©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2020; 8(1): 29-37
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.29
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.29
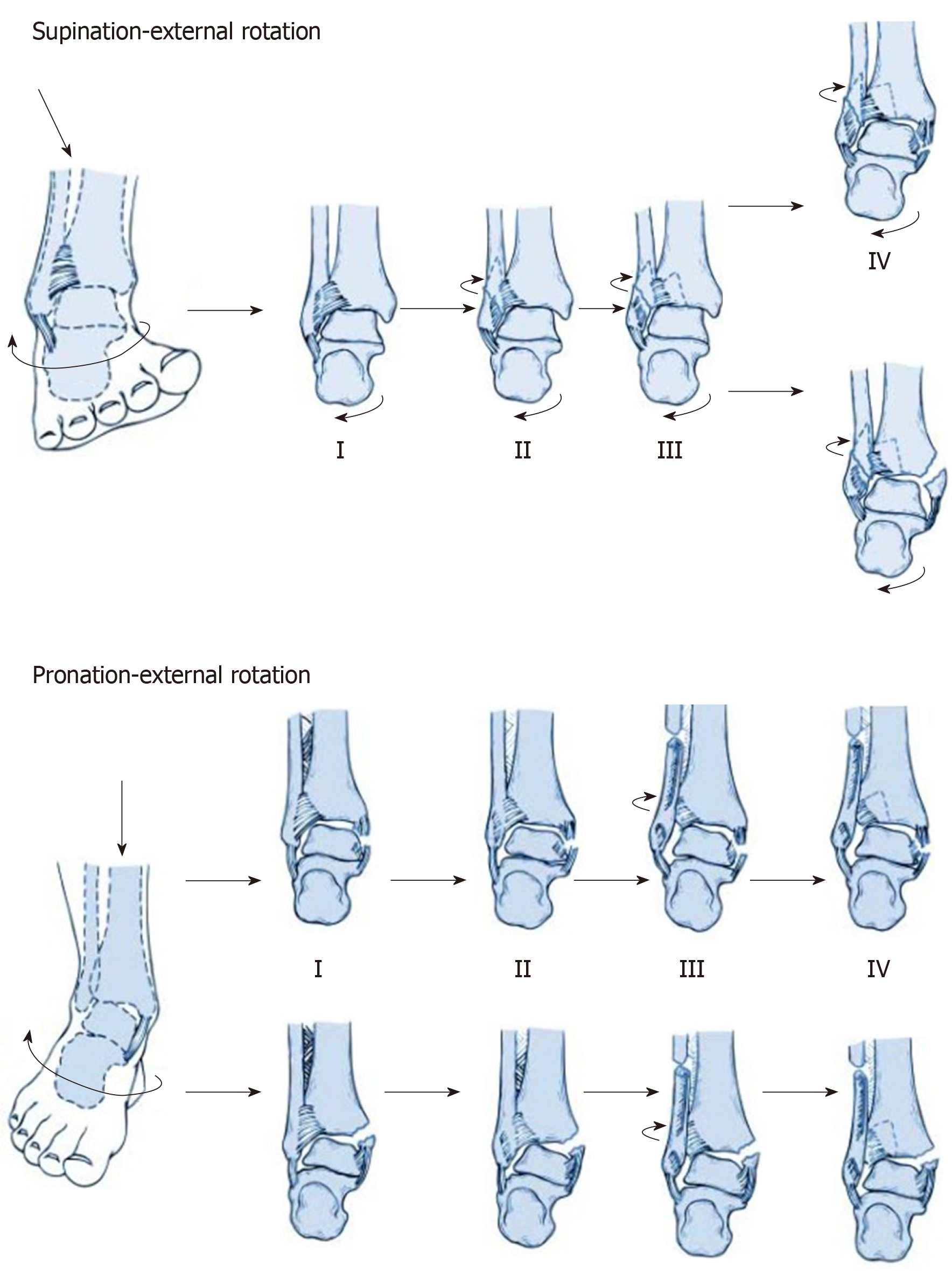
Figure 1 The injury mechanisms of supination-external rotation grade IV and pronation-external rotation grade IV groups.
