©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2021; 9(26): 7772-7785
Published online Sep 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i26.7772
Published online Sep 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i26.7772
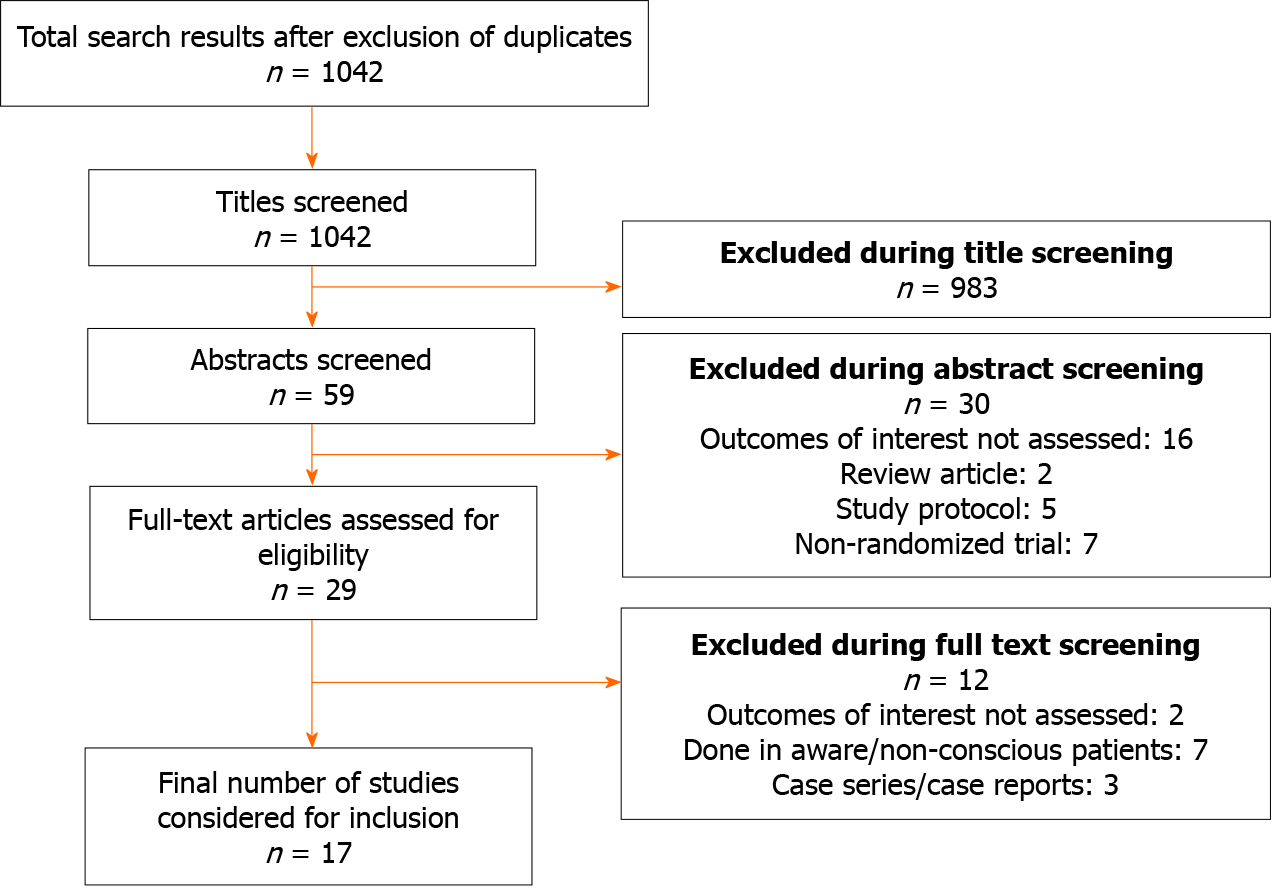
Figure 1 Selection process of the studies included in the review.
