©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. May 6, 2019; 7(9): 1021-1027
Published online May 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i9.1021
Published online May 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i9.1021
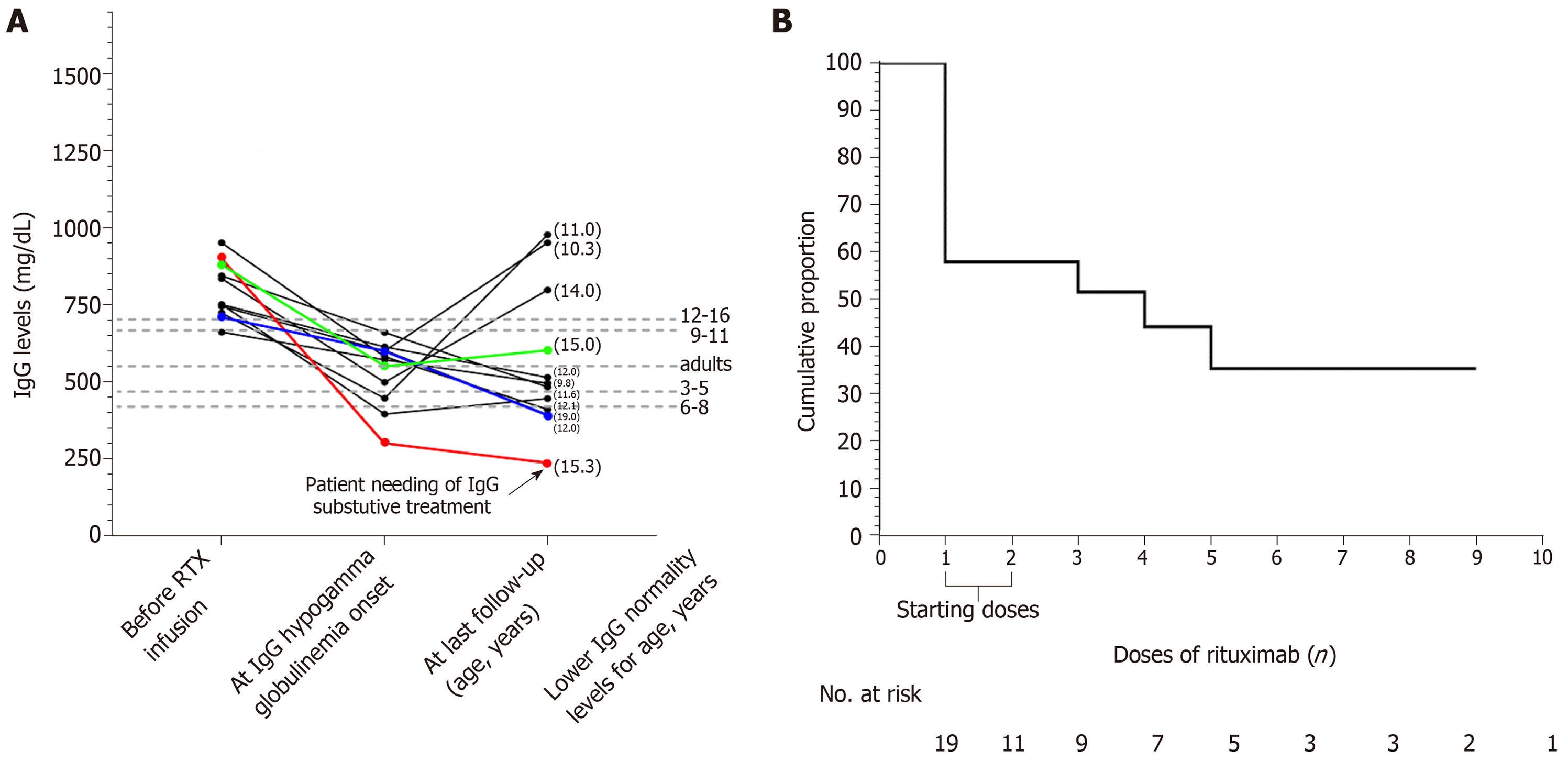
Figure 1 Trend of the IgG values among patients presenting IgG hypogammaglobulinemia and survival from IgG hypogammaglobulinemia.
A: Trend of the IgG values among patients presenting with IgG hypogammaglobulinemia. Eight patients (dark coloured) developed IgG hypogammaglobulinemia after the “starting doses” (7 out of 8 patients showed IgG hypogammaglobulinemia at the scheduled follow-up 3 mo after the RTX “starting doses”, and one patients developed IgG hypogammaglobulinemia 24 mo after the RTX infusion), one (green coloured) patient after the third dose (this patient showed IgG hypogammaglobulinemia 3 mo after the third dose), one (blue coloured) after the fourth (this patient showed IgG hypogammaglobulinemia 3 mo after the fourth dose), and one (red coloured) after the fifth dose (this patient showed IgG hypogammaglobulinemia 13 mo after the fifth dose); B: Survival from IgG hypogammaglobulinemia. The cumulative proportion of patients free of IgG hypogammaglobulinemia was 57.8% after the first dose of RTX, 51.5% after the third dose, 44.1% after the fourth dose, and 35.5% after the fifth dose. The time between the RTX infusion and IgG hypogammaglobulinemia onset is specified in the legend of Figure 1A. RTX: Rituximab; IgG: Immunoglobulin G.
- Citation: Marzuillo P, Guarino S, Esposito T, Di Sessa A, Orsini SI, Capalbo D, Miraglia del Giudice E, La Manna A. Rituximab-induced IgG hypogammaglobulinemia in children with nephrotic syndrome and normal pre-treatment IgG values. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(9): 1021-1027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i9/1021.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i9.1021