©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2020; 8(22): 5535-5546
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5535
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5535
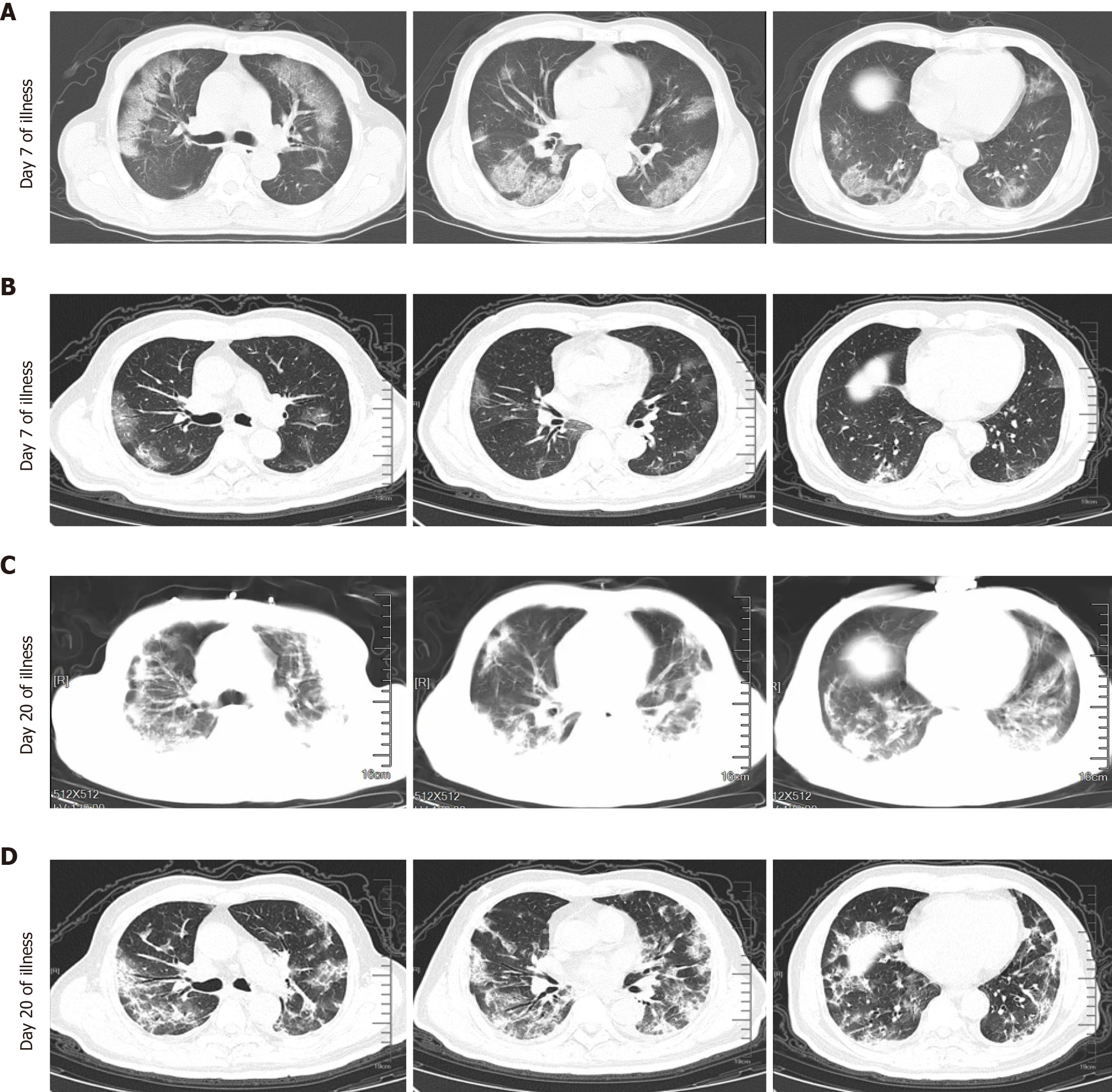
Figure 1 Chest computed tomography of critical coronavirus disease 2019 patients with different severity.
A: Chest computed tomography (CT) of a 71-year-old man (non-survivor, case 1) showed multifocal and bilateral ground-glass opacities (GGO) in the alveolitis stage (Day 7 of illness); B: Chest CT of a 73-year-old male patient (survivor, case 2) exhibited slight GGO in the alveolitis stage (Day 7 of illness); C: Classified into the fibrosis stage (Day 20 of illness) and Chest CT (case 1) showed bilateral massive shadows of high density and GGO, accompanied by the air bronchogram sign and reticular pattern in the fibrosis stage; and D: Chest CT (case 2) showed that bilateral and multifocal lesions were observed with a combination of mixed GGO, reticular pattern, bronchiectasis and few consolidation (Day 20 of illness).
