©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2020; 8(10): 1871-1877
Published online May 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1871
Published online May 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1871
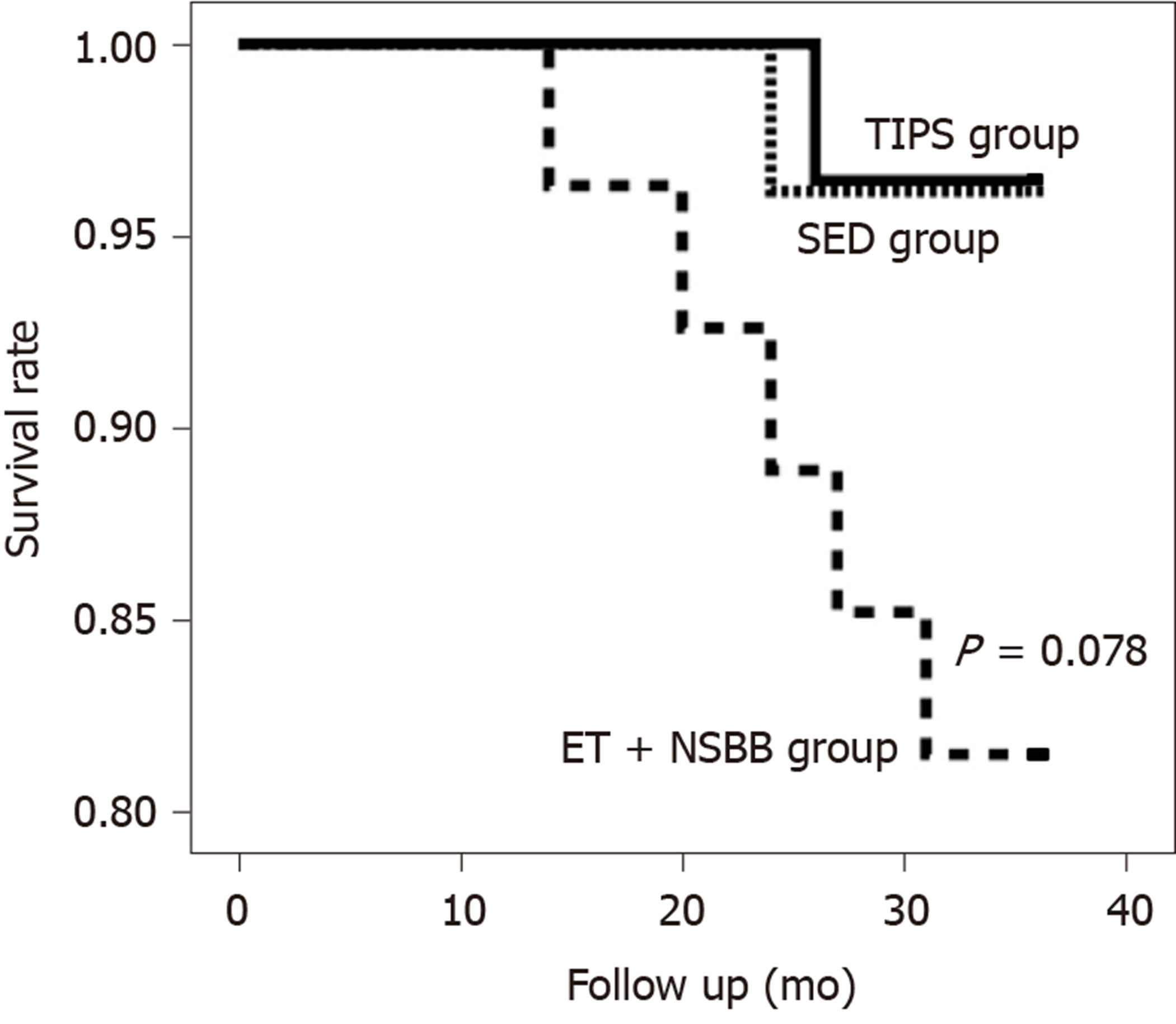
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival following idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, splenectomy plus esophagogastric devascularization and endoscopic therapy + non-selective β-blockers.
TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; SED: Splenectomy plus esophagogastric devascularization; ET + NSBB: Endoscopic therapy + non-selective β-blockers.
