©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2021; 9(31): 9670-9679
Published online Nov 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9670
Published online Nov 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9670
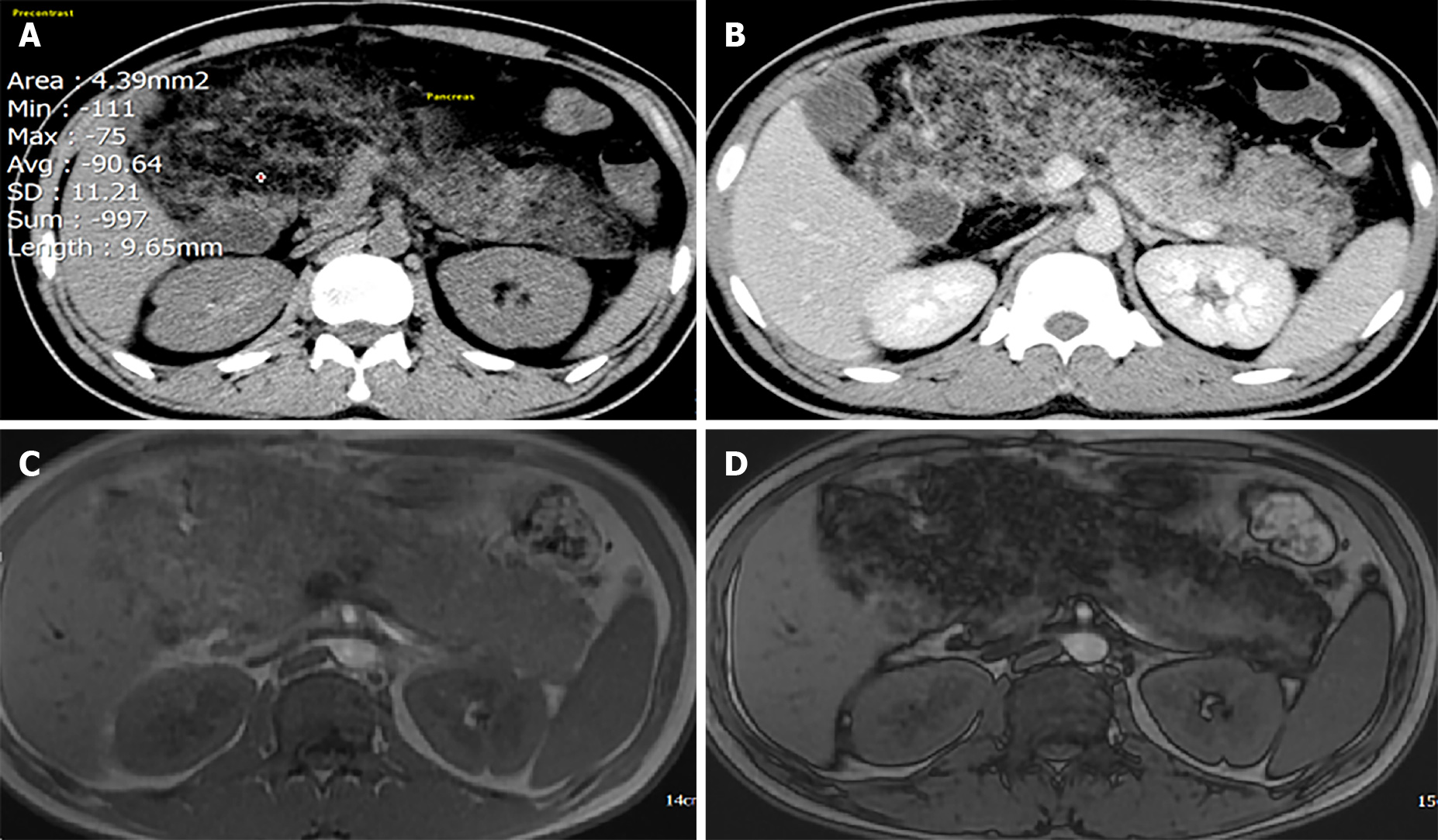
Figure 1 Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
A: Plain CT: density of the pancreatic parenchyma was uniformly decreased to the same level as that of the surrounding fatty tissue (attenuation value = 90.64 HU); B: Contrast-enhanced CT: Pancreatic parenchyma was absent, completely replaced by fat; C and D: MRI of the pancreas. In- and out-phase MRI respectively show a typical global (C) hyperintensity; and (D) fat suppression.
