©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2019; 7(5): 548-561
Published online Mar 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i5.548
Published online Mar 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i5.548
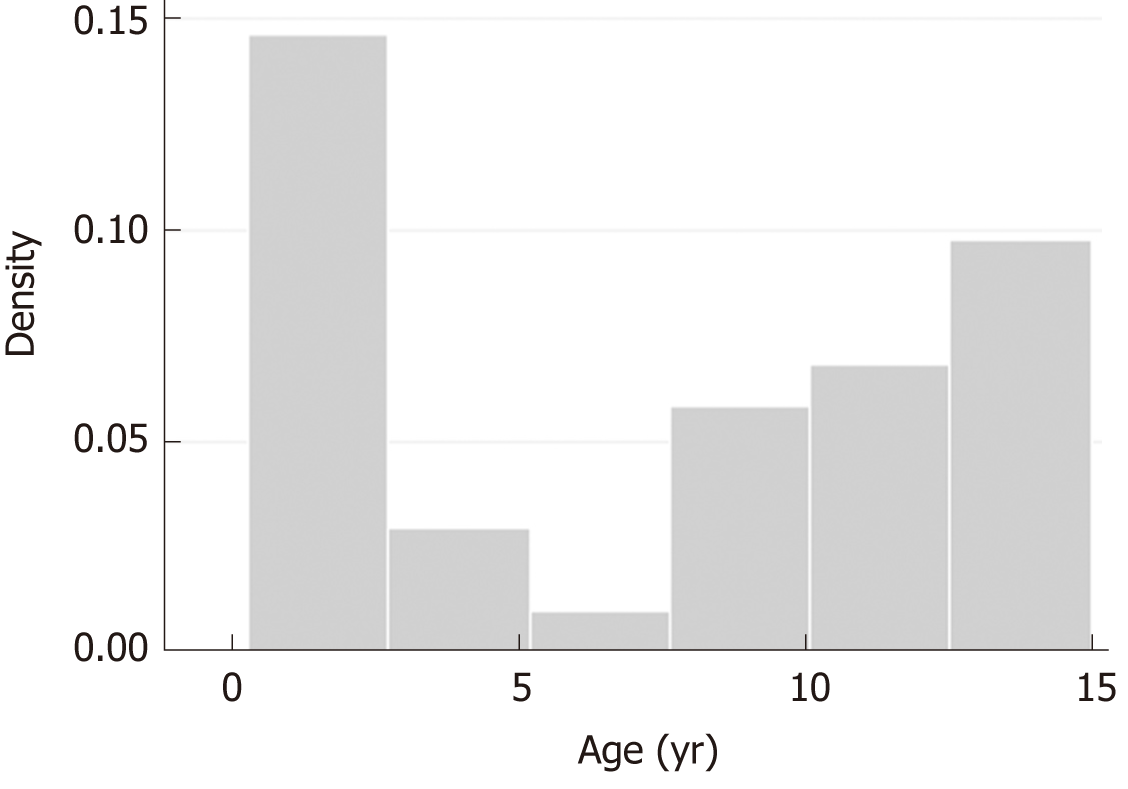
Figure 1 Histogram showing the age distribution of myocarditis pediatric population.
Most patients (70%) were children younger than 2-years-old (35%), and older than 12-years-old (35%).
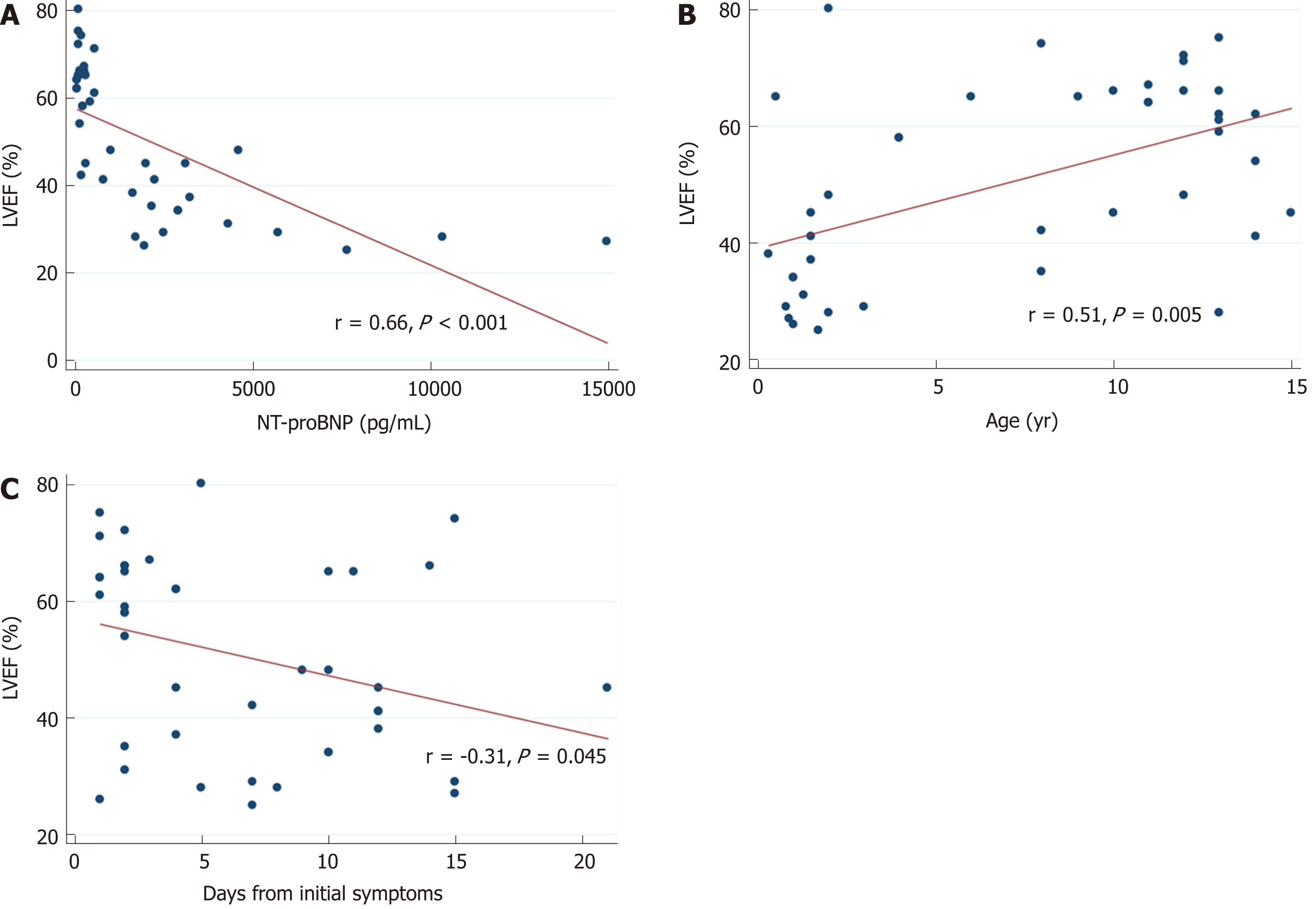
Figure 2 Correlations between left ventricular ejection fraction at admission and (A) N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels, (B) age, and (C) days of evolution of the disease.
NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide.
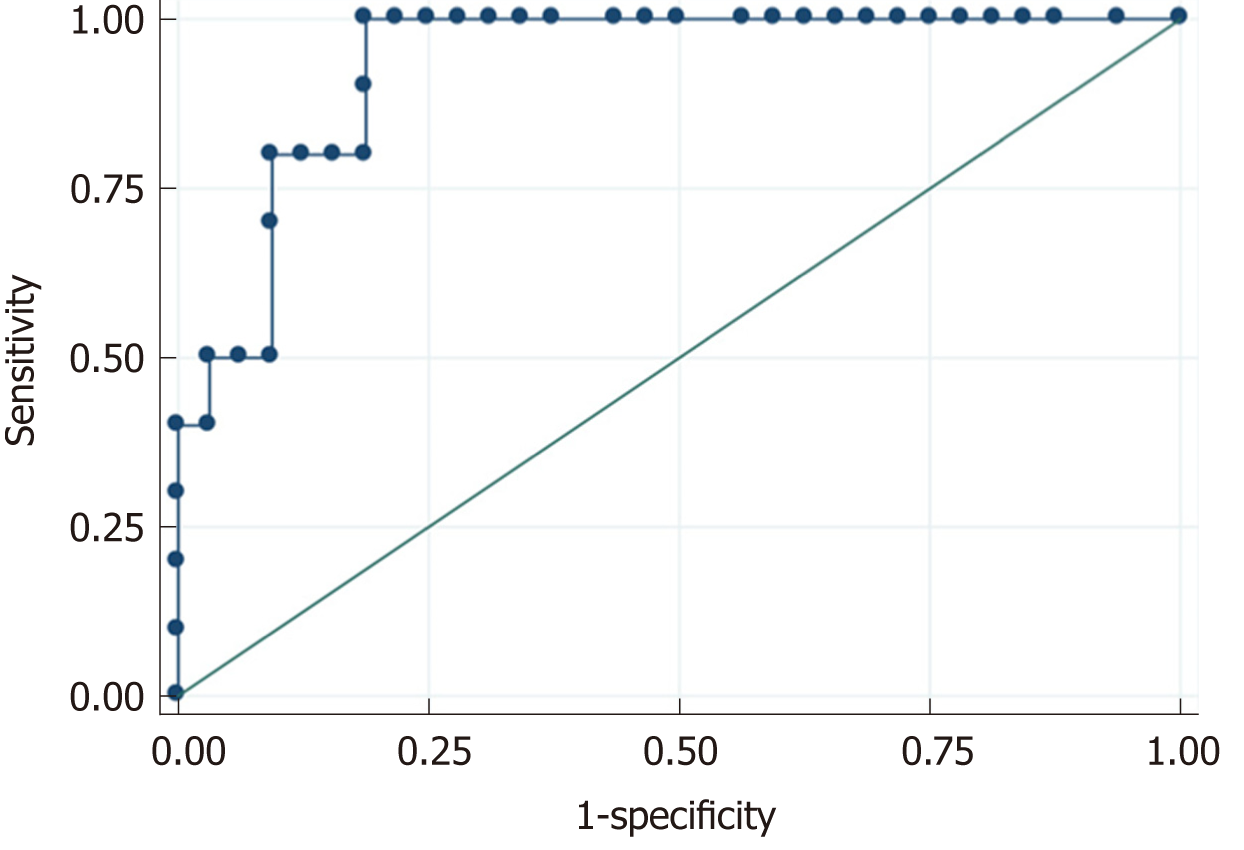
Figure 3 Area under receiver operating characteristic curve of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide for determining left ventricular ejection fraction < 30%.
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide presented a high diagnostic accuracy for severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction on echocardiography with an area under curve of 0.931 (95%CI: 0.858-0.995, P < 0.001). The best cut-off point was 2000 pg/mL, with a sensitivity of 90%, specificity of 81%, positive predictive value of 60%, and negative predictive value of 96%.
- Citation: Rodriguez-Gonzalez M, Sanchez-Codez MI, Lubian-Gutierrez M, Castellano-Martinez A. Clinical presentation and early predictors for poor outcomes in pediatric myocarditis: A retrospective study. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(5): 548-561
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i5/548.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i5.548