©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2020; 8(20): 4922-4929
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4922
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4922
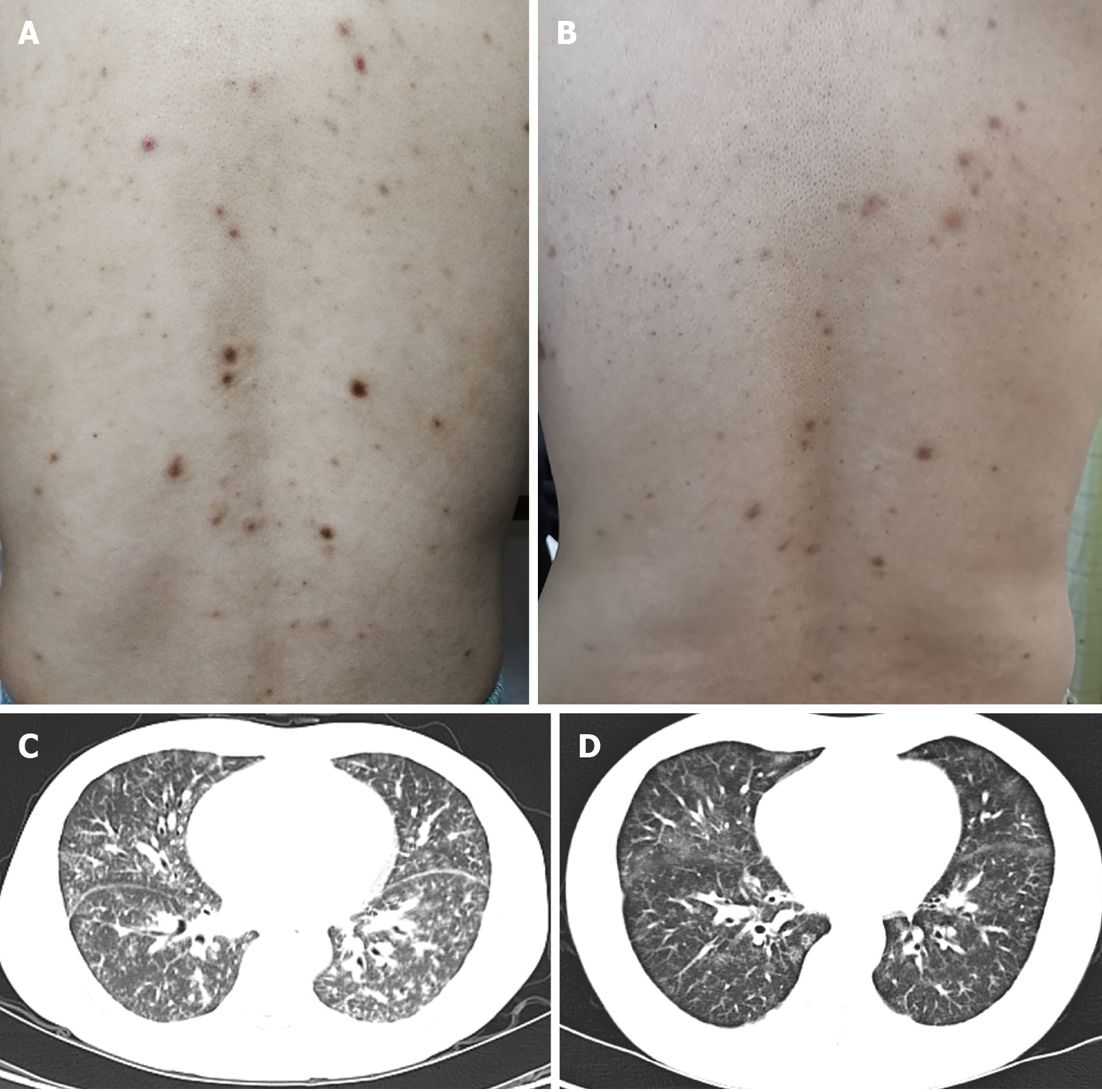
Figure 1 Skin lesions and chest computed tomography findings before and after treatment.
A: Innumerable symmetric brownish-red macules, papules, and plaques about 0.2-1 cm in diameter distributed in the back before treatment; B: The skin lesion improved 9 mo after treatment; C: Parenchymal window setting of the chest computed tomography showed diffuse ground-glass opacities in two lobes before treatment; D: The lung lesion improved 9 mo after treatment.