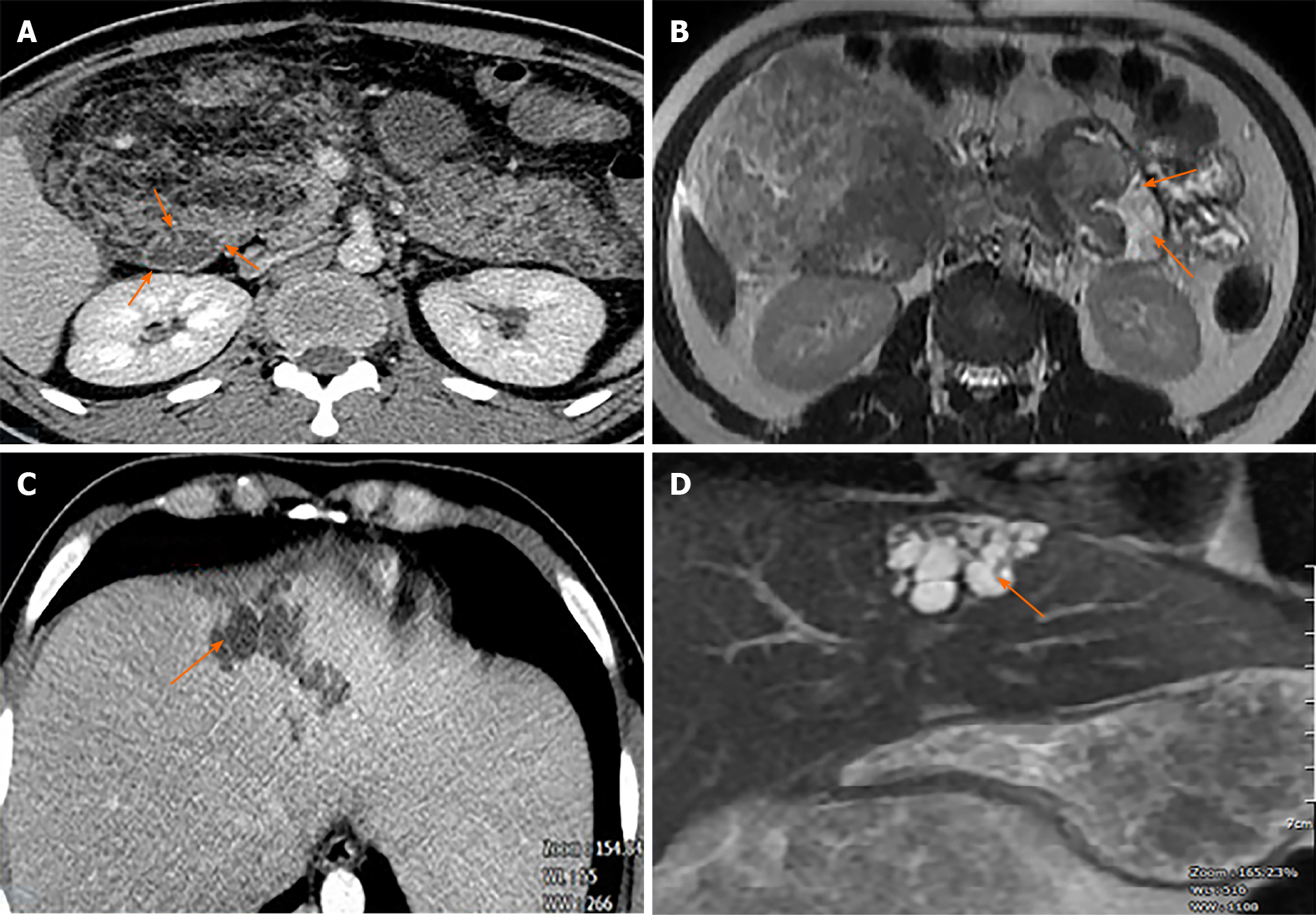
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
A: CECT showing fatty tissue infiltration into duodenal wall (orange arrows); B: MRI also showed fatty tissue infiltration into duodenal wall (orange arrows); C: CECT scan showed hypoechoic saccular dilatations in segment IV of the liver; D: T2-weighted MRI showed segmental biliary ectasia (arrow).
