©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2020; 8(20): 4708-4718
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4708
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4708
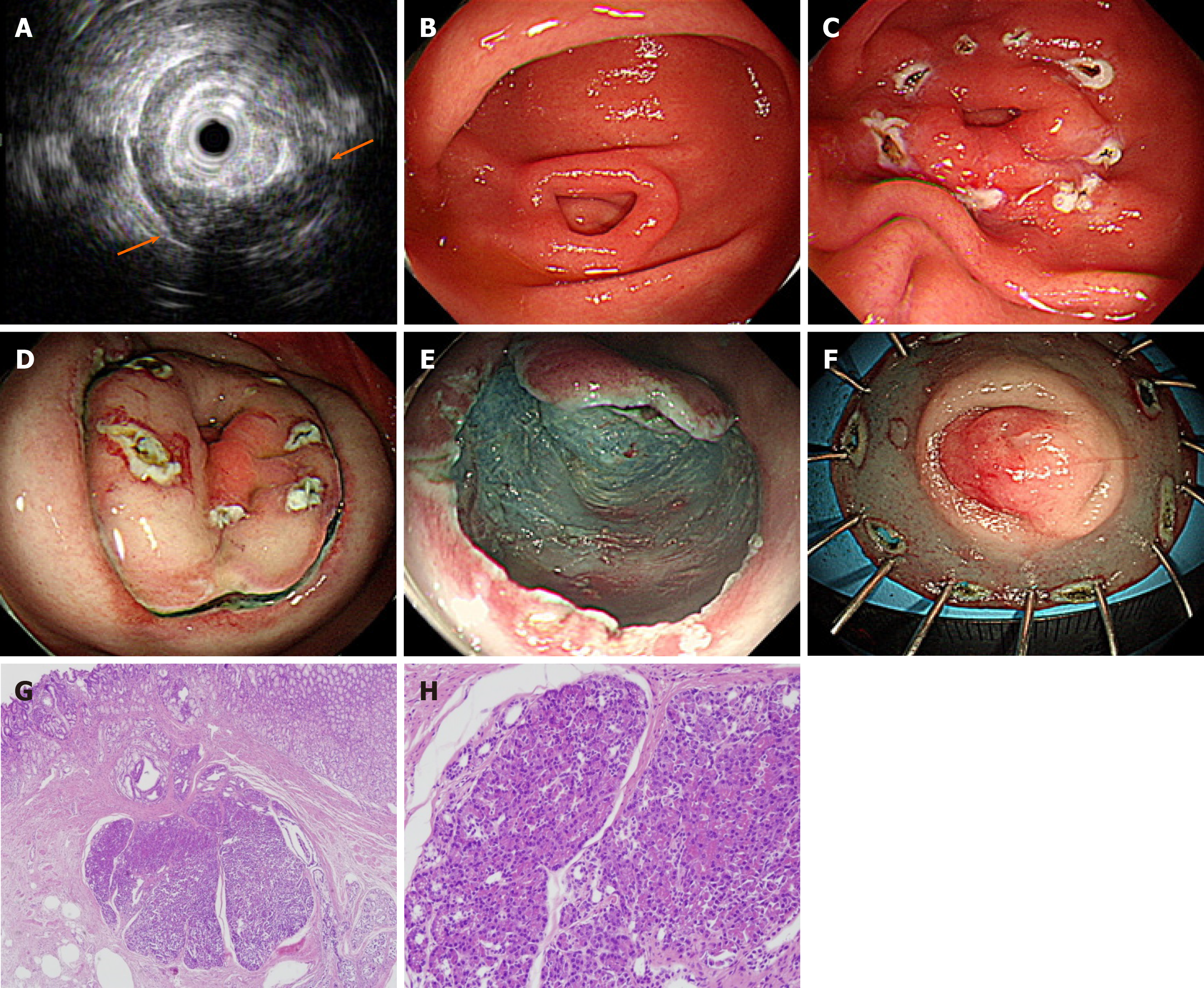
Figure 1 Endoscopic submucosal dissection of complicated gastric heterotopic pancreas (patient 5).
A: Endoscopic ultrasonography image showing a homogeneous hypoechoic lesion with cystic (hypoechoic) foci that was located within the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th layers; B: A 1.5 cm subepithelial tumor with umbilication was observed on the greater curvature of the antrum; C: The lesion borders were marked; D: Saline with epinephrine was submucosally injected, and a circumferential mucosal incision was made; E: The submucosal connective tissue and part of the muscularis propria were dissected; F: The resected specimen was fixed; G: Heterotopic pancreas is located in the submucosa underlying intact gastric mucosa (hematoxylin-eosin; original magnification, × 40); H: Normal pancreatic acini with ducts are noted (× 200).