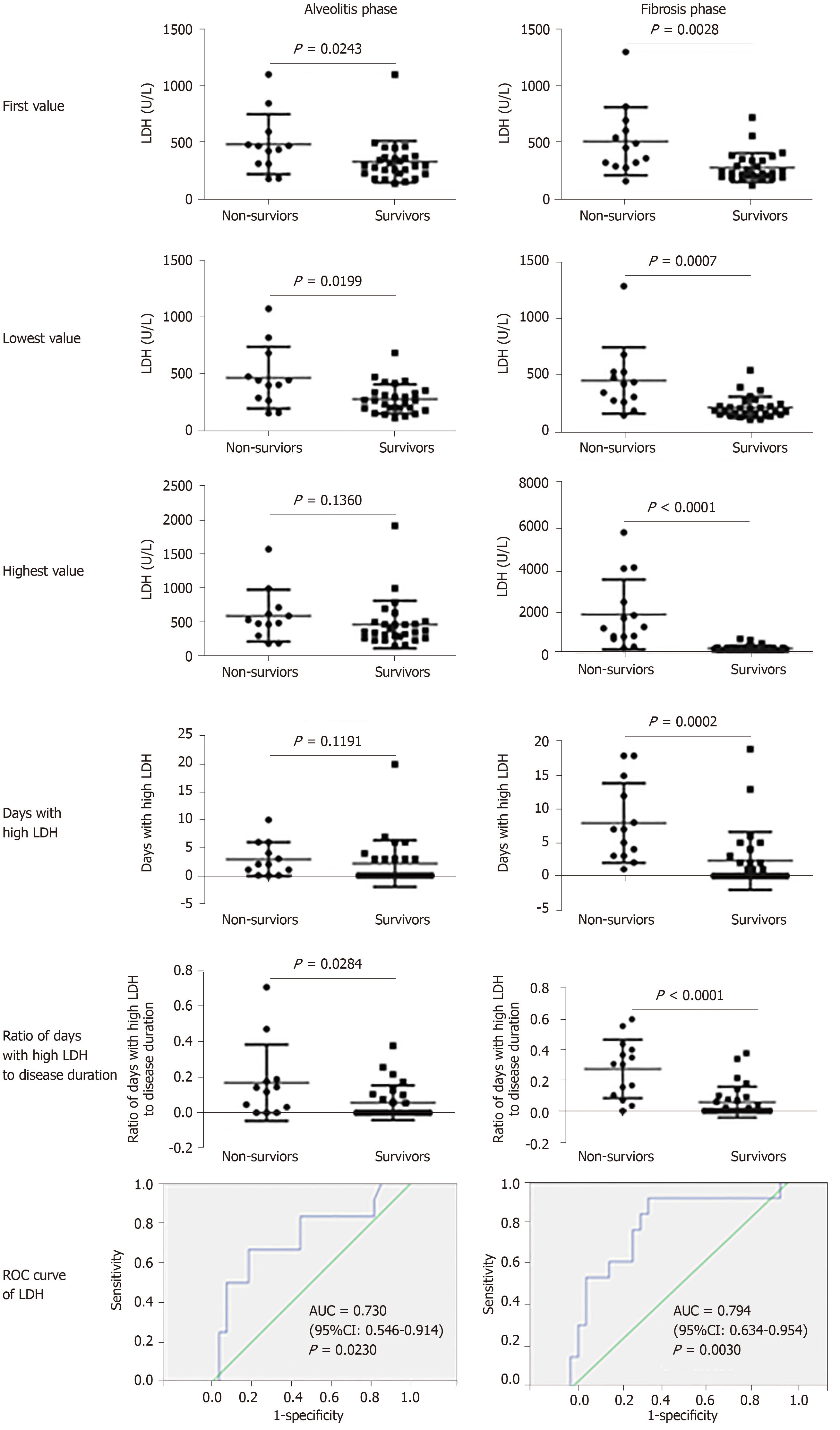
Figure 2 The relationship between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and the prognosis of patients with critical coronavirus disease 2019.