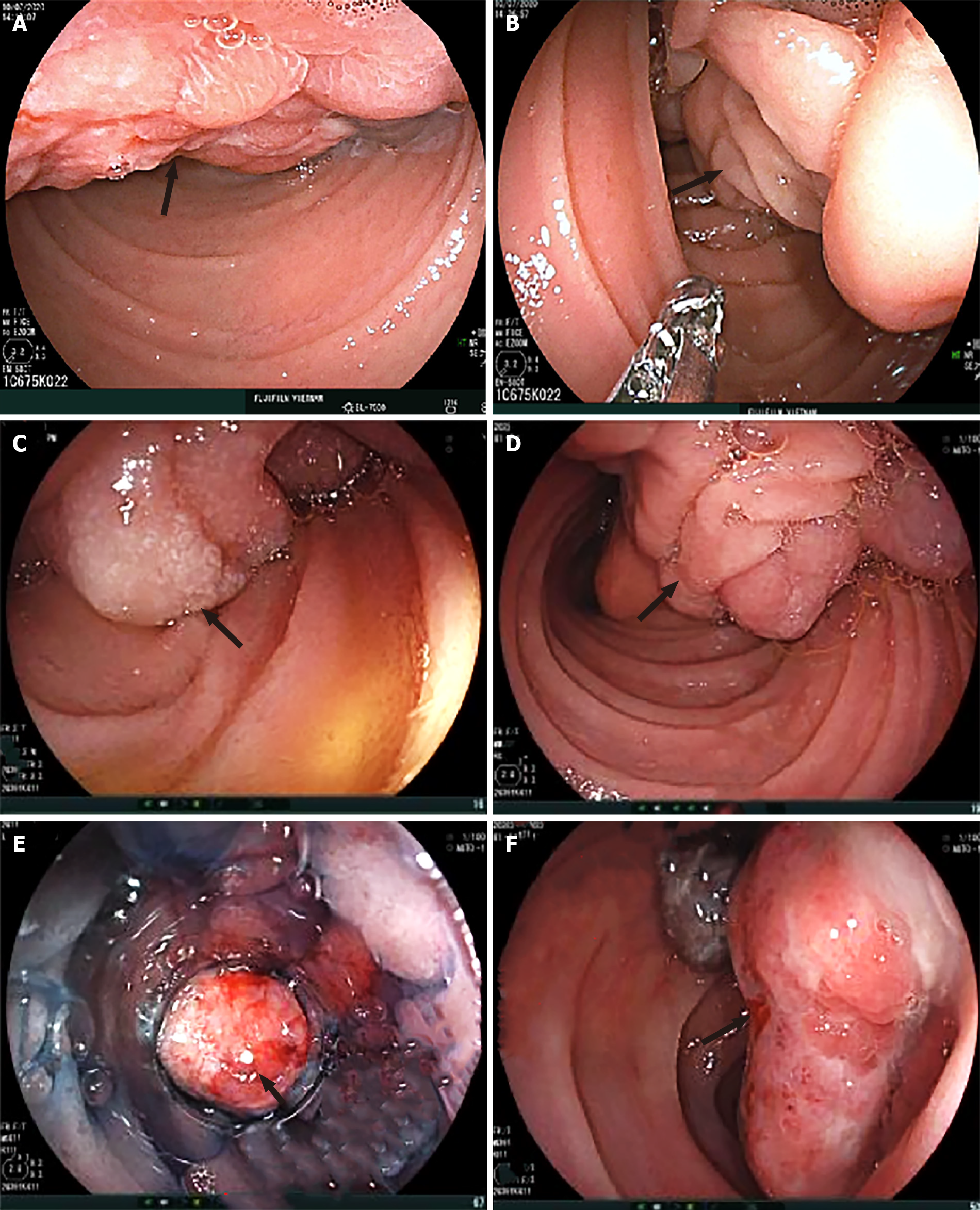
Figure 3 Endoscopic appearance of the submucosal tumor arising from the duodenum (arrows).
A: Irregular surface with shallow ulcers; B–D: A thick stalk below the head portion of the tumor; E and F: Surface ulcers with bleeding.