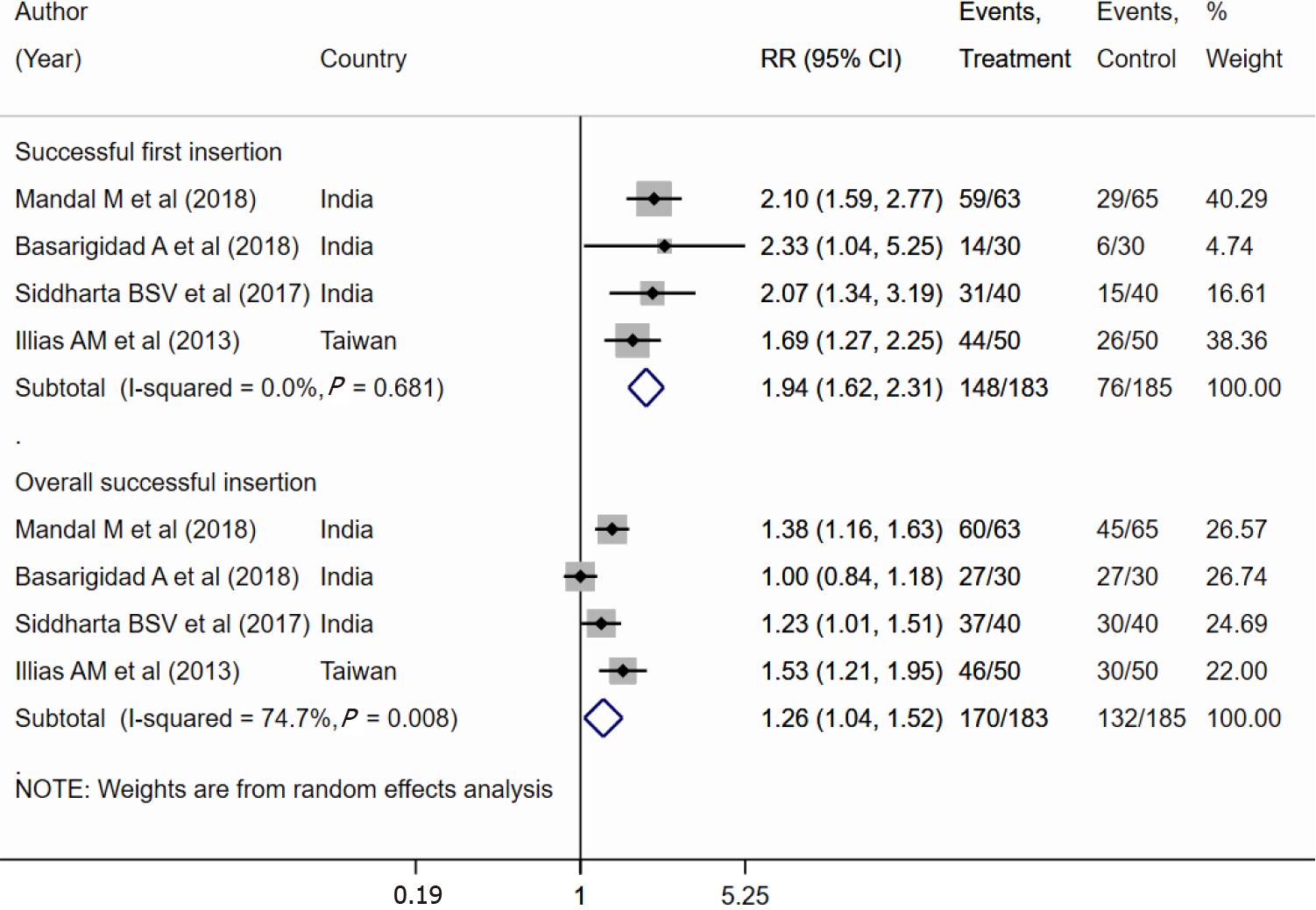
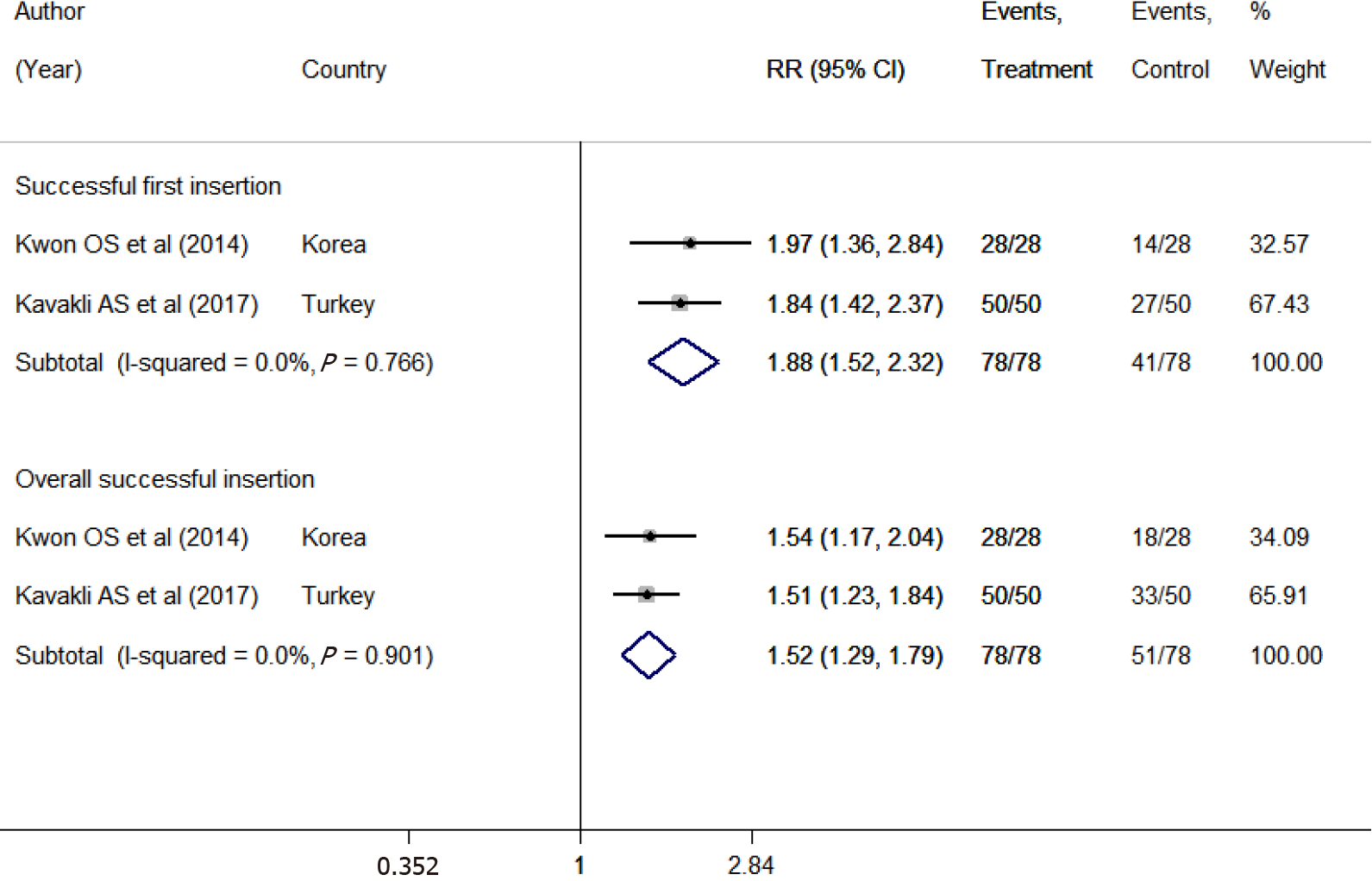
Figure 2 Comparison between the conventional technique and the reverse Sellick’s maneuver in terms of successful first and overall insertions.
RR: Relative risk; CI: Confidence interval.
