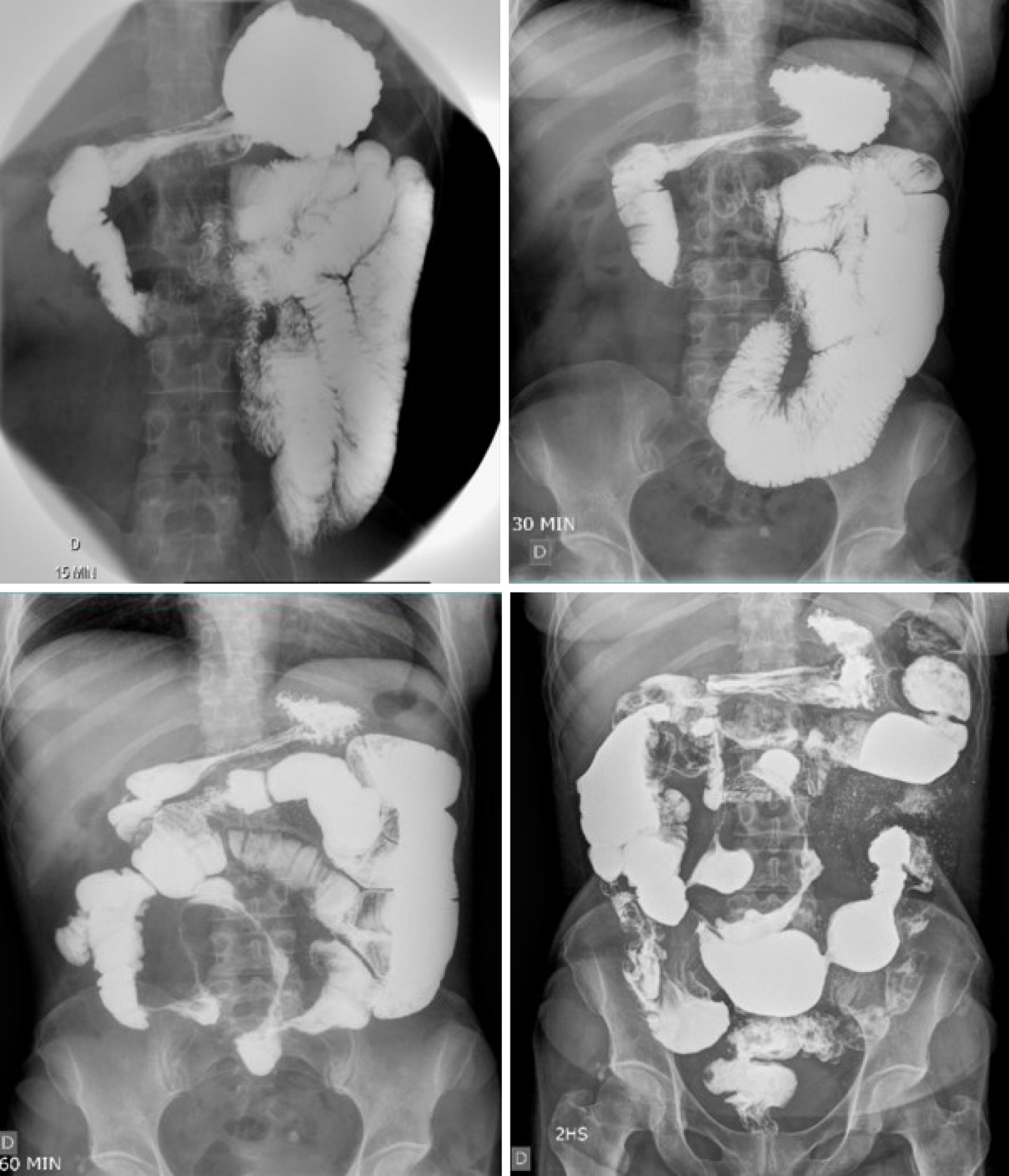
Figure 1 Small bowel follow-through showing accelerated intestinal transit.
Areas of stenosis in portions of the ileum, and the ileocecal valve with filiform aspect interspersed with areas of intestinal dilation. Presence of mucous relief irregularity with “cobblestone” images due to filiform ulcerations.