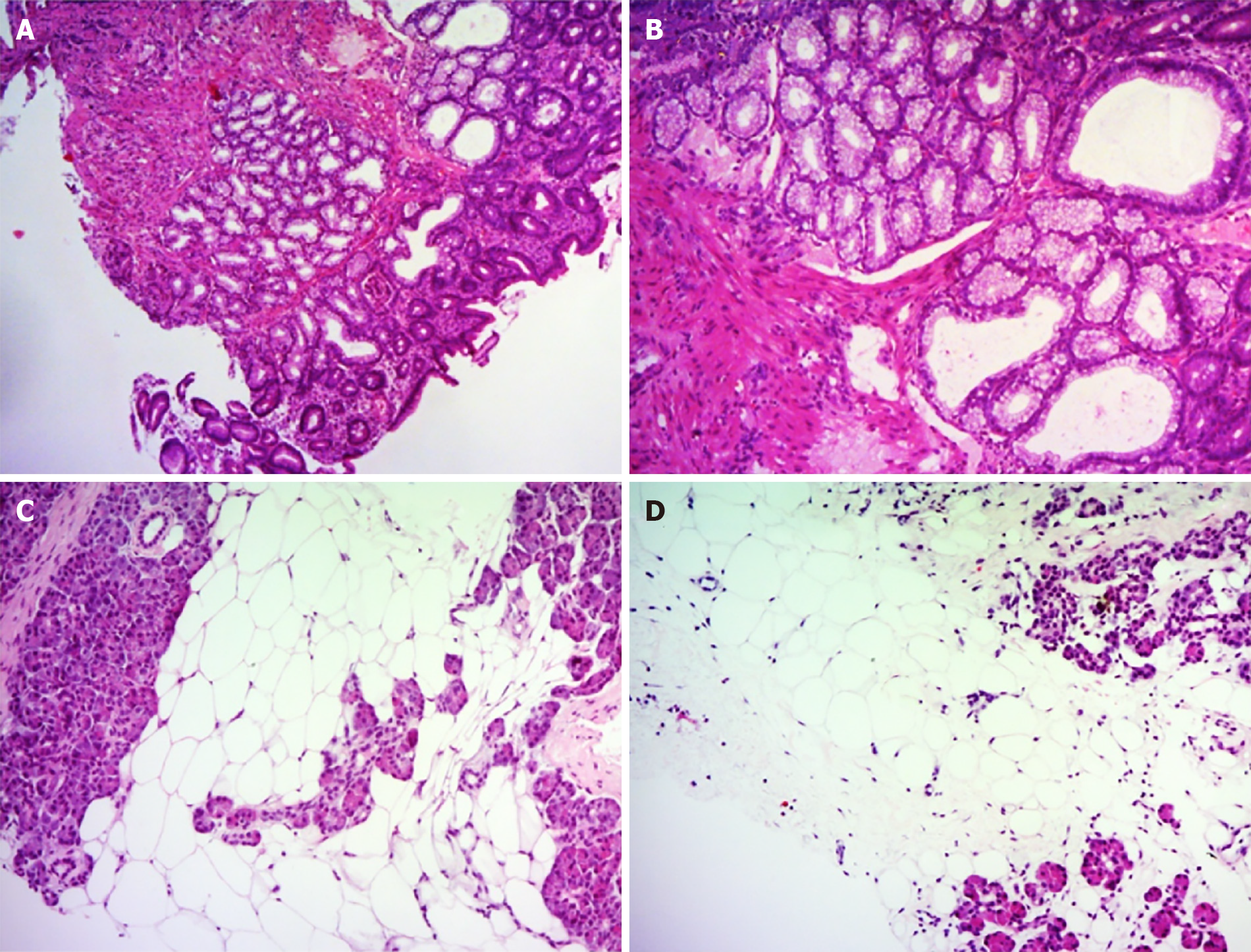
Figure 4 Histological findings of duodenal and pancreatic biopsy specimens.
A and B: The duodenal biopsy showed lobulated proliferation of submucosal Brunner’ glands comprising benign-looking acini lined by mucous cells with basal nuclei without atypia, which was consistent with Brunner’s gland hyperplasia. C and D: Percutaneous pancreatic biopsies revealed adipose tissue replacing the pancreatic parenchyma. Some pancreatic acini were identified with a scattered distribution. Hematoxylin and eosin stain (A–D). Original magnification: (A, C, D) × 40, (B) × 100.
- Citation: Nguyen LC, Vu KT, Vo TTT, Trinh CH, Do TD, Pham NTV, Pham TV, Nguyen TT, Nguyen HC, Byeon JS. Brunner’s gland hyperplasia associated with lipomatous pseudohypertrophy of the pancreas presenting with gastrointestinal bleeding: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(31): 9670-9679
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i31/9670.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9670