©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2021; 9(31): 9333-9349
Published online Nov 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9333
Published online Nov 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9333
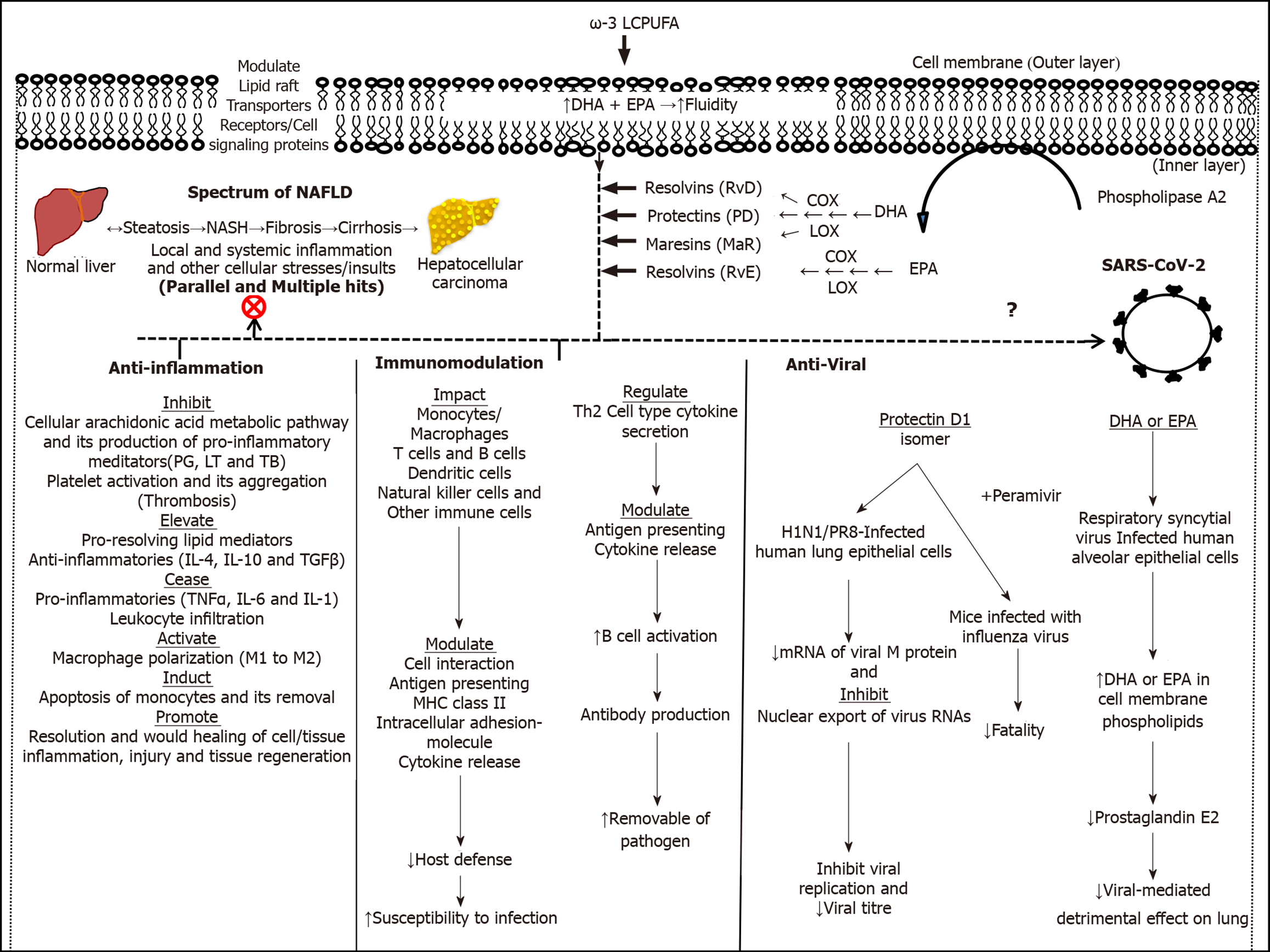
Figure 1 Schematic summary of the therapeutic potential of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and their derived lipid mediators.
ω-3 LCPUFA: Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids; COX: Cyclooxygenase; DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid; EPD: Eicosapentaenoic acid; IL: Interleukin; LOX: Lipoxygenase; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; PG: Prostaglandin; TX: Thromboxane; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; ⊗: Inhibitory effect, ↓: Decrease; ↑: Increase.