The first, lowest and highest values of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), together with the days with high LDH (≥ 397.0 U/L in the alveolitis phase and ≥ 263.0 U/L in the fibrosis phase according to the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, respectively) and the ratio of the days with high LDH to disease duration were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test between non-survivors and survivors in the alveolitis phase and fibrosis phase. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase.
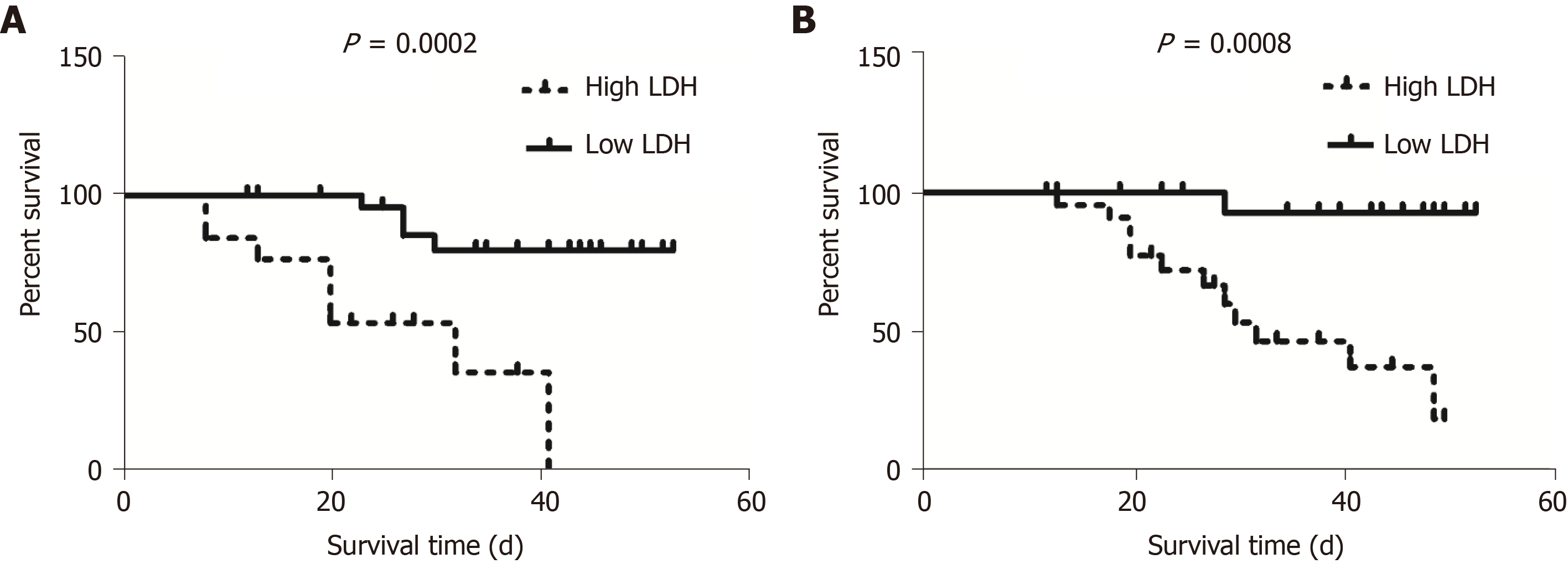
Figure 3 Association between the first value of serum lactate dehydrogenase and survival time of patients with critical coronavirus disease 2019.
Kaplan-Meier analysis and the log-rank test were performed to analyze the association between the first values of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and the survival time of patients with critical coronavirus disease 2019. A: Patients with high LDH (≥ 397.0 U/L) had a significantly shorter survival time compared to those with low LDH (< 397.0 U/L) in the alveolitis phase; B: Patients with high LDH (≥ 263.0 U/L) also had a significantly shorter survival time compared to those with low LDH (< 263.0 U/L) in the fibrosis phase. LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase.
Figure 4 Proportion of non-survivors with detectable severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 until death in the alveolitis and fibrosis phase.
All non-survivors (100.0%) who died in the alveolitis stage had a persistent positive test for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 until death. Only 5 patients (35.7%) who died in the pulmonary fibrosis stage had positive virus nucleic acid test results. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
- Citation: Lv XT, Zhu YP, Cheng AG, Jin YX, Ding HB, Wang CY, Zhang SY, Chen GP, Chen QQ, Liu QC. High serum lactate dehydrogenase and dyspnea: Positive predictors of adverse outcome in critical COVID-19 patients in Yichang. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(22): 5535-5546
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i22/5535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5535