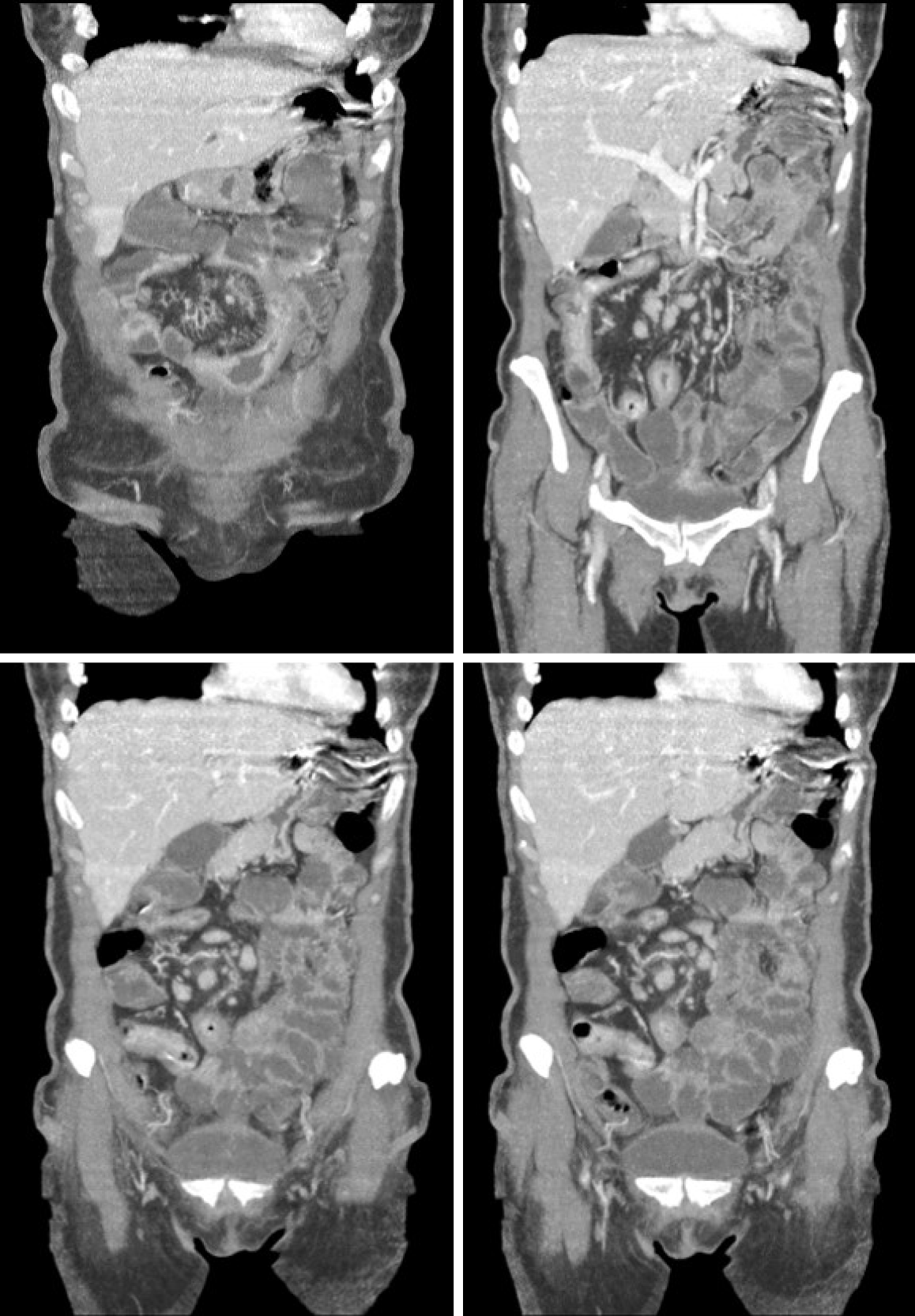
Figure 2 Computed tomography enterography.
Mucosal irregularities consistent with ulcerations in the small intestine, stenosis and dilation in the terminal ileum, and thickening of the intestinal wall with hypervascularity of the mesentery and vascular dilatation (comb sign).
