©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2021; 9(27): 8232-8241
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i27.8232
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i27.8232
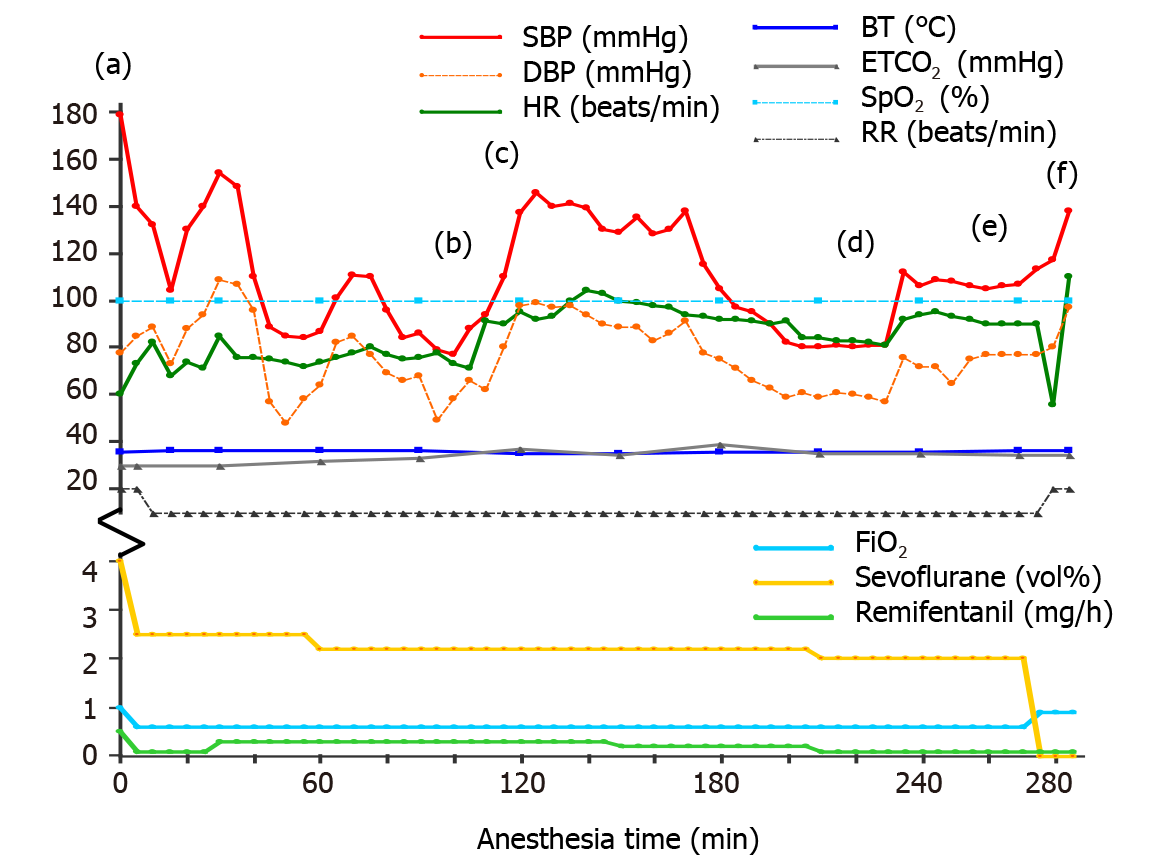
Figure 1 The vital signs and drugs used during the operation.
Intravenous drugs: (a) Propofol 70 mg and rocuronium 50 mg; (b) Ephedrine 10 mg; (c) Rocuronium 10 mg; (d) Ephedrine 5 mg; (e) Ramosetron 0.3 mg and ketorolac 30 mg; and (f) Pyridostigmine 10 mg and glycopyrrolate 0.4 mg. SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; HR: Heart rate; BT: Body temperature; ETCO2: End-tidal CO2; SpO2: Oxygen saturation; RR: Respiratory rate; FiO2: Fraction of inspired oxygen.
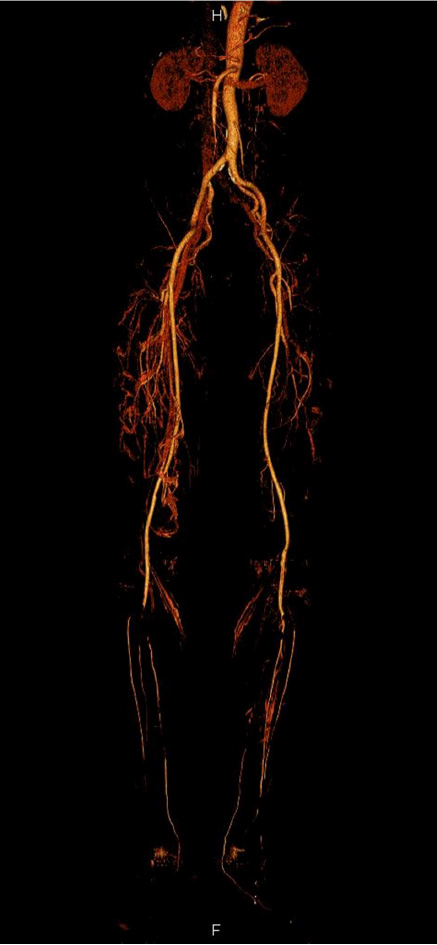
Figure 2 Computed tomography angiography findings.