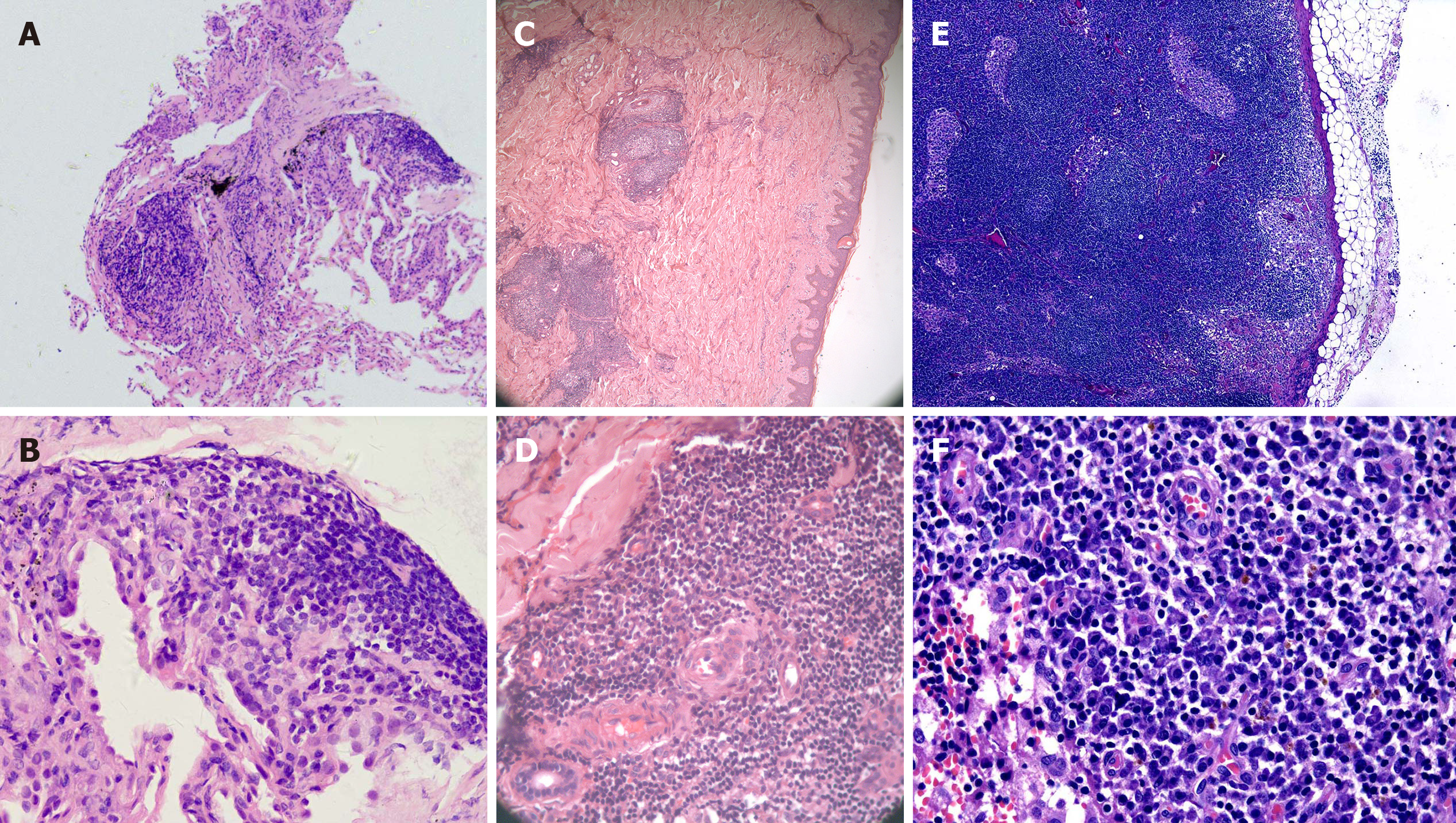
Figure 2 Histopathology of the lung (A and B), skin (C and D), and lymph node (E and F).
A, C, and E: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) × 50; B, D, and F: H&E × 400. A and B: Fibrous tissue hyperplasia accompanied by infiltration of a few lymphocytes and plasma cells in the lung; C and D: The epidermis was basically normal, lymphoid follicular-like hyperplasia was observed in the superficial and deep layers of the dermis, and medium-density plasma cells and lymphocytes infiltrated around the blood vessels and glands with no atypia; E and F: Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia mainly occurred in the paracortical region, and plasma cells mainly infiltrated in the medulla region. The structure of the lymph node was intact, and no transparent small angiogenesis was found.
- Citation: Han PY, Chi HH, Su YT. Idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease with pulmonary and cutaneous lesions treated with tocilizumab: A case report . World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(20): 4922-4929
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i20/4922.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4922