©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2020; 8(20): 5030-5035
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.5030
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.5030
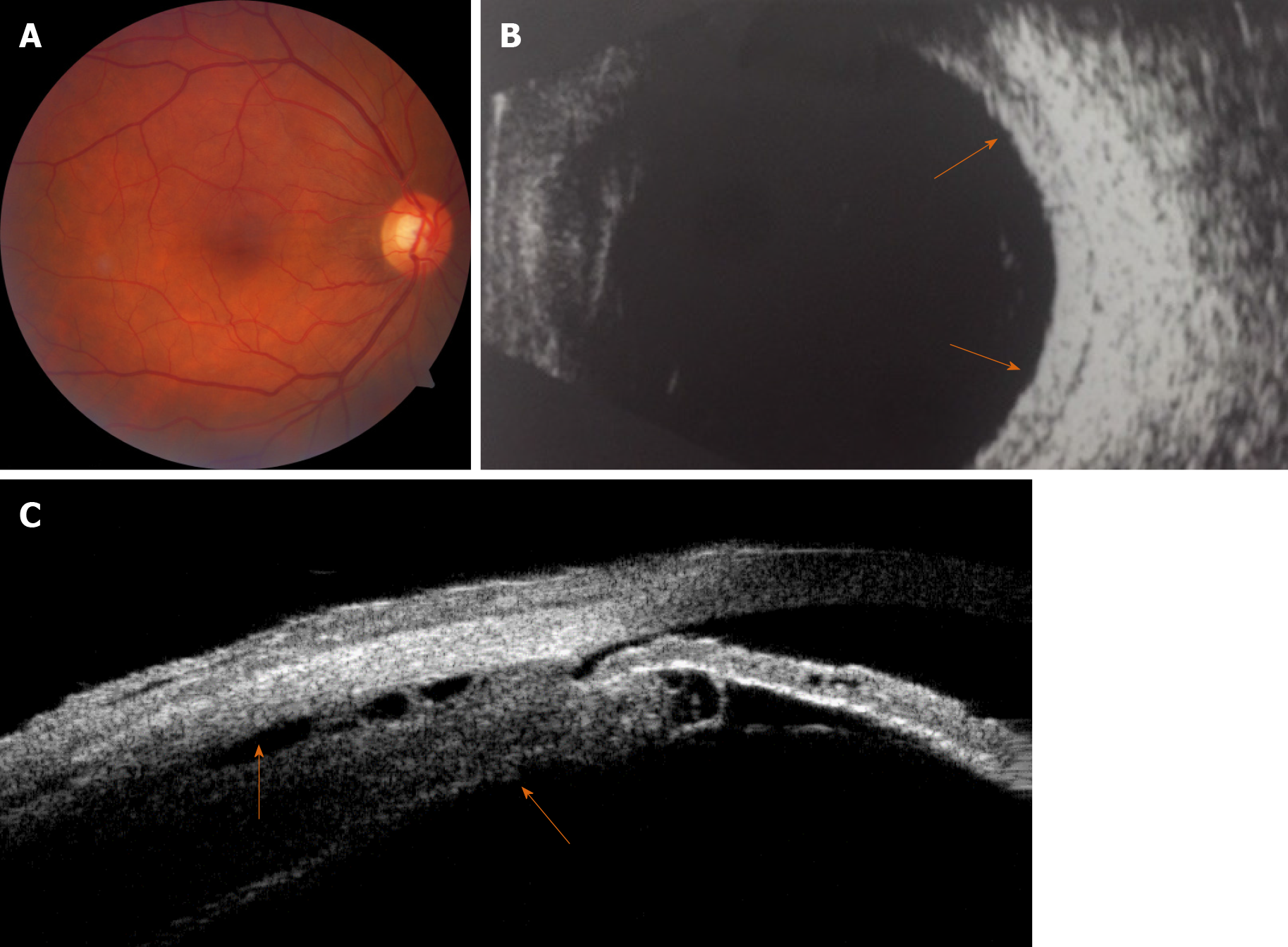
Figure 1 Color fundus imaging, B-scan ultrasonography and ultrasound biomicroscopy for the right eye before treatment.
A: Fundus photography revealed retinal folds around the optic disk in the right eye; B: B-scan ultrasonography revealed increased scleral thickening (orange arrows); C: Ultrasound biomicroscopy revealed edema and detachment of the ciliary body (orange arrows).