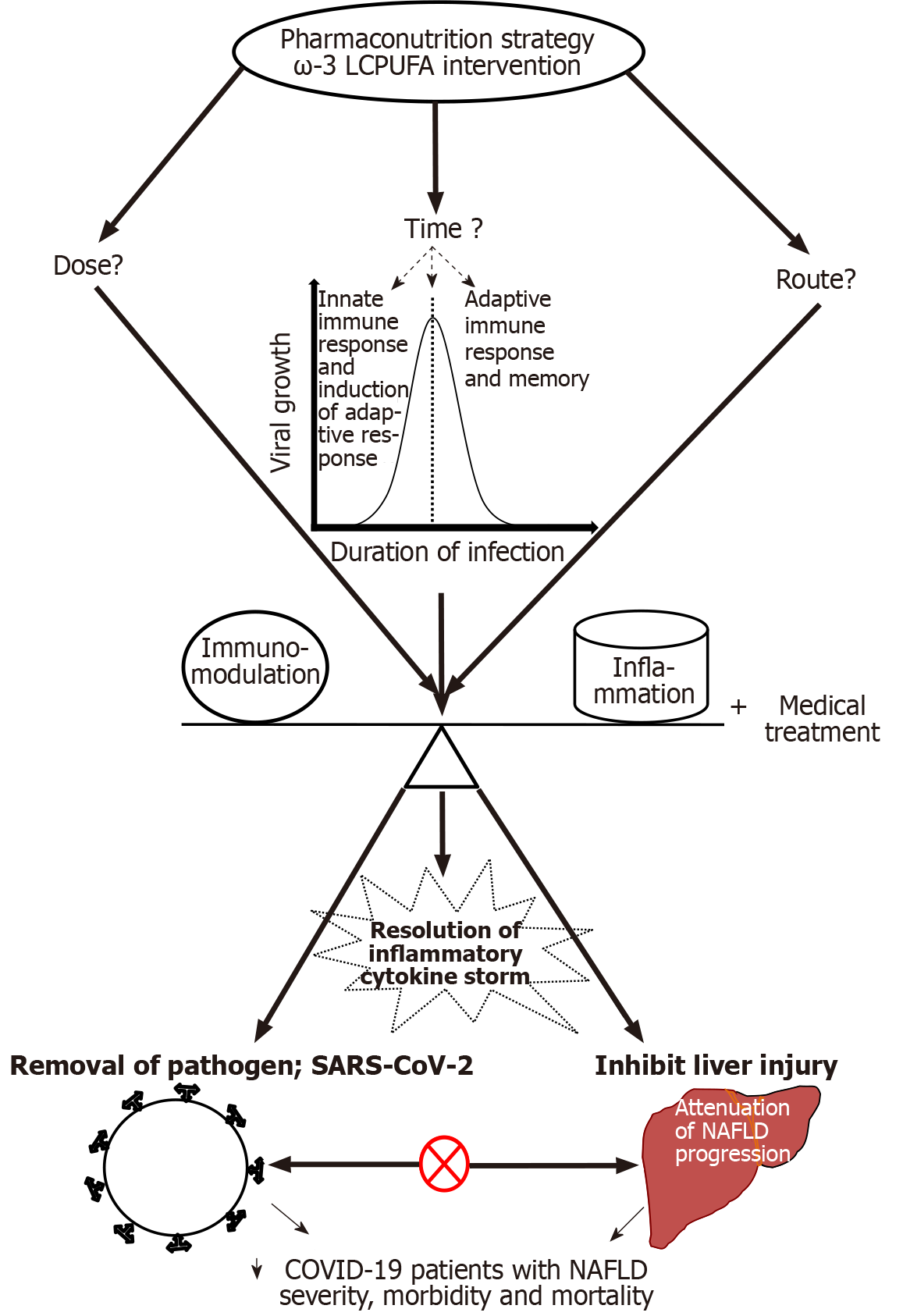
Figure 2 Schematic summary of the pharmaconutrition strategy and possible outcomes: ⊗ - Disconnecting bi-directional relationship between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and ↓ - decrease.
ω-3 LCPUFA: Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Jeyakumar SM, Vajreswari A. Pharmaconutrition strategy to resolve SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory cytokine storm in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(31): 9333-9349
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i31/9333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9333