©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2020; 8(22): 5663-5669
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5663
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5663
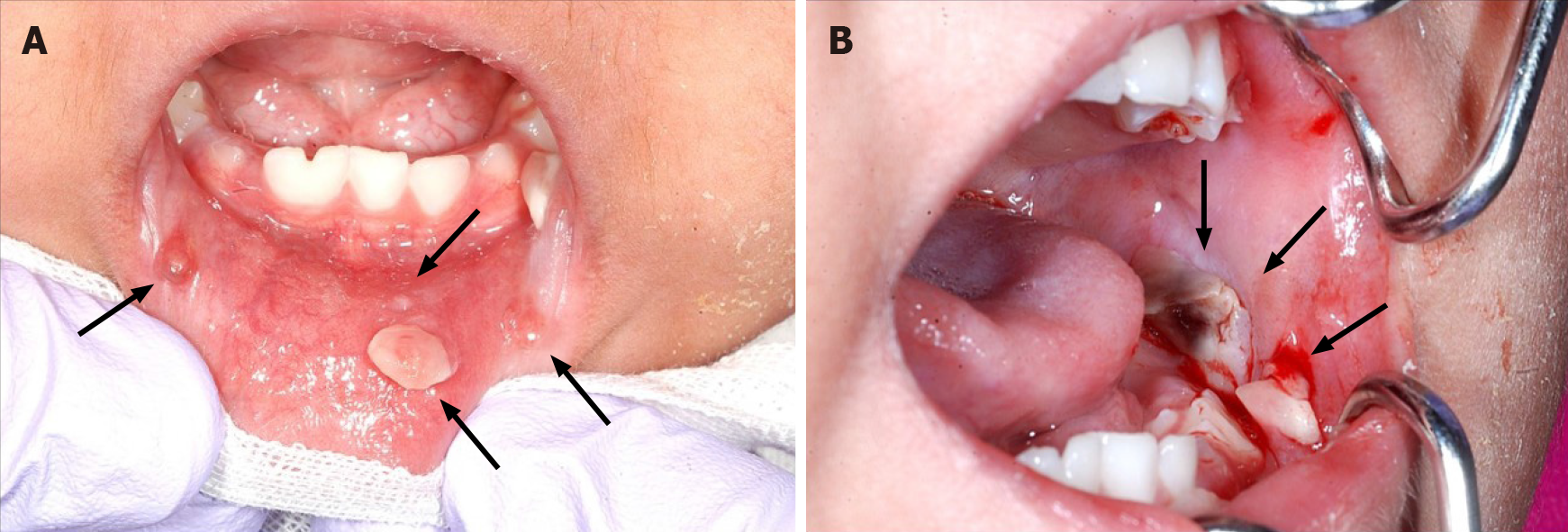
Figure 1 Oral mucositis of the lip and buccal region.
There were no findings suggesting lichen planus. A: A pedunculated nodule 8 mm × 5 mm in size and a sessile nodule 2 mm × 2 mm in size in the lower lip mucosa (arrow); B: The left buccal mucosa was grayish-white with a bleeding nodule (arrow).