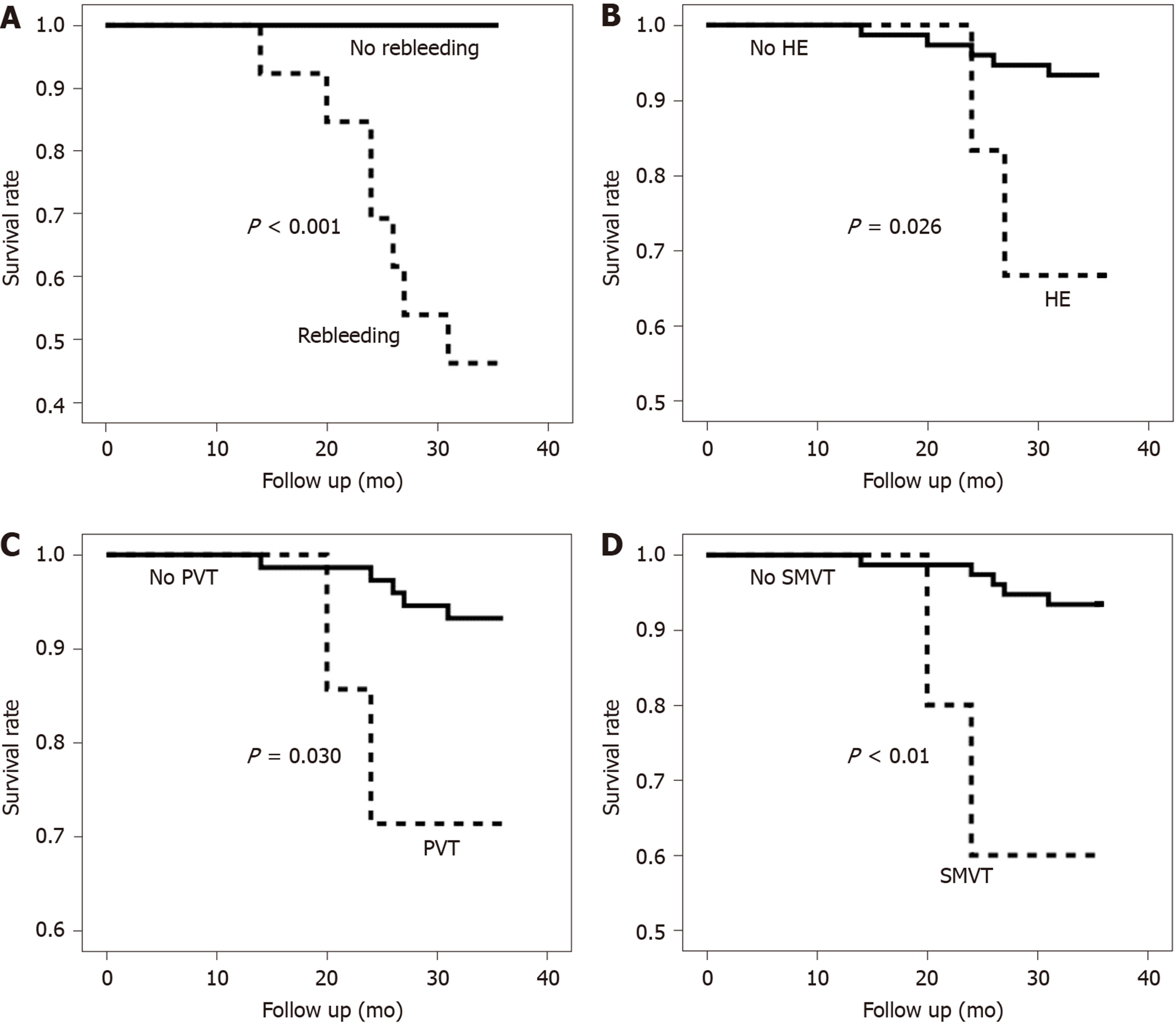
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival following idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension with different complications.
A: Rebleeding; B: Hepatic encephalopathy; C: Portal vein thrombosis; D: Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis. HE: Hepatic encephalopathy; PVT: Portal vein thrombosis; SMVT: Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis.
- Citation: He FL, Qi RZ, Zhang YN, Zhang K, Zhu-Ge YZ, Wang M, Wang Y, Jia JD, Liu FQ. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and splenectomy are more effective than endoscopic therapy for recurrent variceal bleeding in patients with idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(10): 1871-1877
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i10/1871.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1871