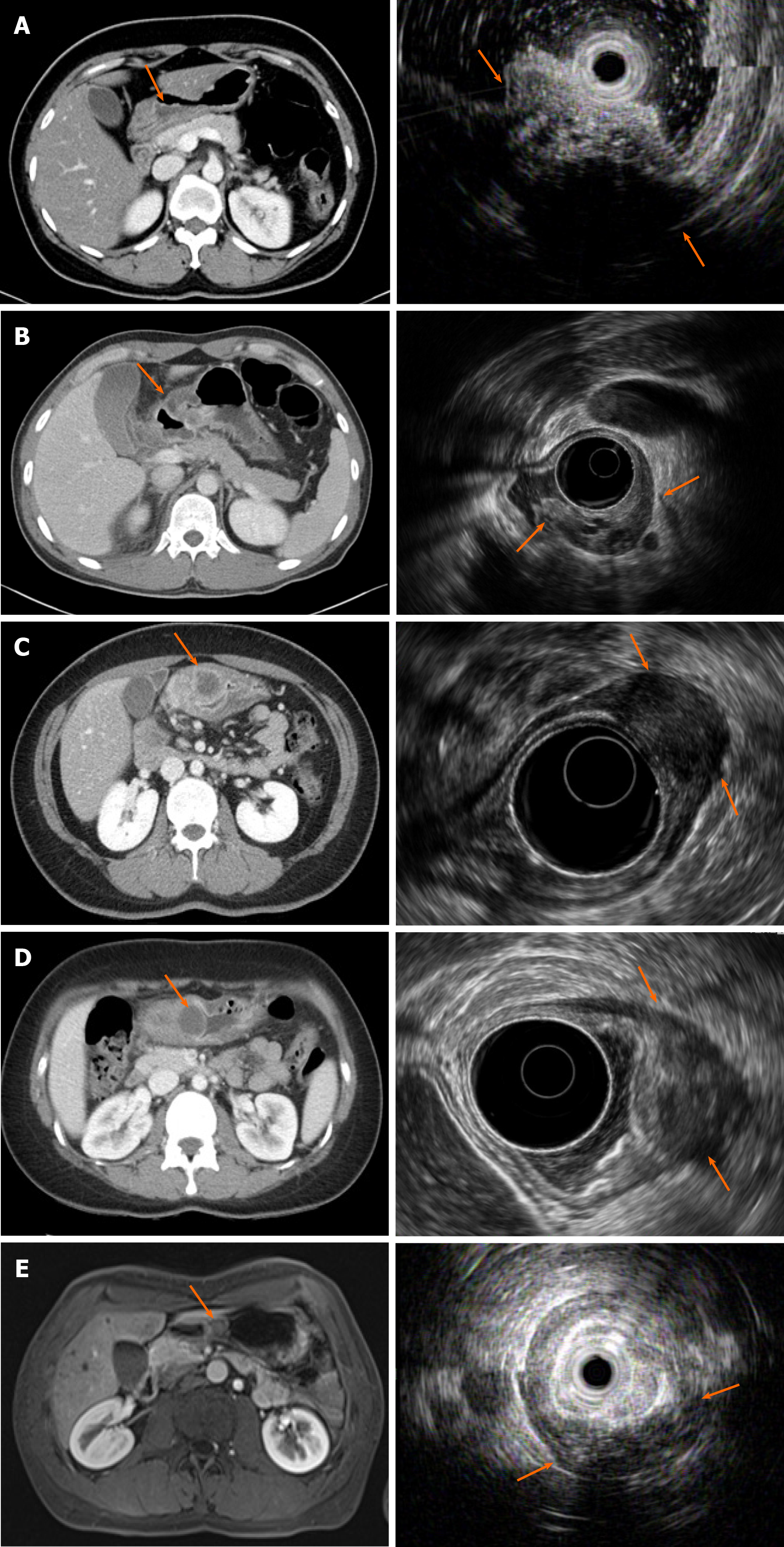
Figure 2 Computed tomography and endoscopic ultrasonography images of each patient at the time of diagnosis of complicated gastric heterotopic pancreas.
A-E: Correspond to patient 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively. The computed tomography and endoscopic ultrasonography findings of each patient are summarized in Table 1.