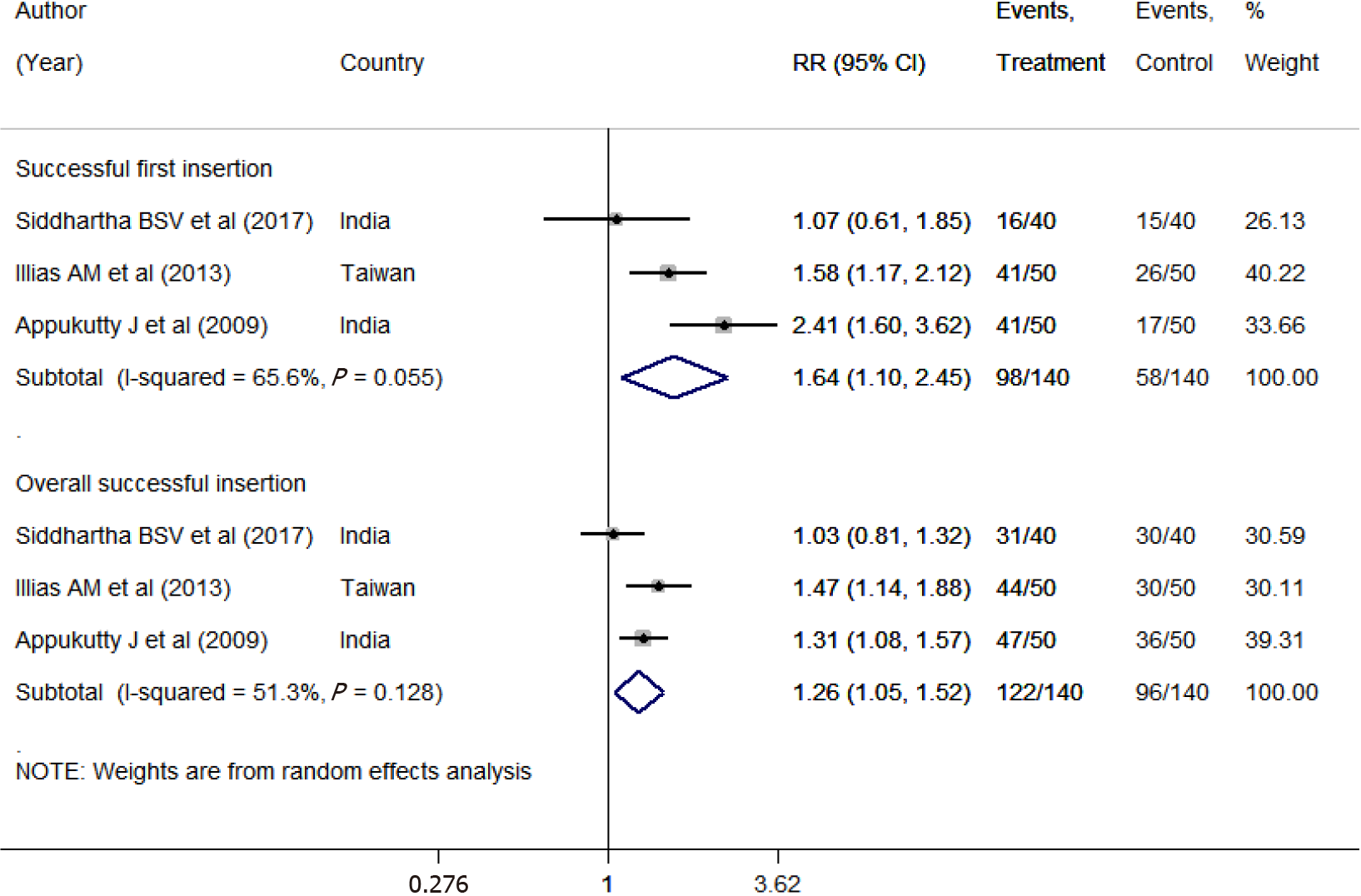
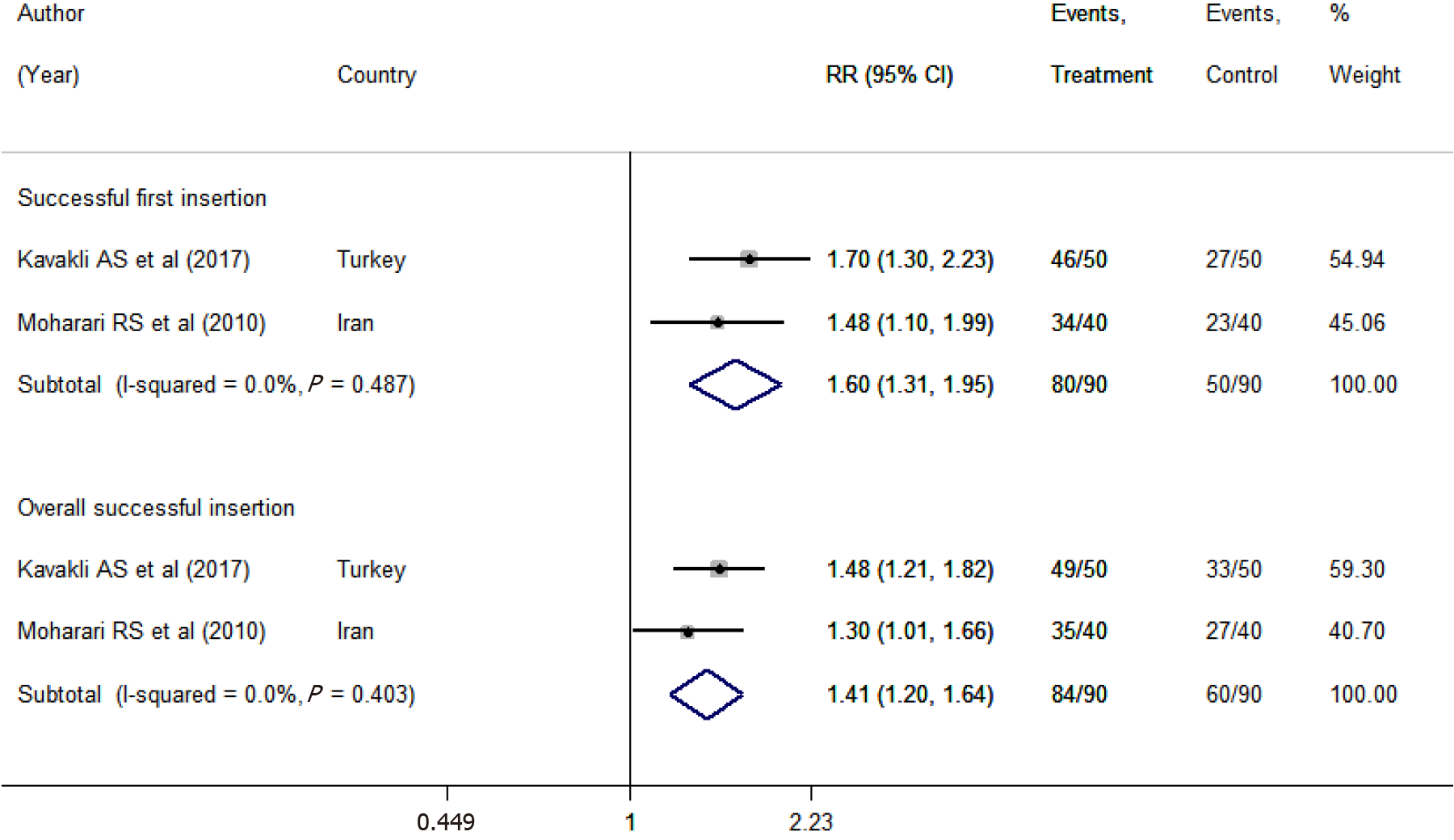
Figure 3 Comparison between the conventional technique and neck flexion with lateral neck pressure in terms of successful first and overall insertions.
RR: Relative risk; CI: Confidence interval.