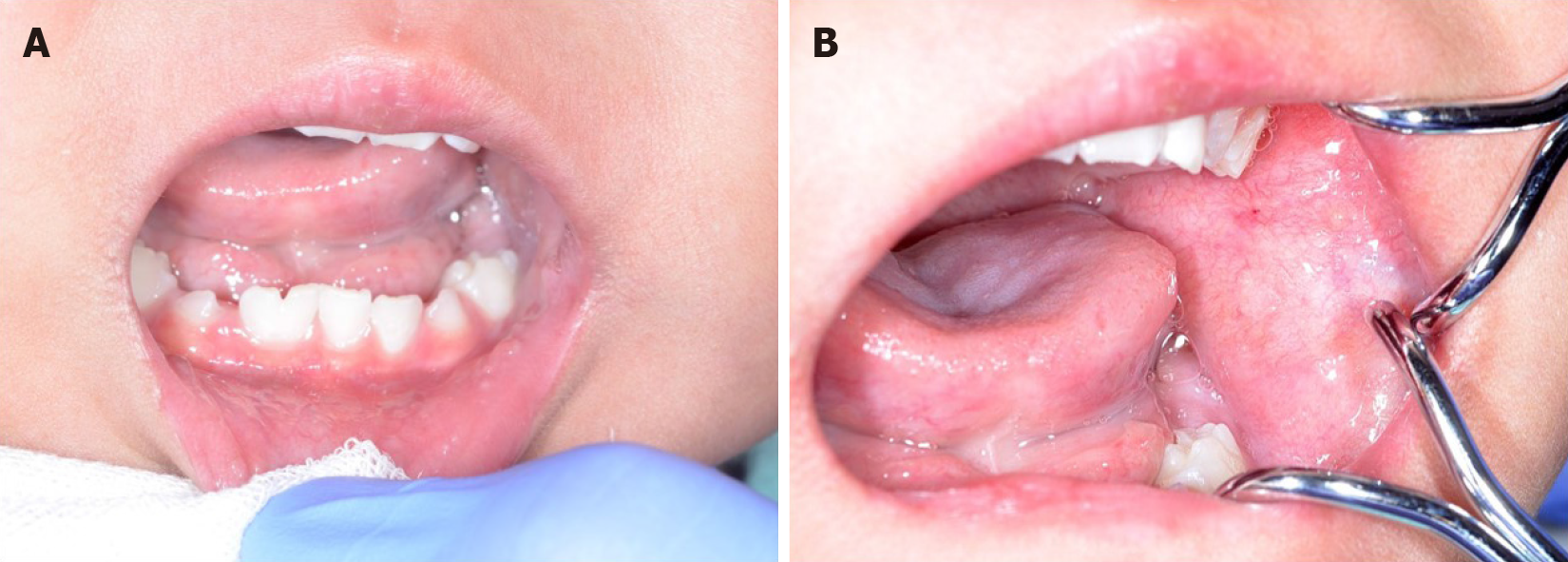
Figure 2 One month after the first visit, all lesions spontaneously reduced.
A and B: Oral nodules in the lower lip mucosa had disappeared 1 mo after the first visit.
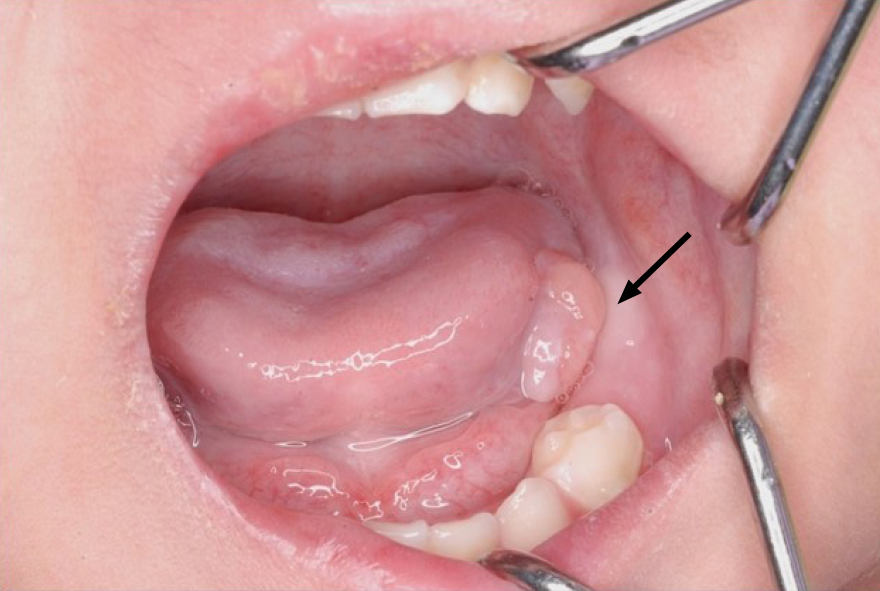
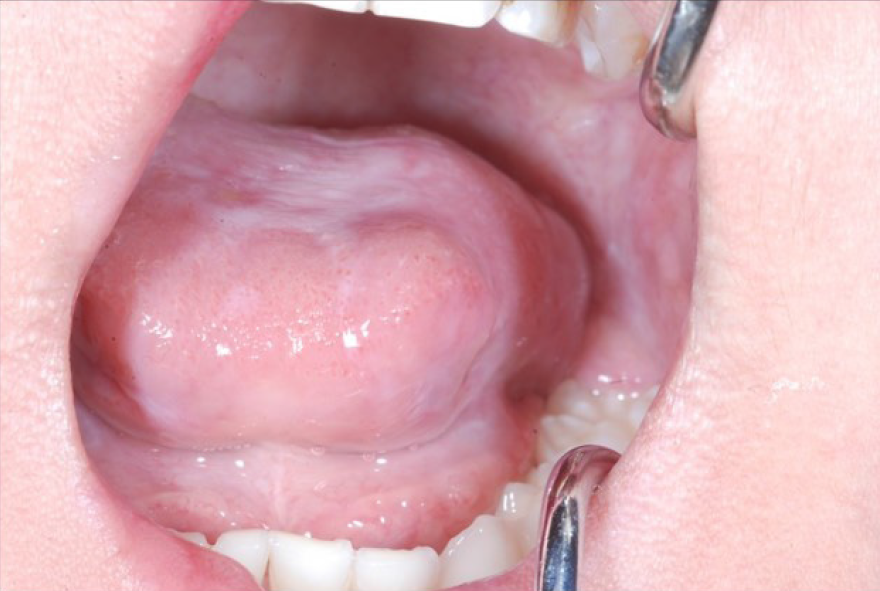
Figure 3 An elastic, soft, pedunculated nodule 12 mm in diameter was detected on the left tongue margin (arrow).