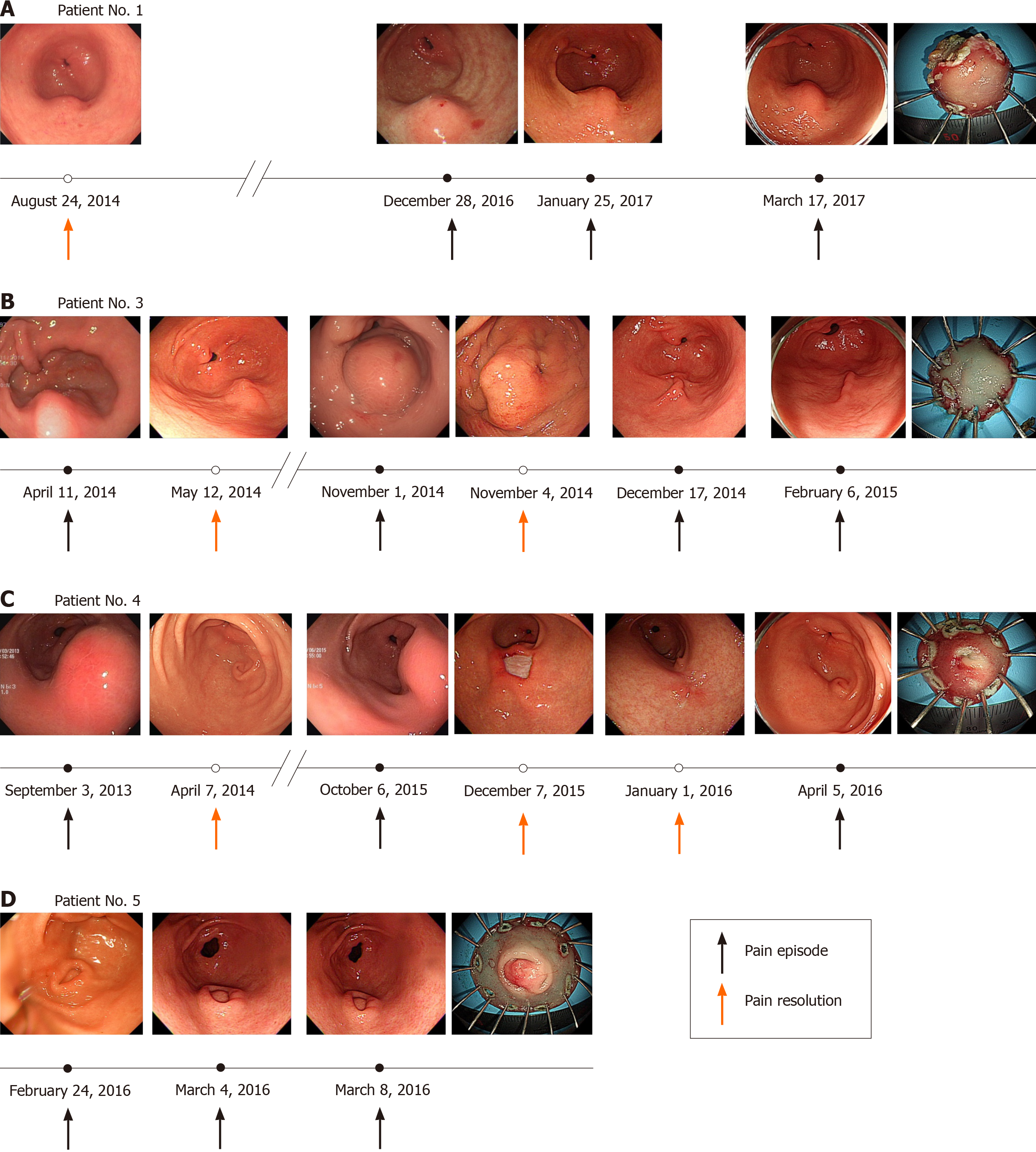
Figure 3 The clinical course of lesion size according to abdominal pain are summarized.
A: Patient 1; B: Patient 3; C: Patient 4; D: Patient 5.