Figure 2 The process of three dimensional fracture mapping in the software programs.
The ankle fracture fragments were reconstructed, reduced and normalized to optimally match the standard template. Smooth curves were constructed on the model surface and then overlapped.
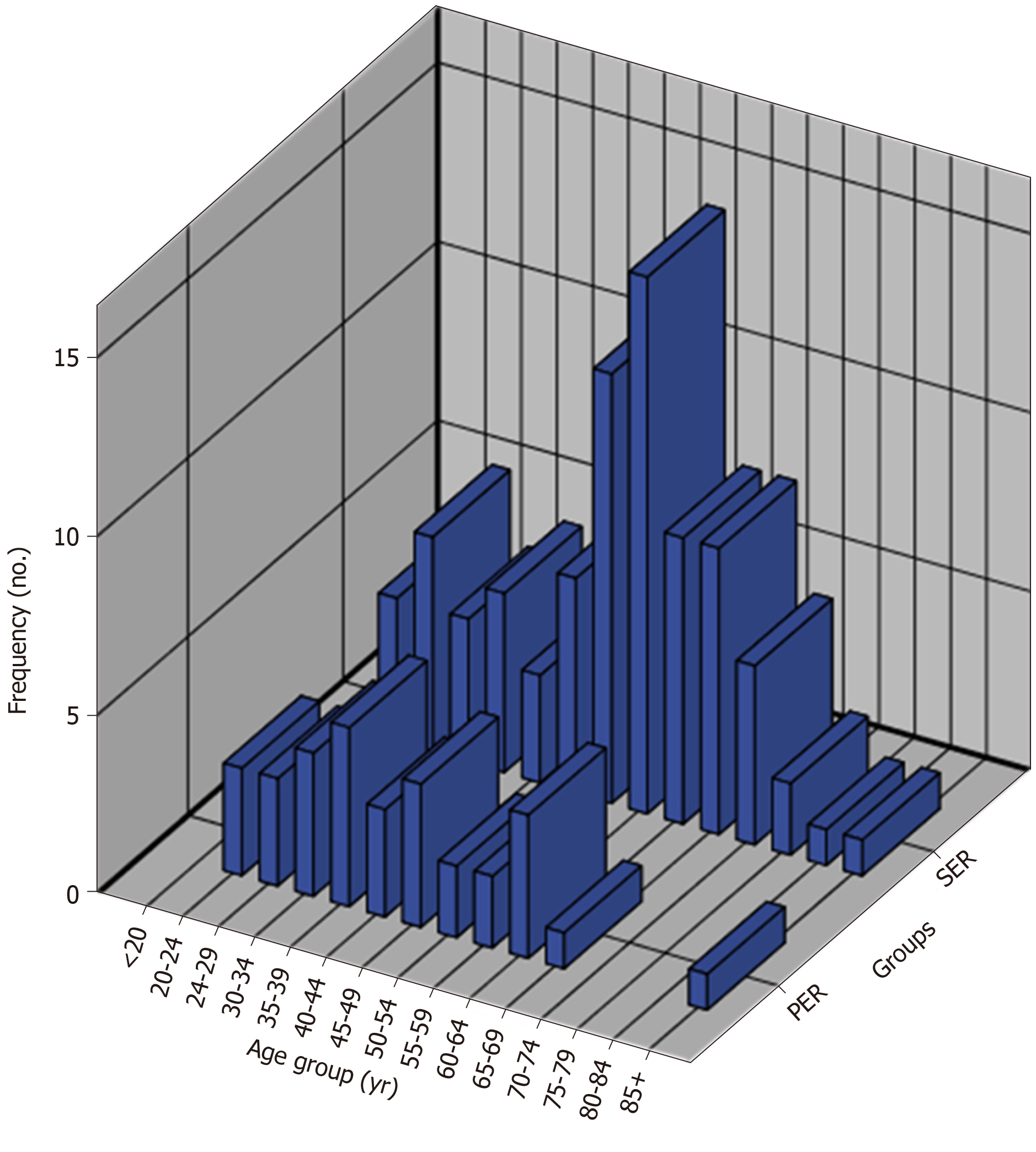
Figure 3 Histogram of the age groups of all subjects.