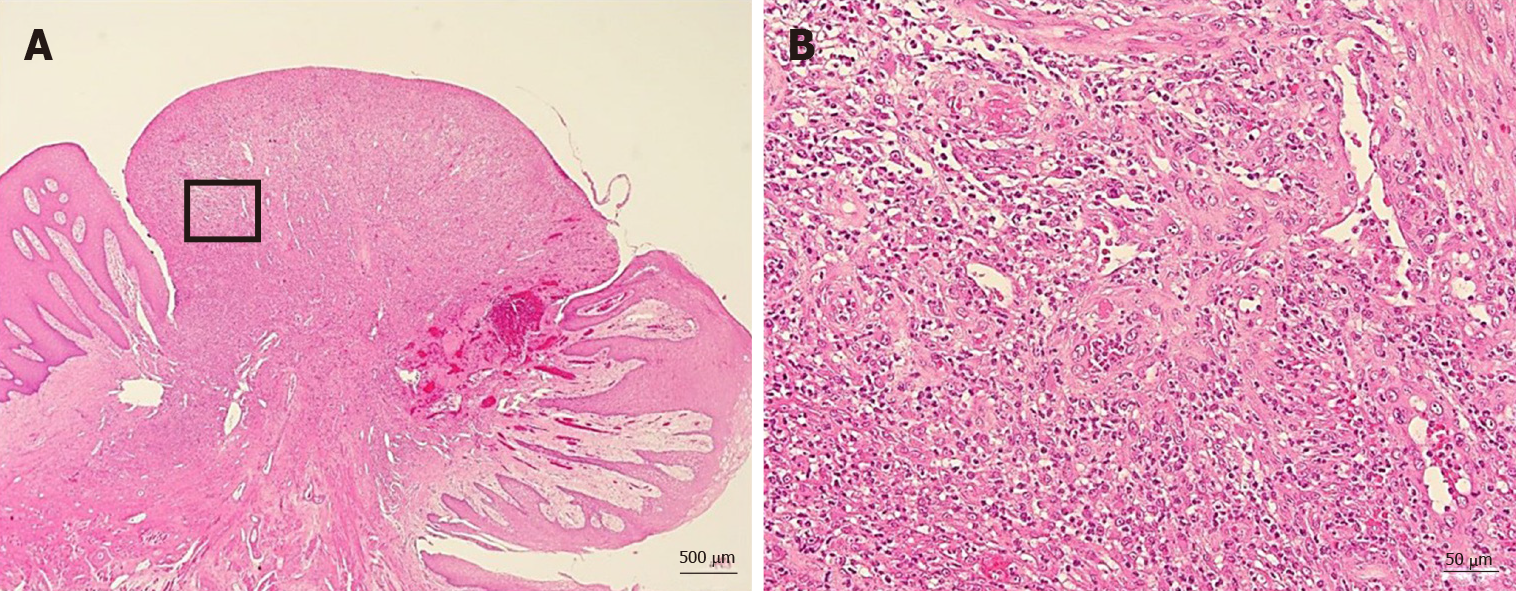
Figure 4 No malignancy was reported nor were there any inclusion bodies suggestive of cytomegalovirus infection.
A: Histological examination of the excised tongue nodule showing granulation tissue with capillaries and fibroblasts (Hematoxylin-eosin stain × 20, bar = 500 µm); B: Moderate infiltration with inflammatory cells, notably neutrophils. There was no malignancy or inclusion bodies suggestive of cytomegalovirus infection (Hematoxylin-eosin, × 200, bar = 50 µm).
Figure 5 We observed no recurrence of the lesion at 1 year and 5 mo after the procedure.
- Citation: Uesugi A, Tsushima F, Kodama M, Kuroshima T, Sakurai J, Harada H. Oral granuloma in a pediatric patient with chronic graft-versus-host disease: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(22): 5663-5669
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i22/5663.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5663