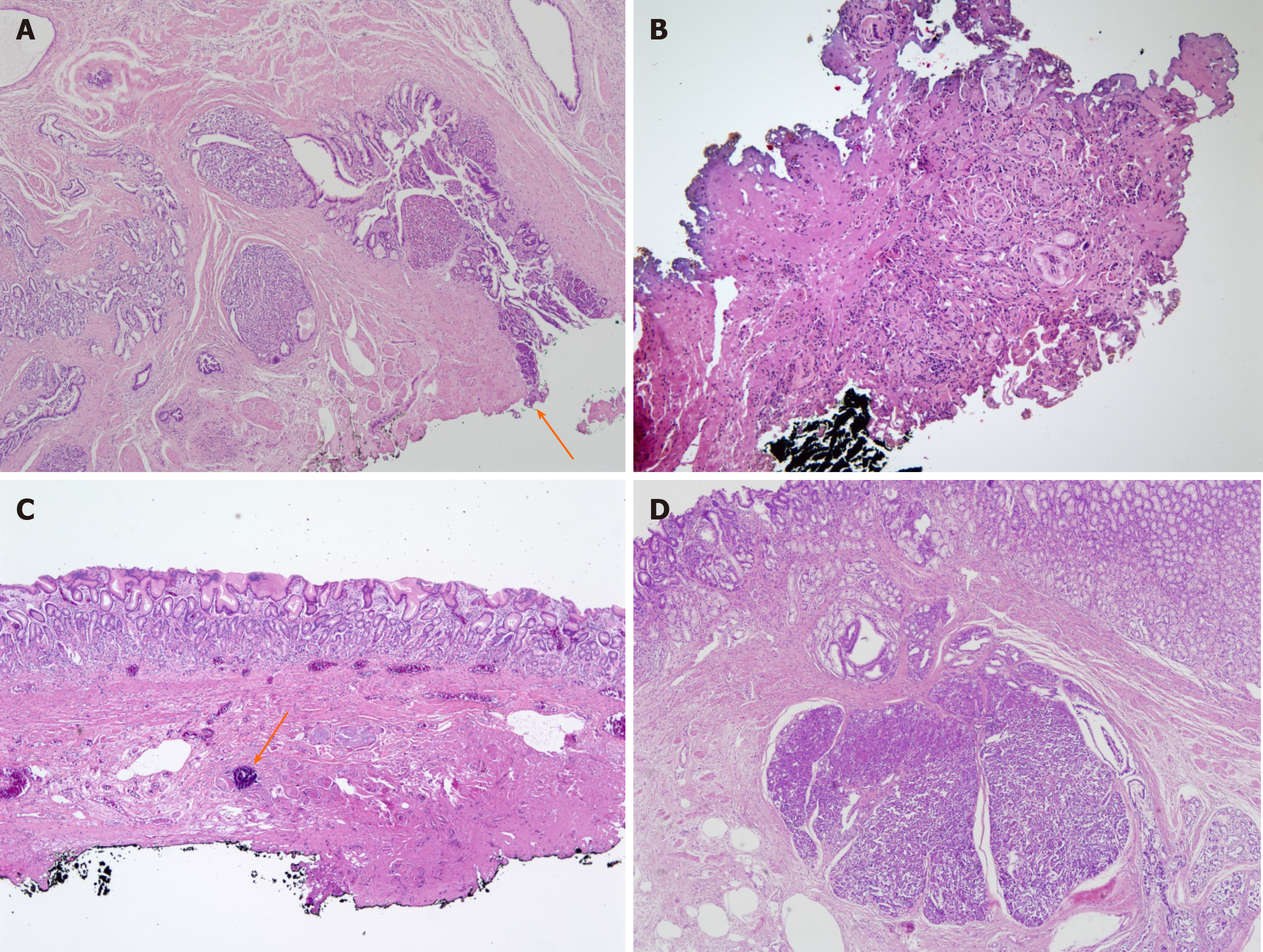
Figure 4 Representative histologic images of gastric heterotopic pancreas.
A: Patient 1: Pancreatic tissue is in proper muscle with involvement of resection margin (arrow) (hematoxylin-eosin; original magnification, × 40); B: Patient 3: There is focal nest of cells and bluish material with fibrosis and severe cautery artifact (× 100); C: Patient 4: Submucosal fibrosis with foreign body reaction and dystrophic calcification (arrow) was noted (× 40); D: Patient 5: Pancreatic tissue is in submucosa overlying gastric mucosa (× 40).
- Citation: Noh JH, Kim DH, Kim SW, Park YS, Na HK, Ahn JY, Jung KW, Lee JH, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Jung HY. Endoscopic submucosal dissection as alternative to surgery for complicated gastric heterotopic pancreas. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(20): 4708-4718
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i20/4708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4708