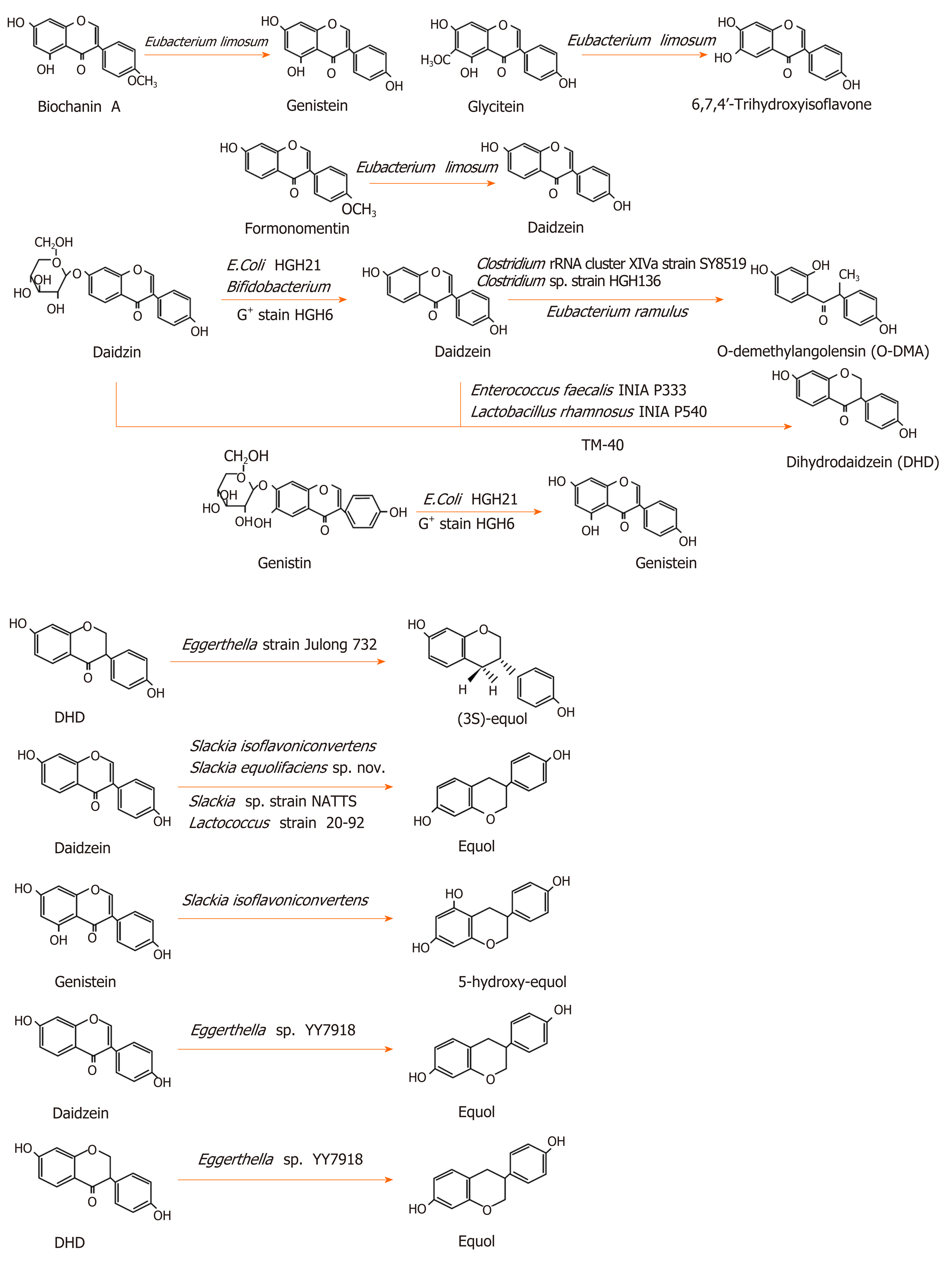
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2020; 8(11): 2081-2091
Published online Jun 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2081
Published online Jun 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2081
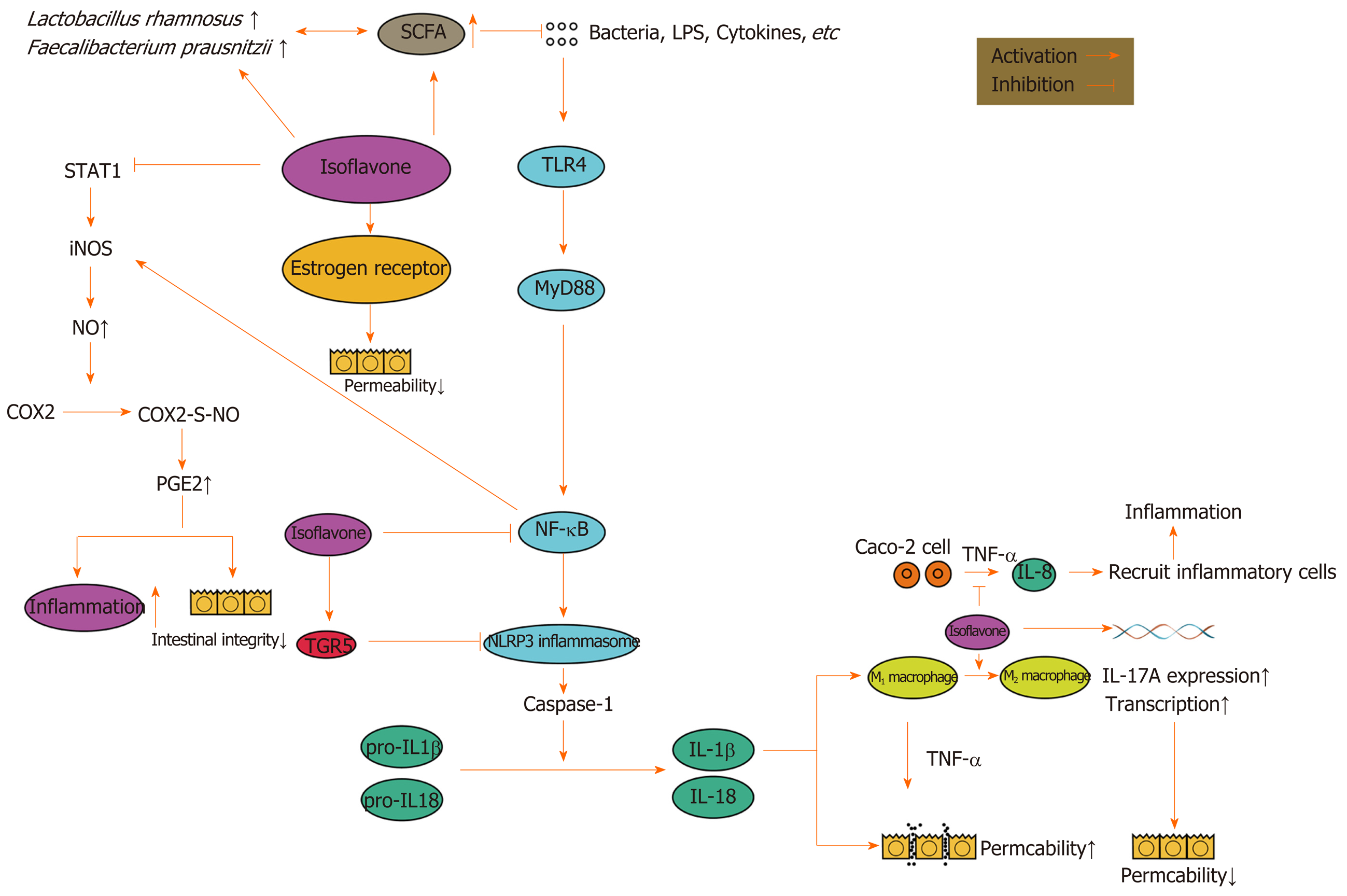
Figure 2 The effects of isoflavones on inflammatory bowel disease.
SCFA: Short-chain fatty acids; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; COX2: NO: Nitric oxide; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3: NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-8: Interleukin-8.
- Citation: Wu ZY, Sang LX, Chang B. Isoflavones and inflammatory bowel disease. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(11): 2081-2091
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i11/2081.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2081