Filling defects are seen in the bilateral popliteal arteries, bilateral proximal anterior tibial arteries, and bilateral tibioperoneal trunks.
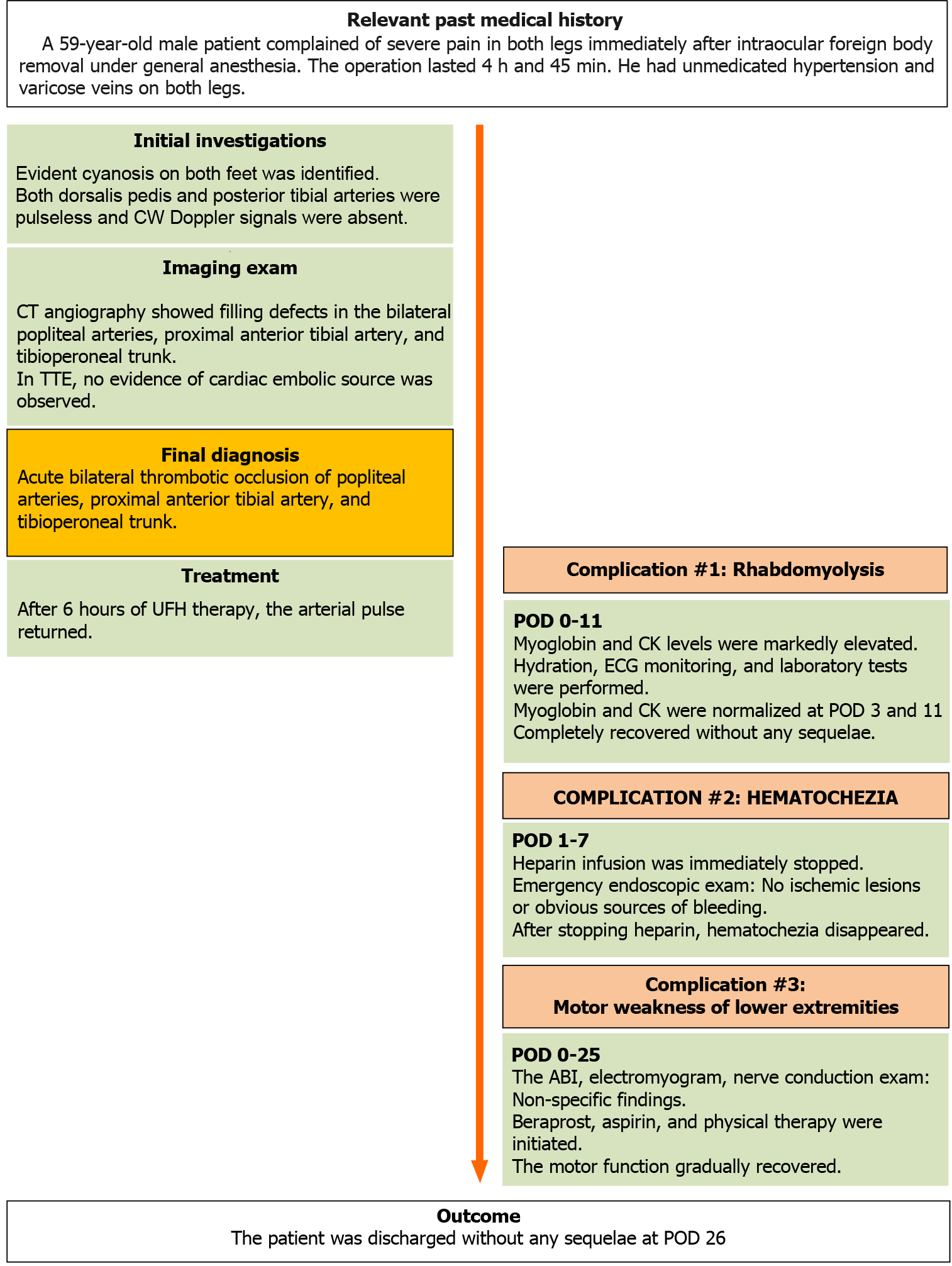
Figure 3 Case report timeline.
CW: Continuous wave; TTE: Transthoracic echocardiogram; UFH: Unfractionated heparin; ABI: Ankle brachial index; POD: Postoperative day.
- Citation: Jeon S, Hong JM, Lee HJ, Kim E, Lee H, Kim Y, Ri HS, Lee JJ. Acute lower extremity arterial thrombosis after intraocular foreign body removal under general anesthesia: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(27): 8232-8241
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i27/8232.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i27.8232