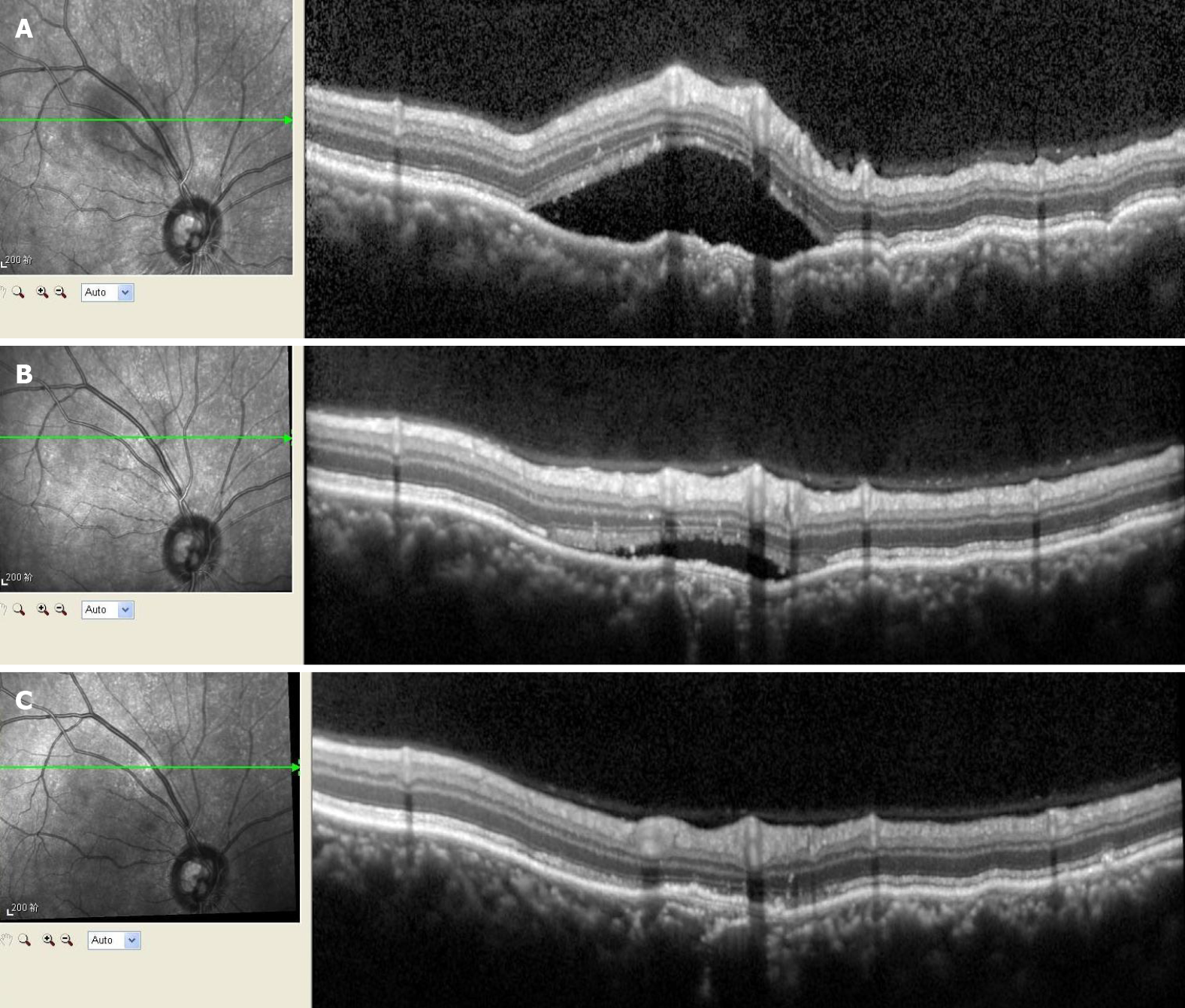
Figure 2 Optical coherence tomography for the right eye before and after treatment.
A: The optical coherence tomography showed the neuroepithelial layer as raised and wrinkled, with fluid underneath it, above the temporal part of the optic disc; B: The subretinal fluid around the optic disc had been gradually absorbed during the 2-wk treatment period; C: The subretinal fluid had been completely absorbed during the complete 2-mo treatment period.
- Citation: Li YZ, Qin XH, Lu JM, Wang YP. Monocular posterior scleritis presenting as acute conjunctivitis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(20): 5030-5035
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i20/5030.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.5030