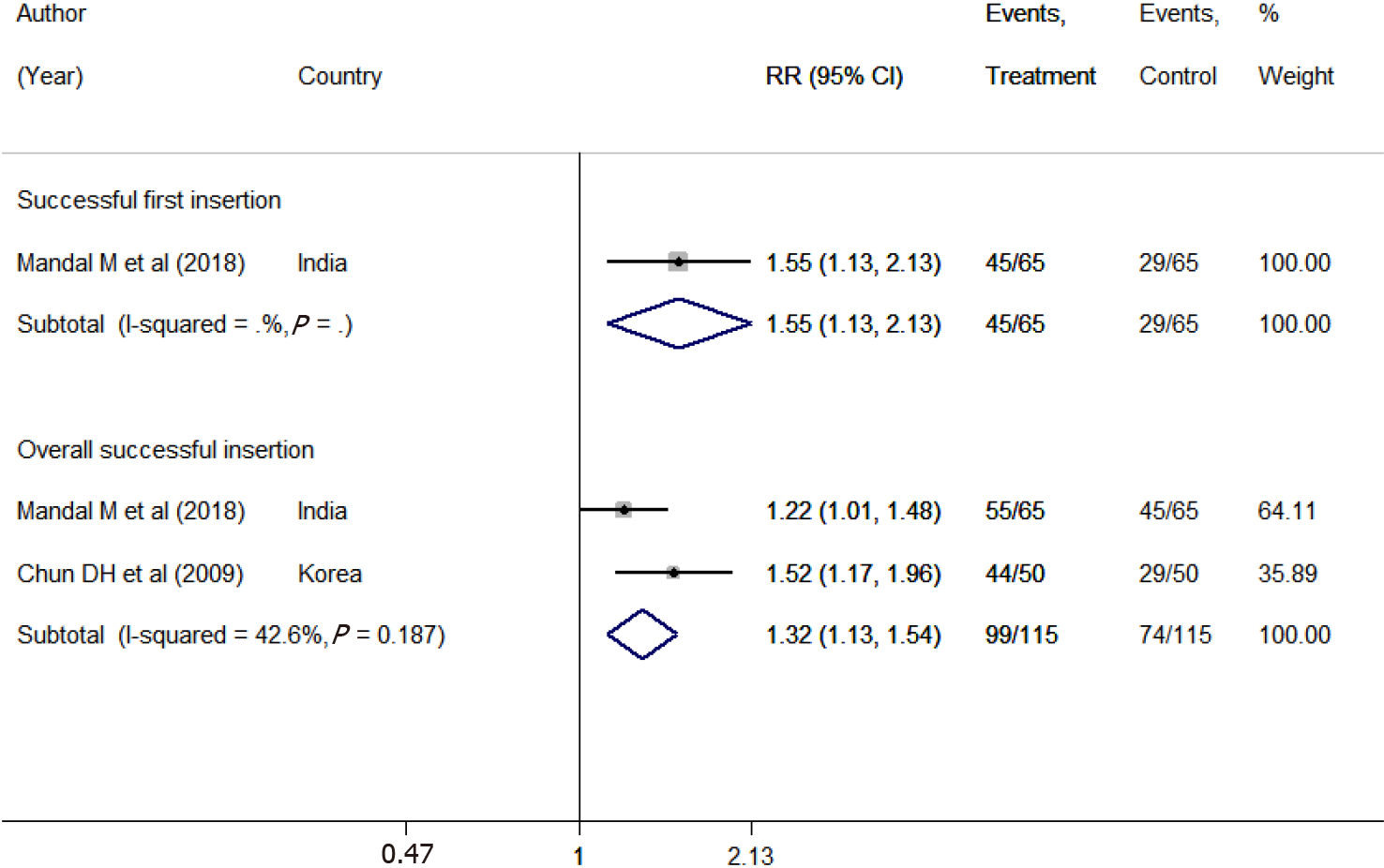
Figure 4 Comparison between the placement of a normal nasogastric tube and frozen nasogastric tube in terms of successful first and overall insertions.
RR: Relative risk; CI: Confidence interval.
Figure 5 Comparison between the conventional nasogastric tube placement technique and endotracheal tube-assisted placement in terms of successful first and overall insertions.
RR: Relative risk; CI: Confidence interval.
Figure 6 Comparison between the conventional nasogastric tube placement technique and video-assisted placement in terms of successful first and overall insertions.
RR: Relative risk; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Ou GW, Li H, Shao B, Huang LM, Chen GM, Li WC. Comparison of different methods of nasogastric tube insertion in anesthetized and intubated patients: A meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(26): 7772-7785
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i26/7772.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i26.7772