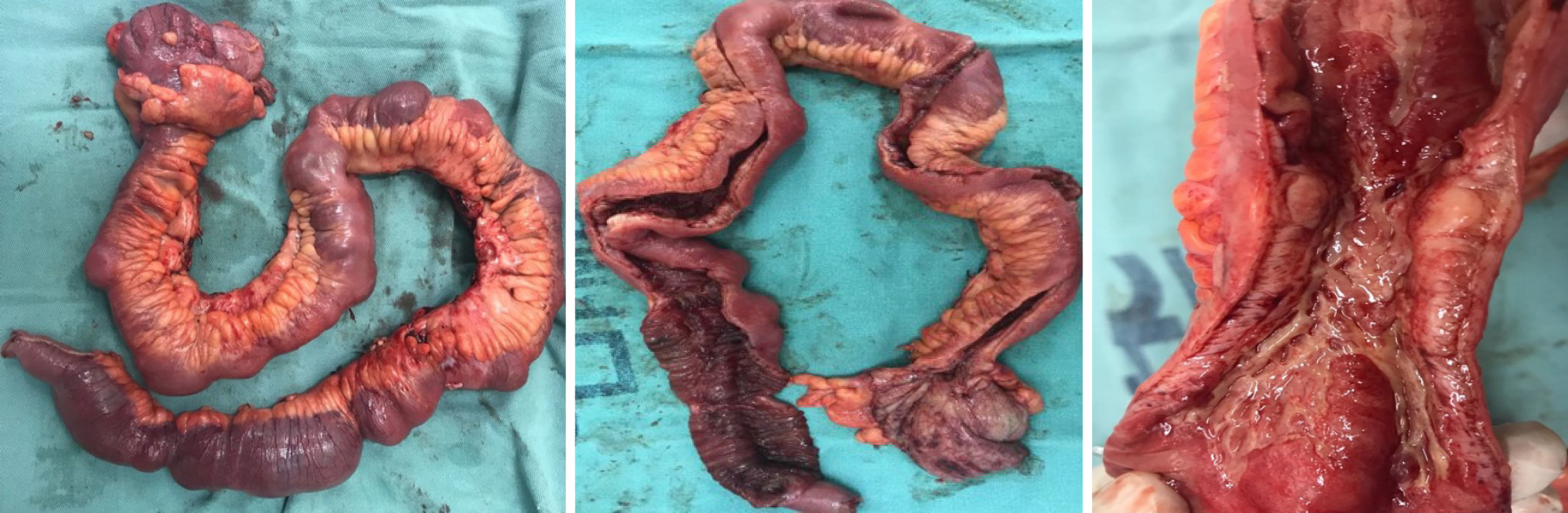
Figure 3
Surgical specimen measuring 70 cm showing severe disease with thickening of the ileum associated with ulcerations, stenosis, and dilation and mesenteric infiltration.
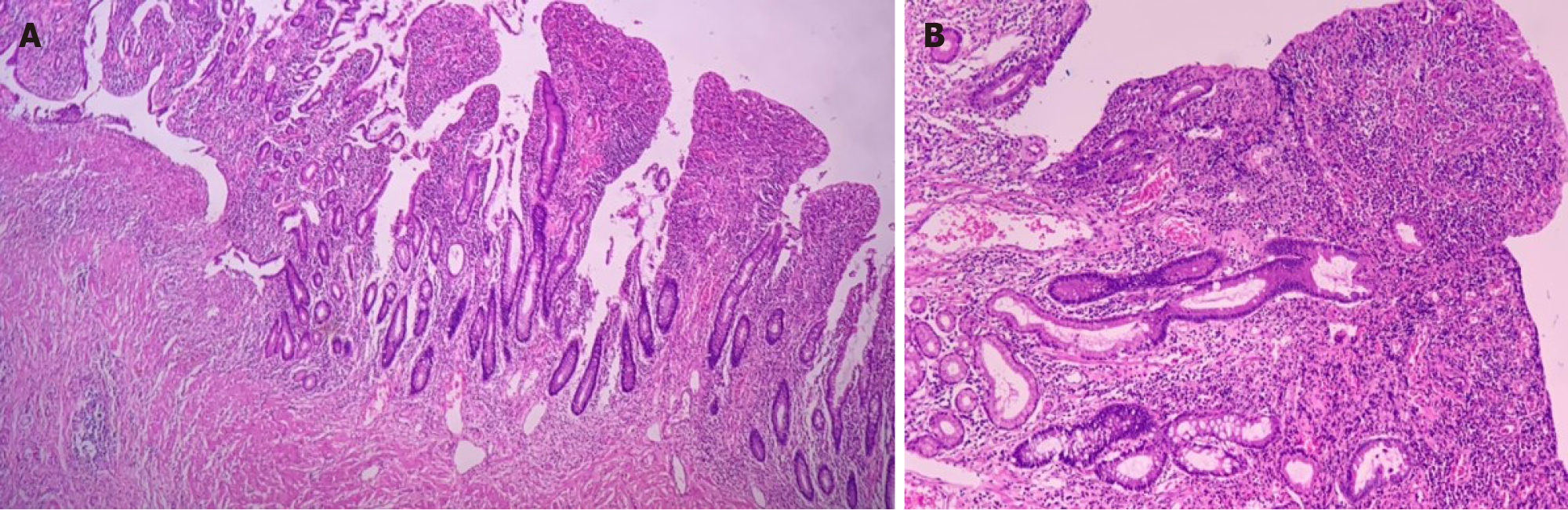
Figure 4 Histopathological diagnosis.
A: Chronic transmural inflammation with ulceration, intense submucosal fibrosis, and granulation tissue formation (H&E, 40 ×); B: Chronic colitis with ulceration, extensive chronic inflammatory infiltrate with plasmacytosis, architectural distortion of crypts, and partial loss of goblet cells (H&E, 100 ×).
- Citation: Grillo TG, Almeida LR, Beraldo RF, Marcondes MB, Queiróz DAR, da Silva DL, Quera R, Baima JP, Saad-Hossne R, Sassaki LY. Heart failure as an adverse effect of infliximab for Crohn's disease: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(33): 10382-10391
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i33/10382.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10382