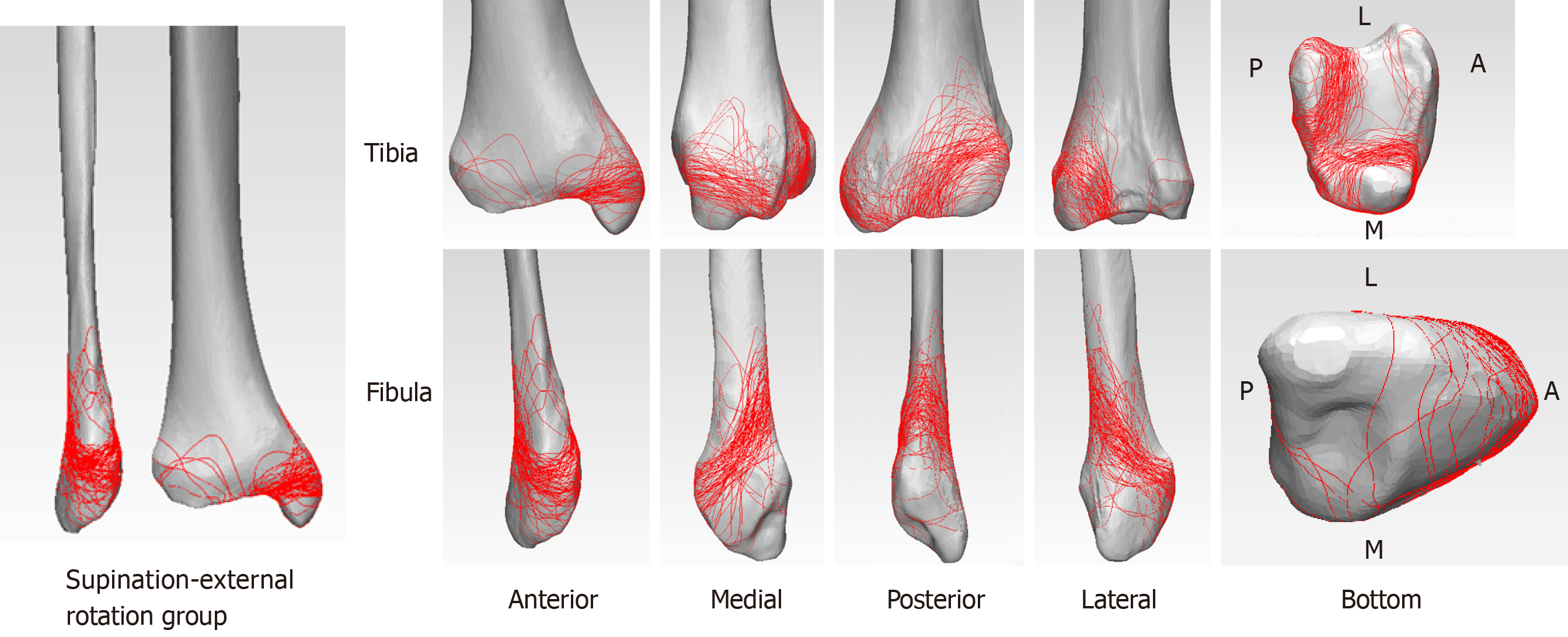
Figure 4 The three dimensional fracture maps of supination-external rotation grade IV group.
Distribution analyses on posterior malleolus fracture lines indicated that the supination-external rotation grade IV group tended to have higher linear density but more concentrated and orderly distribution fracture lines compared to the pronation-external rotation grade IV groups.
Figure 5 The three dimensional fracture maps of pronation-external rotation grade IV group.
This group tended to have more extensive and unorganized distribution fracture lines compared to the supination-external rotation grade IV group.
- Citation: Su QH, Liu J, Zhang Y, Tan J, Yan MJ, Zhu K, Zhang J, Li C. Three-dimensional computed tomography mapping of posterior malleolar fractures. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(1): 29-37
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i1/29.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.29